319d007e87296bb412c8a9c36551b98e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
Building A Knowledge Based Economy (KBE) * Money, Time and Talent ! History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
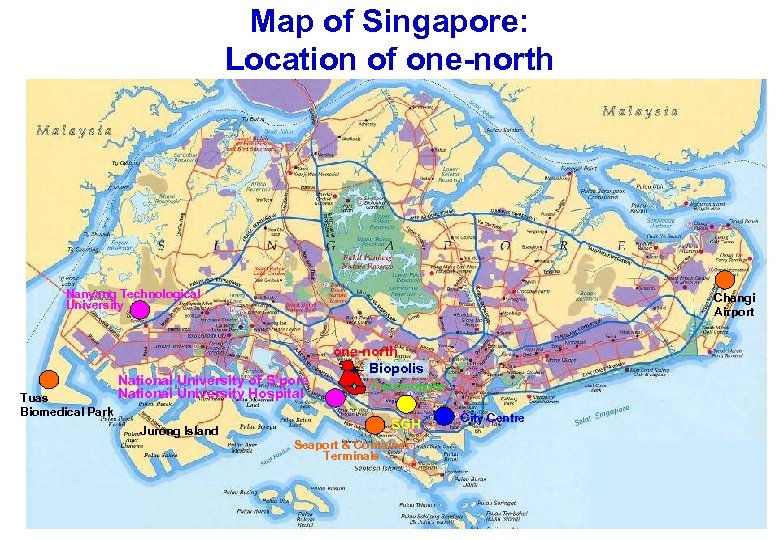
Map of Singapore: Location of one-north Nanyang Technological University Tuas Biomedical Park Changi Airport National University of S’pore National University Hospital Jurong Island one-north Biopolis Fusionopolis SGH Seaport & Container Terminals City Centre

Singapore’s Economic Progress Innovator of new products & services Knowledge. Intensive Technology-intensive Capital-intensive Skills-intensive Labour-intensive History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise m eep K o p ng u vi !
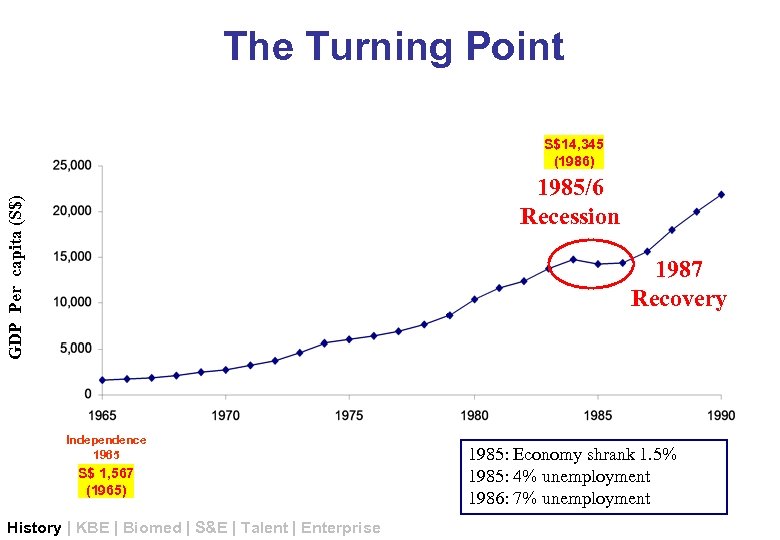
The Turning Point S$14, 345 (1986) GDP Per capita (S$) 1985/6 Recession 1987 Recovery Independence 1965 S$ 1, 567 (1965) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 1985: Economy shrank 1. 5% 1985: 4% unemployment 1986: 7% unemployment
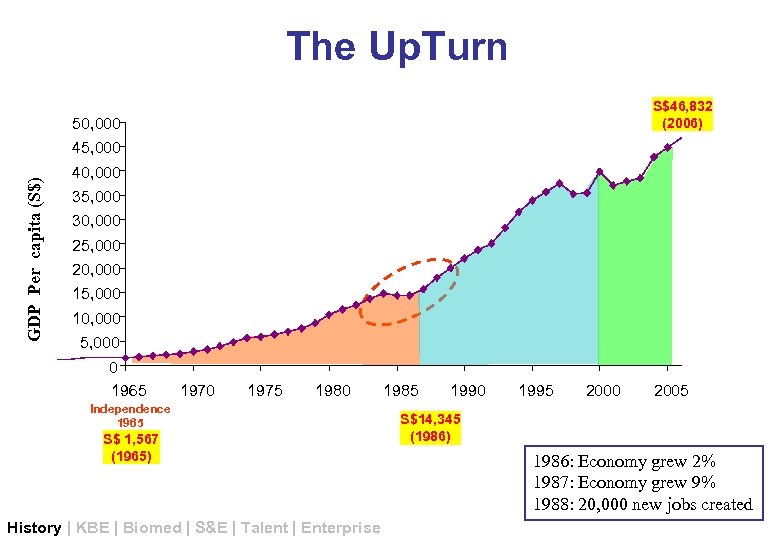
The Up. Turn S$46, 832 (2006) 50, 000 GDP Per capita (S$) 45, 000 40, 000 35, 000 30, 000 25, 000 20, 000 15, 000 10, 000 5, 000 0 1965 1970 1975 1980 Independence 1965 S$ 1, 567 (1965) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 S$14, 345 (1986) 1986: Economy grew 2% 1987: Economy grew 9% 1988: 20, 000 new jobs created
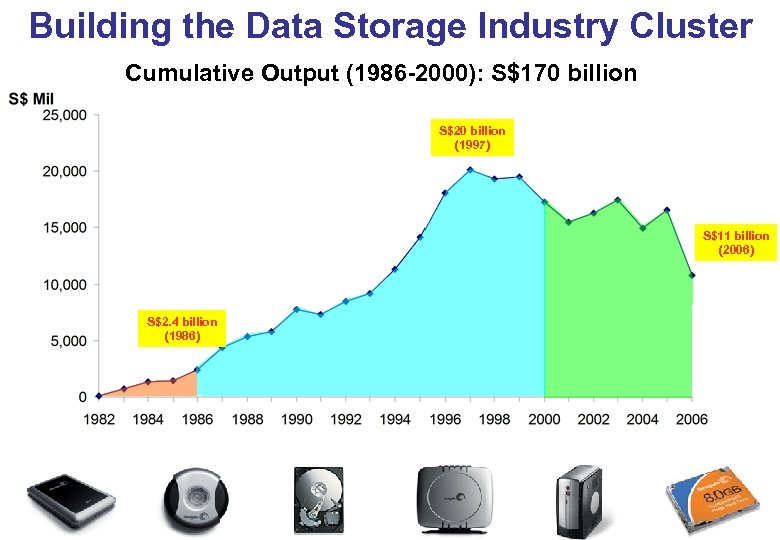
Building the Data Storage Industry Cluster Cumulative Output (1986 -2000): S$170 billion S$20 billion (1997) S$11 billion (2006) S$2. 4 billion (1986)
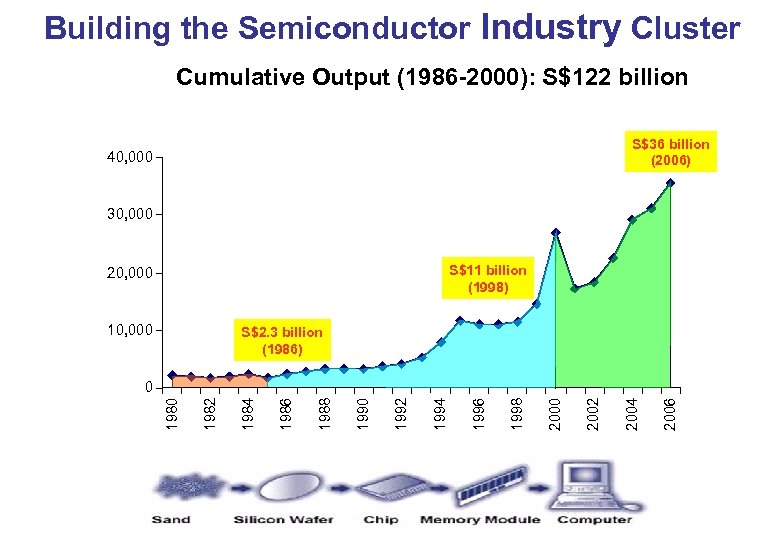
Building the Semiconductor Industry Cluster Cumulative Output (1986 -2000): S$122 billion S$36 billion (2006) 40, 000 30, 000 S$11 billion (1998) 20, 000 10, 000 S$2. 3 billion (1986) 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 1988 1986 1984 1982 1980 0
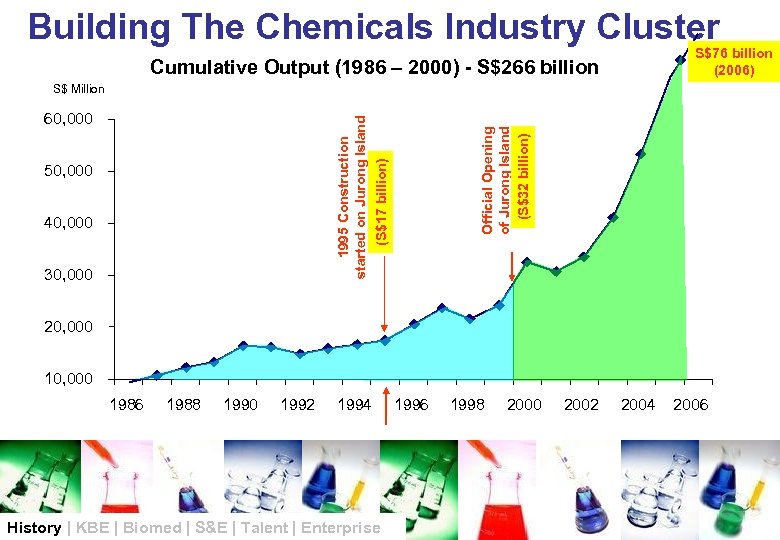
Building The Chemicals Industry Cluster S$76 billion (2006) Cumulative Output (1986 – 2000) - S$266 billion S$ Million 50, 000 40, 000 30, 000 Official Opening of Jurong Island (S$32 billion) 1995 Construction started on Jurong Island (S$17 billion) 60, 000 20, 000 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006
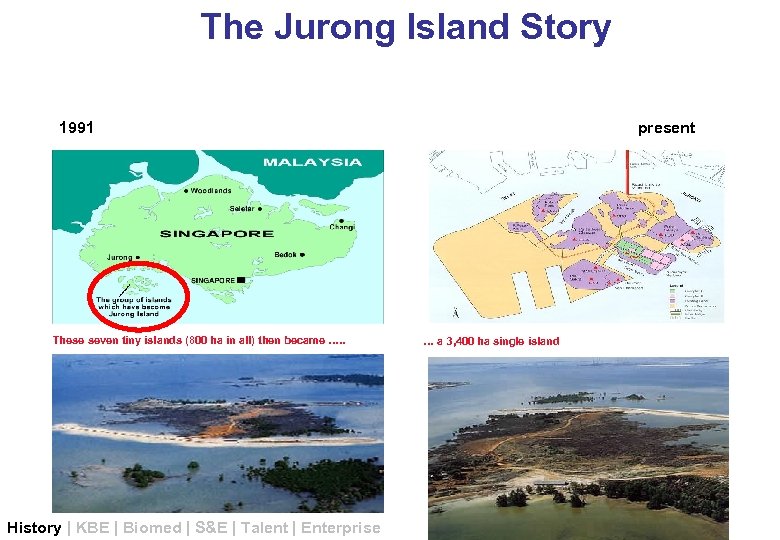
The Jurong Island Story 1991 These seven tiny islands (800 ha in all) then became …. . History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise present … a 3, 400 ha single island

Jurong Chemical Island …. Today Jurong Island Today … a 3, 400 ha single island
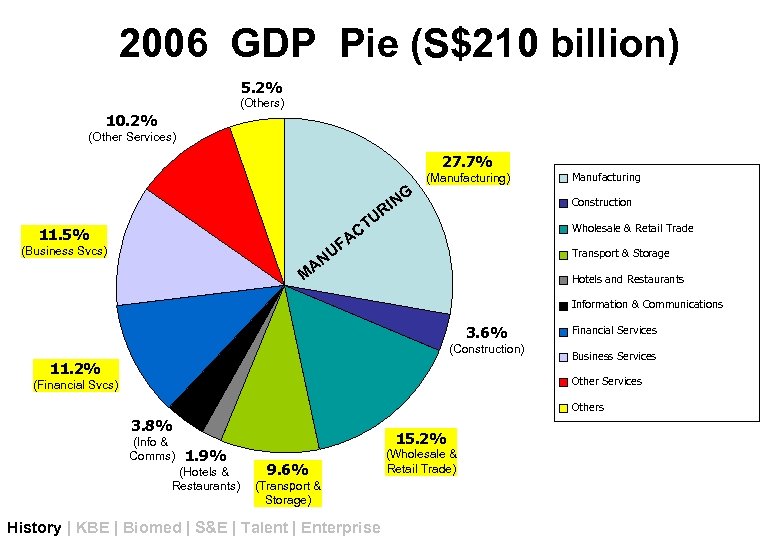
2006 GDP Pie (S$210 billion) 5. 2% (Others) 10. 2% (Other Services) 27. 7% (Manufacturing) G IN R Construction U CT A UF 11. 5% (Business Svcs) Manufacturing Wholesale & Retail Trade Transport & Storage AN M Hotels and Restaurants Information & Communications 3. 6% (Construction) 11. 2% Financial Services Business Services Other Services (Financial Svcs) Others 3. 8% (Info & Comms) 1. 9% (Hotels & Restaurants) 15. 2% 9. 6% (Transport & Storage) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise (Wholesale & Retail Trade)
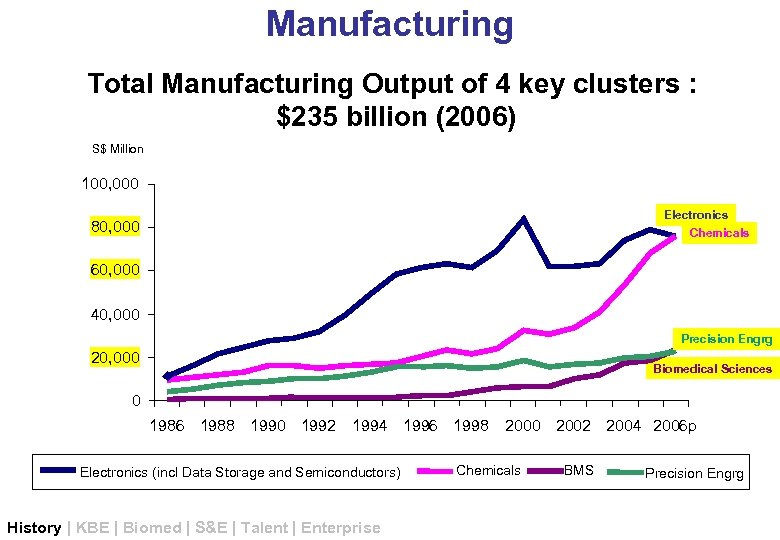
Manufacturing Total Manufacturing Output of 4 key clusters : $235 billion (2006) S$ Million 100, 000 Electronics Chemicals 80, 000 60, 000 40, 000 Precision Engrg 20, 000 Biomedical Sciences 0 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 Electronics (incl Data Storage and Semiconductors) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 2000 2002 2004 2006 p Chemicals BMS Precision Engrg
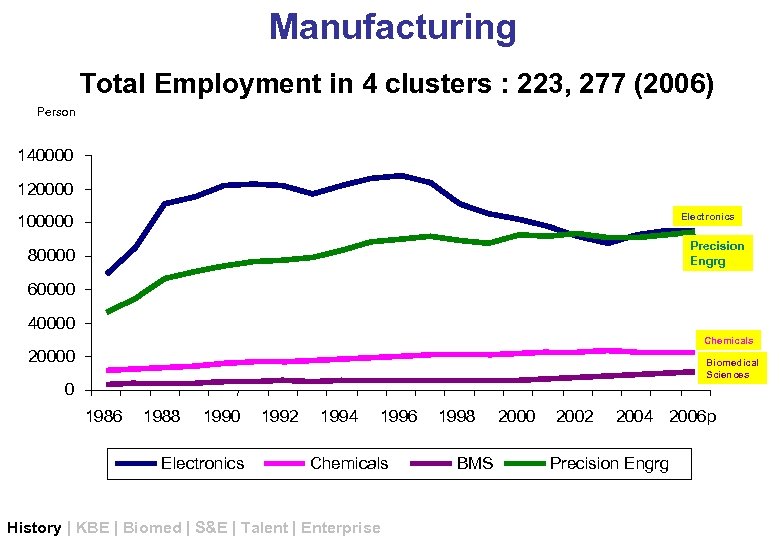
Manufacturing Total Employment in 4 clusters : 223, 277 (2006) Person 140000 120000 Electronics 100000 Precision Engrg 80000 60000 40000 Chemicals 20000 Biomedical Sciences 0 1986 1988 1990 Electronics 1992 1994 1996 Chemicals History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 1998 BMS 2000 2002 2004 2006 p Precision Engrg

Creation of 4 clusters of growth Singapore has promoted and attracted 4 waves of investments: * Data storage (1986 -1990) * Semiconductors (1991 -1995) * Chemicals (1996 to 2000) * Biomedical industries (2001 to 2006)
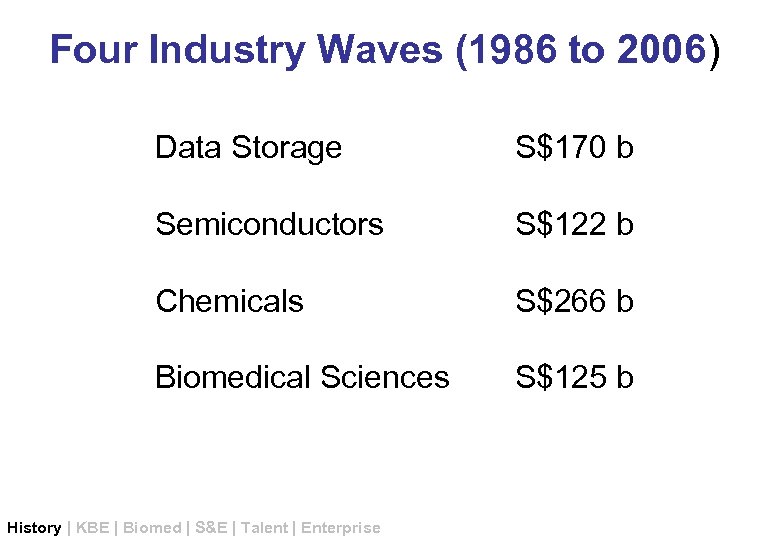
Four Industry Waves (1986 to 2006) Data Storage S$170 b Semiconductors S$122 b Chemicals S$266 b Biomedical Sciences S$125 b History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
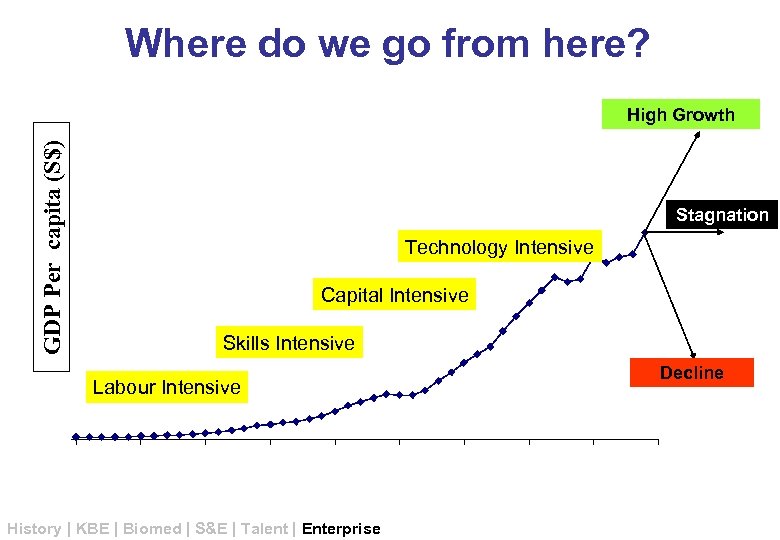
Where do we go from here? GDP Per capita (S$) High Growth Stagnation Technology Intensive Capital Intensive Skills Intensive Labour Intensive History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Decline
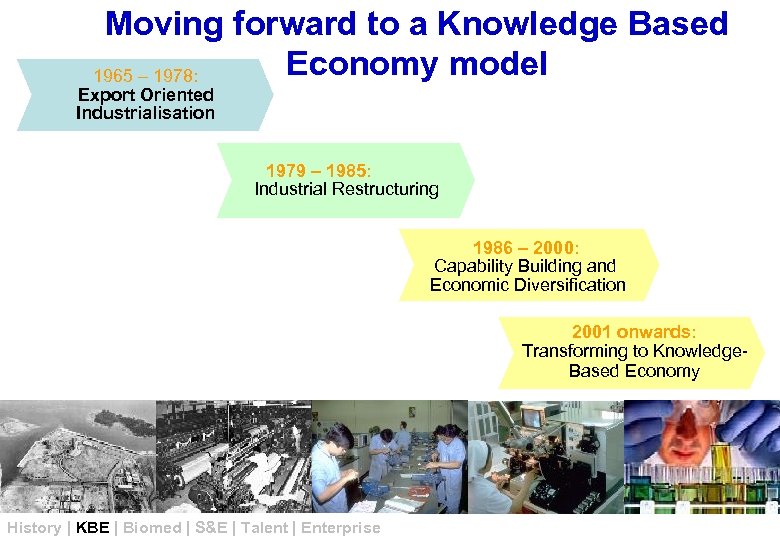
Moving forward to a Knowledge Based Economy model 1965 – 1978: Export Oriented Industrialisation 1979 – 1985: Industrial Restructuring 1986 – 2000: Capability Building and Economic Diversification 2001 onwards: Transforming to Knowledge. Based Economy History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

From Manufacturing to Knowledge-Based Economy • An Economy based on cost efficiency is not sustainable in the long term • Move up the Value chain with focus on high valueadded activities • Graduate Education is a necessity for high valueadded R&D-oriented industries • Research Development Production Marketing Distribution Servicing History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

What is a Knowledge-Based Economy? Create, Own + Exploit (COE) Knowledge Ø How do we create knowledge and useful ideas? R&D and innovation. Ø Where? New high growth areas like biomedical sciences, nanotechnology, energy. Ø Why? R&D generates intellectual property (IP) and this is the “real value-added” R&D complements our manufacturing core. Coupling the two will create clusters of high value-added activity. History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
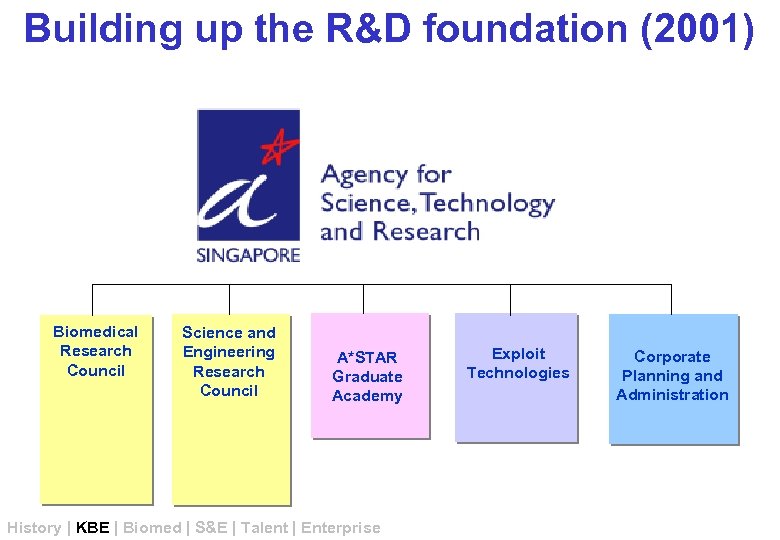
Building up the R&D foundation (2001) Biomedical Research Council Science and Engineering Research Council A*STAR Graduate Academy History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Exploit Technologies Corporate Planning and Administration
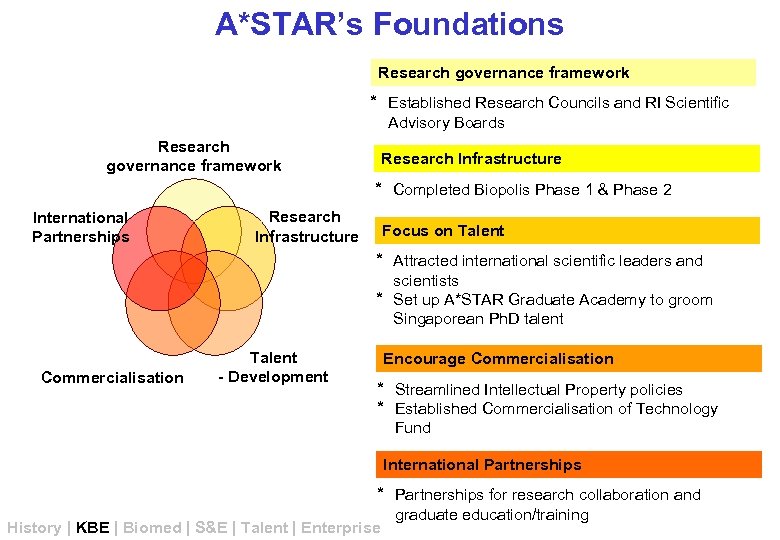
A*STAR’s Foundations Research governance framework * Established Research Councils and RI Scientific Advisory Boards Research governance framework Research Infrastructure * Completed Biopolis Phase 1 & Phase 2 International Partnerships Research Infrastructure Focus on Talent * Attracted international scientific leaders and scientists * Set up A*STAR Graduate Academy to groom Singaporean Ph. D talent Commercialisation Talent - Development Encourage Commercialisation * Streamlined Intellectual Property policies * Established Commercialisation of Technology Fund International Partnerships * Partnerships for research collaboration and History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise graduate education/training

A snapshot of Singapore’s current R&D scene History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
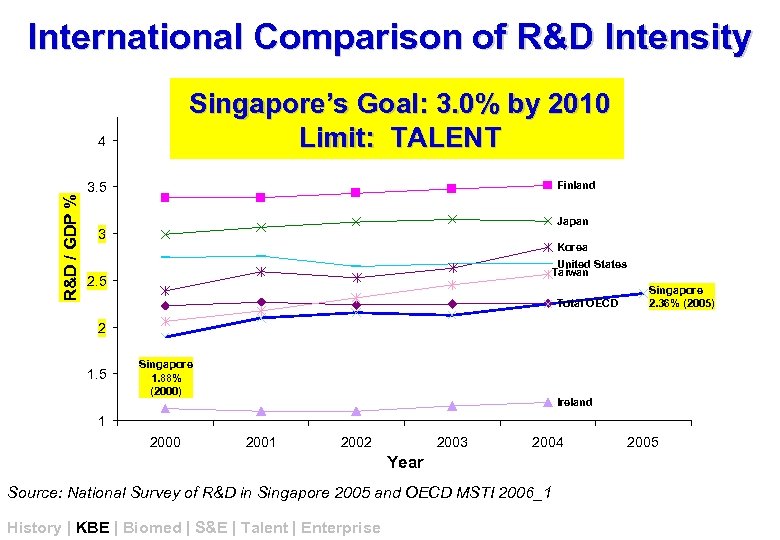
International Comparison of R&D Intensity Singapore’s Goal: 3. 0% by 2010 Limit: TALENT R&D / GDP % 4 Finland 3. 5 Japan 3 Korea United States Taiwan 2. 5 Total OECD Singapore 2. 36% (2005) 2 1. 5 Singapore 1. 88% (2000) Ireland 1 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Year Source: National Survey of R&D in Singapore 2005 and OECD MSTI 2006_1 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 2005
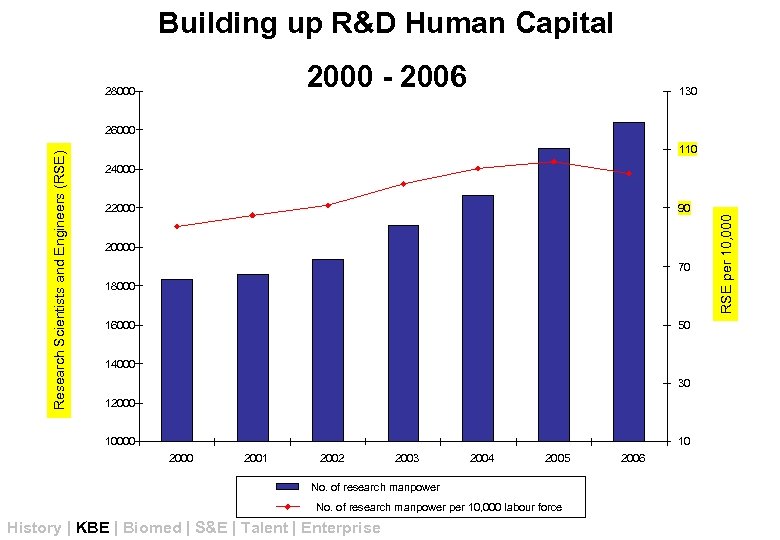
Building up R&D Human Capital 2000 - 2006 28000 130 110 24000 22000 90 20000 70 18000 16000 50 14000 30 12000 10 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 No. of research manpower per 10, 000 labour force History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 2006 RSE per 10, 000 Research Scientists and Engineers (RSE) 26000
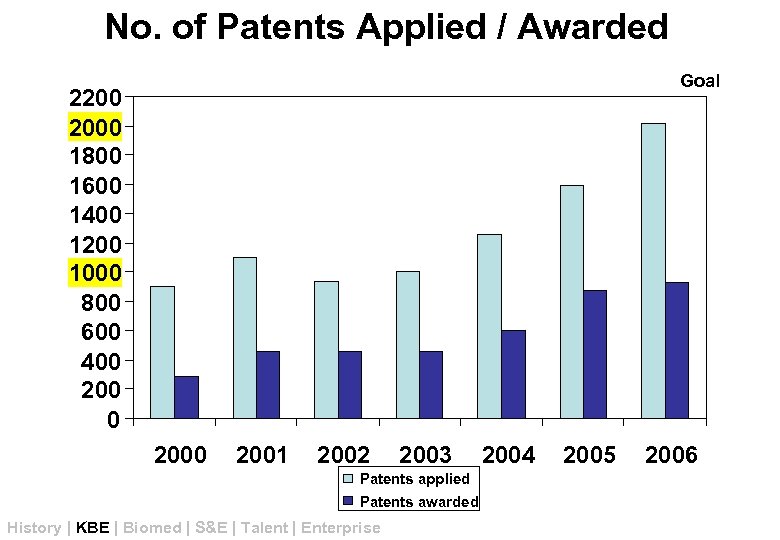
No. of Patents Applied / Awarded Goal 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 2001 2002 2003 Patents applied Patents awarded History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 2004 2005 2006

Building up Biomedical Sciences 2001 A*STAR History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
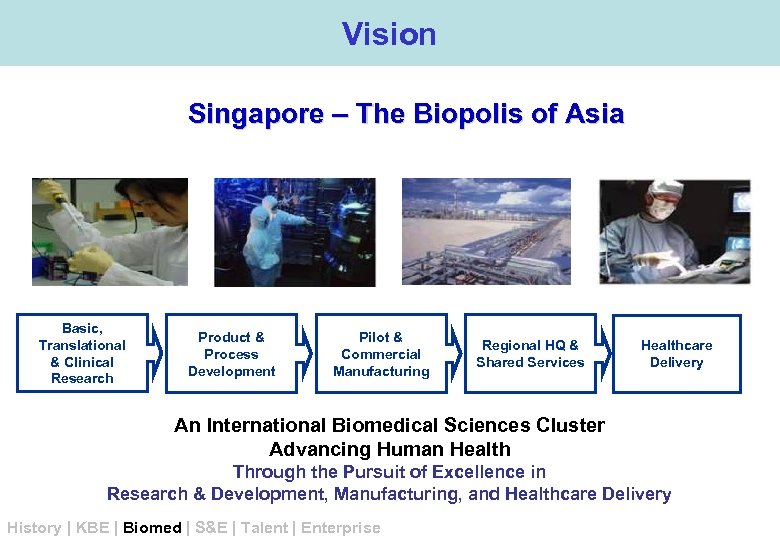
Vision Singapore – The Biopolis of Asia Basic, Translational & Clinical Research Product & Process Development Pilot & Commercial Manufacturing Regional HQ & Shared Services Healthcare Delivery An International Biomedical Sciences Cluster Advancing Human Health Through the Pursuit of Excellence in Research & Development, Manufacturing, and Healthcare Delivery History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
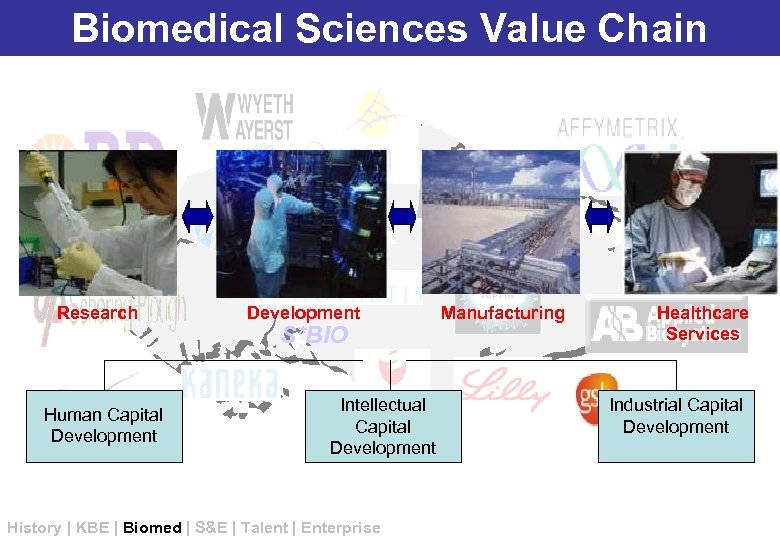
Biomedical Sciences Value Chain Research Human Capital Development S*BIO Intellectual Capital Development History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Manufacturing Healthcare Services Industrial Capital Development

How It All Started…. Prof. John Wong A/Prof. Kong Hwai Loong n 000 e 2 u h. J t Prof. Tan Chorh Chuan 26

BMS International Advisory Council Sir Richard Sykes (Chairman) Imperial College (UK) Dr Sydney Brenner The Salk Institute (USA) Dr Leland Hartwell Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (USA) Dr Peter Gruss Max Planck Society (Germany) Dr John Bell University of Oxford (UK) Dr Colin Blakemore Medical Research Council (UK) Dr Harriet Wallberg-Henriksson Karolinska Institutet (Sweden) Dr Suzanne Cory WEHI (Australia) Dr William Evans St Jude (USA) Dr Helen Hobbs UT Southwestern (USA) Dr Anthony Pawson Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute (Canada) Dr John Mendelssohn (Co-Chairman) MD Anderson (USA) Dr Tadataka Yamada Gates Foundation (USA) Dr Rolf Zinkernagel University of Zurich (Switzerland) Sir Philip Cohen University of Dundee (UK) Dr John Reed (Emeritus) Burnham Institute (USA) Dr David Baltimore (Emeritus) California Institute of Technology (USA) Dr Philippe Kourilsky (Emeritus) College de France (France) Dr Alan Bernstein (Emeritus) Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Canada) Dr Richard Lerner (Emeritus) Scripps Research Institute (USA) Sir George Radda (Emeritus) University of Oxford (UK) Dr Samuel Barondes (Emeritus) University of California, San Francisco (USA) Dr Stanley N. Cohen (Emeritus) Stanford University (USA) Dr David I. Hirsh (Emeritus) Columbia University (USA) Dr Susan Lindquist (Emeritus) Whitehead Institute of Biomedical Research (USA) Dr Paul A. Marks (Emeritus) Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (USA) Dr Alan Munro (Emeritus) University of Cambridge (UK) Sir Keith Peters (Emeritus) Glaxo. Smith. Kline (UK) Dr Hans Wigzell (Emeritus) Karolinska Institutet (Sweden) Dr Axel Ullrich (Emeritus) Max-Planck Institute of Biochemistry (Germany) Dr John Shine (Emeritus) Garvan Institute of Medical Research (Australia)

Breaking New Ground in 2001 … Biopolis History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
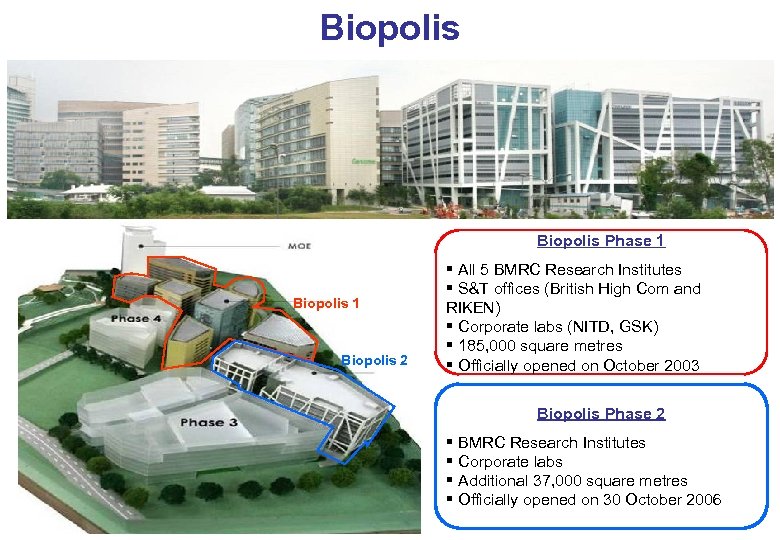
Biopolis Phase 1 Biopolis 2 § All 5 BMRC Research Institutes § S&T offices (British High Com and RIKEN) § Corporate labs (NITD, GSK) § 185, 000 square metres § Officially opened on October 2003 Biopolis Phase 2 § BMRC Research Institutes § Corporate labs § Additional 37, 000 square metres § Officially opened on 30 October 2006

BMRC Research Institutes Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) Bioprocessing Technology Institute (BTI) Bioinformatics Institute (BII) Genome Institute of Singapore (GIS) Institute of Bioengineering & Nanotechnology (IBN) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Institute of Medical Biology (IMB) Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS)
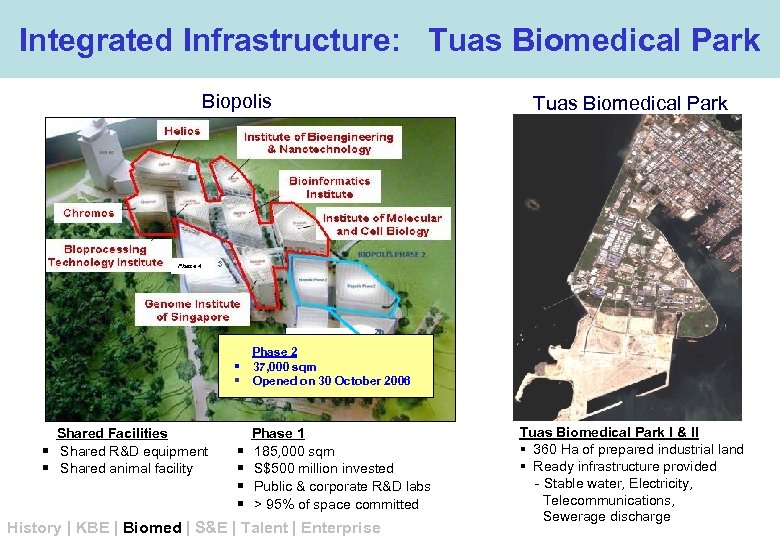
Integrated Infrastructure: Tuas Biomedical Park Biopolis Tuas Biomedical Park Phase 4 Phase 3 Phase 2 § 37, 000 sqm § Opened on 30 October 2006 Shared Facilities § Shared R&D equipment § Shared animal facility § § Phase 1 185, 000 sqm S$500 million invested Public & corporate R&D labs > 95% of space committed History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Tuas Biomedical Park I & II § 360 Ha of prepared industrial land § Ready infrastructure provided - Stable water, Electricity, Telecommunications, Sewerage discharge
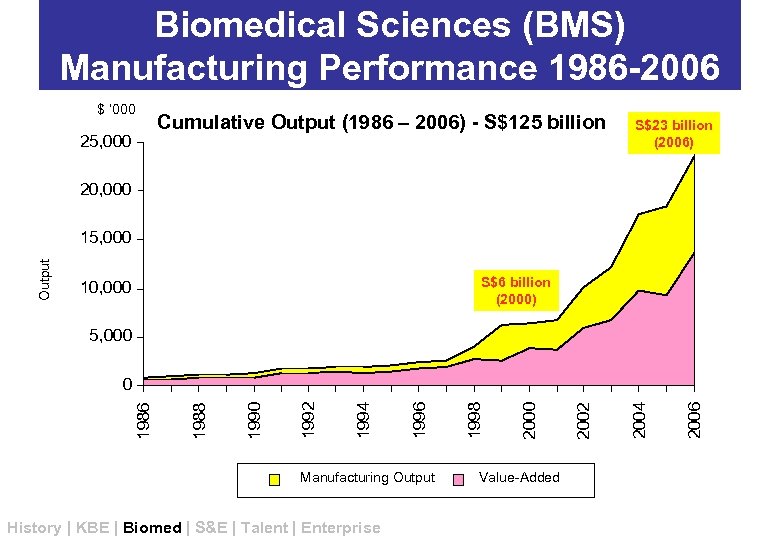
Biomedical Sciences (BMS) Manufacturing Performance 1986 -2006 $ ‘ 000 25, 000 Cumulative Output (1986 – 2006) - S$125 billion S$23 billion (2006) 20, 000 Output 15, 000 S$6 billion (2000) 10, 000 5, 000 Manufacturing Output History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Value-Added 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 1988 1986 0
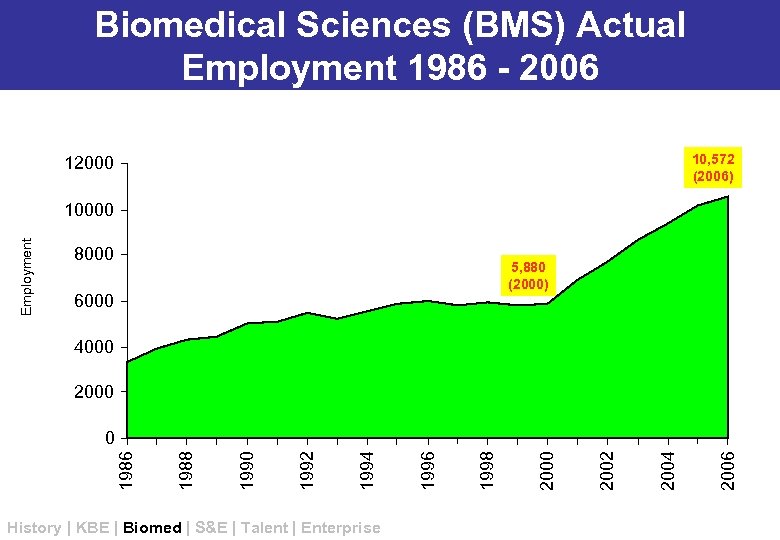
Biomedical Sciences (BMS) Actual Employment 1986 - 2006 10, 572 (2006) 12000 Employment 10000 8000 5, 880 (2000) 6000 4000 2000 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 1988 1986 0
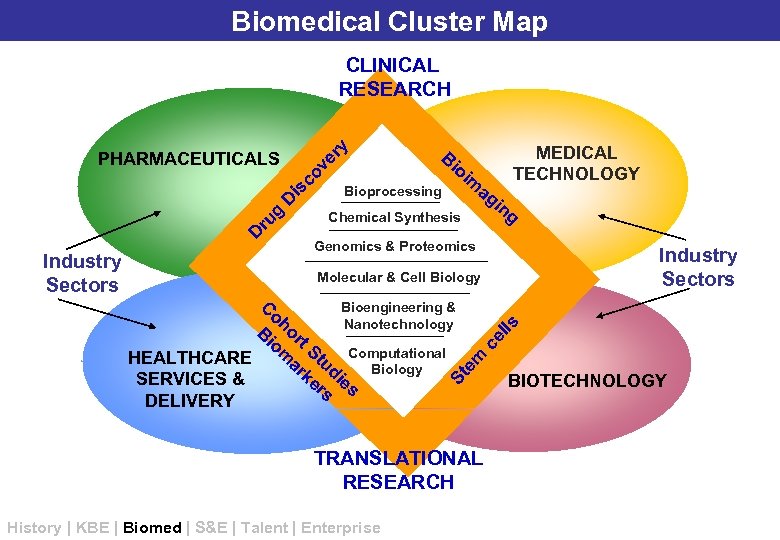
Biomedical Cluster Map ry CLINICAL RESEARCH D ru g D is co ve PHARMACEUTICALS Bioprocessing oi MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY m Chemical Synthesis ag in g Genomics & Proteomics Industry Sectors ce C Bioengineering & oh Nanotechnology B or io t m St HEALTHCARE ar ud Computational ke ie Biology SERVICES & rs s DELIVERY lls Molecular & Cell Biology St em Industry Sectors Bi TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise BIOTECHNOLOGY
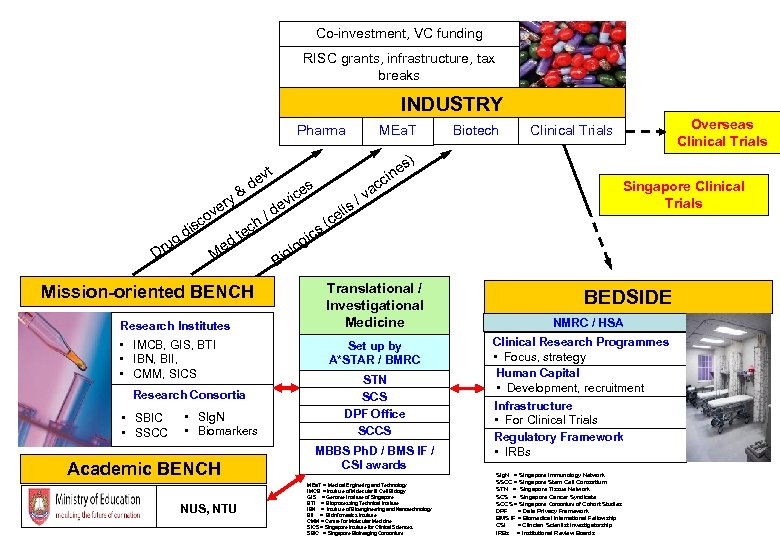
Co-investment, VC funding RISC grants, infrastructure, tax breaks INDUSTRY MEa. T Pharma vt de y & r s di g ru D ve co Mission-oriented BENCH Research Institutes • IMCB, GIS, BTI • IBN, BII, • CMM, SICS Research Consortia • SBIC • SSCC • SIg. N • Biomarkers Academic BENCH NUS, NTU e d h / c te d Me s ice v o iol B Overseas Clinical Trials s) c Singapore Clinical Trials s ll ce ( s gic va / e cin Biotech Translational / Investigational Medicine Set up by A*STAR / BMRC STN SCS DPF Office SCCS MBBS Ph. D / BMS IF / CSI awards MEa. T = Medical Enginering and Technology IMCB = Institute of Molecular & Cell Biology GIS = Genome Institute of Singapore BTI = Bioprocessing Technical Institute IBN = Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology BII = Bioinformatics Institute CMM = Centre for Molecular Medicine SICS = Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences SBIC = Singapore Bioimaging Consortium BEDSIDE NMRC / HSA Clinical Research Programmes • Focus, strategy Human Capital • Development, recruitment Infrastructure • For Clinical Trials Regulatory Framework • IRBs SIg. N = Singapore Immunology Network SSCC = Singapore Stem Cell Consortium STN = Singapore Tissue Network SCS = Singapore Cancer Syndicate SCCS = Singapore Consortium of Cohort Studies DPF = Data Privacy Framework BMS IF = Biomedical International Fellowship CSI = Clincian Scientist Investigatorship IRBs = Institutional Review Boards
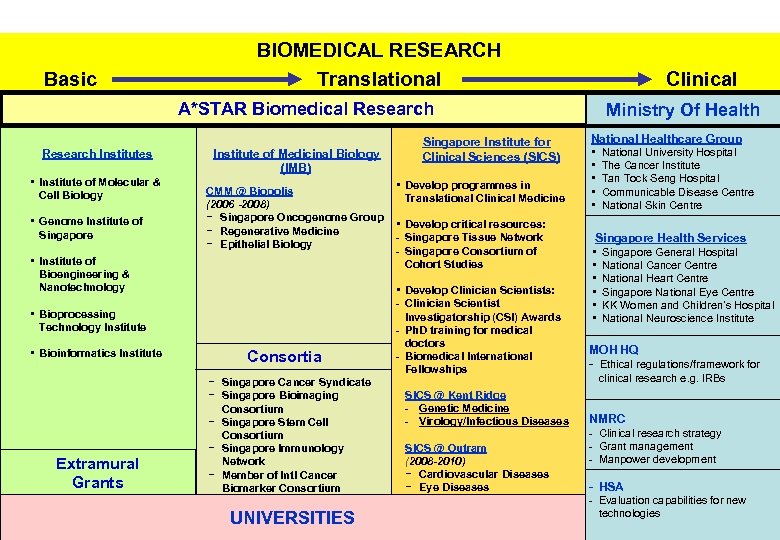
Basic BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH Translational A*STAR Biomedical Research Institutes • Institute of Molecular & Cell Biology • Genome Institute of Singapore Institute of Medicinal Biology (IMB) CMM @ Biopolis (2006 -2008) − Singapore Oncogenome Group − Regenerative Medicine − Epithelial Biology • Institute of Bioengineering & Nanotechnology • Bioprocessing Technology Institute • Bioinformatics Institute Extramural Grants Consortia − Singapore Cancer Syndicate − Singapore Bioimaging Consortium − Singapore Stem Cell Consortium − Singapore Immunology Network − Member of Intl Cancer Biomarker Consortium UNIVERSITIES Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) • Develop programmes in Translational Clinical Medicine • Develop critical resources: - Singapore Tissue Network - Singapore Consortium of Cohort Studies • Develop Clinician Scientists: - Clinician Scientist Investigatorship (CSI) Awards - Ph. D training for medical doctors - Biomedical International Fellowships SICS @ Kent Ridge - Genetic Medicine - Virology/Infectious Diseases SICS @ Outram (2008 -2010) − Cardiovascular Diseases − Eye Diseases Clinical Ministry Of Health National Healthcare Group • National University Hospital • The Cancer Institute • Tan Tock Seng Hospital • Communicable Disease Centre • National Skin Centre Singapore Health Services • Singapore General Hospital • National Cancer Centre • National Heart Centre • Singapore National Eye Centre • KK Women and Children’s Hospital • National Neuroscience Institute MOH HQ - Ethical regulations/framework for clinical research e. g. IRBs NMRC - Clinical research strategy - Grant management - Manpower development - HSA - Evaluation capabilities for new technologies
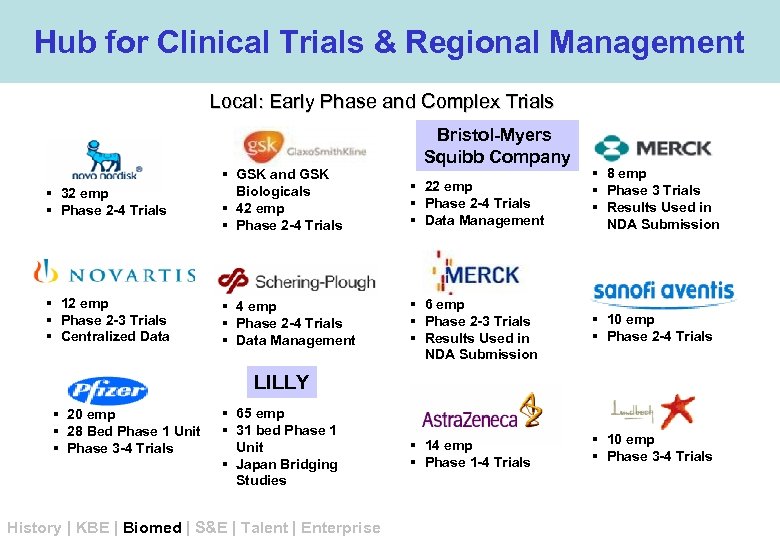
Hub for Clinical Trials & Regional Management Local: Early Phase and Complex Trials Bristol-Myers Squibb Company § 32 emp § Phase 2 -4 Trials § GSK and GSK Biologicals § 42 emp § Phase 2 -4 Trials § 22 emp § Phase 2 -4 Trials § Data Management § 8 emp § Phase 3 Trials § Results Used in NDA Submission § 12 emp § Phase 2 -3 Trials § Centralized Data § 4 emp § Phase 2 -4 Trials § Data Management § 6 emp § Phase 2 -3 Trials § Results Used in NDA Submission § 10 emp § Phase 2 -4 Trials § 14 emp § Phase 1 -4 Trials § 10 emp § Phase 3 -4 Trials LILLY § 20 emp § 28 Bed Phase 1 Unit § Phase 3 -4 Trials § 65 emp § 31 bed Phase 1 Unit § Japan Bridging Studies History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
Fusion of Science and Engineering History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
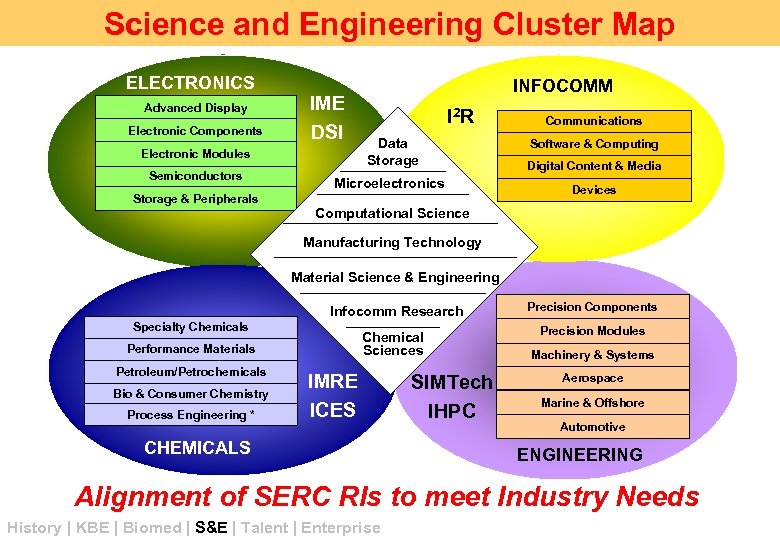
Science Engineering Industry Clusters Science &and Engineering Cluster Map ELECTRONICS Advanced Display Electronic Components IME DSI Storage & Peripherals I 2 R Communications Data Storage Digital Content & Media Microelectronics Devices Electronic Modules Semiconductors INFOCOMM Software & Computing Computational Science Manufacturing Technology Material Science & Engineering Infocomm Research Specialty Chemicals Chemical Sciences Performance Materials Petroleum/Petrochemicals Bio & Consumer Chemistry Process Engineering * IMRE ICES CHEMICALS SIMTech IHPC Precision Components Precision Modules Machinery & Systems Aerospace Marine & Offshore Automotive ENGINEERING Alignment of SERC RIs to meet Industry Needs History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
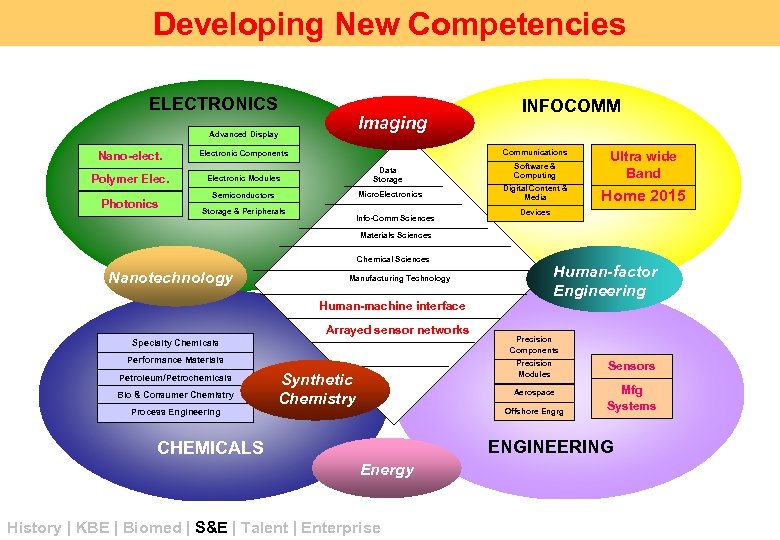
Developing New Competencies ELECTRONICS Imaging Advanced Display Nano-elect. Polymer Elec. Photonics Communications Electronic Components Electronic Modules Data Storage Semiconductors Micro. Electronics Storage & Peripherals INFOCOMM Info-Comm Sciences Software & Computing Ultra wide Band Digital Content & Media Home 2015 Devices Materials Sciences Chemical Sciences Nanotechnology Human-factor Engineering Manufacturing Technology Human-machine interface Arrayed sensor networks Specialty Chemicals Performance Materials Petroleum/Petrochemicals Bio & Consumer Chemistry Process Engineering Precision Components Precision Machinery & Systems Modules Synthetic Chemistry Aerospace Offshore Engrg Sensors Mfg Systems ENGINEERING CHEMICALS Energy History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

SERC Research Institutes Data Storage Institute (DSI) Institute of Microelectronics (IME) Institute for Chemical & Engineering Sciences (ICES) Institute for Infocomm Research (I 2 R) Institute of High Performance Computing (IHPC) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech) Institute of Materials Research & Engineering (IMRE)

Attracting and Anchoring Corporate R&D activities SERC RIs initiated 838 Industry R&D projects from FY 01 -FY 06* History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise * As of 31 st December 2006
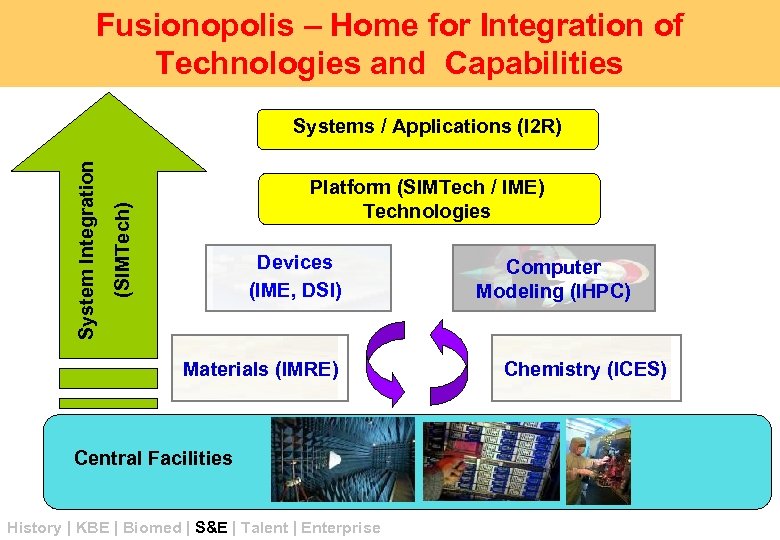
Fusionopolis – Home for Integration of Technologies and Capabilities Platform (SIMTech / IME) Technologies (SIMTech) System Integration Systems / Applications (I 2 R) Devices (IME, DSI) Materials (IMRE) Central Facilities History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Computer Modeling (IHPC) Chemistry (ICES)

Fusionopolis Phase 1 Facilities SERC, CPAD, ETPL, I 2 R, IHPC, DSI (network storage), SIMTech (Industrial Informatics) located at Fusionopolis Phase 1 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
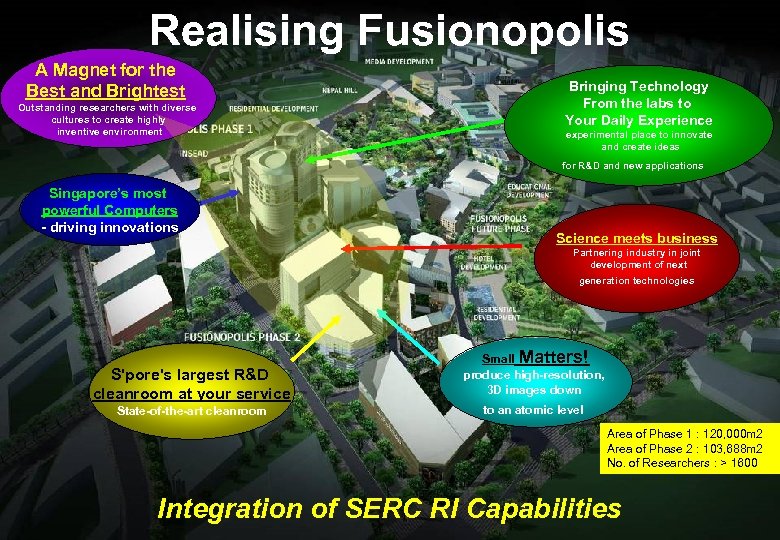
Realising Fusionopolis A Magnet for the Best and Brightest Outstanding researchers with diverse cultures to create highly inventive environment Bringing Technology From the labs to Your Daily Experience experimental place to innovate and create ideas for R&D and new applications Singapore’s most powerful Computers - driving innovations Science meets business Partnering industry in joint development of next generation technologies S'pore's largest R&D cleanroom at your service State-of-the-art cleanroom Small Matters! produce high-resolution, 3 D images down to an atomic level Area of Phase 1 : 120, 000 m 2 Area of Phase 2 : 103, 688 m 2 No. of Researchers : > 1600 Integration of SERC RI Capabilities
One-North
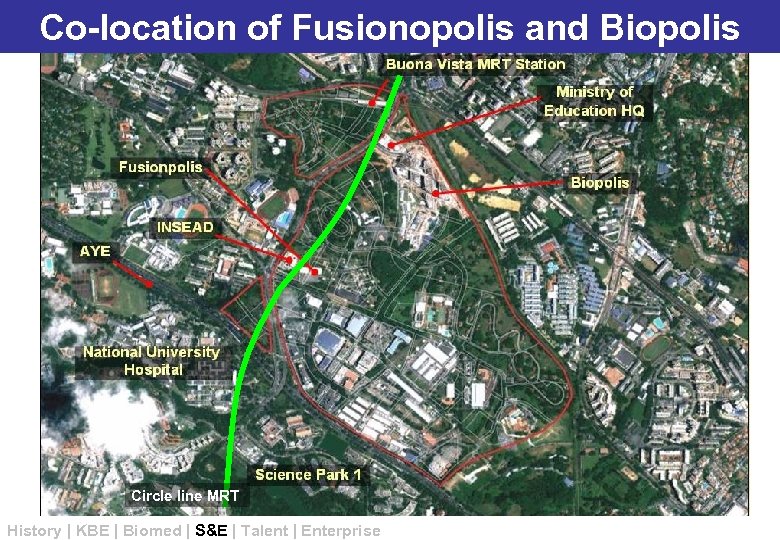
FUSIONpolis – Aerial and Co-location of Fusionopolis view Biopolis Circle line MRT History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

HUMAN CAPITAL make up a Knowledge. Based Economy (KBE) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

Human Capital - Whales History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

Attracting International Talent (Whales) When physician-scientists Judith Swain and Ed Holmes take up their posts in Singapore…, they will join a star-studded community at one of the world’s most rapidly developing biomedical research centres. …they are the latest of many Western scientists who have headed for the impressive facilities of the tiny citystate. Sir David Lane Executive Director, IMCB & Executive Dy Chmn (BSTG), BMRC Dr Judith Swain Executive Director, SICS Naturejobs, 5 Jul 06 Sir George Radda Chairman, SBIC Dr Edison Liu Executive Director, GIS 2001 Dr Yoshiaki Ito PI, IMCB 2002 Dr Jackie Ying Executive Director, IBN 2003 Dr Edward Holmes Executive Dy Chmn (TCSG), BMRC & Chmn, NMRC Dr Axel Ullrich Director, SOG Lab 2004 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Dr Birgitte Lane Executive Director, IMB Dr Neal Copeland & Dr Nancy Jenkins PIs, IMCB 2005 Dr Philippe Kourilsky Chairman, SIg. N Dr Phil Ingham PI, IMCB Dr Jean Paul Thiery PI, IMCB 2006

Human Capital - Guppies History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
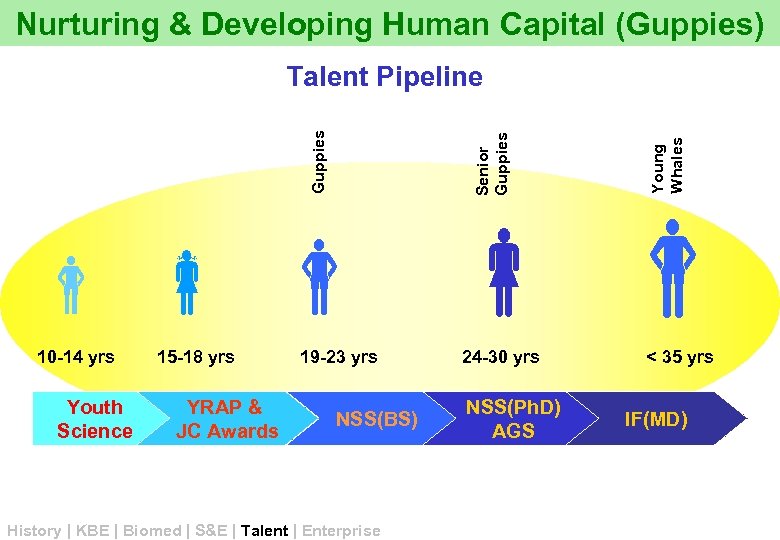
Nurturing & Developing Human Capital (Guppies) 10 -14 yrs Youth Science 15 -18 yrs YRAP & JC Awards 19 -23 yrs NSS(BS) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise 24 -30 yrs NSS(Ph. D) AGS Young Whales Senior Guppies Talent Pipeline < 35 yrs IF(MD)
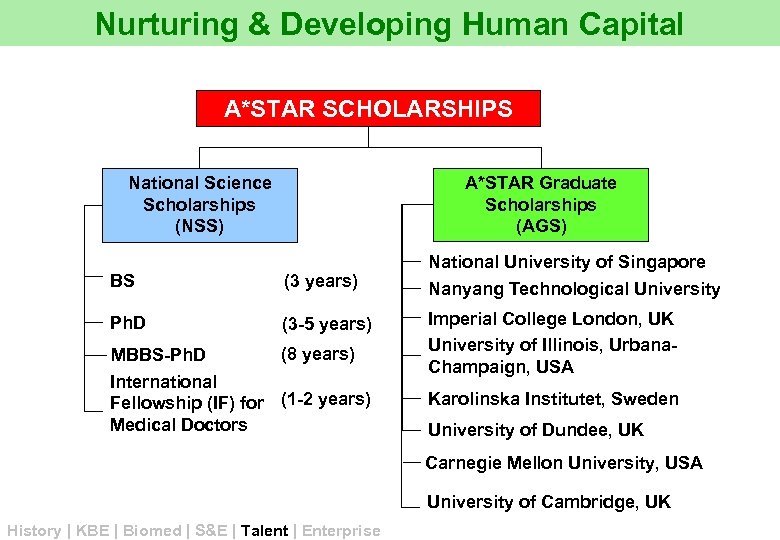
Nurturing & Developing Human Capital A*STAR SCHOLARSHIPS National Science Scholarships (NSS) A*STAR Graduate Scholarships (AGS) National University of Singapore BS (3 years) Nanyang Technological University Ph. D (3 -5 years) Imperial College London, UK University of Illinois, Urbana. Champaign, USA (8 years) MBBS-Ph. D International Fellowship (IF) for (1 -2 years) Medical Doctors Karolinska Institutet, Sweden University of Dundee, UK Carnegie Mellon University, USA University of Cambridge, UK History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

Human Capital: International Guppies MIT Physics (Malaysia) MIT Chemical Engineering (Germany) Stanford Chemical Engineering (Shanghai) MIT Bio Engineering (Hong Kong) Stanford Computer Science (India) MIT Chemical Engineering (Vietnam)

Human Capital: Singapore Guppies Rockefeller Bacteriology Medicine/Ph. D Duke Stanford Biochemistry Medicine/Ph. D Camrbidge, London Stanford Biochemistry Computer Science Carnegie-Mellon

International Linkages History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

A*STAR Partners in Ph. D Training LOCAL OVERSEAS • • Ph. D studies in Biomedical Sciences, Physical Sciences and Engineering Scholars are supervised throughout their course of study Upon completion, Scholar is awarded Ph. D degree from the respective university Promotes collaborations between A*STAR Research Institutes & Universities History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
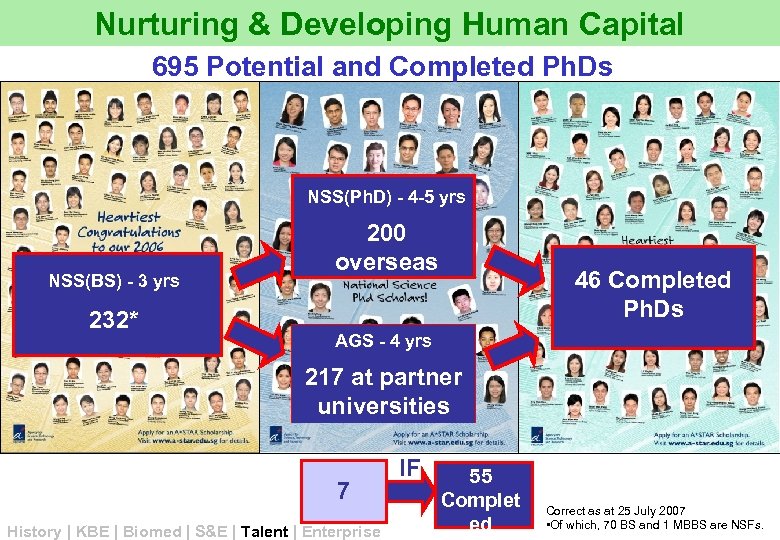
Nurturing & Developing Human Capital 695 Potential and Completed Ph. Ds NSS(Ph. D) - 4 -5 yrs NSS(BS) - 3 yrs 232* 200 overseas 46 Completed Ph. Ds AGS - 4 yrs 217 at partner universities 7 History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise IF 55 Complet ed Correct as at 25 July 2007 • Of which, 70 BS and 1 MBBS are NSFs.

Completed Ph. Ds Ang Hwee Ching Biomedical Sciences (30) Koh Kian Peng Ho Han Kiat Keefe Chng Science & Engineering (16) As of July 07 Tracy Ho Yeo Sze Ling Foo Yong Lim Anwesha Dey Chow Keat Theng Lim Chin Yan Low Yen Ling Max Fun Ng Sean Pin Andrew Wan Amanda Chan Wee Boon Yu Teo Hsiang Ling Leong Siang Huei Chan Kok Ping Chit Fang Cheok Quek Su Ying Yuen Chau Cleo Choong Gary Ng Sum Huan Chua Yang Choo Ng Kee Woei Zhang Rui Wong Ee Tsin Ho Ying Swan Andrea Pillai Ng Ching Ging Leong Li Ming Loo Li Shen Andrew Ang Ng San, Susanne Yeo Yong Kee Yar Kar Peo Tng Hui Ching, Emilia Chaw Kwan Chun
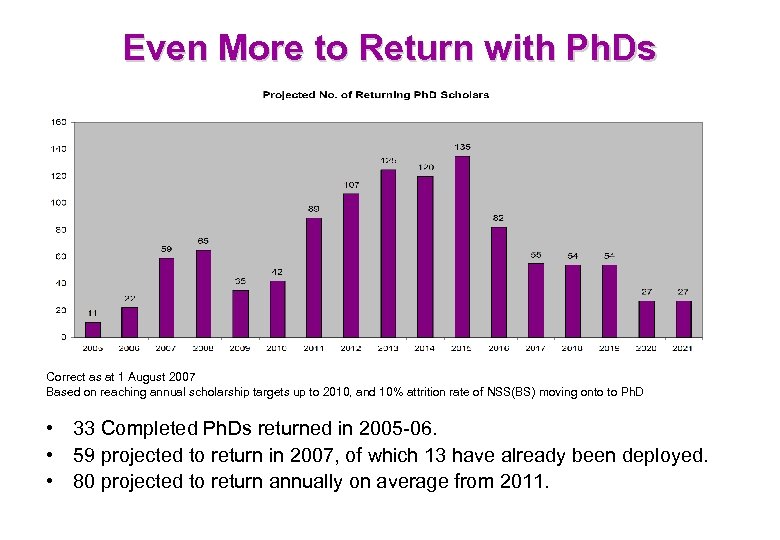
Even More to Return with Ph. Ds Correct as at 1 August 2007 Based on reaching annual scholarship targets up to 2010, and 10% attrition rate of NSS(BS) moving onto to Ph. D • 33 Completed Ph. Ds returned in 2005 -06. • 59 projected to return in 2007, of which 13 have already been deployed. • 80 projected to return annually on average from 2011.

R&D Intellectual Property LOCAL ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Sustainable Vibrant Economy

Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs) • 46% of GDP and 63% of employment • Local SMEs: 25% of GDP and 51% of employment • Small is NOT Beautiful. Few small enterprises survive in the long term • Elephants can Dance • Challenges: Ø How to sustain broad-based economic growth? Ø How to encourage Innovation and Creativity? History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
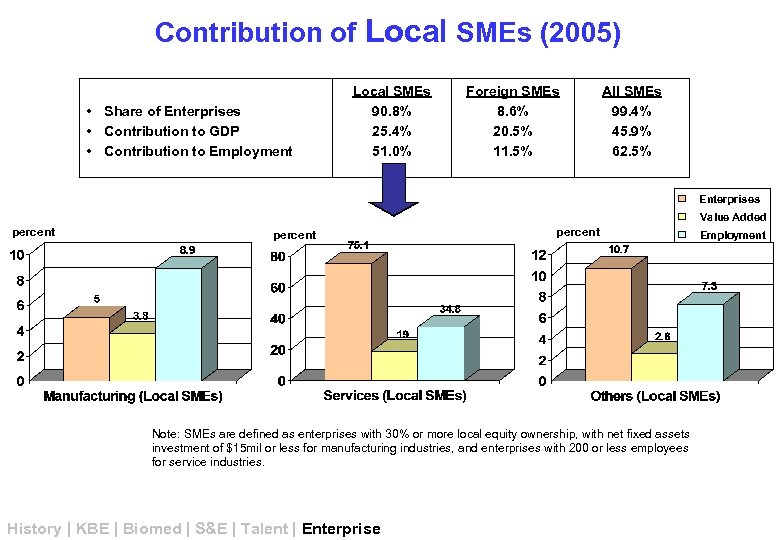
Contribution of Local SMEs (2005) • Share of Enterprises • Contribution to GDP • Contribution to Employment Local SMEs 90. 8% 25. 4% 51. 0% Foreign SMEs 8. 6% 20. 5% 11. 5% All SMEs 99. 4% 45. 9% 62. 5% Enterprises Value Added percent Note: SMEs are defined as enterprises with 30% or more local equity ownership, with net fixed assets investment of $15 mil or less for manufacturing industries, and enterprises with 200 or less employees for service industries. History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Employment
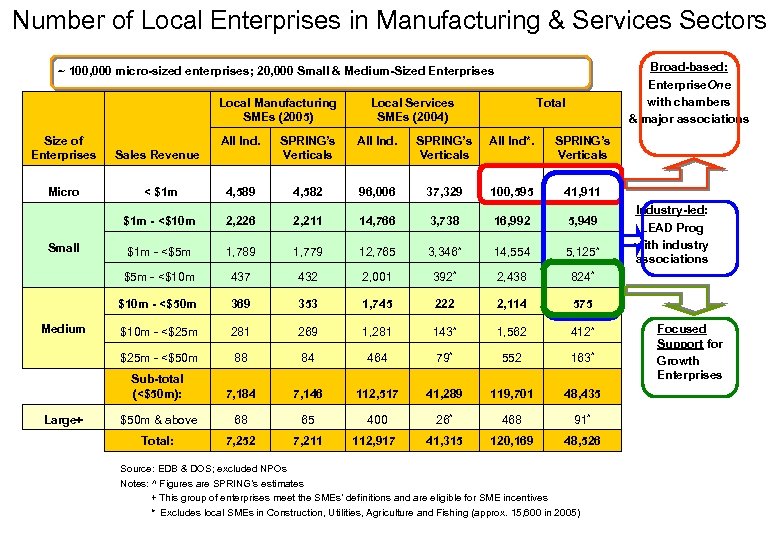
Number of Local Enterprises in Manufacturing & Services Sectors Broad-based: Enterprise. One with chambers & major associations ~ 100, 000 micro-sized enterprises; 20, 000 Small & Medium-Sized Enterprises Local Manufacturing SMEs (2005) Size of Enterprises Sales Revenue Micro Total Local Services SMEs (2004) All Ind*. SPRING’s Verticals < $1 m 4, 589 4, 582 96, 006 37, 329 100, 595 41, 911 2, 226 2, 211 14, 766 3, 738 16, 992 5, 949 $1 m - <$5 m 1, 789 1, 779 12, 765 3, 346^ 14, 554 5, 125^ 437 432 2, 001 392^ 2, 438 824^ 369 353 1, 745 222 2, 114 575 $10 m - <$25 m 281 269 1, 281 143^ 1, 562 412^ $25 m - <$50 m 88 84 464 79^ 552 163^ Sub-total (<$50 m): SPRING’s Verticals $10 m - <$50 m Large+ All Ind. $5 m - <$10 m Medium SPRING’s Verticals $1 m - <$10 m Small All Ind. 7, 184 7, 146 112, 517 41, 289 119, 701 48, 435 $50 m & above 68 65 400 26^ 468 91^ Total: 7, 252 7, 211 112, 917 41, 315 120, 169 48, 526 Source: EDB & DOS; excluded NPOs Notes: ^ Figures are SPRING’s estimates + This group of enterprises meet the SMEs’ definitions and are eligible for SME incentives * Excludes local SMEs in Construction, Utilities, Agriculture and Fishing (approx. 15, 600 in 2005) Industry-led: LEAD Prog with industry associations Focused Support for Growth Enterprises

“EVERY GREAT OAK TREE STARTED AS A DETERMINED ACORN” Acorn TO HAVE A FOREST OF OAK TREES, WE NEED TO SEED MANY (SURVIVING) ACORNS! Oak Trees History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
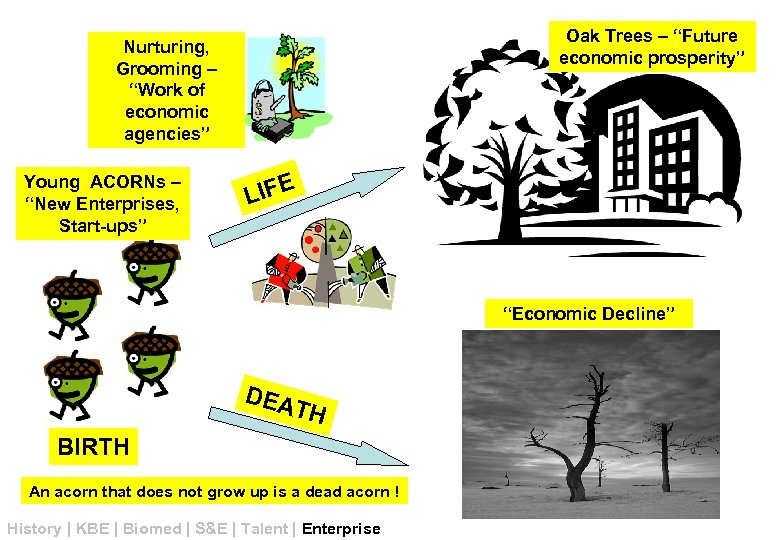
Oak Trees – “Future economic prosperity” Nurturing, Grooming – “Work of economic agencies” Young ACORNs – “New Enterprises, Start-ups” LIFE “Economic Decline” DEA TH BIRTH An acorn that does not grow up is a dead acorn ! History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
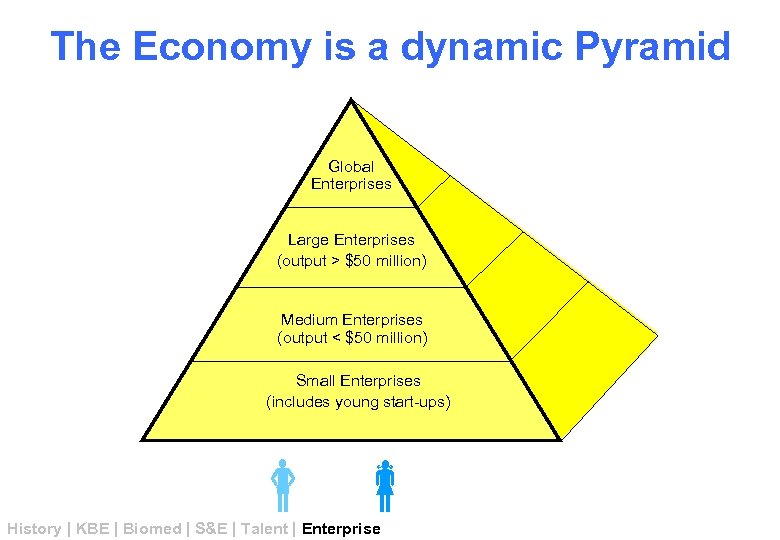
The Economy is a dynamic Pyramid Global Enterprises Large Enterprises (output > $50 million) Medium Enterprises (output < $50 million) Small Enterprises (includes young start-ups) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
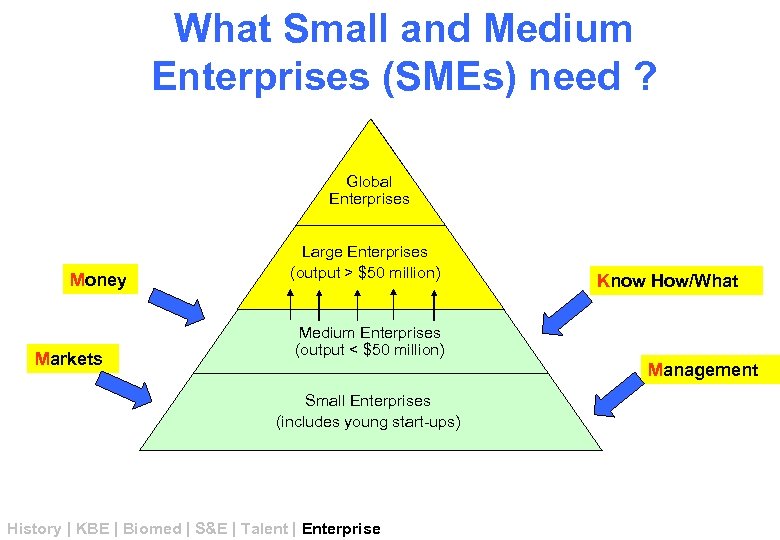
What Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) need ? Global Enterprises Money Markets Large Enterprises (output > $50 million) Know How/What Medium Enterprises (output < $50 million) Management Small Enterprises (includes young start-ups) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
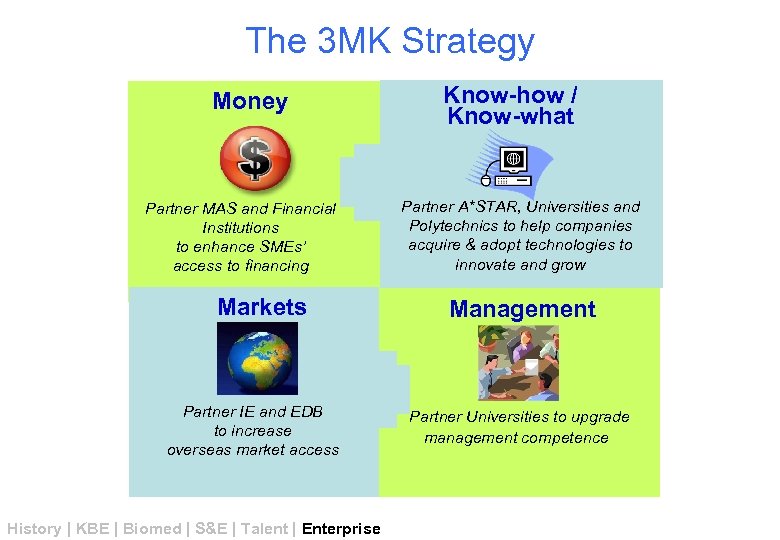
The 3 MK Strategy Money Partner MAS and Financial Institutions to enhance SMEs’ access to financing Markets Partner IE and EDB to increase overseas market access History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise Know-how / Know-what Partner A*STAR, Universities and Polytechnics to help companies acquire & adopt technologies to innovate and grow Management Partner Universities to upgrade management competence
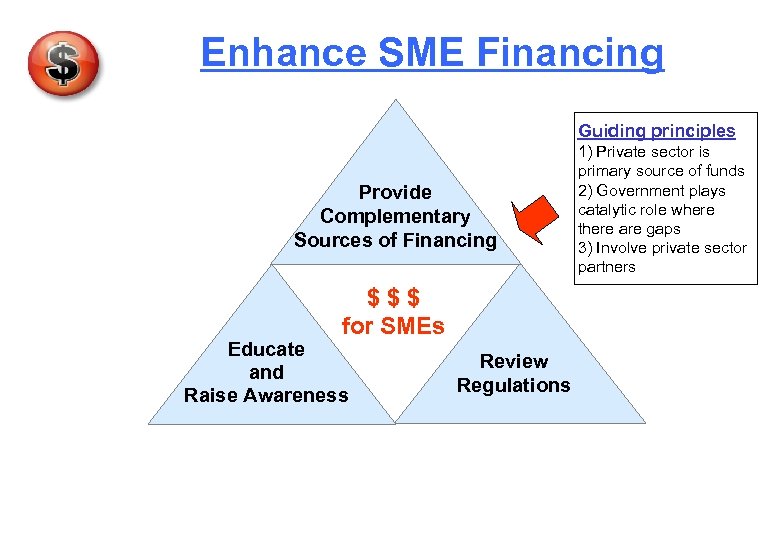
Enhance SME Financing Guiding principles Provide Complementary Sources of Financing $$$ for SMEs Educate and Raise Awareness Review Regulations 1) Private sector is primary source of funds 2) Government plays catalytic role where there are gaps 3) Involve private sector partners

Improve Access to Overseas Markets § § Facilitate access to Global markets § Provide Export Technical Assistance Link SMEs to MNCs and foreign SMEs History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
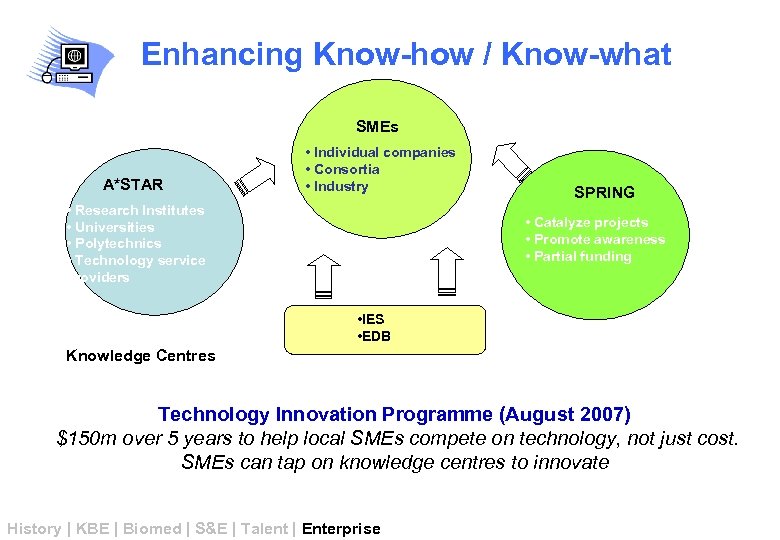
Enhancing Know-how / Know-what SMEs A*STAR • Individual companies • Consortia • Industry • Research Institutes • Universities • Polytechnics • Technology service providers SPRING • Catalyze projects • Promote awareness • Partial funding • IES • EDB Knowledge Centres Technology Innovation Programme (August 2007) $150 m over 5 years to help local SMEs compete on technology, not just cost. SMEs can tap on knowledge centres to innovate History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

Upgrade Management Skills Management Development Programme (April 2007) • Co-fund and train 1, 000 SME CEOs and Managers over 5 years • Funded local Universities to develop curriculum for SMEs • EMBA and Executive Development courses History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise

3 G – Grow, Glow and Globalise EDB Global Enterprises A*STAR - Generating Know How - Attracting Overseas Investments Large Enterprises (output > $50 million) IE Singapore - Oversee Markets Access - Attracting Whales (Talent) Medium Enterprises (output < $50 million) SPRING Small Enterprises (includes young start-ups) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise - Enterprise development

Key Challenges for Singapore • Face Global Competition • Transit from Manufacturing to “know-how”, a Knowledge Based Economy (KBE) • Nurture an Enterprise culture: - Passion (risk taking) - Determination (hard work) - Vision (Global) - Focus (Operational) History | KBE | Biomed | S&E | Talent | Enterprise
319d007e87296bb412c8a9c36551b98e.ppt