546cc54928a567a05e5dc34da903f0b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Building an Automation Framework around Open Source Technologies Charles Thangamuthu 20 th November 2010 Disclaimer – This is a personal case study and does not represent PTC’s view on the topic

Thanks Silicon. India! 2

Before we step in…. What this presentation is § An example of how open source tools can be used to form an automation framework § To say there are solutions readily available for many of your problems – don’t have to reinvent the wheel § More of a case study What this presentation is not § Does not say open source technology is better than commercial testing tools § Does not say the components talked about are the best in their class § Does not talk about a PTC proprietary or certified framework § Does not claim all your automation woes are solved 3
Topics § Automation Framework – Definition – Requirements – Functions § Generic Architecture § Framework components – – – Automation Tool Version Control System Continuous Integration Test Runner Data Manager § Advantages – Flexibility – Scalability § Benefits 4
Test Automation Framework Definition - What is it? § Automation Framework is not a single tool or process but a collection of tools and processes working together to support automated testing of an application § Is an integrated environment that sets the rules, assumptions, concepts and tools to aid automated testing § It integrates function libraries, test data, object details and various reusable modules § These components act as building blocks which can be assembled to represent a business process 5
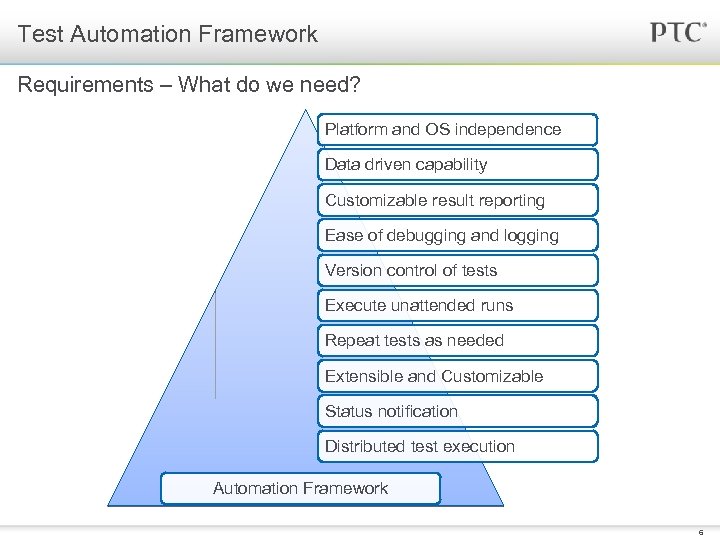
Test Automation Framework Requirements – What do we need? Platform and OS independence Data driven capability Customizable result reporting Ease of debugging and logging Version control of tests Execute unattended runs Repeat tests as needed Extensible and Customizable Status notification Distributed test execution Automation Framework 6
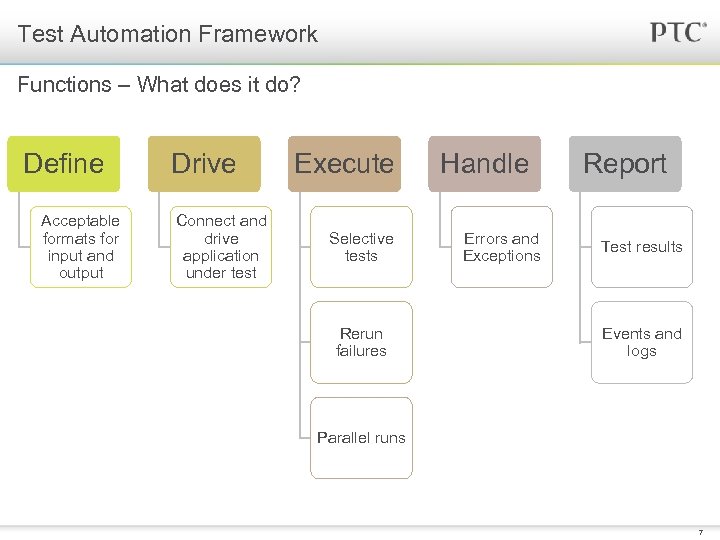
Test Automation Framework Functions – What does it do? Define Acceptable formats for input and output Drive Connect and drive application under test Execute Selective tests Rerun failures Handle Errors and Exceptions Report Test results Events and logs Parallel runs 7
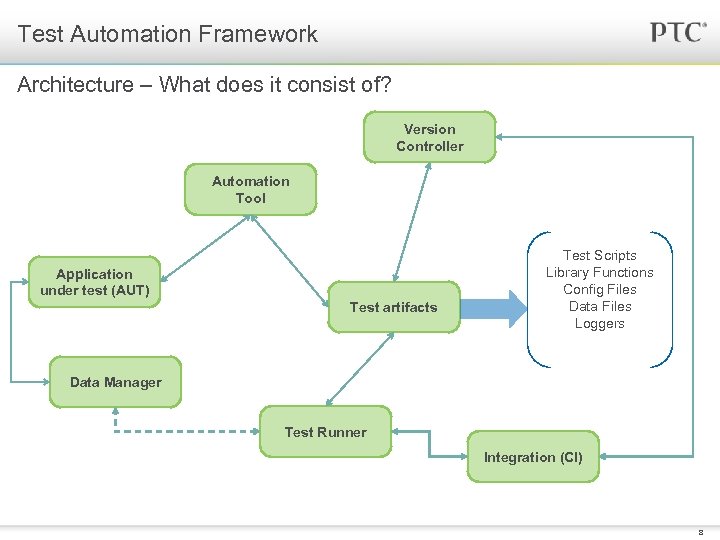
Test Automation Framework Architecture – What does it consist of? Version Controller Automation Tool Application under test (AUT) Test artifacts Test Scripts Library Functions Config Files Data Files Loggers Data Manager Test Runner Integration (CI) 8
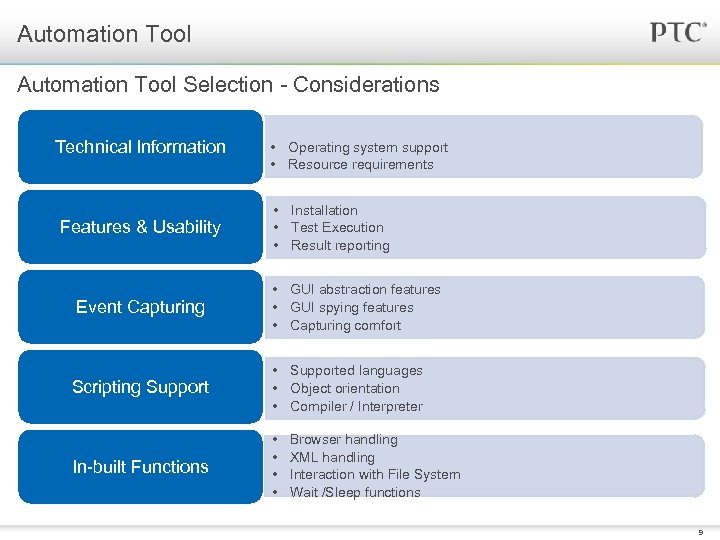
Automation Tool Selection - Considerations Technical Information Features & Usability Event Capturing • Operating system support • Resource requirements • Installation • Test Execution • Result reporting • GUI abstraction features • GUI spying features • Capturing comfort Scripting Support • Supported languages • Object orientation • Compiler / Interpreter In-built Functions • • Browser handling XML handling Interaction with File System Wait /Sleep functions 9

Automation Tool Selection – Considerations continued… Integrated Development Environment Data Driven Testing Result Reporting Documentation Community Support • Editor features • Debugger • Version management • Supported file formats • Output formats • Flexibility for customization • Ease of use • Users manual • Online help • • FAQs WIKIs Forums Technical support 10
Automation Tool Focus on Selenium 11
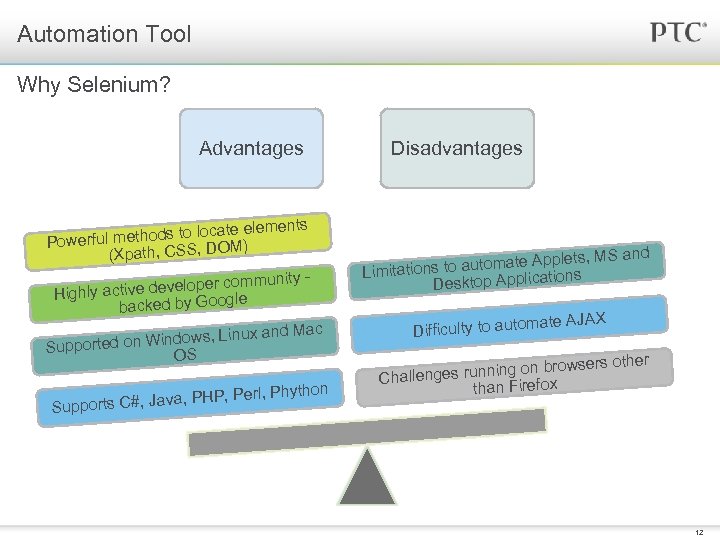
Automation Tool Why Selenium? Advantages te elements l methods to loca ) Powerfu M (Xpath, CSS, DO ommunity ctive developer c Highly a le backed by Goog ux and Mac on Windows, Lin Supported OS rl, Phython PHP, Pe pports C#, Java, Su Disadvantages , MS and automate Applets Limitations to tions Desktop Applica ate AJAX Difficulty to autom rowsers other ges running on b Challen than Firefox 12
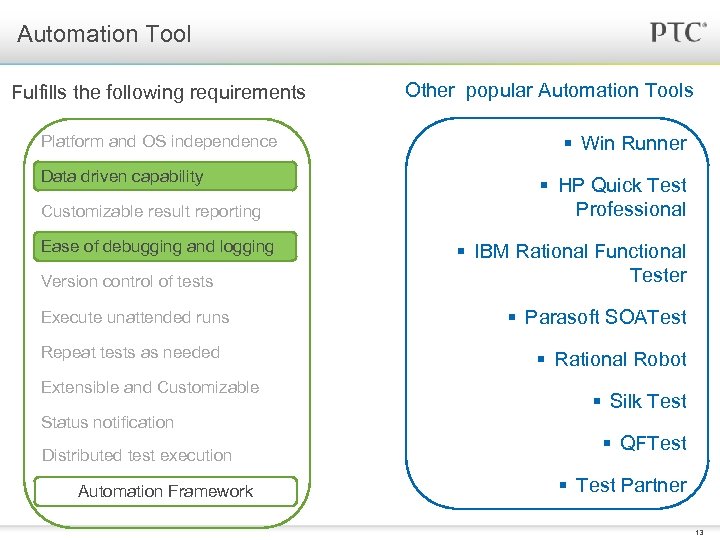
Automation Tool Fulfills the following requirements Platform and OS independence Data driven capability Customizable result reporting Ease of debugging and logging Version control of tests Execute unattended runs Repeat tests as needed Extensible and Customizable Status notification Distributed test execution Automation Framework Other popular Automation Tools § Win Runner § HP Quick Test Professional § IBM Rational Functional Tester § Parasoft SOATest § Rational Robot § Silk Test § QFTest § Test Partner 13
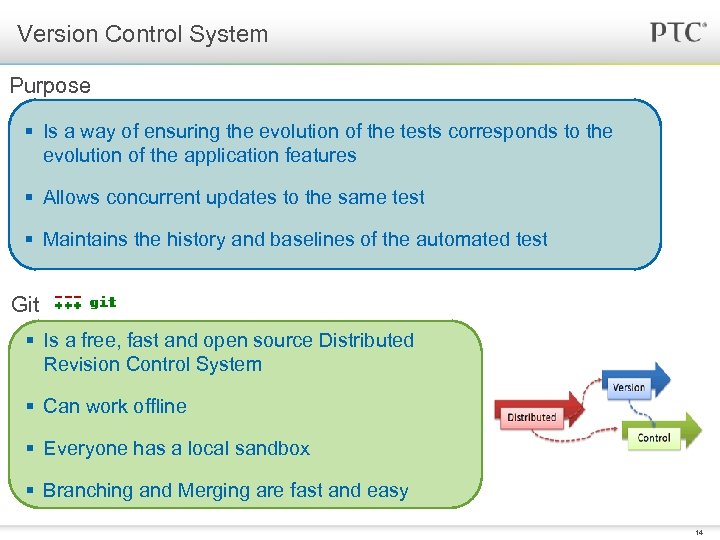
Version Control System Purpose § Is a way of ensuring the evolution of the tests corresponds to the evolution of the application features § Allows concurrent updates to the same test § Maintains the history and baselines of the automated test Git § Is a free, fast and open source Distributed Revision Control System § Can work offline § Everyone has a local sandbox § Branching and Merging are fast and easy 14
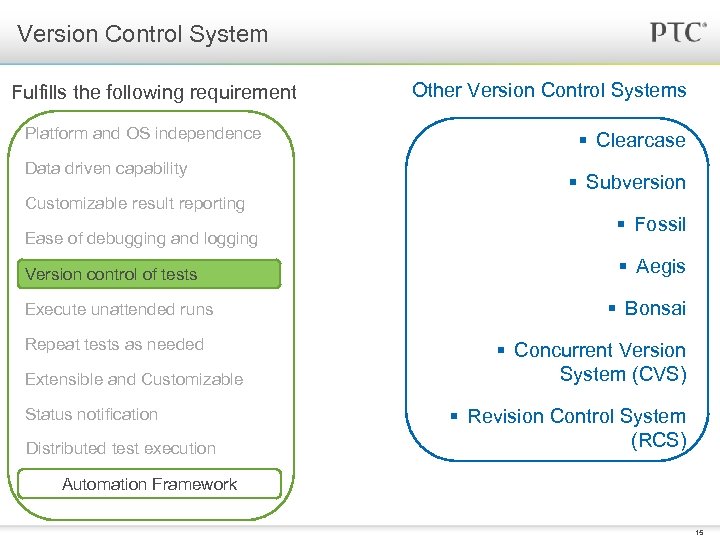
Version Control System Fulfills the following requirement Platform and OS independence Data driven capability Customizable result reporting Ease of debugging and logging Version control of tests Execute unattended runs Repeat tests as needed Extensible and Customizable Status notification Distributed test execution Other Version Control Systems § Clearcase § Subversion § Fossil § Aegis § Bonsai § Concurrent Version System (CVS) § Revision Control System (RCS) Automation Framework 15
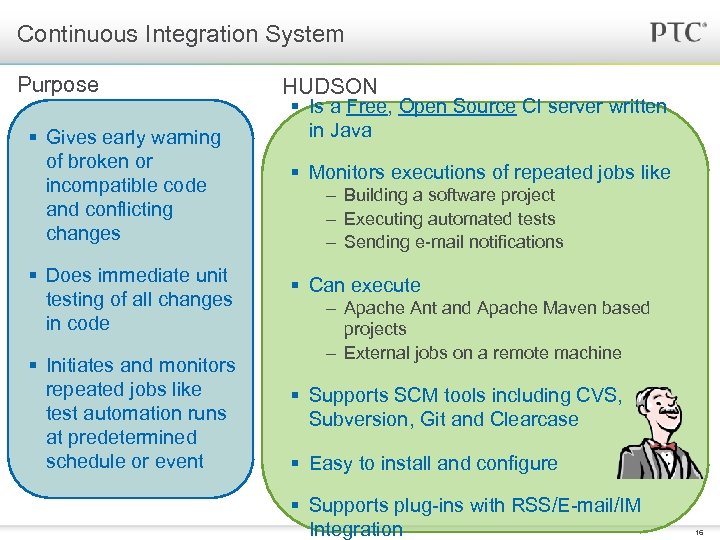
Continuous Integration System Purpose § Gives early warning of broken or incompatible code and conflicting changes § Does immediate unit testing of all changes in code § Initiates and monitors repeated jobs like test automation runs at predetermined schedule or event HUDSON § Is a Free, Open Source CI server written in Java § Monitors executions of repeated jobs like – Building a software project – Executing automated tests – Sending e-mail notifications § Can execute – Apache Ant and Apache Maven based projects – External jobs on a remote machine § Supports SCM tools including CVS, Subversion, Git and Clearcase § Easy to install and configure § Supports plug-ins with RSS/E-mail/IM Integration 16
Continuous Integration System Fulfills the following requirements Other CI Systems Platform and OS independence Data driven capability Customizable result reporting Ease of debugging and logging Version control of tests Execute unattended runs Repeat tests as needed Extensible and Customizable Status notification § Cruise. Control. NET § Cruise. Control. rb § Apache Gump § Apache Continuum § Build. Bot § CABIE Distributed test execution Automation Framework 17
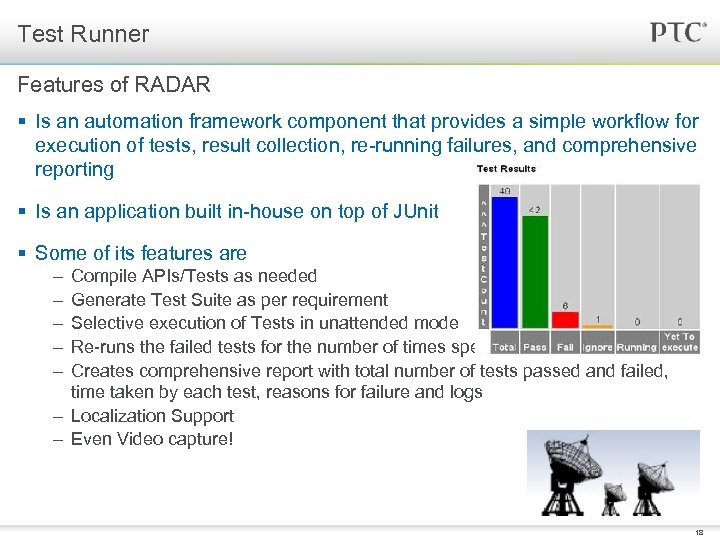
Test Runner Features of RADAR § Is an automation framework component that provides a simple workflow for execution of tests, result collection, re-running failures, and comprehensive reporting § Is an application built in-house on top of JUnit § Some of its features are – – – Compile APIs/Tests as needed Generate Test Suite as per requirement Selective execution of Tests in unattended mode Re-runs the failed tests for the number of times specified Creates comprehensive report with total number of tests passed and failed, time taken by each test, reasons for failure and logs – Localization Support – Even Video capture! 18
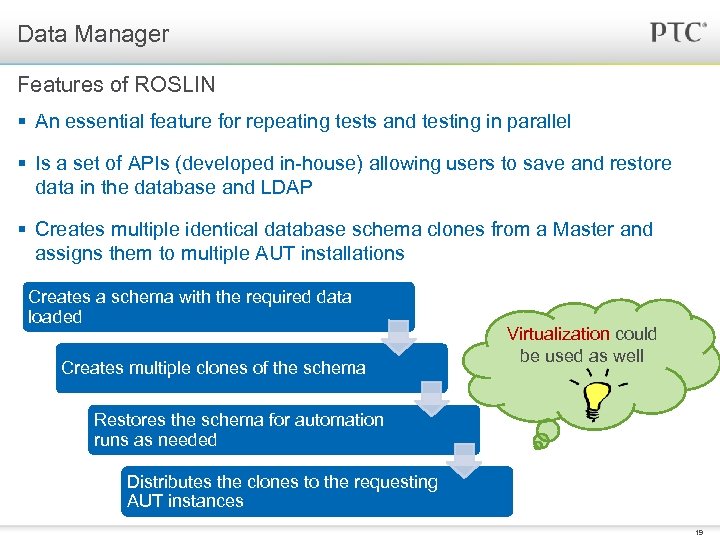
Data Manager Features of ROSLIN § An essential feature for repeating tests and testing in parallel § Is a set of APIs (developed in-house) allowing users to save and restore data in the database and LDAP § Creates multiple identical database schema clones from a Master and assigns them to multiple AUT installations Creates a schema with the required data loaded Creates multiple clones of the schema Virtualization could be used as well Restores the schema for automation runs as needed Distributes the clones to the requesting AUT instances 19
Test Runner & Data Manager Fulfill the following requirements Platform and OS independence Data driven capability Customizable result reporting Ease of debugging and logging Version control of tests Execute unattended runs Repeat tests as needed Extensible and Customizable Status notification Distributed test execution Automation Framework 20
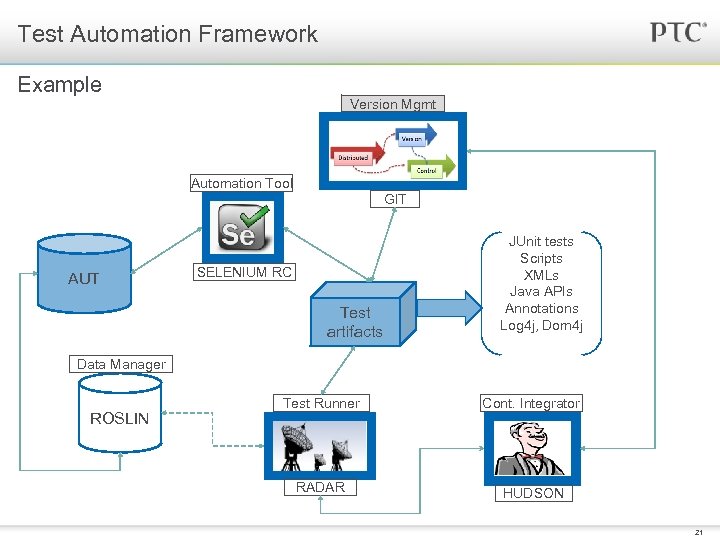
Test Automation Framework Example Version Mgmt Automation Tool GIT AUT SELENIUM RC Test artifacts JUnit tests Scripts XMLs Java APIs Annotations Log 4 j, Dom 4 j Data Manager ROSLIN Test Runner Cont. Integrator RADAR HUDSON 21

Advantages - Flexibility Framework design considerations § Reduce maintenance efforts to a minimum § Provide a means to help people with lesser programming expertise to create automated tests § A common infrastructure for the Development and QA teams to build and execute automated tests What is a Solvent layer? § Solvents are a set of API that help create Selenium tests, without executing Selenium commands directly § Solvents package the logic and Selenium commands required to perform various user actions into simple, reusable classes § If you are wondering what’s in the name - Solvents reduce the amount of Selenium required to create a test (sometimes to none) thereby diluting Selenium, hence the name ‘Solvent’ 22
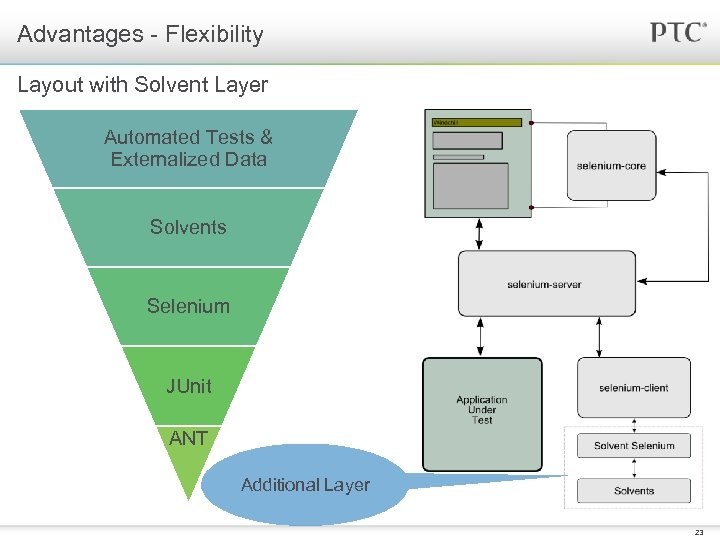
Advantages - Flexibility Layout with Solvent Layer Automated Tests & Externalized Data Solvents Selenium JUnit ANT Additional Layer 23
Advantages - Flexibility Advantages of the additional layer § It aids reusability of code § They can be ‘wired’ together to form test scenarios § Changes need to be made at a single place and not in multiple tests § Makes the test / script more readable POINT TO NOTE – The automation framework is flexible enough to accommodate an additional layer as needed 24
Advantages - Scalability Other possibilities § The framework could be integrated with tools that help determine code coverage like Corbertura, EMMA and Jtest – Assess if the testing done is sufficient – Analyze if the testing focus is as planned § Mechanism for code review like Gerrit could be integrated with the framework – Enforce standards, conventions and best practices for creating tests – Inspect the overall quality of the tests 25
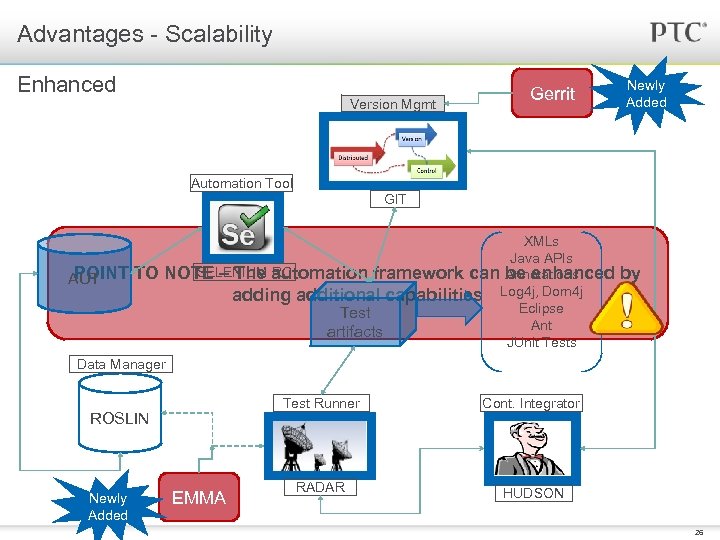
Advantages - Scalability Enhanced Version Mgmt Gerrit Newly Added Automation Tool GIT POINT TO AUT XMLs Java APIs SELENIUM RC NOTE – The automation framework can Annotations be enhanced adding additional capabilities Log 4 j, Dom 4 j Eclipse Test Ant artifacts JUnit Tests by Data Manager Test Runner ROSLIN Newly Added EMMA Cont. Integrator RADAR HUDSON 26
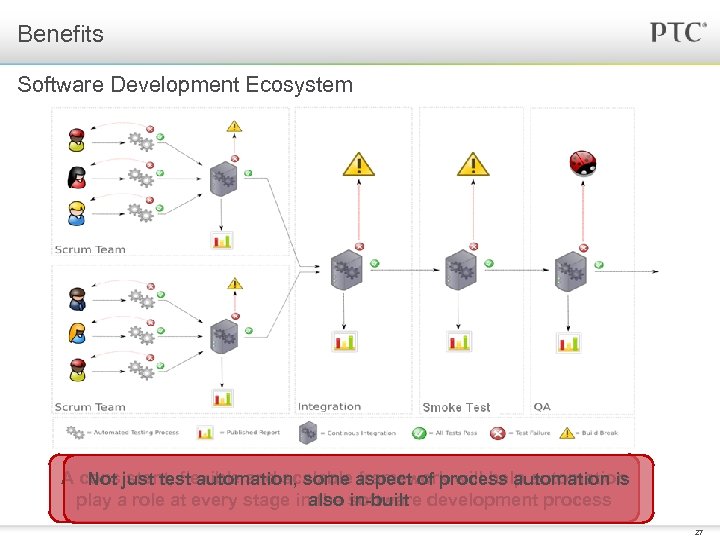
Benefits Software Development Ecosystem A consistent, flexible and scalable aspect of process automation is Not just test automation, some framework will help automation play a role at every stage inalso software development process the in-built 27

Benefits Key Advantages § Maintainability – Significantly reduces the test maintenance effort § Reusability – Due to modularity of test cases and library functions § Manageability – Effective test design, execution, and traceability § Accessibility – To design, develop & modify tests whilst executing § Availability – Scheduled execution can run unattended on a 24/7 basis § Reliability – Due to advanced error handling and scenario recovery § Flexibility – Framework independent of AUT or environment § Measurability – Customizable reporting of test results ensure quality 28

546cc54928a567a05e5dc34da903f0b1.ppt