04b5da4b3d4093ae6cf96814eacc2ea1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Building IT Leadership: Revisiting Key Issues BCS London May 17 th 2007 Presenter: Leslie Willcocks Professor of Technology Work And Globalization London School of Economics and Political Science email: l. p. willcocks@lse. ac. uk (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Does IT Matter? 2 Carr, N. , "IT Doesn't Matter, " Harvard Business Review, Vol. 81, 5, May 2003, pp. 41 -49. Friedman, Thomas, The World is Flat, Farrar, Strauss, and Giroux, New York, 2005, pages 3 to 172 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Nicholas Carr: Does IT Matter? Harvard Bus. School Press, 2004 • IT is just a commodity: “IT is an infrastructure technology like the steam engine, railroad, telegraph, telephone” • IT is no longer a source of competitive advantage: “The core functions of IT—data storage, data processing, and data transport—have become available and affordable to all. ” 3 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Nicholas Carr: Does IT Matter? Harvard Bus. School Press, 2004 • Spend less. Studies show that the companies with the biggest IT investments rarely post the best financial results. • Follow, don't lead. Moore's Law guarantees that the longer you wait to make an IT purchase, the more you'll get for your money. • Focus on vulnerabilities, not opportunities. Even a brief disruption in the availability of the technology can be devastating. 4 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Friedman: The Ten Flatteners • • Platform Building 11/9/89 (PC revolution: Windows) 8/9/95 (Internet Revolution: Netscape goes public) Work Flow Software (application protocols let computers talk to computers) Open-sourcing (Best software is available to everyone) Platform Use • Outsourcing (global sourcing of knowledge work) • Offshoring (moving facilities to cheapest location lowers prices, stimulates the economy) 5 7. Supply-Chaining (eating sushi in Arkansas) 8. Insourcing (allows small firms to act big) 9. In-forming (Google, Yahoo, MSN) 10. Platform Enhancement 11. 10. The Steroids (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Key Issues For IT Executives - 2006 -7 Top Ten Management Concerns: 1. IT and Business Alignment 2. Attracting, Developing and Retaining IT Professionals 3. Security and Privacy 4. IT Strategic Planning 5. Project management capability 6. Introducing Rapid Business Solutions 7. Speed and Agility (new to top ten) 8. True Return on Individual IT Investments 9. Measuring The Value of IT Investments 10. IT Governance 6 Note: - 70% organisations are Maturity 2/3 on alignment (out of 5) See Luftman et al. (2006) MISQE Key Issues for IT Executives for earlier surveys (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
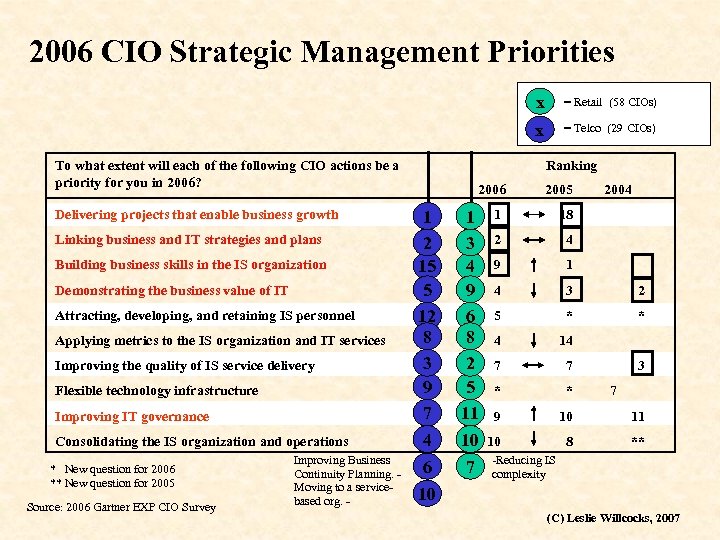
2006 CIO Strategic Management Priorities x x To what extent will each of the following CIO actions be a priority for you in 2006? 2006 1 1 Linking business and IT strategies and plans 2 2 Building business skills in the IS organization 3 15 5 12 8 6 3 9 8 7 4 1 3 4 9 6 8 2 5 11 10 6 7 Attracting, developing, and retaining IS personnel Applying metrics to the IS organization and IT services Improving the quality of IS service delivery Flexible technology infrastructure Improving IT governance Consolidating the IS organization and operations * New question for 2006 ** New question for 2005 Source: 2006 Gartner EXP CIO Survey Improving Business Continuity Planning. Moving to a servicebased org. - = Telco (29 CIOs) Ranking Delivering projects that enable business growth Demonstrating the business value of IT = Retail (58 CIOs) 2005 2004 1 18 2 4 9 1 4 3 2 5 * * 4 14 7 7 * * 9 10 11 10 8 ** 3 7 -Reducing IS complexity 10 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Key Issues: Some Food For Thought. . . 1. Technology 2. Strategy 3. People 4. Structure 5. Governance 6. Eight IT Differentiators 8 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Key Issues For IT Executives 2006 -7 Top Six Application and Technology Developments: 1. Web services (new to top 6) 2. Business Intelligence 3. Security Technologies 4. Business Process Management (new to top six) 5. Customer Portals (new to top 6) 6. Systems Integration Other: SOA XML EAI/M Corporate performance mmt. CRM 9 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
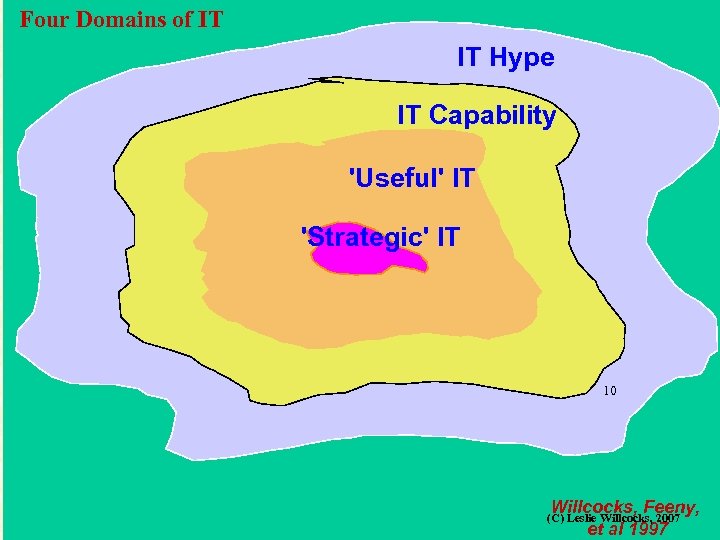
Four Domains of IT IT Hype IT Capability 'Useful' IT 'Strategic' IT 10 Willcocks, Feeny, et al 1997 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Key Issues: Some Food For Thought. . . 1. Technology 2. Strategy 3. People 4. Structure 5. Governance 6. Eight IT Differentiators 11 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
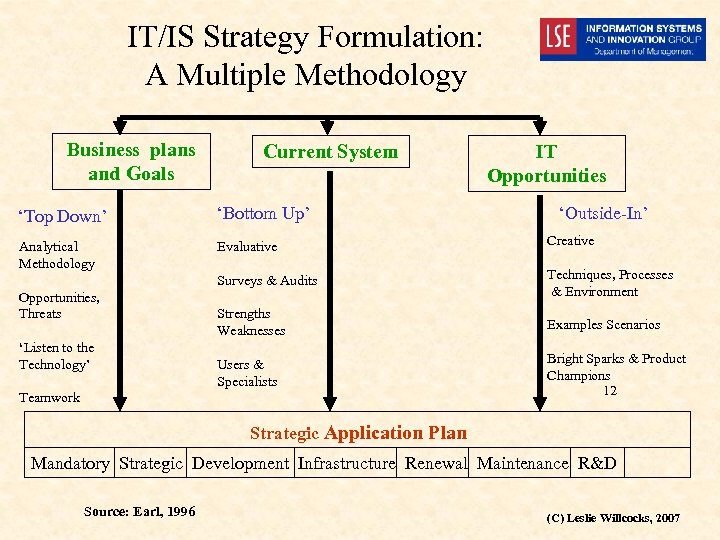
IT/IS Strategy Formulation: A Multiple Methodology Business plans and Goals Current System IT Opportunities ‘Top Down’ ‘Bottom Up’ Analytical Methodology Evaluative Creative Surveys & Audits Techniques, Processes & Environment Strengths Weaknesses Examples Scenarios Users & Specialists Bright Sparks & Product Champions 12 Opportunities, Threats ‘Listen to the Technology’ Teamwork ‘Outside-In’ Strategic Application Plan Mandatory Strategic Development Infrastructure Renewal Maintenance R&D Source: Earl, 1996 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
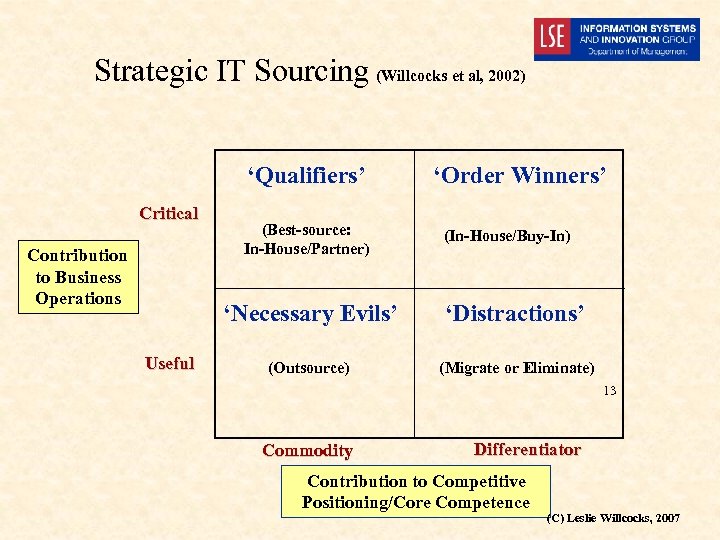
Strategic IT Sourcing (Willcocks et al, 2002) ‘Qualifiers’ Critical Contribution to Business Operations (Best-source: In-House/Partner) ‘Order Winners’ (In-House/Buy-In) ‘Necessary Evils’ Useful ‘Distractions’ (Outsource) (Migrate or Eliminate) 13 Commodity Differentiator Contribution to Competitive Positioning/Core Competence (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
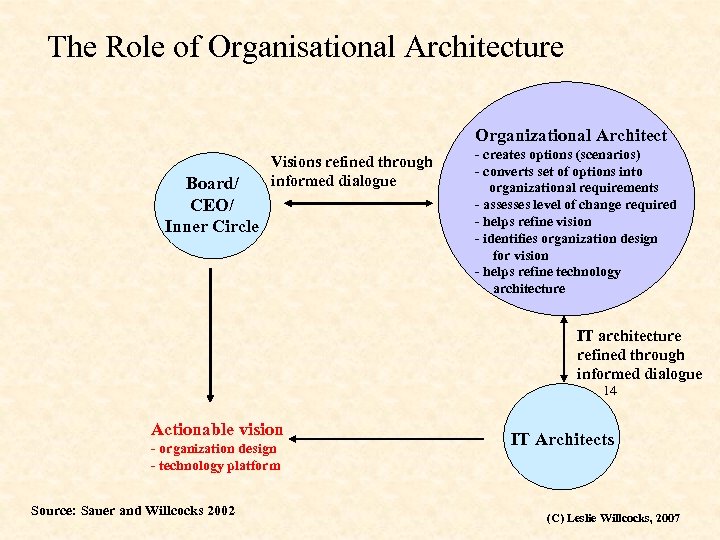
The Role of Organisational Architecture Organizational Architect Board/ CEO/ Inner Circle Visions refined through informed dialogue - creates options (scenarios) - converts set of options into organizational requirements - assesses level of change required - helps refine vision - identifies organization design for vision - helps refine technology architecture IT architecture refined through informed dialogue 14 Actionable vision - organization design - technology platform Source: Sauer and Willcocks 2002 IT Architects (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Key Issues: Some Food For Thought. . . 1. Technology 2. Strategy 3. People 4. Structure 5. Governance 6. Eight IT Differentiators 15 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
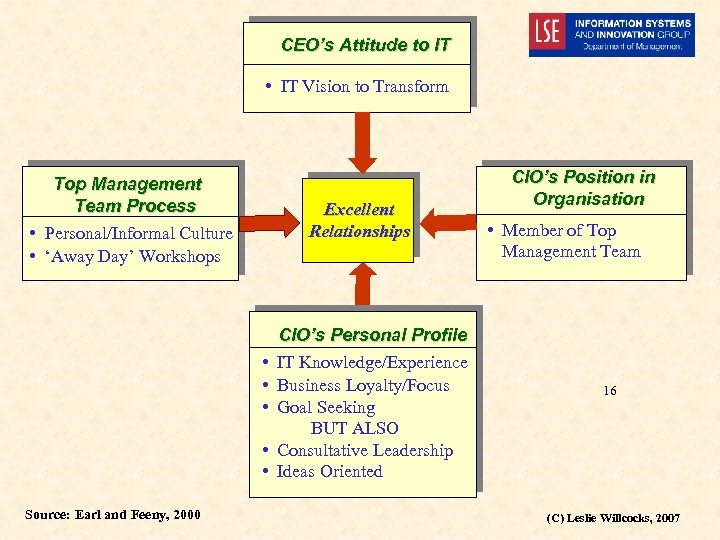
CEO’s Attitude to IT • IT Vision to Transform Top Management Team Process • Personal/Informal Culture • ‘Away Day’ Workshops Excellent Relationships • • • Source: Earl and Feeny, 2000 CIO’s Personal Profile IT Knowledge/Experience Business Loyalty/Focus Goal Seeking BUT ALSO Consultative Leadership Ideas Oriented CIO’s Position in Organisation • Member of Top Management Team 16 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
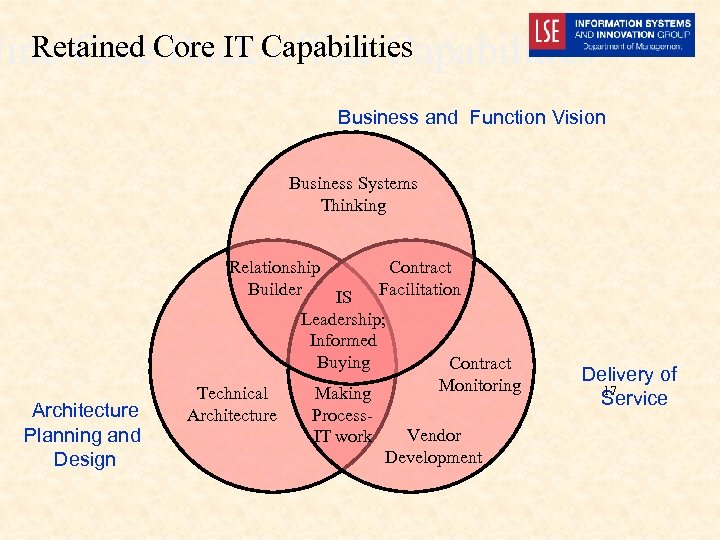
Retained Back-office Capabilities Nine Core IT Capabilities Business and Function Vision Business Systems Thinking Architecture Planning and Design Relationship Contract Builder Facilitation IS Leadership; Informed Buying Contract Monitoring Technical Making Architecture Process. IT work Vendor Development Delivery of 17 Service

Key Issues: Some Food For Thought. . . 1. Technology 2. Strategy 3. People 4. Structure and Governance 5. Eight IT Differentiators 18 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
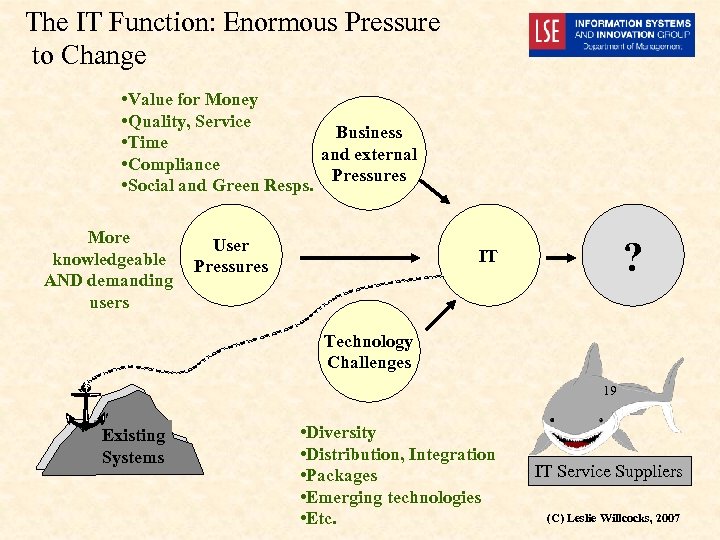
The IT Function: Enormous Pressure to Change • Value for Money • Quality, Service Business • Time and external • Compliance Pressures • Social and Green Resps. More knowledgeable AND demanding users User Pressures ? IT Technology Challenges 19 Existing Systems • Diversity • Distribution, Integration • Packages • Emerging technologies • Etc. IT Service Suppliers (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
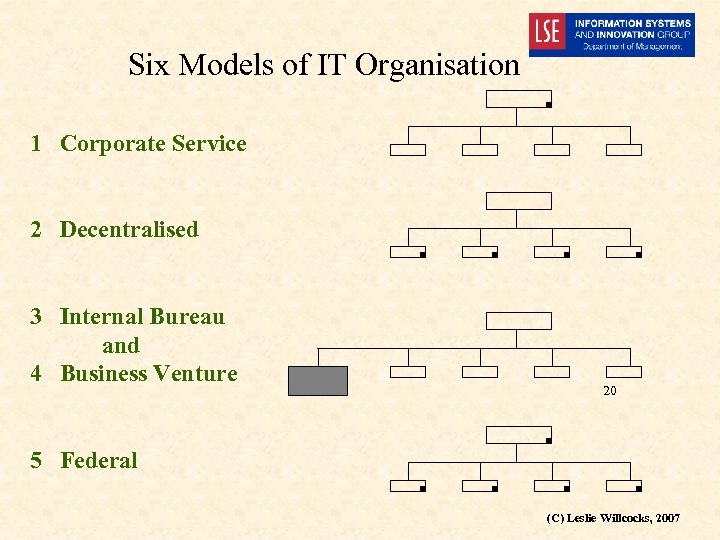
Six Models of IT Organisation 1 Corporate Service 2 Decentralised 3 Internal Bureau and 4 Business Venture 20 5 Federal (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
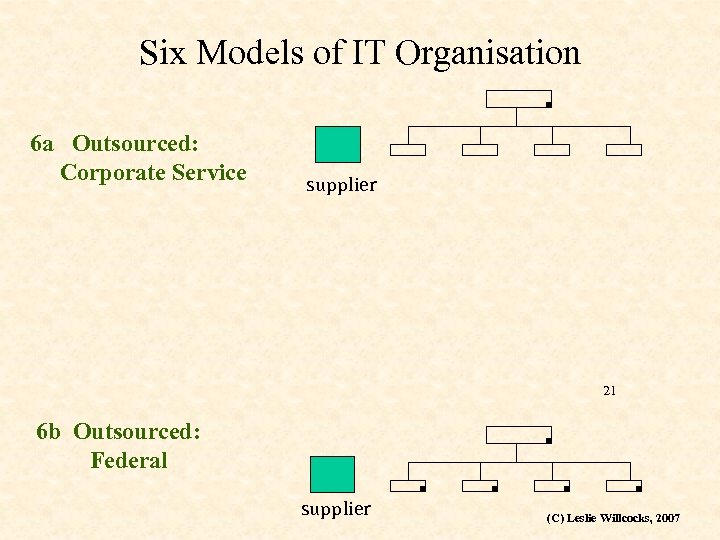
Six Models of IT Organisation 6 a Outsourced: Corporate Service supplier 21 6 b Outsourced: Federal supplier (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Governance Defined “IT governance—specifying the framework for decision rights and accountabilities to encourage desirable behaviour in the use of IT. ” –Weill, MISQE, 2004 • Decision rights and inputs • Desirable behaviour e. g sharing, reuse, cost savings, innovation, growth 22 • Mechanisms – IT council, architecture office, SLAS… • Business value – responsibilities, accountabilities, metrics… (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Stronger IT Governance Is Needed: • IT has become more important, but less under ‘control’ of the IT function • Firms face major new opportunities and risks as IT migrates outside the IT department • Complexity and ‘rogue’ behaviour need to be managed • Links to, and learning from, corporate governance • Top IT performers govern IT differently depending on objectives – asset usage, revenue growth, flexibility, ROA/profits • The business must help by: – Understanding what is possible, and not possible, in IT – Providing more explicit direction on the business approach and priorities – Disciplining its own behaviour, cooperating more 23 – Addressing complexity head on – Being engaged in its IT governance and management responsibilities – Making some uncomfortable choices e. g on shared services/applications…. . (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

Important IT Governance Concepts • IT Principles – Clarifying the business role of IT • IT Architecture – Defining integration and standardisation requirements • IT Infrastructure – Determining shared and enabling services • Business Application Needs – Specifying the business need for purchased or internally developed 24 IT applications • IT Investment and Prioritization – Choosing which initiatives to fund and how much to spend Weill and Ross, 2004 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
Summary: Eight I. T. Differentiators • Listen to the technology; be informed by globalization dynamics (Friedman, 2005: Moscella, 1997, 2004) • IT governed as a strategic portfolio by to relevant stakeholders (Willcocks et al. 2003: Weill and Ross, 2005) • IT led by a credible CIO, influential amongst senior business execs. including CEO (Feeny and Ross, 2000) • Disciplined mixed sourcing strategy, management, and delivery regime (Cullen and Willcocks, 2004: Willcocks and Lacity, 2006 • Business maturity to manage IT as a strategic resource (Willcocks et al. 1997; Broadbent et al. 2005) • Retain specific key IT capabilities (Willcocks and Lacity 2006) • Ensure key supplier capabilities (Feeny et al. , 2005) • Core organizational project management capability (Willcocks et al. , 2003) Ensure Value for IT Spend 25 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007

USEFUL REFERENCES 1. Willcocks, L. et al. (2003) Making IT Count: Strategy, Delivery and Infrastructure. Butterworth-Heinemann 2. Willcocks, L. and Lacity, M. (2007) Global Sourcing of Business and IT Services. Palgrave, London 3. Sauer, C. and Willcocks, L. (2002) Evolution of the Organizational Architect. Sloan Management Review, April. 4. Weill, P. and Ross, J. (2004) IT Governance. Harvard Business Press, Boston 5. Willcocks, L. et al. (1997) Managing IT As A Strategic Resource. Mc. Graw Hill, Maidenhead 6. Earl and Feeny (2000) How to be a CEO in an Information Age, . Sloan Management Review, Winter 26 (C) Leslie Willcocks, 2007
04b5da4b3d4093ae6cf96814eacc2ea1.ppt