9a41027923e97218b80f2c45a4a58c92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

BUILDING AND SECURING GOVERNMENT DRUPAL SITES IN THE CLOUD #acquia

Presenters Michael Lemire Director of Information Security michael. lemire@acquia. com Chris Brown Technical Account Manager chris. brown@acquia. com Jim Salem Vice President of Cloud Services jim. salem@acquia. com

Agenda • Review Current US Government Compliance landscape • Learn how to achieve Federal Compliance in the Cloud • International and Developing Compliance Standards • Case Study - Defense Security Cooperative Agency (DSCA) • How Acquia achieved a compliant ready hosting platform.

The Opportunity • Governments are expanding use of Drupal • Drupal is open source • Cost effective vs proprietary licensed software • Proven secure • Drupal facilitates shared development between agencies • Federal Government has prioritized a Cloud First Strategy • Federal Cloud Computing Strategy by Vivek Kundra, former US Fed CIO • Recognition of fundamental shift to cloud • Targets $20 B of $80 B annual federal IT spending for cloud • Significant cost savings to governments • -more agile, and is more easier scalable • Similar initiatives in the UK, Australia, all over • We are at the tip of the iceberg!

Current US Government Compliance Landscape FISMA, DIACAP and Fed. RAMP are standardized approaches to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for information systems utilized by the Federal government. FISMA - Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002. Do. D agencies. Applicable to non- DIACAP – Department of Defense Information Assurance Certification and Accreditation Process. Applicable to Do. D related agencies. With both FISMA and DIACAP each information system must be documented, reviewed by independent third party assessor and authorized by authorizing officials. Time consuming, expensive

Coming Soon - Fed. RAMP - Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program • Establishes an “authorize once, use many times” framework for cloud computing products and services. Fed. RAMP is meant to supersede FISMA and DIACAP for cloud products. • Fed. RAMP was established on Dec 8, 2011 via a memorandum produced by the Federal Chief Information Officer and is due to achieve Initial Operating Capacity in 2012. • Based on the same NIST publications as FISMA with added controls pertinent to the cloud • Fed. RAMP Concept of Operations – defines how the Fed. RAMP process will work • http: //www. gsa. gov/graphics/staffoffices/Fed. RAMP_CONOPS. pdf

Important NIST Publications and Standards FIPS 199 – Security categorization of the information system according to its Confidentiality, Availability and Integrity requirements • • What type of data? Importance to national security? Determine “High water mark” (low, medium, high) NIST 800 -53 rev 3 – Security Controls documented in the SSP All domains of security are covered and must be documented Risk Assessment, Personnel, System Acquisition, Physical and Environmental, Contingency Planning, Configuration Management, Incident Response, Security Awareness Training, Authentication, Logging and Audit, Network Security and Encryption Rev 4 now in draft – adds add’l mobile and cloud controls NIST 800 -30 – Risk Assessments Defines process for assessing risk and how to apply the process to the organizational, mission and information system levels.
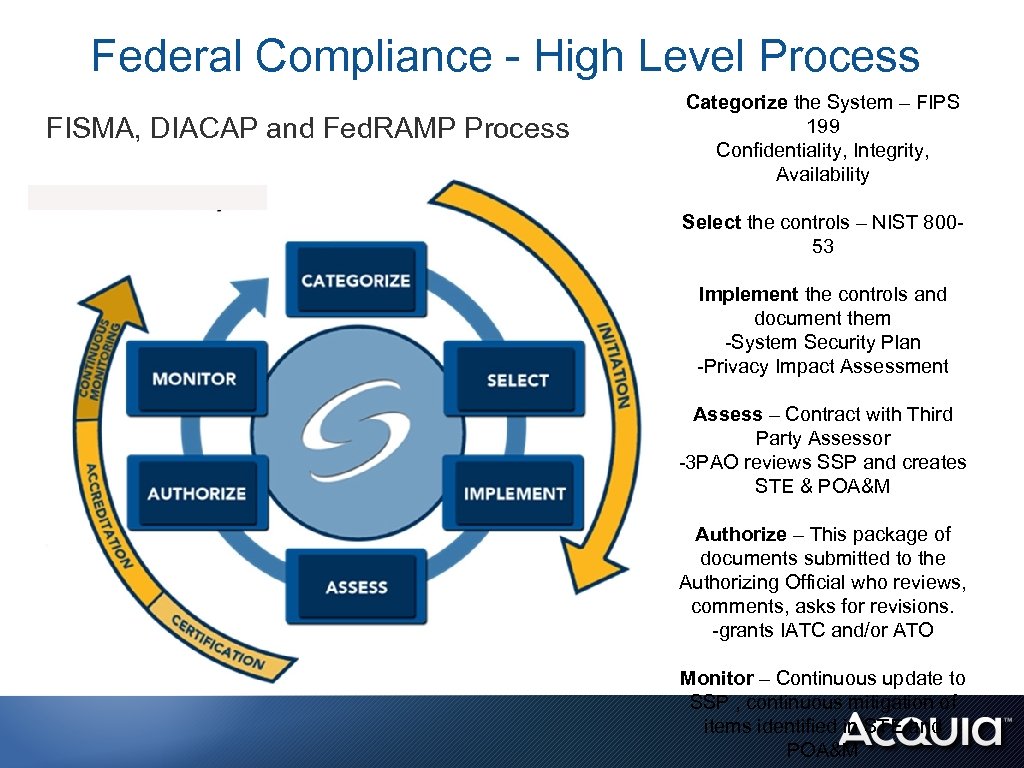
Federal Compliance - High Level Process FISMA, DIACAP and Fed. RAMP Process Categorize the System – FIPS 199 Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Select the controls – NIST 80053 Implement the controls and document them -System Security Plan -Privacy Impact Assessment Assess – Contract with Third Party Assessor -3 PAO reviews SSP and creates STE & POA&M Authorize – This package of documents submitted to the Authorizing Official who reviews, comments, asks for revisions. -grants IATC and/or ATO Monitor – Continuous update to SSP , continuous mitigation of items identified in STE and POA&M

Accomplishing Federal Compliance in the Cloud Service Providers may be responsible for the entire set of controls, or they may be shared in a Shared Responsibility Model Examples: Saa. S may be built on Paa. S Ex: Drupal. Gardens Paa. S may be built on Iaa. S Ex: Acquia Managed Cloud Three primary layers in the shared responsibility model: • Application Layer (Drupal) • OS Stack Layer (Linux, Windows, Database, etc) • Infrastructure Layer (Datacenter, network) *Each entity must document the controls for which they are responsible for. *
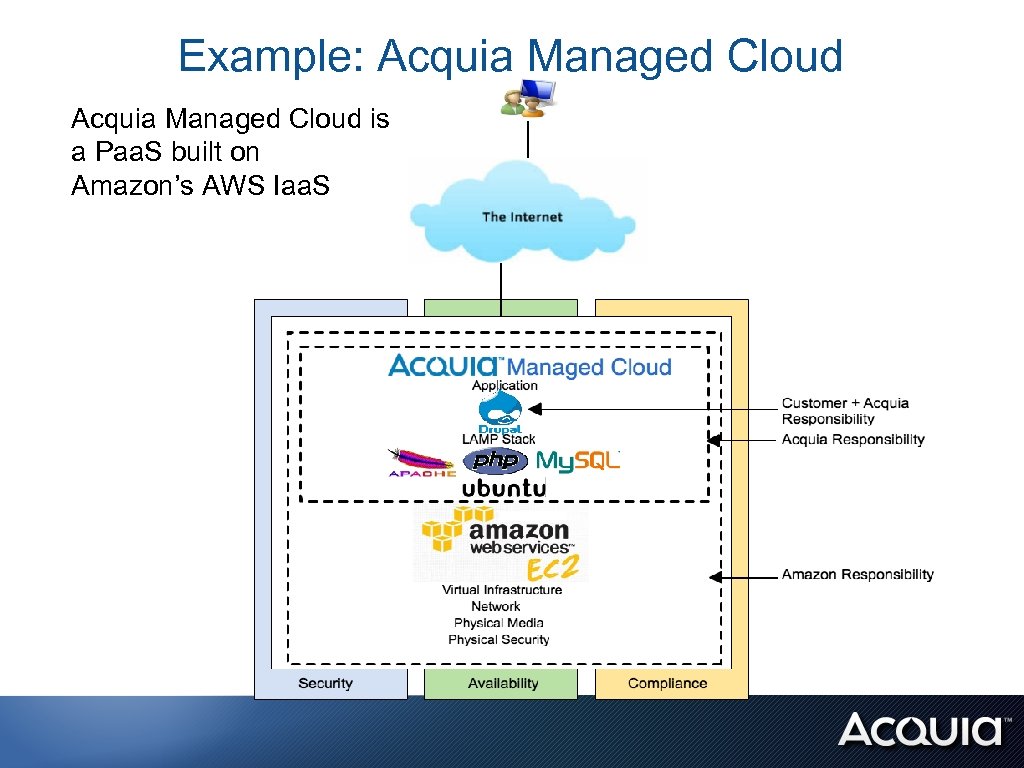
Example: Acquia Managed Cloud is a Paa. S built on Amazon’s AWS Iaa. S
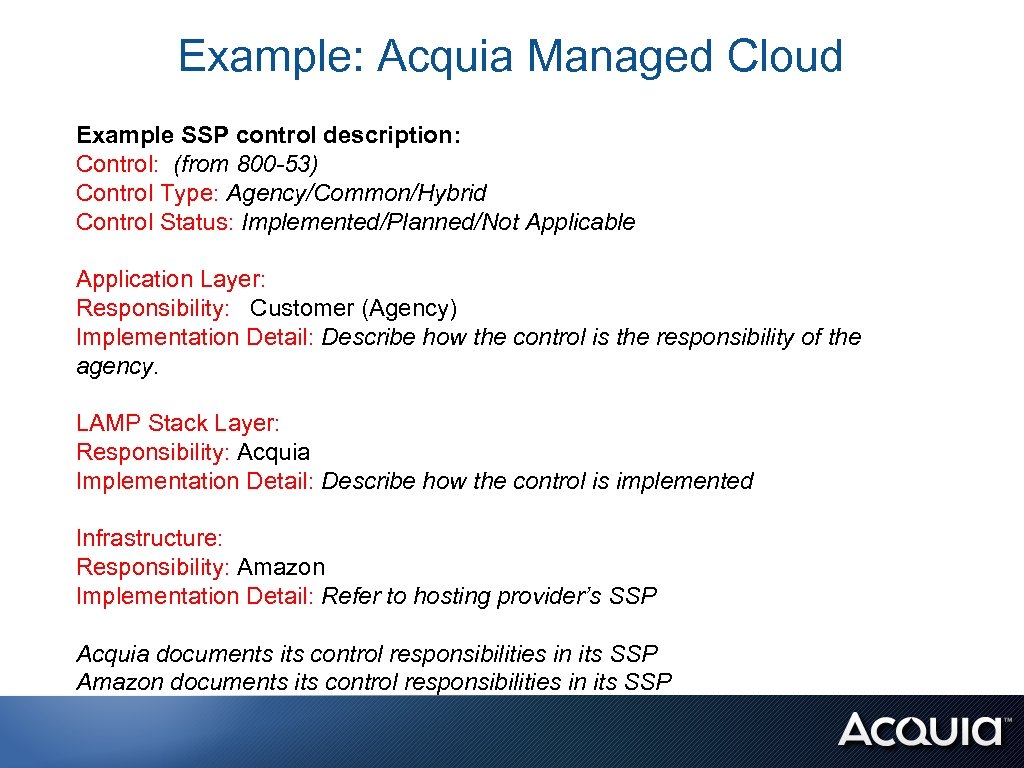
Example: Acquia Managed Cloud Example SSP control description: Control: (from 800 -53) Control Type: Agency/Common/Hybrid Control Status: Implemented/Planned/Not Applicable Application Layer: Responsibility: Customer (Agency) Implementation Detail: Describe how the control is the responsibility of the agency. LAMP Stack Layer: Responsibility: Acquia Implementation Detail: Describe how the control is implemented Infrastructure: Responsibility: Amazon Implementation Detail: Refer to hosting provider’s SSP Acquia documents its control responsibilities in its SSP Amazon documents its control responsibilities in its SSP

International Compliance Landscape ISO/IEC 27002 – -Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Similar to NIST 800 -53 controls; more flexible in that organizations may define the controls which are applicable to its environment. Risk Assessment Security Policies Asset Management HR / Personnel Communications and Networks Access Control System Acquisition, development Continuity Planning Two levels of ISO compliance -self evaluation based on the standards -certification by a third party auditor

Developing Cloud Compliance Standards Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) – organization which promotes best practices for security within Cloud Computing. The CSA is led by a broad coalition of industry practitioners, corporations, associations and other key stakeholders in cloud computing field. Two important CSA initiatives CSA Security Guidance – Recommendations and guidance for cloud service providers to security their clouds according to best practices (Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S service providers) CSA Consensus Initiative Questionnaire –designed to help CSP’s gauge their controls against best practices as defined by the CSA https: //cloudsecurityalliance. org/

Mapping Compliance Standards to Each Other Cloud Service Providers have a number of compliance objectives, each requiring painstakingly long review of standards and gauging adherence to the specified controls. CSA’s Control Compliance Matrix helps ease the process of compliance with sometimes redundant compliance standards. Example: achieving compliance with NIST 800 -53 largely achieves ISO 27002 compliance, the BITS Shared Assessment standard, COBIT, PCI and HIPAA. See Cloud Security Alliance Control Matrix: https: //cloudsecurityalliance. org/
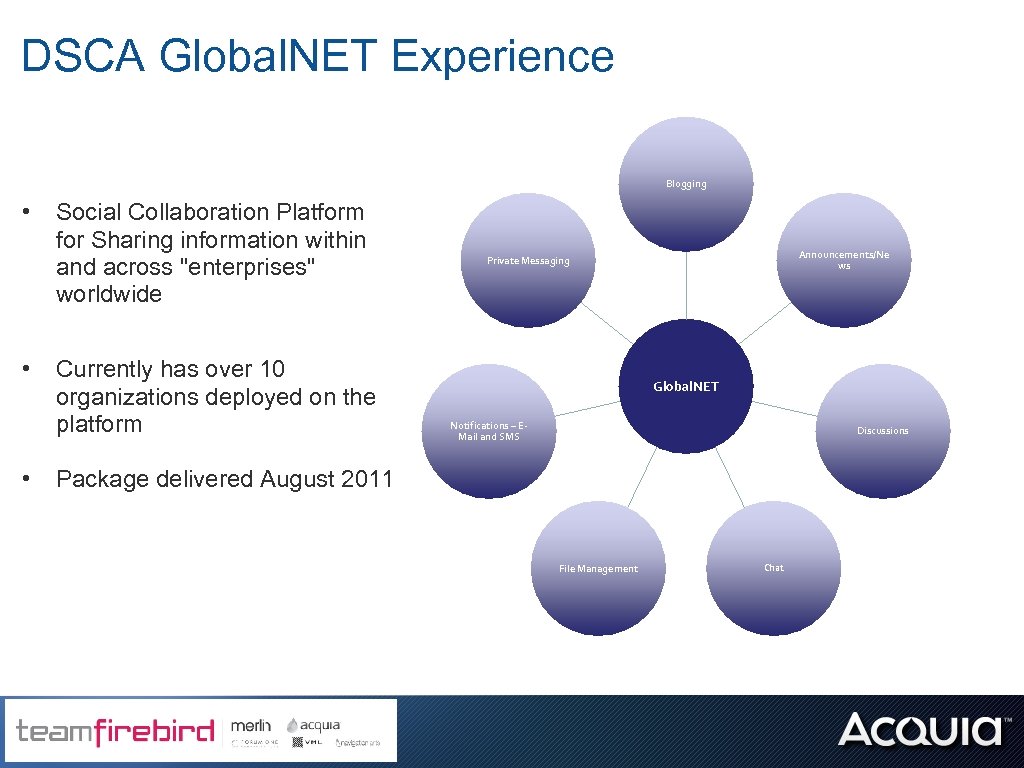
DSCA Global. NET Experience Blogging • • • Social Collaboration Platform for Sharing information within and across "enterprises" worldwide Currently has over 10 organizations deployed on the platform Announcements/Ne ws Private Messaging Global. NET Notifications – EMail and SMS Discussions Package delivered August 2011 File Management Chat
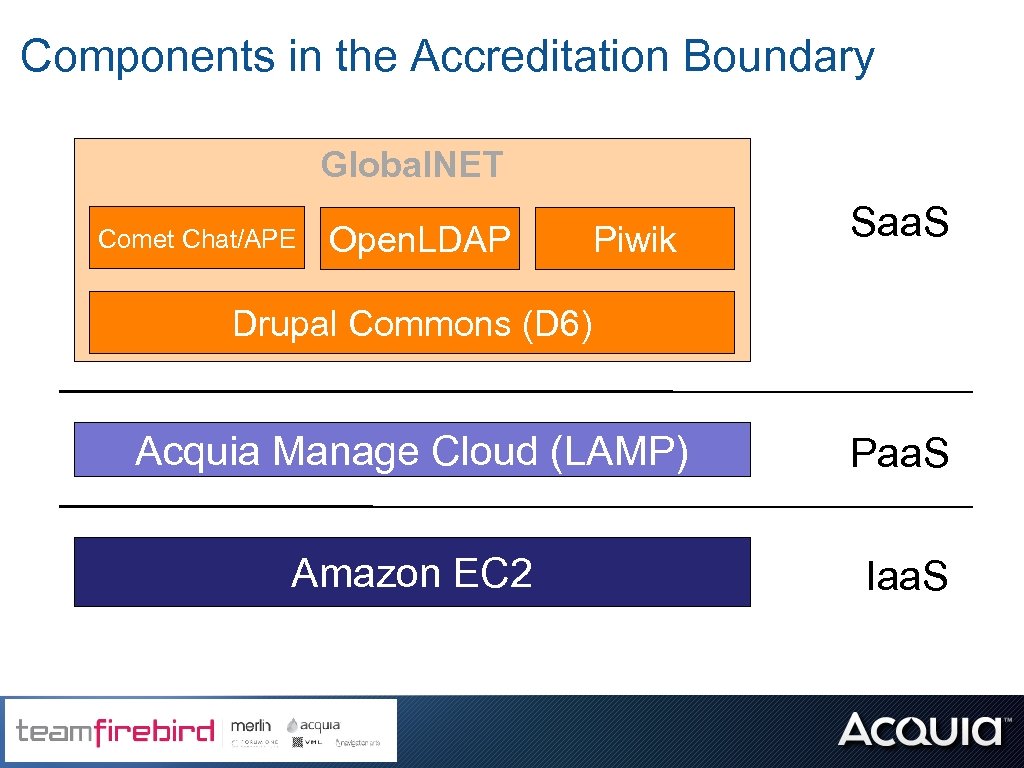
Components in the Accreditation Boundary Global. NET Comet Chat/APE Open. LDAP Piwik Saa. S Drupal Commons (D 6) Acquia Manage Cloud (LAMP) Paa. S Amazon EC 2 Iaa. S
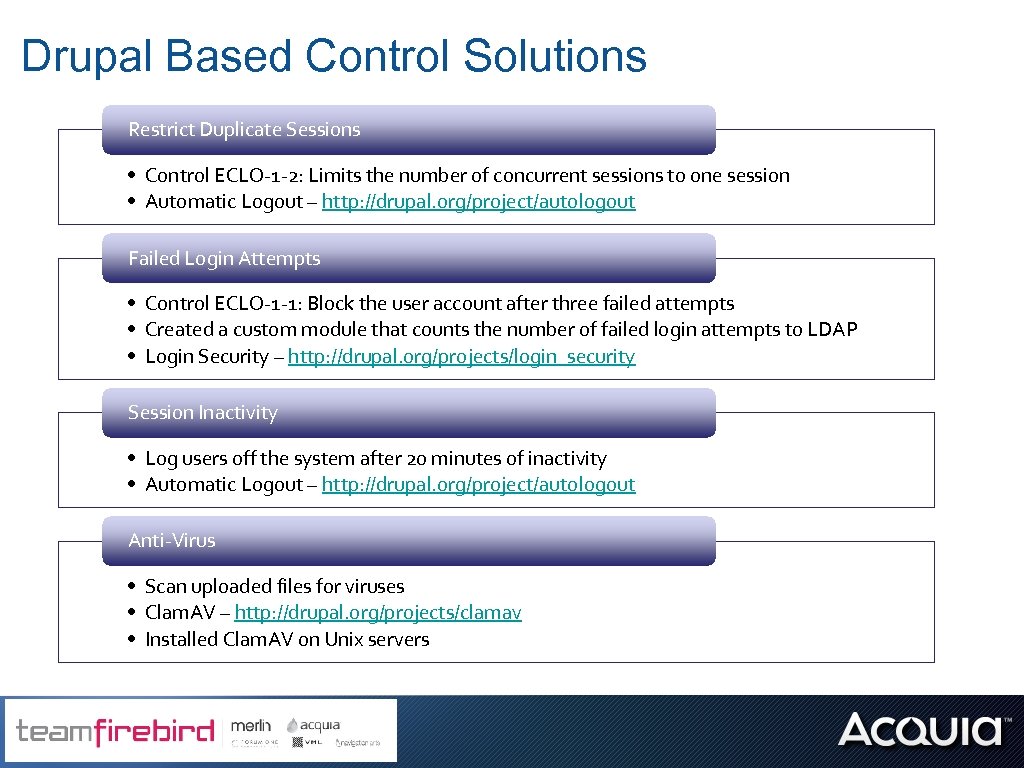
Drupal Based Control Solutions Restrict Duplicate Sessions • Control ECLO-1 -2: Limits the number of concurrent sessions to one session • Automatic Logout – http: //drupal. org/project/autologout Failed Login Attempts • Control ECLO-1 -1: Block the user account after three failed attempts • Created a custom module that counts the number of failed login attempts to LDAP • Login Security – http: //drupal. org/projects/login_security Session Inactivity • Log users off the system after 20 minutes of inactivity • Automatic Logout – http: //drupal. org/project/autologout Anti-Virus • Scan uploaded files for viruses • Clam. AV – http: //drupal. org/projects/clamav • Installed Clam. AV on Unix servers

External Application Control Implementation • Data between all third party applications is encrypted over SSL • Password encryption • Use the LDAP Module to provision accounts in LDAP • Passwords in LDAP are SHA-1 (FIPS 140 -2 compliant) Encrypted • Governance • Users with elevated accounts should have a not-elevated account on system • User approval and role assignment policies • User 1 should not be used
Challenges Cloud and Drupal Accreditation • Common Critera/NIAP for Drupal • • Expensive Process that needs a sponsor What modules would be put through the process? How would adding different modules affect the Certification? • Governance around user 1 account to ensure it is not used as a group account • Multi-tenancy of the Cloud • • • Hardware Software Shared Disks • Shared Responsibility Model • • • How are the swim lanes of responsibility draw between the parties involved? SLA agreements between each of the parties Security Responsibility

Building a Compliance-Ready Infrastructure • • • Drupal Stack Architecture Robust and secure Server Management Architecture y! rl a Controlled access Standard, reproducible configurations Policies and Procedures Documented and auditable Consistent Test, Test ta S E rt
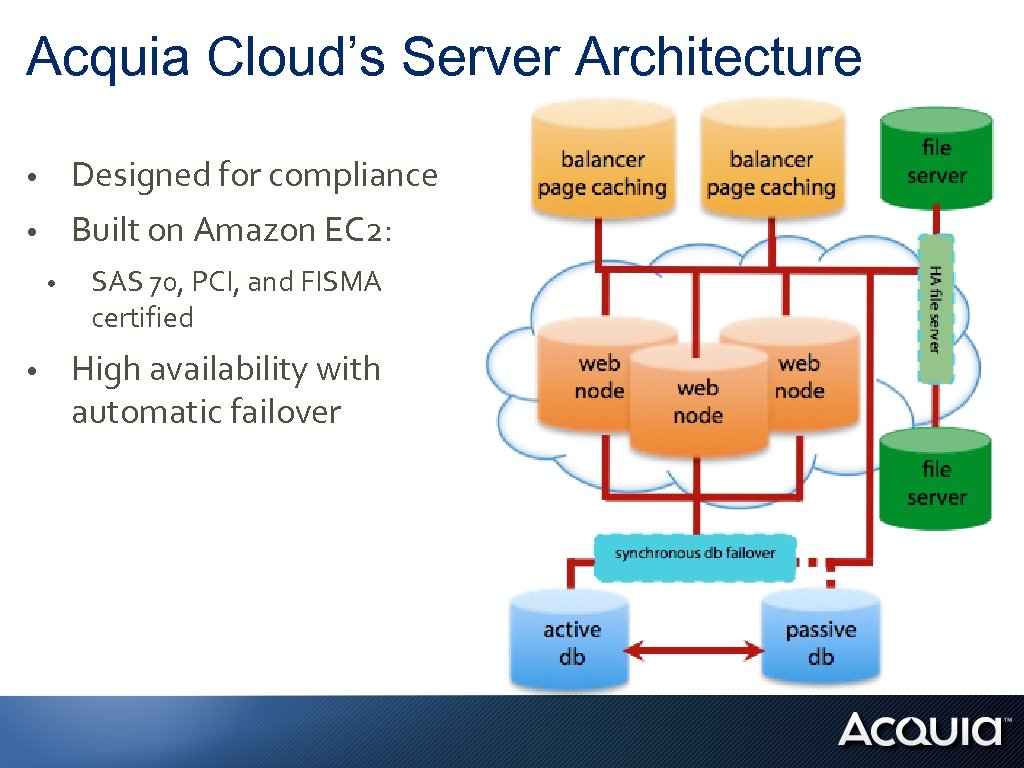
Acquia Cloud’s Server Architecture • Designed for compliance • Built on Amazon EC 2: • • SAS 70, PCI, and FISMA certified High availability with automatic failover
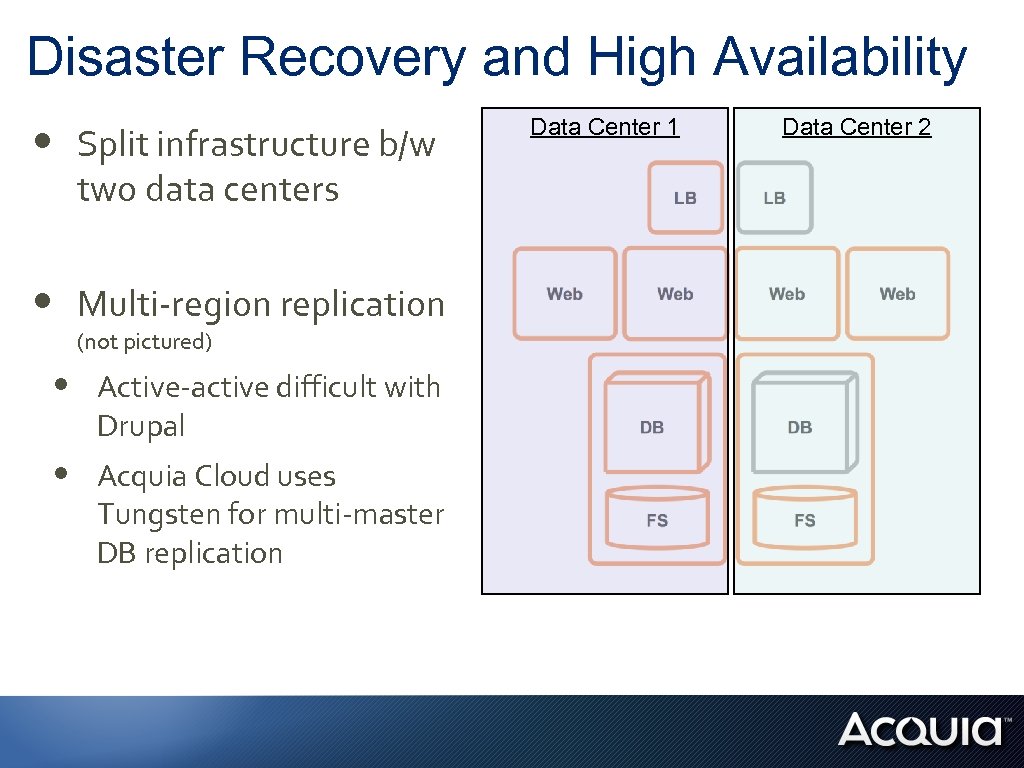
Disaster Recovery and High Availability • Split infrastructure b/w two data centers • Multi-region replication (not pictured) • Active-active difficult with Drupal • Acquia Cloud uses Tungsten for multi-master DB replication Data Center 1 Data Center 2
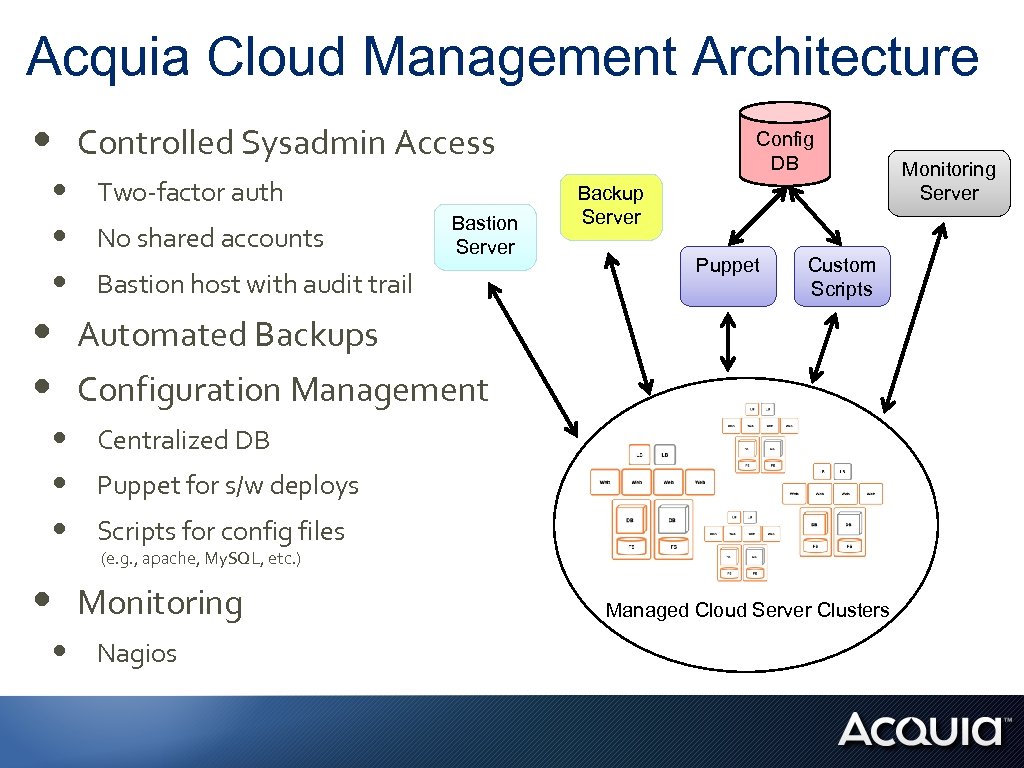
Acquia Cloud Management Architecture • • • Controlled Sysadmin Access Two-factor auth No shared accounts Bastion Server Bastion host with audit trail Config DB Backup Server Puppet Custom Scripts Automated Backups Configuration Management Centralized DB Puppet for s/w deploys Scripts for config files (e. g. , apache, My. SQL, etc. ) Monitoring Nagios Managed Cloud Server Clusters Monitoring Server

Policies and Procedures • • Start small and build up Write them down and follow them Key Policies Access control Change management Disaster recovery Security review Crisis management

Test, Test Anything that is not tested will not work (for long) • • Automated system tests Verify you can continue to deploy servers consistently Positive and negative security tests On-going vulnerability scans Simulated failures Untested failovers and redundancies will NOT work! Backup verification Test the processes too!

9a41027923e97218b80f2c45a4a58c92.ppt