
BUDGETING

A budget is a financial plan and a list of all planned expenses and revenues. It is a plan for saving, borrowing and spending.

The purpose of budgeting is to: Establish the cost constraint for a project, program, or operation. Provide a forecast of revenues and expenditures, that is, construct a model of how our business might perform financially if certain strategies, events and plans are carried out. Enable the actual financial operation of the business to be measured against the forecast.

Business plan is a roadmap for future development. It describes business, its objectives, financial forecasts and your market. A budget is a plan to: - Control finances - Ensure can continue to fund current commitments - Enable to make confident financial decisions and meet objectives - Ensure having enough money for future projects

Benefits of business budget: - Manage money effectively - Allocate appropriate resources to projects - Monitor performance - Meet objectives - Improve decision-making - Identify problems before they occur such as the need to raise finance or cashflow difficulties plan for the future - Increase staff motivation

Creating a budget Creating, monitoring and managing a budget is key to business success Questions: -What are the projected sales for the budget period? Be realistic - if you overestimate, it will cause you problems in the future. -What are the direct costs of sales - ie costs of materials, components or subcontractors to make the product or supply the service? - What are the fixed costs or overheads?
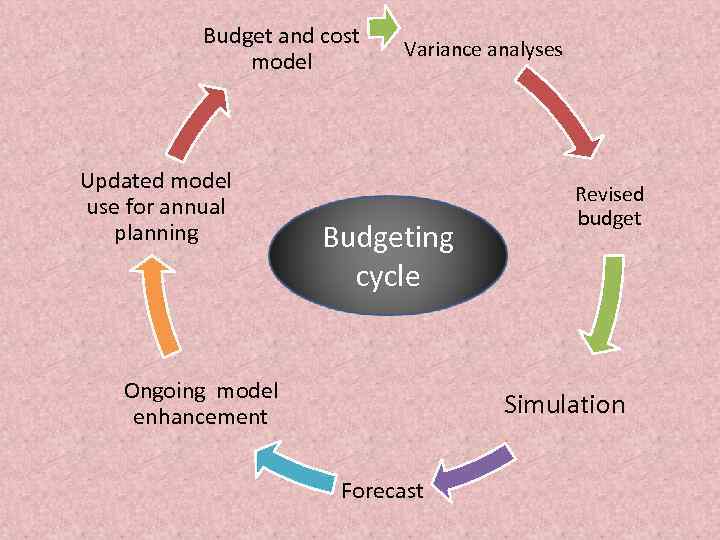
Budget and cost model Updated model use for annual planning Variance analyses Budgeting cycle Ongoing model enhancement Revised budget Simulation Forecast

The fixed costs and overheads should be broken down by type, eg: - cost of premises, including rent or mortgage, business rates and service charges - staff costs - eg pay, benefits, National Insurance - utilities - eg heating, lighting, telephone or internet connection - printing, postage and stationery - vehicle expenses - equipment costs - advertising and promotion - travel and subsistence expenses - legal and professional costs, including insurance

What your budget will need to include: -Projected cashflow - your cash budget projects your future cash position on a month-by-month basis. Budgeting in this way is vital for small businesses as it can pinpoint any difficulties you might be having. It should be reviewed at least monthly.

Costs - typically, your business will have three kinds of costs: - fixed costs - items such as rent, rates, salaries and financing costs - variable costs - including raw materials, overtime and tax - one-off capital costs - for example, purchases of computer equipment or premises

To forecast the costs, it can help to look at last year's records and contact the suppliers for quotes Revenues - sales or revenue forecasts are typically based on a combination of your sales history and how effective you expect your future efforts to be. Using the sales and expenditure forecasts, projected profits can be prepared for the next 12 months. This will enable to analyse the margins and other key ratios such as return on investment.