BRONCHIAL ASTHMA DR WADAH KHRIESAT KAUH JUSTCASE SCENARIO


BRONCHIAL ASTHMA DR WADAH KHRIESAT KAUH JUST

CASE SCENARIO Khalid 14 years old come to the clinic c/o shortness of breath for one day duration. He is a known asthmatic patient for more than 8 years, he visited A/E frequently. His school performance is below average, with frequent absence from school due to his illness. HOW YOU WILL PROCEED DURING THIS CONSULTATION ?

What are your objectives in caring for bronchial asthma patient ? Prevent troublesome symptoms night and day Prevent serious attacks Require little or no reliever medication Have productive, physical, psychological, and social active lives
WHAT IS BRONCHIAL ASTHMA? Asthma is a CHRONIC INFLAMMATORY disorder of the airways. Chronically inflamed airways are hyper responsive; they become obstructed and airflow is limited by bronchoconstriction,mucus plugs, and increased inflammation when airways are exposed to various risk factors.
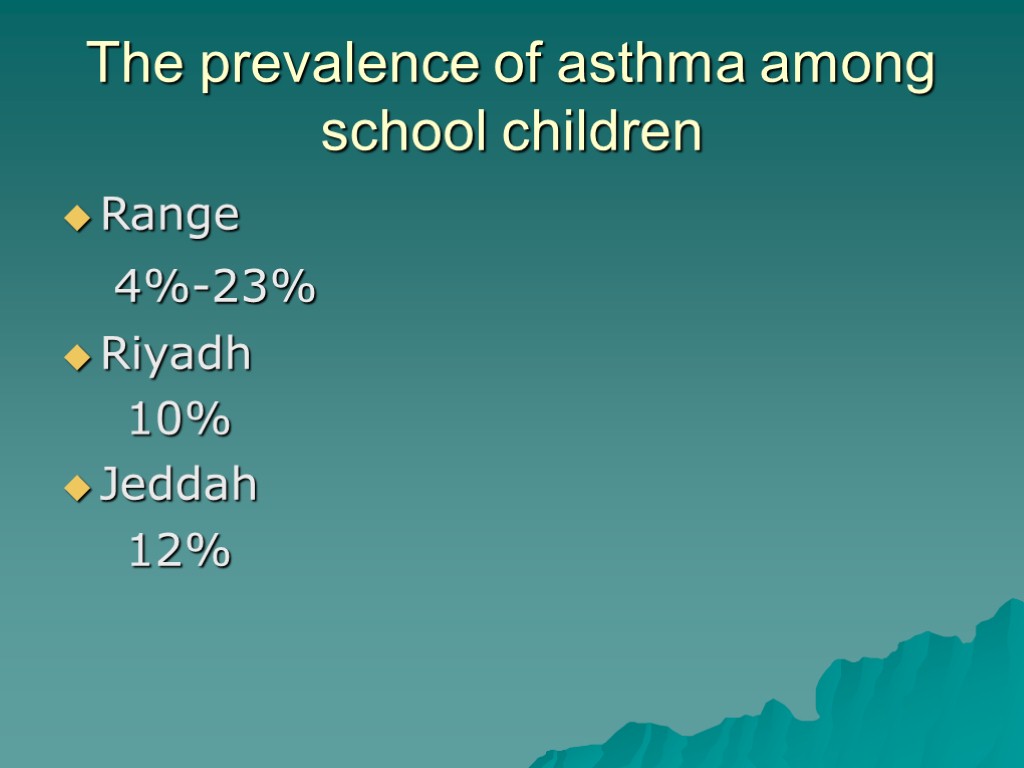
The prevalence of asthma among school children Range 4%-23% Riyadh 10% Jeddah 12%

What is the Pathophysiology? Trigger Factor Mast cell Mediators : histamine,prostaglandin,leukotrienes,as well as cytokines. Inflammatory cells Sustained Inflammatory response Contraction of airway smooth muscles (Bronchoconstriction)

Pathophysiology (Cont.) Airway wall swelling (mucosal edema) Airway hyper responsiveness Chronic changes Hypertrophy of the smooth muscles, thickening of the basement membrane Airway remodeling There is good evidence that asthma occurs in families.

What are the Triggering Factors? Domestic dust mites Air pollution Tobacco smoke Occupational irritants Cockroach Animal with fur Pollen

Triggering Factors ( cont.) Respiratory (viral) infections Chemical irritants Strong emotional expressions Drugs ( aspirin, beta blockers)

CASE SCENARIO Ahmed 6 years old come to primary care clinic with his father c/o chronic cough for the last 3 months, mainly at night . How you will approach this patient?

HOW TO DIAGNOSE BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ? Consultation skill Relevant History -Symptom -history of allergic disease -Family history -Environmental history -Exclusion of other medical condition

Diagnosis of B.A ( cont.) Relevant physical examination Investigation Do you need to do investigation? Why ? Follow up Medical record Role of Peak Flow Meter

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 1. Upper airway obstruction – glottic dysfunction. 2. Acute LV failure – pulmonary oedema. 3. Pulmonary embolism. 4. Endobronchial disease. 5. Chronic bronchitis. 6. Eosinophilic pneumonia. 7. Carsinoid syndrome. 8. Vasculitis.

CLASSIFY ASTHMA SEVERITY Mild intermittent Asthma (step1) Mild persistent Asthma (step2) Moderate persistent Asthma (step3) Severe persistent Asthma (step4)

How to manage and control Bronchial Asthma Educate patients to develop a partnership in asthma care Assess and monitor asthma severity Avoid exposure to trigger factors Establish individual medication plans for long term management in children and adults

How to manage and control Bronchial Asthma ( cont.) Establish individual plans to manage asthma attacks Provide regular follow up care.

Stepwise approach

MANAGEMENT 3 Acute severe asthma: 1. Immediate Rx: O2 40-60% via mask or cannula + β2 agonist (salbutamol 5mg) via nebulizer + Prednisone tab 30-60mg and/or hydrocortisone 200mg IV. With lifethreatening features add 0.5mg ipratropium to nebulized β2 agonist + Aminophyllin 250mg IV over 20 min or salbutamol 250ug over 10 min. 2. Subsequent Rx: Nebulized β2 agonist 6 hourly + Prednisone 30-60mg daily or hydrocortisone 200mg 6 hourly IV + 40-60% O2.

QUESTIONS ????

THANK YOU WITH MY BEST REGARDS







bronchial_asthma.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

