e9cf96bece48685cbe9aeaf5d8fc7349.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

BSAC Standardized Disc Susceptibility Testing Method - User Group Meeting. Cardiff, 13 May 2010 Vitek 2 – A User Experience. Nathan Reading Senior Biomedical Scientist Sandwell and West Birmingham Hospitals NHS Trust

1 Year B. V. (before Vitek. . ) • Previously. . – Disc susceptibilities for >90% isolates • • • Urines Blood Cultures (Direct and Repeats) Respiratory Ocular General – swabs etc – Agar Dilution MIC’s • All Pseudomonads • Resistant gram negatives • Ad-hoc organism/difficult infections – Gradient Tests • Difficult organisms • Adhoc testing/confirmations

1 Year B. V. (before Vitek. . ) Staffing required. . 1 Senior BMS W. T. E. 2 x BMS W. T. E. 0. 5 MLA W. T. E. Daily/Weekly Tasks Reading Plates/Setting Up Disc Susceptibility Plates and pouring Agar Dilution Plates/Preparing Antibiotic Stocks and Dilutions/Setting up MIC plates/Reading MIC Plates. Working Day 8 am-5 pm Weekday 8 am-12 pm Saturdays (All sensitivities bar MIC’s read, all sensitivities put up bar urinary isolates) 8 am-1 pm Sundays (Only Blood Culture and MRSA sensitivities setup/read)

Sensitivity testing 1 Year AV (after Vitek. . . ) • 1 x Senior BMS WTE • 1 x BMS WTE • 0. 6 x. MLA WTE – Reduced staff overhead – Senior BMS freed to look after our organism collection • All sensitivity testing complete >90% time by 4 pm • Sensitivity testing ready for release to clinician by 10 -11 am • We do not release same day sensitivity testing. . – Do not wish to retract incorrect reports – Our working days structure currently means that cards not going onto Vitek until mid morning earliest

Sensitivity testing 1 Year AV • Gram negatives – UTI • Use Chromogenic Media • E. coli – treated as E. coli, Vitek Sens • Coliform group – Vitek Sens and Automated ID also – Systemic -Fermenters • Automated ID and Sensitivity Test – Non fermenters • Automated ID or Basic Manual ID • Automated Sensitivity Test Blood Cultures – Direct disc susceptibility – in-house dilution protocol • Repeats by Vitek

Sensitivity testing 1 Year AV • Gram positives – Staphylococci • Vitek Sensitivity • Manual ‘traditional’ ID • API/Vitek GP Card for discrepant organisms – Enterococci • Vitek Sensitivity • Antibiogram/API/Vitek GP card if speciation needed – Beta Haem Streptococci • Vitek (Group B) and Discs (All others) • Fastidious Organisms – Discs!

Issues - Flexability Card ‘make up’ will never perfect for every user – Bespoke cards can be made for individuals For our UTI’s No Amikacin on UTI card – only Gent We now disc test Amikacin on Gent I/R Aminoglycoside rules cant work properly No Mecillinam Our clinicians want Mecillinam on all Trim R isolates of E. coli/Kleb/Proteus can be 30% isolates!

Issues – Antibiotic Concentrations • Rifampicin – Card tests at 0. 25, 0. 5 and 2 mg/L – Calling range 0. 25 -4 mg/L – EUCAST/BSAC ‘S’ cut off = 0. 06 mg/L ‘I‘= 0. 12 -0. 5 ‘R’ =>0. 5 – Card does not test low enough to determine S using BSAC/EUCAST breakpoints • Recent card revision did not solve this • Now need to disc test on ad-hoc basis if clinicians require result

Issues – Antibiotic Concentrations • Mupirocin – Card tests 1 mg/L • Calling range 2 -8 mg/L! BSAC ranges S= ≤ 4 I= 8 -256 R >256 – Need to disc test to differentiate I from R • Mupirocin decolonisation may still work if Intermediate • Recent revision to cards did not solve this. . .

Detection of resistance • Detection of Hyperproduction of K 1 enzyme in Kleb oxytoca – No Aztreonam on UTI Card AST N 144 – Need to rely on Inhibitor Resistance and Cefotaxime which can be variable – Offline Synergy Test • Cefpodoxime/Cefpodoxime+Clav+Boronic Acid • Aztreonam disc testing
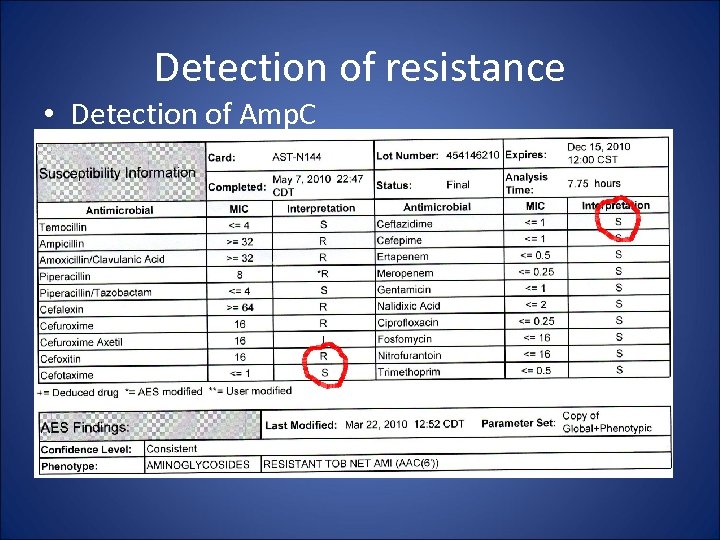
Detection of resistance • Detection of Amp. C
Detection of Amp. C • Cefoxitin Resistant • 3 rd Gen Ceph’s = S • Check ID – Some Chromogenic agars mis-identify Citrobacter species (may have natural Amp. C) • Check ESBL/Confirmation Test – Cefpodoxime/Cefpodoxime+Clav+Boronic Acid – If negative synergy – probable impermeability/porin loss – If positive synergy with Boronic Acid/Clav/Cefpodozime = Amp. C

Detection of Resistance • Detection of ESBL • Compared 296 urinary isolates screened with HMRZ -86 a chromogenic 3 rd gen Cephalosporin – Vitek missed 11 ESBL producers out of a total of 42 – Situation improved a little on software update • ? algorithms changed • Still misses some low expression of ESBL

Solution ? • All of the missed isolates (ESBL&Amp. C) reduced zone to Cefpodoxime 10 ug disc • ? Need a Vitek card containing Cefpodoxime • 18 missed isolates E. coli/Klebsiella • 10 ESBL Missed with routine card • 7 Amp. C Missed with routine card • 1 K oxytoca (included for interest)
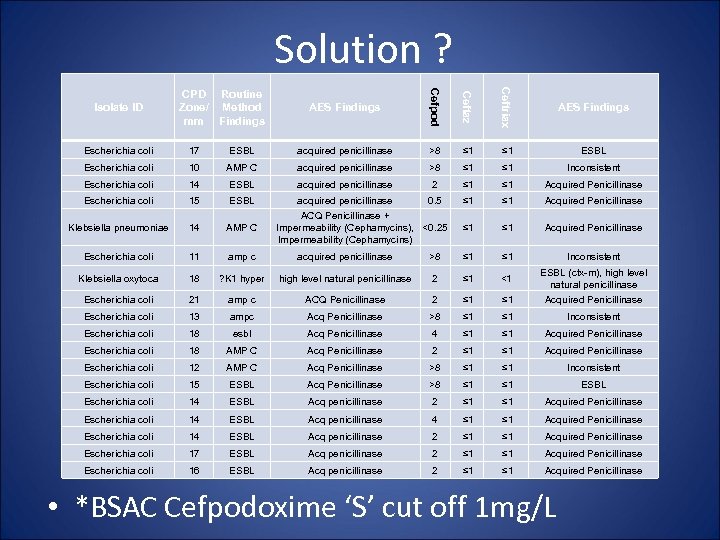
Solution ? Cefpod Ceftaz Ceftriax AES Findings Escherichia coli 17 ESBL acquired penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 ESBL Escherichia coli 10 AMP C acquired penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 Inconsistent Escherichia coli 14 ESBL acquired penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 15 ESBL acquired penicillinase 0. 5 ≤ 1 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Inconsistent Isolate ID CPD Routine Zone/ Method mm Findings AES Findings ACQ Penicillinase + Impermeability (Cephamycins), <0. 25 Impermeability (Cephamycins) Klebsiella pneumoniae 14 AMP C Escherichia coli 11 amp c acquired penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 Klebsiella oxytoca 18 ? K 1 hyper high level natural penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 <1 Escherichia coli 21 amp c ACQ Penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 ESBL (ctx-m), high level natural penicillinase Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 13 ampc Acq Penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 Inconsistent Escherichia coli 18 esbl Acq Penicillinase 4 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 18 AMP C Acq Penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 12 AMP C Acq Penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 Inconsistent Escherichia coli 15 ESBL Acq Penicillinase >8 ≤ 1 ESBL Escherichia coli 14 ESBL Acq penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 14 ESBL Acq penicillinase 4 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 14 ESBL Acq penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 17 ESBL Acq penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase Escherichia coli 16 ESBL Acq penicillinase 2 ≤ 1 Acquired Penicillinase • *BSAC Cefpodoxime ‘S’ cut off 1 mg/L

Solution ? • 16/18 isolates all had MIC for Cefpodoxime >1 mg/L (BSAC breakpoint) • Include Cefpodoxime on card? – With or without CAZ, CTX?

Detection of Resistance • What is this isolate? • System highlights MRSA as possible mechanism – changes Cefoxitin result from Negative to POSITIVE

Solution ? • All isolates showing this change – PBP 2’ Latex (Oxoid/Mast) • 20 minute test – If +ve therefore MRSA – If –ve need to rule out MRSA still. • Cefoxitin 10 disc on Iso. Sensitest • Mec. A PCR • Our own mini study – partially complete – 20 isolates Oxacillin ‘R’ / Cefox Screen Changed to +ve – 10 strains Mec. A negative (Internal control Nuc +ve = S. aureus) – All 10 PBP 2’ Latex Negative

Difficult isolates • Mucoid isolates – esp Pseudomonads – Difficult to get a smooth inoculum – May give false resistance/susceptibility – Need a plan B • MIC? • Gradient Test? • Discs?
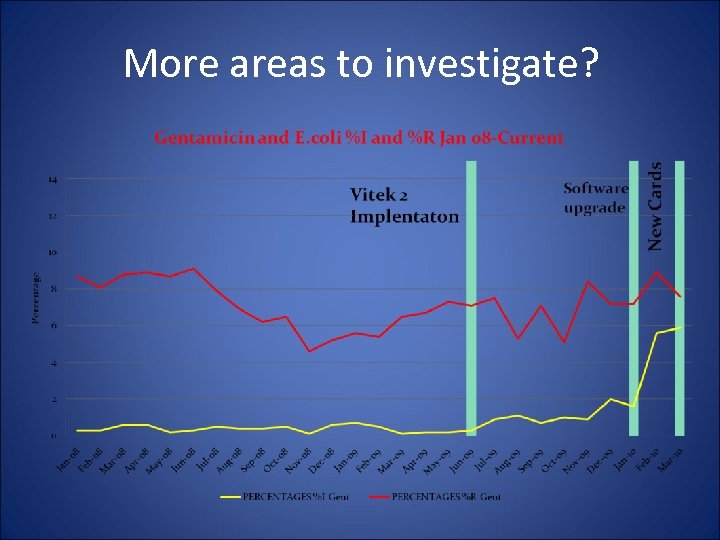
More areas to investigate?

New and Emerging Phenotypes • July 2009 • Our first Isolate of NDM-1 Carbapenemase in Klebsiella pneumoniae – Detected by Vitek 2 • Subsequent challenge with further strains from other centres also detected as expected • Isolates with VIM, IMP and KPC isolates also detected. • Carbapenemases, the new ESBL?
Summary • Automated systems not panacea for solving lack of AST knowledge within laboratory. – Some users may find more questions than answers • BSAC method still required to fill in the gaps – Not just fastidious organisms • Some areas could be optimised to enhance detection of important isolates • Some cards need to be improved for UK/EUCAST breakpoints

Summary – the positives • Reduction of staff overhead • Improved speed of results – We at City dont make best use of all benefits of automation • Can be used to upskill knowledge of AST and mechanisms of resistance • Simple to use and well supported by the company.
e9cf96bece48685cbe9aeaf5d8fc7349.ppt