BCII-Week 13-Doors.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

BUILDING CONSTRUCTION II ECM 3154 WEEK 13 DOORS Power. Point® Slides by Zamzarina Bt Md. Judyar Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 1

CHAPTER OVERVIEW • Last Updated: This chapter brings the student through the internal fixtures and fittings of doors. © LMS SEGi education group 2

LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Last Updated: Highlights on the performance requirements and types of door. Introducing students to door frames, linings and drawing plans of various types of door. © LMS SEGi education group 3

LEARNING OUTCOMES • • • Last Updated: Students must be familiar with the types of door available. These knowledge is necessary especially in the decision making process since door is one of the building elements. Understand the properties of various units of door as they relate to fire, security, privacy and operation. © LMS SEGi education group 4

INTRODUCTION • • • Last Updated: Doors are used to provide security, privacy, and fire protection to access openings in interior and exterior walls. The choices are depends on traffic passing through the opening and the door’s appearance. In residential work interior doors provide privacy and some degree of security and often, an important part of the exterior design. © LMS SEGi education group 5
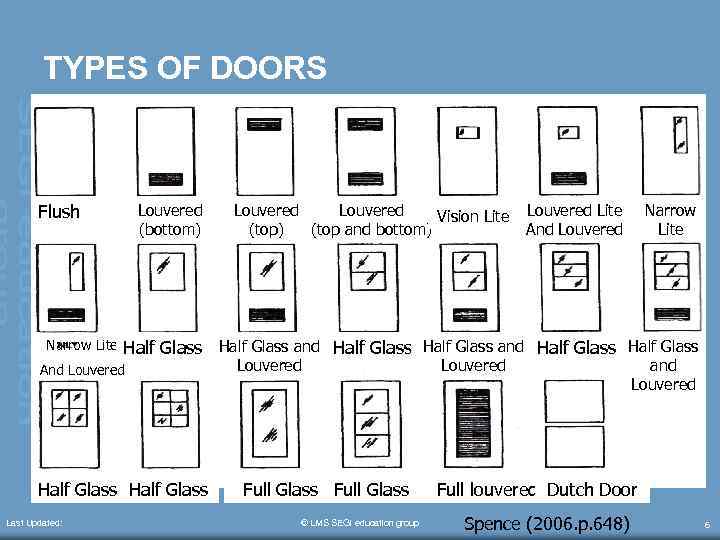
TYPES OF DOORS Flush Narrow Lite Louvered (bottom) Louvered Lite And Louvered Narrow Lite Half Glass and Half Glass And Louvered Half Glass Last Updated: Louvered Vision Lite (top) (top and bottom) Louvered Full Glass © LMS SEGi education group Louvered and Louvered Full louvered Dutch Door Spence (2006. p. 648) 6

CLASSIFICATIONS OF DOORS • Can be as external or internal door. • External door usually thicker and more robust in design than internal doors since they have more function to fulfill Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 7
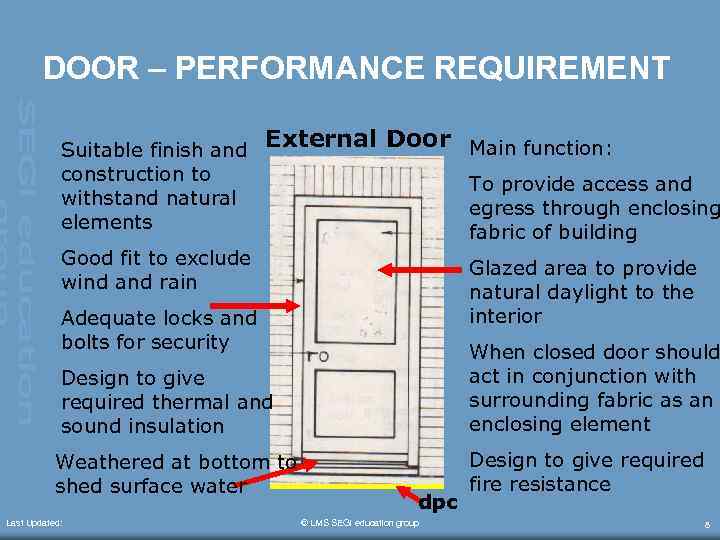
DOOR – PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENT Suitable finish and construction to withstand natural elements External Door Main function: To provide access and egress through enclosing fabric of building Good fit to exclude wind and rain Glazed area to provide natural daylight to the interior Adequate locks and bolts for security Design to give required thermal and sound insulation When closed door should act in conjunction with surrounding fabric as an enclosing element Weathered at bottom to shed surface water Design to give required fire resistance Last Updated: dpc © LMS SEGi education group 8
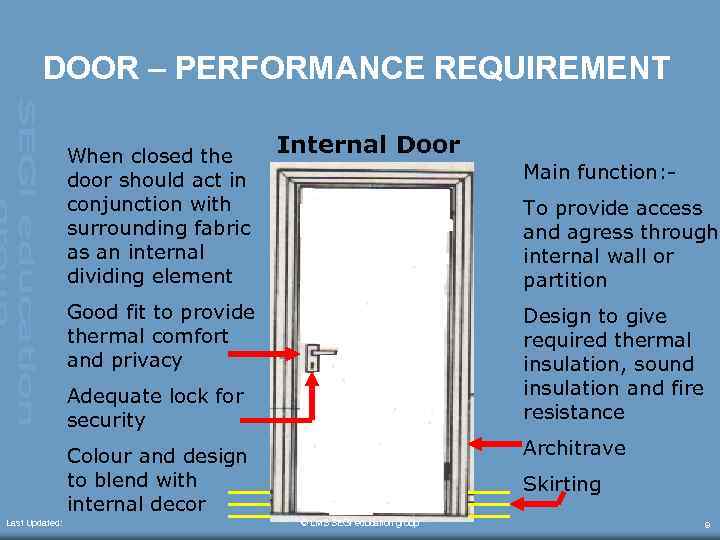
DOOR – PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENT When closed the door should act in conjunction with surrounding fabric as an internal dividing element Internal Door Main function: To provide access and agress through internal wall or partition Good fit to provide thermal comfort and privacy Design to give required thermal insulation, sound insulation and fire resistance Adequate lock for security Architrave Colour and design to blend with internal decor Last Updated: Skirting © LMS SEGi education group 9

TERMINOLOGY • • Last Updated: Door frame – consists of a sill, 2 post of jamb and a head Door head (lintel) – support the weight of the wall above Door jamb – vertical member of the door frame Architrave – sealing of the junction between the frame and the wall © LMS SEGi education group 10
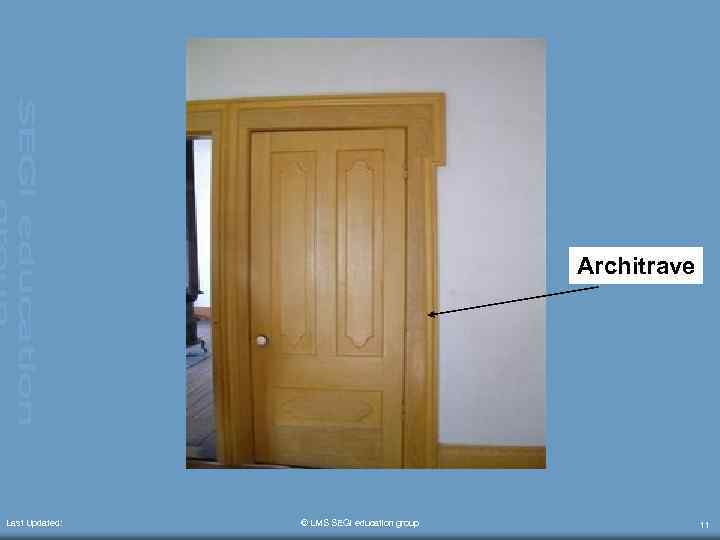

Architrave Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 11
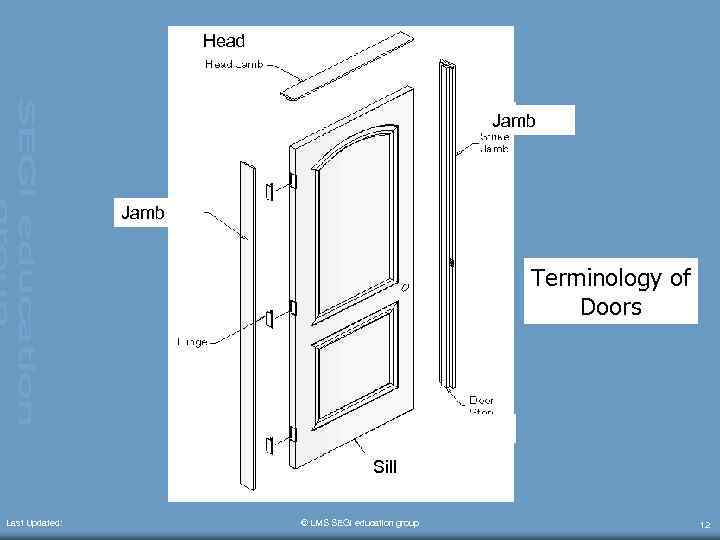
Head Jamb Terminology of Doors Sill Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 12

DESIGN REQUIREMENTS • • Last Updated: Operable (can be open and close) Ironmongery (hinges, door lock, etc) Strength and stability (for security) Fire resistance (exit route requirements) © LMS SEGi education group 13

DESIGN REQUIREMENTS (CONT’D) • • Last Updated: Weather protection Sound insulation (for privacy) Aesthetic Durability © LMS SEGi education group 14

EXTERNAL DOOR • • Last Updated: These door are available in a variety of types and style, either in timber, aluminium alloy or steel. The majority of external doors are however made from timber, the metal doors being mainly confined to fully glazed doors such as ‘patio doors’. © LMS SEGi education group 15

EXTERNAL DOORS – TYPES (CONT’D) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 16
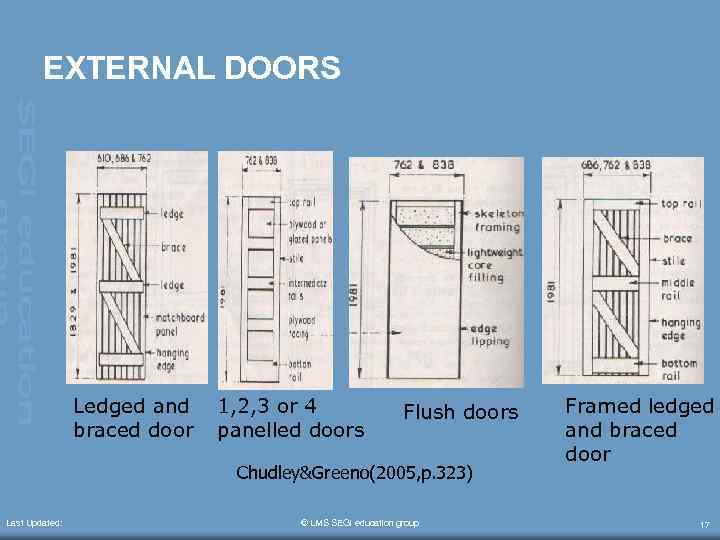
EXTERNAL DOORS Ledged and braced door 1, 2, 3 or 4 panelled doors Flush doors Chudley&Greeno(2005, p. 323) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group Framed ledged and braced door 17

EXTERNAL DOOR FRAMES • • • Last Updated: Door frame are available for all standard external doors and can be obtained with a fixed solid or glazed panel above a door height transom Door frames are available for doors opening inwards or outwards Most door frames are made to the recommendations set out in BS 1567 © LMS SEGi education group 18
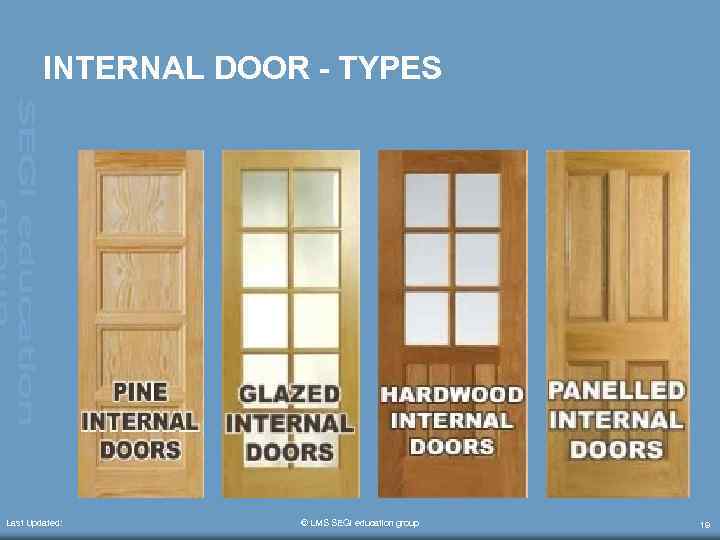
INTERNAL DOOR - TYPES Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 19

INTERNAL DOOR – TYPES (CONT’D) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 20

MATCHBOARDED DOORS • • Last Updated: These doors can be used as external or internal doors Are not particularly attractive in appearance It is simple and cheap to construct The use of this type of door is limited to buildings such as sheds, farm house, cottage, etc © LMS SEGi education group 21

FLUSH DOOR • • • Last Updated: The flush door construction can be considered either skeleton core doors or solid core doors The advantage of solid core doors are having a good sound insulation and provide a higher degree of fire resistance Solid flush door is suitable for the internal/ external use Flush door has the advantage of a plain face which is easy to clean and decorate Flush door can be faced with hardboard, plywood or a plastic laminate © LMS SEGi education group 22

FIRE RESISTANT DOOR • • Last Updated: These doors provide an effective barrier to the passage of fire from time to time designated by a reference coding The performance of fire door is simplified by expressing the category with the initials FD and the integrity in minutes numerically © LMS SEGi education group 23

FIRE RESISTANT DOOR (CONT’D) • • Last Updated: For example: FD 60 indicates a fire door with 60 minutes integrity These doors appear the same as ordinary flush door For one hour, an additional layer of 5 mm asbestos partition boards is bonded to each side of the flaxboard Internally the door is divided at mid height with a 65 mm central rail, and each half is filled with flaxboard or 9. 5 mm plasterboard nailed to each side of a timber framework. With a 4 mm veneered plywood facing an overall thickness of 45 mm, this construction satisfies the half-hour specification © LMS SEGi education group 24

FIRE RESISTANT DOOR (CONT’D) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 25

FIRE RESISTANT DOORS (CONT’D) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 26

FIRE RESISTANT DOORS Spencer(2006, p. 651) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 27
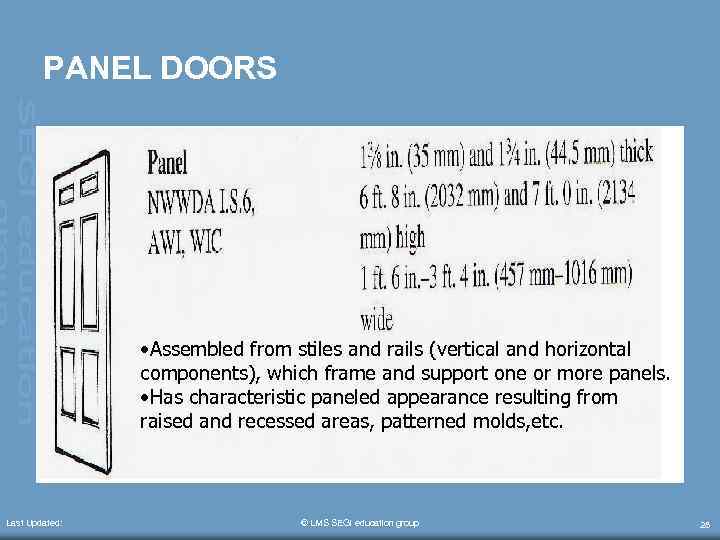
PANEL DOORS • Assembled from stiles and rails (vertical and horizontal components), which frame and support one or more panels. • Has characteristic paneled appearance resulting from raised and recessed areas, patterned molds, etc. Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 28
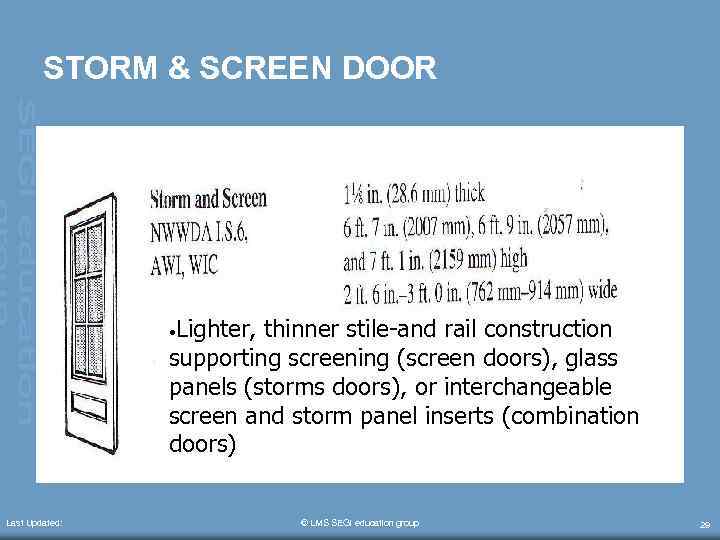
STORM & SCREEN DOOR • Lighter, thinner stile-and rail construction supporting screening (screen doors), glass panels (storms doors), or interchangeable screen and storm panel inserts (combination doors) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 29
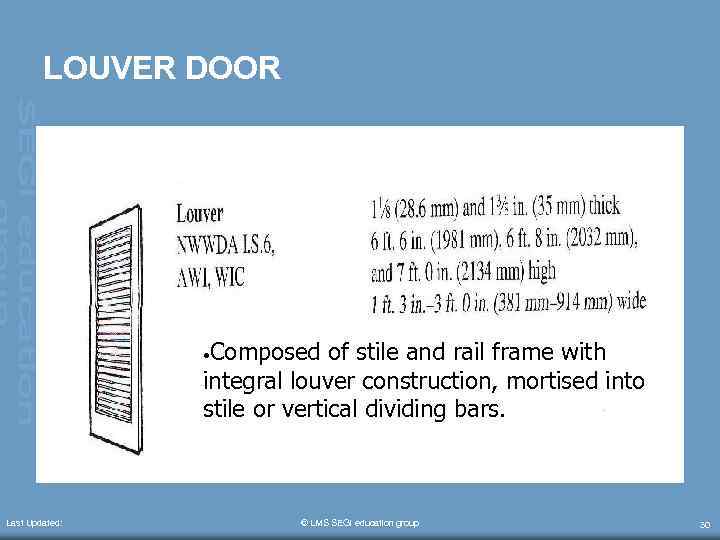
LOUVER DOOR • Composed of stile and rail frame with integral louver construction, mortised into stile or vertical dividing bars. Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 30

ACCORDION FLODING DOOR Assembled from narrow wood strips or single wood slats, 3 ½ in. (89 mm) to 5 in. (127 mm) wide, with fabric, plastic or metal hinges, resembling long drapeline doors. Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 31
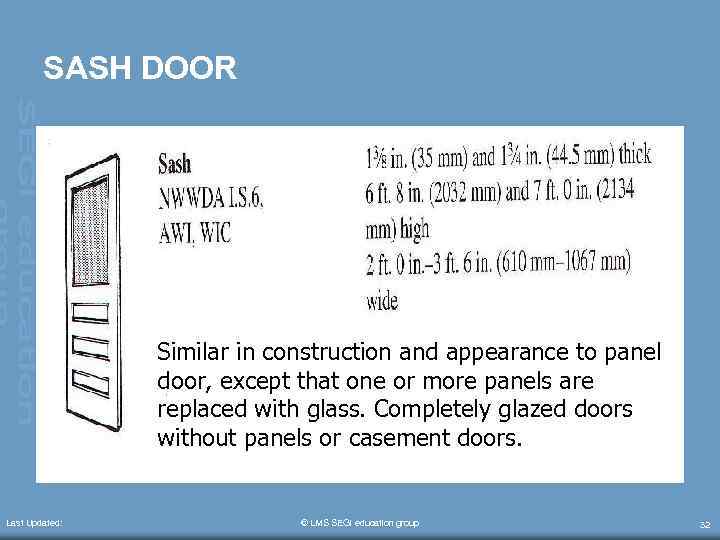
SASH DOOR Similar in construction and appearance to panel door, except that one or more panels are replaced with glass. Completely glazed doors without panels or casement doors. Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 32
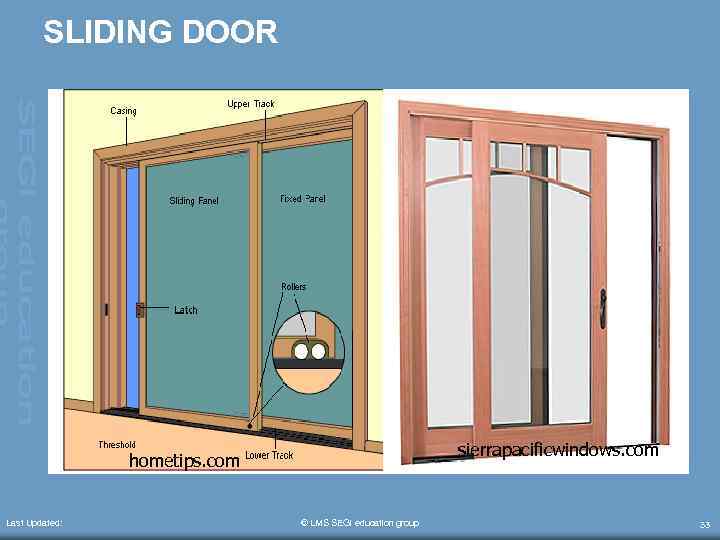
SLIDING DOOR sierrapacificwindows. com hometips. com Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 33

SLIDING DOOR • • Last Updated: Sliding door may be used in all forms of buildings from the small garage to the large industrial structure They may be incorporated into a design for any of the following reasons: • As an alternative to a swing door to conserve space or where it is not possible to install a swing door due to space restrictions • As a movable partition used in preference to a demountable partition because of the frequency with which it could be moved © LMS SEGi education group 34

SLIDING DOOR (CONT’D) • Last Updated: Many types of patent sliding door are available to suit all needs but these can usually be classified by the way the doors operate: • Straight sliding • These can be of a single leaf or designed to run on adjacent and parallel track to give one parking © LMS SEGi education group 35

SLIDING DOOR (CONT’D) • Last Updated: End folding doors • These are sliding and folding doors which are used for wider openings than the straight doors given above • They usually consists of a series of leaves operating with a bottom guide track so that the folding leaves can be parked to the sides of the openings © LMS SEGi education group 36
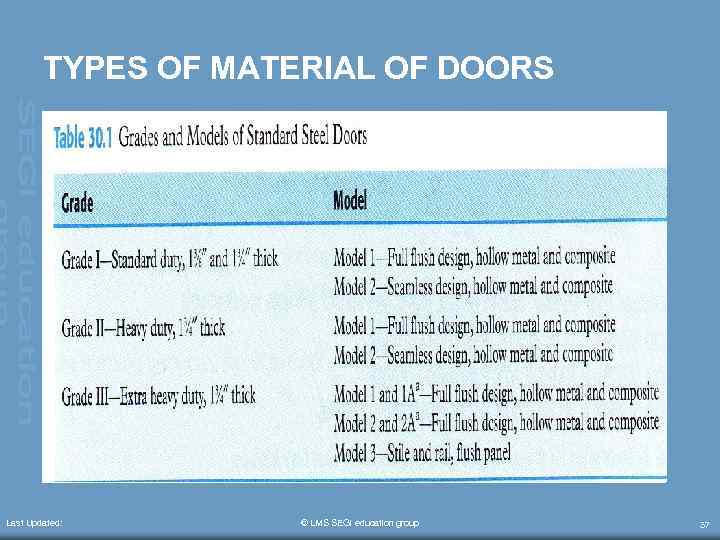
TYPES OF MATERIAL OF DOORS Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 37
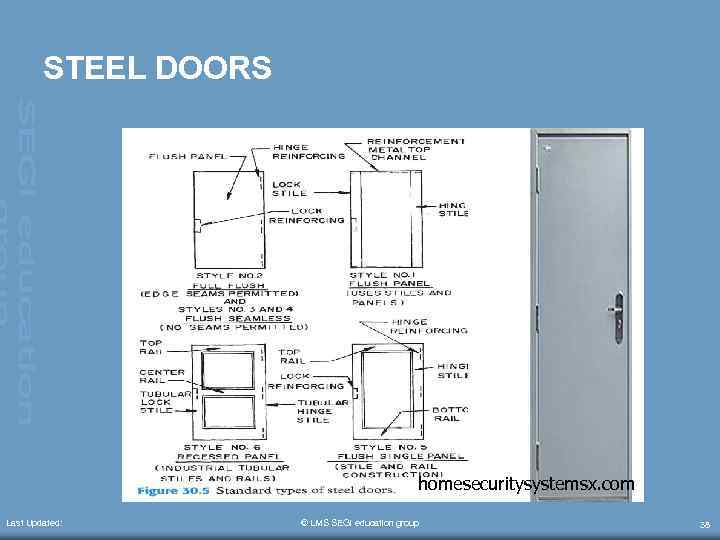
STEEL DOORS homesecuritysystemsx. com Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 38

SPECIAL DOORS These insulated rolling service doors have either steel or aluminium interiors and exteriors skins separated by a closed cell urethane foam insulation core Spencer(2006, p. 654) Last Updated: During the hours this business is open it is totally exposed to the public and rolling grille doors provide security during closed hours yet permit the interior to be visible. © LMS SEGi education group 39

SPECIAL DOORS Spencer(2006, p. 653) Last Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 40

QUIZZES 1. 2. Last Updated: Describe the performance requirements of door. ……………………………………………………………… Identify any Four type of door. ……………………. © LMS SEGi education group 41

KEY TERMS 1. Demountable partition Definition The movable wall system shall offer maximum flexibility and reusability to accommodate frequent and quick relocation work without loss of materials, damage or modification to panels or to adjoining structures such as ceilings, fixed walls and floors. 2. Folding leaves Definition • One of a pair of doors or windows or a separately movable division of a folding or sliding door. 3. FD Definition Fire resistant door Last Updated: 2/11/2018 Updated: © LMS SEGi education group 42

REFERENCES • • • Last Updated: Chudley, R. , & Greeno, R. , 2005. Construction Technology, 4 th ed. England: Pearson. Chudley, R. , & Greeno, R. , 2001. Advanced Construction. Technology, 3 rd ed. England: Longman. Spence, W. , D. , 2006. Construction Materials, Methods, and Techniques, 2 nd ed. US: Delmar. © LMS SEGi education group 43

REFERENCES • • • Last Updated: Chudley, R. , & Greeno, R. , 2005. Construction Technology, 4 th ed. England: Pearson. Chudley, R. , & Greeno, R. , 2001. Advanced Construction. Technology, 3 rd ed. England: Longman. Spence, W. , D. , 2006. Construction Materials, Methods, and Techniques, 2 nd ed. US: Delmar. hometips. com retrieved 22 nd August 2011 sierrapacificwindows. com retrieved 22 nd August 2011 © LMS SEGi education group 44

• Last Updated: Thank you © LMS SEGi education group 45
BCII-Week 13-Doors.ppt