Sustainable Energy Development.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 28

Brynhildur Davidsdottir University of Iceland SUSTAINABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT

Sustainable Development and Energy Sustainable Energy Development History Definitions What is needed? Indicators

Sustainable Energy Development The development of sustainable energy systems has ‘emerged as one of the priority issues in the move towards global sustainability’ (Malkina-Pykh et al. 2002)

Three SD Milestones • UN Conference Human Environment in Stockholm 1972 - first conference on the nexus between environment and economy defined environmental dimension • Rio summit 1992 - emphasized the economic dimension • Johannesburg 2002 - emphasized the social dimension

Brief History • No specific chapter on energy in Agenda 21 - but mentioned in chapter on the atmosphere • “…to reduce adverse effects on the atmosphere from the energy sector by promoting policies and programmes as appropriate, to increase the contribution of environmentally sound and costeffective energy systems, particularly new and renewable ones, through less polluting and more efficient energy production, transmission, distribution and use. ”

Brief History • Finally mentioned in UN-GA-SS 19 • “need for a movement towards sustainable patterns of production, distribution, and use of energy and, emphasizing the overarching significance of energy for sustainable development” • CSD 9 (2001) focus on energy led to the publication “energy and the challenge of sustainability”. • No direct link from energy to MDG

Brief History • World energy council focuses on energy for sustainable development after 2002 – Achieving access to commercial energy for the two billion people in the world who do not now have it; – developing stable regional trade policies, clear legal frameworks, and sensible regulations for energy development; – keeping all energy options open, including the safe use of nuclear power and the promotion of renewables; – increasing efficiency through competition and technology diffusion; – implementing advanced, cleaner technologies to reduce the impact of human-induced emissions on the quality of human life and the natural world around us.

Brief history • UNFCCC implements CDM in 2001 in the Marrakech Accord • Johannesburg – energy issue intensely debated. No agreement reached on renewable energy targets • Much focus on energy and poverty. Access to high quality energy defined as a basic human right. • Issue really does not emerge as a core issue of SD until after 2000.

Sustainable Energy Development Defined as “the provision of adequate energy services at affordable cost in a secure and environmentally benign manner, in conformity with social and economic development needs” (IAEA/IEA 2001)

Sustainable Energy Development “improving access to reliable, affordable, economically viable, socially acceptable and environmentally sound energy services and resources, taking into account national specificities and circumstances through various means such as enhanced rural electrification and decentralized energy systems, increased use of renewable energy, cleaner liquid and gaseous fuels and enhanced energy efficiency. ” (Johannesburg declaration 2002)

SED Themes/Goals Taken together with the IAEA definition there are four central goals/themes of SED that emerge - 4 Themes/goals towards SED: • Improve technical and economic efficiency (Econ D) • Improve energy security (supply and infrastructure); diversifying, decentralize, increasing supply, local sources, renewable (Econ D) • Reduce environmental impact (environmental dimension) • Expand access and affordability (social dimension) Multi-objective policy and decision-making E. g. Energy and Environmental policy interlinked!

A bit more on Energy Security Definitions: “Availability of energy at all times in various forms, in sufficient quantities and at affordable prices” (WEA 1998) Energy Security refers to a resilient energy system that is able to withstand various threats such as attacks, supply disruptions and environmental threats such as climate change – and thus a secure energy system guarantees continuous availability of energy, of various types in sufficient quantities and at reasonable prices (NCSL)

Core Concepts in Energy Security Infrastructure vulnerability • Centralized Production • Distribution Vulnerability • Options: • Decentralize power production • Increase diversity and redundancy • Enhance surveillance

Core Concepts in Energy Security Supply vulnerability • Rely on polluting and scarce fossil fuels • Imports from unstable regions • Options: • Enhance energy supply (how? ) • Reduce reliance on imported fuels • Diversify energy supply

Towards a new paradigm

What do we need? • • New decision-tool and revised policies Accounting for multidimensional impact of energy use; Multicriteria analysis or total impact/cost assessment when assessing energy projects Holistic assessment – assess total lifecycle impact Internalize external costs; e. g. taxes Policies towards Sustainable Energy Development – – Shift subsidies towards alternative energy source Facilitate invention, innovation and diffusion Demonstration projects, low interest loans Focus on energy efficiency

What do we need? • Account for and monetize environmental costs associated with energy development and use • Account for all scales; remember environmental impact of alternative resources often not at same scales as fossil fuels • Long term thinking • Ensure access, affordability and availability • Ensure sustainable yield (which is what? )

How do we know if we are moving towards SED?

Energy indicators for SD • Overall Objectives: – To provide information on current energy- related trends in a format that aids decision making at the national level in order to e. g. help countries assess effective energy policies for action on sustainable development. – The indicators should make it easier to see which programmes are necessary for sustainable development and SED.

Energy indicators – second cut • Objective: – guide the implementation of actions urged at the WSSD: (i) to integrate energy into socioeconomic programmes – (ii) to combine more renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced energy technologies to meet the growing need for energy services – (iii) to increase the share of renewable energy options – (iv) to reduce the flaring and venting of gas – (v) to establish domestic programmes on energy efficiency – (vi) to improve the functioning and transparency of information in energy markets – (vii) to reduce market distortions – (viii) to assist developing countries in their domestic efforts to provide energy services to all sectors of their populations.
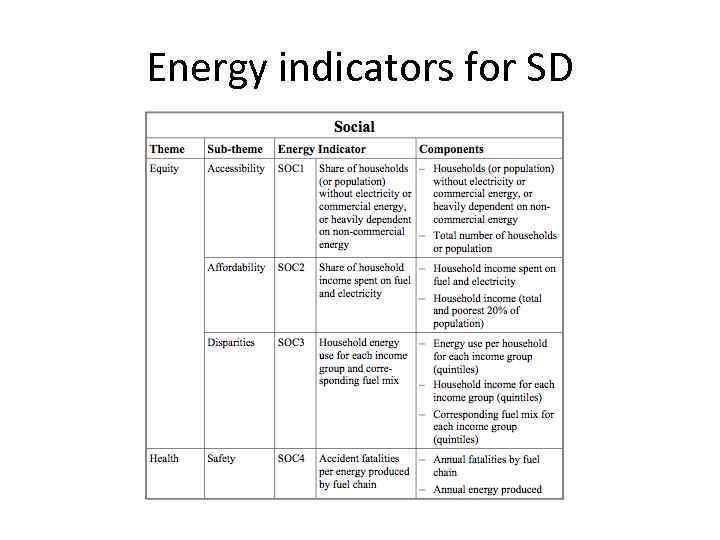
Energy indicators for SD





Moving from indicators to action • Plans to improve each indicators such we move towards sustainable energy development • Not only developing indicators for indicators sake!

Back to the Triangle Energy is central to all three dimensions of SD Source: IAEA 2001

Sustainable Energy Development The development of sustainable energy systems has ‘emerged as one of the priority issues in the move towards global sustainability’ (Malkina-Pykh et al. 2002)
Sustainable Energy Development.pptx