5853d2403afaf0764568eb9df94e0f85.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Budget reform: making it happen Owen Barder United Kingdom

Reform in the real world ØBudget problems in the real world ØBudget Reform and the MTEF ØKey steps in introducing the MTEF ØLessons

South Africa is different ØApartheid u u inequality distortion of public services ØHuman capital & financial administration ØNew quasi-federal structure ØCo-operative governance

Budget problems in the real world ØUnrealistic budgets u unaffordable, undeliverable, deferred ØNo link to behavior u no buy in, cash controls, hidden budget, overspending, link to policy proposals ØAllocation doesn’t reflect priorities u no choice, short termist, distorted, enclaves ØSpending inefficient u low productivity, poor management, corruption, poor planning

Budget problems in the real world ØUnrealistic budgets u unaffordable, undeliverable, deferred ØNo link to behavior u no buy in, cash controls, hidden budget, overspending, link to policy proposals ØAllocation doesn’t reflect priorities u no choice, short termist, distorted, enclaves ØSpending inefficient u low productivity, poor management, corruption, poor planning

Elements of budget reform ØMedium Term Expenditure Framework ØBudget Policy Statement ØNew intergovernmental system ØPublic Financial Management Act ØImproved financial management ØWider public sector Budget Reform White Paper

MTEF: rapid success ØFirst plan April 1997 ØMTEF published March 1998 ØCompare eg Malawi since 1994 ØCompare South Africa 1994 -96

First MTEF 1994 -1996 ØSpreadsheet model ØSectoral analysis ØCross-sectoral links ØCabinet away-day ØSank without trace

Why did it fail? ØNo political buy-in ØNo emphasis on choice ØNo link to budgets ØNo link to budget process ØToo technical

MTEF 1998 ØPersuaded Government u Treasury, Cabinet, Departments Ø 3 -year spending plans all departments ØAnalysis to improve over time ØMTEF replaced budget process

Persuasion ØThree goals of budget u u u aggregate fiscal discipline allocative efficiency technical efficiency ØMTEF delivers all three u especially the first two … ØTarget the message

Persuading Cabinet Ø Political control of the budget Ø Better prioritization Ø Choices at budget stage Ø More certainty: better planning Ø More delivery Ø More cooperative Ø Less central interference Ø Cheaper borrowing Ø More spending Ø “State of the art”

Persuading Departments Ø More cooperative Ø Less central interference Ø Choices at budget stage Ø More certainty: better planning Ø More money (borrowing costs; unspent funds) Ø Better prioritization

MTEF 1998 ØPersuaded Government Ø 3 -year spending plans all departments ØAnalysis to improve over time ØMTEF replaced budget process

Benefits of 3 year plans ØBetter prioritisation ØBetter planning Immediate ØTransparent and credible ØFinancial discipline ØMore spending & delivery ØAffordable policy development

Benefits of analysis ØIdentify choices & quantify ØLink to outputs and outcomes ØAccountability ØBenchmarking ØBetter outcomes Over time

MTEF 1998 ØPersuaded Government Ø 3 -year spending plans all departments ØAnalysis to improve over time ØMTEF replaced budget process

Replacing the process ØEvery department involved ØCompeting for same resources Ø 3 year horizon for everything ØRenaming eg committees ØMTEF to Cabinet, not Budget ØIncreased financial discpline

Lessons ØObtain political commitment u u emphasise empowerment, choice, delivery involve in process ØKeep it simple u u 3 year plans for each department get out of the detail ØMake it matter u u u replace budget process link to financial discipline plans as baselines

Did it succeed? Too early to tell © Zhou En Lai

Did it succeed? Political buy-in Reprioritisation Budgets matter Disciplined policy-making Better analysis Co-operative governance

How to do Budget Reform Obtain political commitment Keep it simple Make it matter After the break: how SA does the MTEF

The MTEF in practice

The MTEF in practice ØWhat is the MTEF? ØAffordable totals ØPutting the budget together ØLessons

South Africa is different ØQuasi federal structure ØCooperative Governance ØGood administrative capacity

What is the MTEF? Three year projections of: Ø growth and inflation Ø revenues, deficit and spending Ø debt interest costs Ø division between tiers of government Ø spending plans by department Ø statement of main outputs Ø contingency reserve } } Available Funds Spending allocations

MTEF process aimed at: Ø Agreeing affordable totals Ø Identifying policy options Ø Building consensus
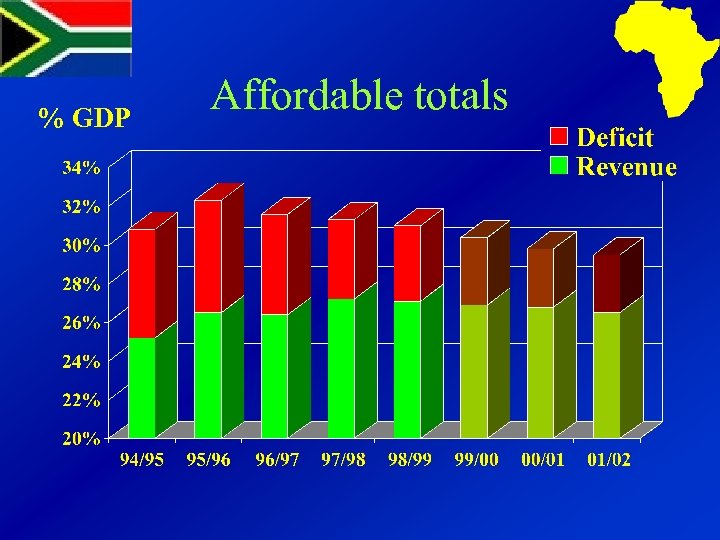
% GDP Affordable totals
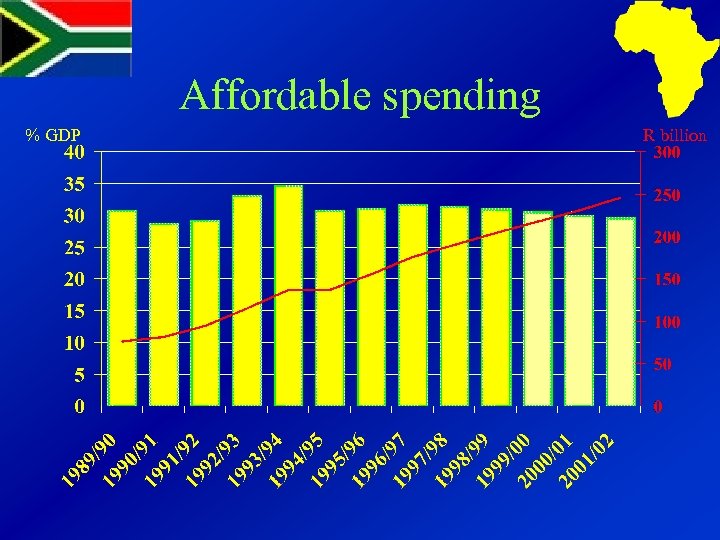
Affordable spending % GDP R billion

Getting totals right ØKeep projections simple ØMake public fiscal commitments ØDecide totals before allocations
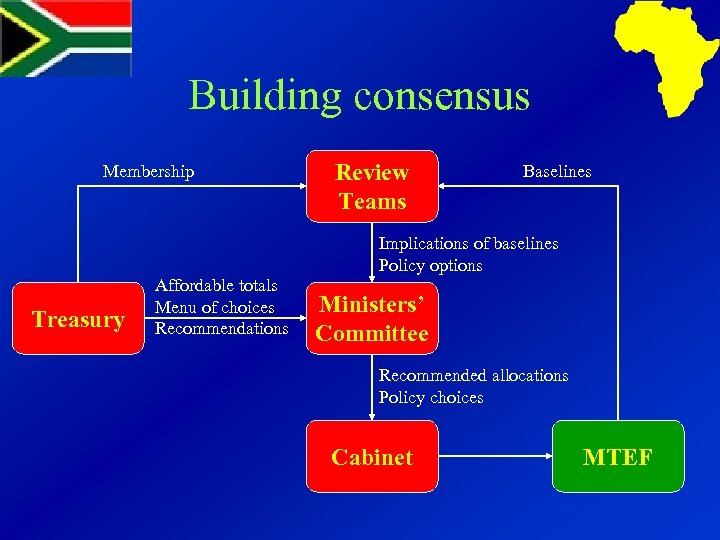
Building consensus Membership Review Teams Baselines Implications of baselines Policy options Treasury Affordable totals Menu of choices Recommendations Ministers’ Committee Recommended allocations Policy choices Cabinet MTEF

Review teams ØWhat? u Health, Education, Welfare, Crime, Personnel, Infrastructure ØWho? u Treasury, line departments, subnational government, consultants ØWhat? u u expenditure trends implications of baseline costed policy options benchmarking

Review teams ØUnique to South Africa ØCooperative governance ØBetter understanding u u Treasury of policy challenges Departments of financial implications ØConsensus building ØOngoing work programmes

Ministerial Committee ØPowerful minority ØIdentifies options ØEvaluates proposals ØRecommends to Cabinet

Cabinet ØForum for competing policies ØImplications of plans ØMenu of policy options ØCollective agreement ØMost important decisions
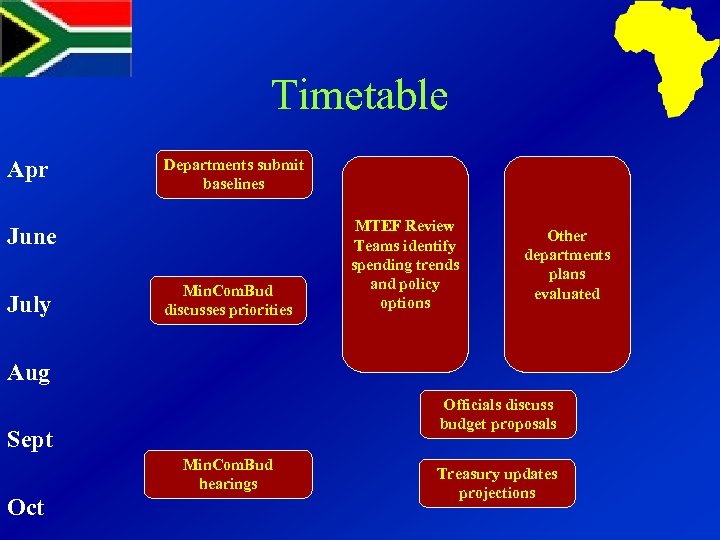
Timetable Apr Departments submit baselines June July Min. Com. Bud discusses priorities MTEF Review Teams identify spending trends and policy options Other departments plans evaluated Aug Officials discuss budget proposals Sept Min. Com. Bud hearings Oct Treasury updates projections
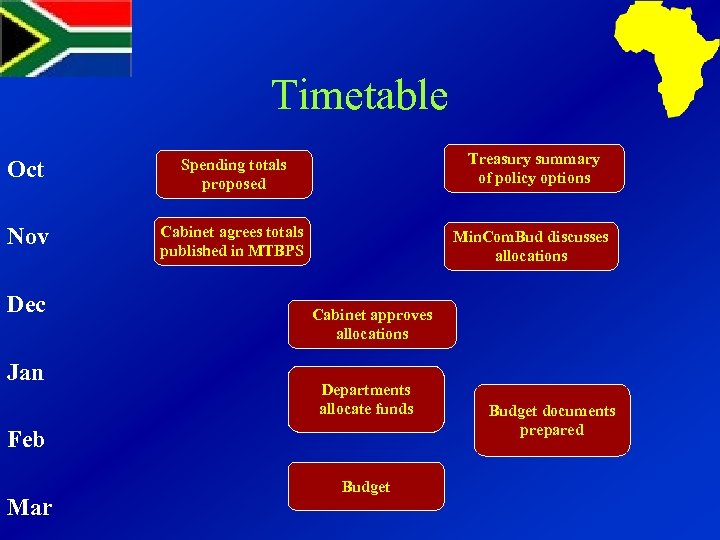
Timetable Oct Spending totals proposed Treasury summary of policy options Nov Cabinet agrees totals published in MTBPS Min. Com. Bud discusses allocations Dec Jan Cabinet approves allocations Departments allocate funds Feb Mar Budget documents prepared

Implementation lessons ØInclude, but control ØListen to departments ØInvolve politicians throughout ØAvoid information overload ØDecide totals first ØDon’t over-prescribe ØFocus on priorities ØPromote transparency

Contact information Owen Barder email: owen@owen. org Department of Finance, South Africa Private Bag X 115, 0001 Pretoria, South Africa website: http: //www. finance. gov. za/

The End Owen Barder
5853d2403afaf0764568eb9df94e0f85.ppt