Bronchitis.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 8

Bronchitis

Bronchitis (Latin bronchitis, bronchial tube from +-itis inflammation) - a disease of the respiratory system in which the inflammatory process involved in the bronchi. Among the ten most common reasons for seeking medical help. In most cases, the cause of acute bronchitis is an infection such as a viral or bacterial, and antibiotic treatment required.
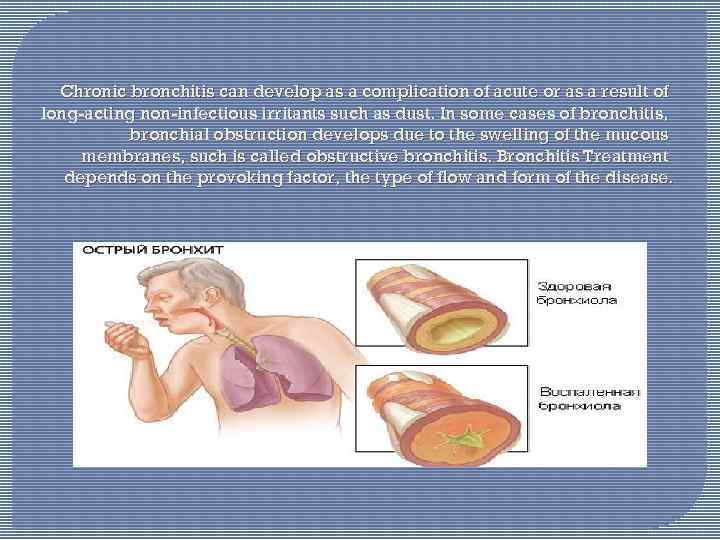
Chronic bronchitis can develop as a complication of acute or as a result of long-acting non-infectious irritants such as dust. In some cases of bronchitis, bronchial obstruction develops due to the swelling of the mucous membranes, such is called obstructive bronchitis. Bronchitis Treatment depends on the provoking factor, the type of flow and form of the disease.

classification Acute bronchitis - acute diffuse inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tracheobronchial tree , characterized by an increase in bronchial secretions with cough and sputum. Chronic bronchitis - diffuse progressive damage the bronchial tree to the restructuring of the secretory apparatus of the mucous membrane with the development of the inflammatory process , accompanied by mucus hypersecretion , a violation of cleansing and protective functions of the bronchial tubes. Acute and chronic bronchitis are significantly different from each other on the etiology , pathogenesis and therapeutics.

Reasons In most cases, the cause of acute bronchitis are viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus, etc. ) and bacteria (pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus, etc. ). Less common causes of bronchitis as mushrooms appear, contact with allergens or inhalation of toxic substances. The most common route of infection - airborne, that is inhaling infected droplets of saliva in contact with the ailing man (during talking, coughing, sneezing, kissing).

Acute bronchitis usually lasts about 10 days. Like other respiratory diseases, bronchitis may be accompanied by a cold or flu , or arise as a consequence, but may begin on its own, without apparent prior occasion. The disease usually begins with a dry cough , which can be strong, especially at night, and may thereby deprive suffering from the disease of normal sleep and rest. After a few days of dry cough becomes a wet cough that may be accompanied by a slight fever , fatigue, headaches.

If the cough lasts for more than a month, is to consult a specialist, pulmonologist and find out whether he respiratory irritation and coughing for any other reason, in addition to inflammation. In some patients with bronchitis prolonged for several months bronchial irritation can lead to asthma. Be sure to consult a doctor if the patient coughs up phlegm with blood in order to prevent serious diseases such as tuberculosis or lung cancer.
Treatment. In most cases, acute bronchitis is caused by a virus, not a bacterial infection, and acute phase usually takes place without the use of antibiotics by itself within a week. Antibiotics are used to treat bronchitis, having a bacterial nature, and sometimes as an aid in cases of suspected or possible complications associated diseases
Bronchitis.pptx