British Parliamentary Format.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20

British Parliamentary Format By Christopher Aden

British Parliamentary Format (BPF) Official format of WUDC Origin – British House of Commons Most widely spread around the world 4 teams (2 speakers in each) competing for ranks Similar to legislative process as opposed to APF (judicial)
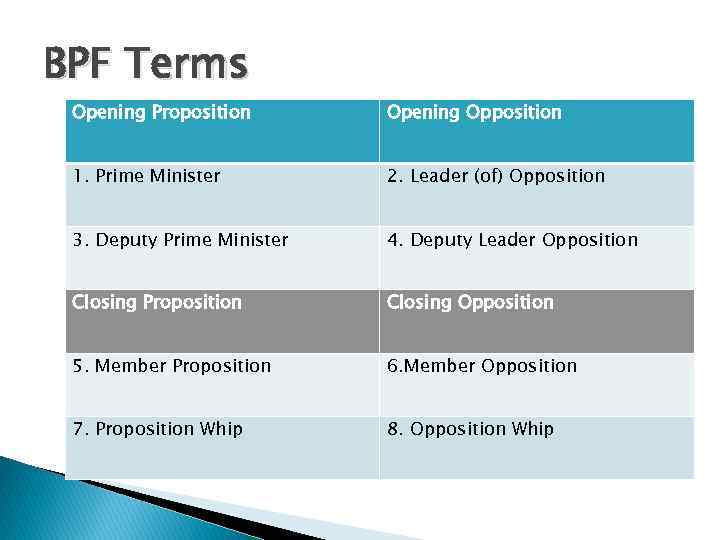
BPF Terms Opening Proposition Opening Opposition 1. Prime Minister 2. Leader (of) Opposition 3. Deputy Prime Minister 4. Deputy Leader Opposition Closing Proposition Closing Opposition 5. Member Proposition 6. Member Opposition 7. Proposition Whip 8. Opposition Whip

BPF Regulations Each speaker 7 minutes. Points of Information (POIs) - allowed (but for the first and last minutes) POIs≈ 15 seconds POIs – may be protests Topic/Resolution = MOTION! Important that each speaker bring smth new in the round

PM’s Speech Special burden: laying out the Case allowing feasible participation of other teams

PM’s Speech Framing (≈1, 5 min): Justified/debatable “Better debate” standard (inclusive of potential opponents’ arguments) Concrete/clear proposal by Proposition Faithful to the motion Informing about future anew arguments from DPM (split strategy)

PM’s Speech Constructive Argumentation(≈4, 5 - 6 min) Usually 3 -4 arguments Arguments may be independent or logically progressive

Leader of Opposition’s Speech Framing: Challenge or accept PM’s interpretation? ◦ PM’s definition not sacrosanct, ◦ but challenging is tricky ◦ Painful for other teams Most important not to deviate

Leader of Opposition’s Speech Deconstructive Argumentation (2 -3 min) ◦ Main task Constructive Argumentation (3 -4 min) ◦ Makes Opposition side more advantageous. ◦ 2 -4 points of independent/logically progressive reasons

Deputy Speeches Framing Focusing on material issues Prioritizing issues ◦ Comparing & contrasting issues in play ◦ Putting forward one’s favorable arguments

Deputy Speeches Deconstructive Argumentation Constructive argumentation ◦ Sustaining team’s position ◦ Reconstruction ◦ Move debate forward ◦ Plant adjudicators in their team’s territory
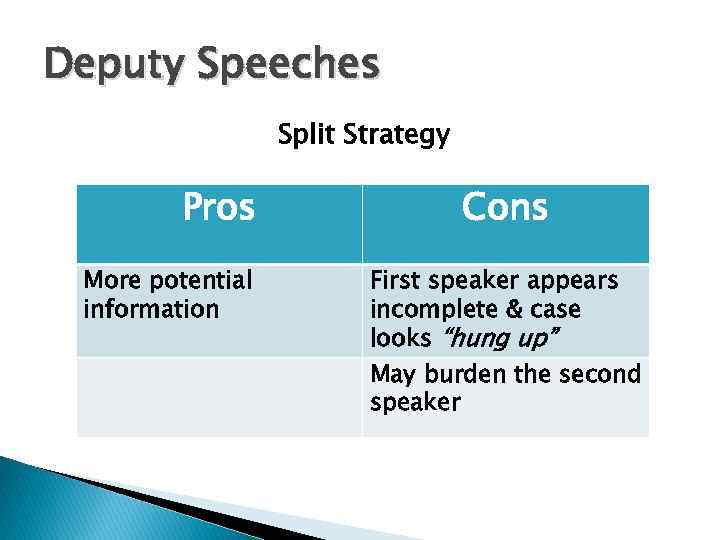
Deputy Speeches Split Strategy Pros More potential information Cons First speaker appears incomplete & case looks “hung up” May burden the second speaker

Member Speeches Establishment of unique argumentative identity = “Extension” At times, deconstruction and a summary of first two benches

Member Speeches Extension: Coopertition (cooperation & competition) with their opening team Extension should be singular in focus And particular, unique and simple

Member Speeches Extension a unified theme New line of argumentation Greater depth and analysis of any other previous arguments Grounding abstract arguments in tangible support But not entirely new debate!!!

Member Speeches Framing Deconstructive Argumentation Constructive Argumentation

Whip Speeches Summary of the round ◦ Speaker-by-speaker ◦ Team-by-team ◦ Summarizing of all arguments Also Constructive and Deconstructive Argumentation ◦ No new arguments ◦ Reconstruction only

Whip Speeches Summaries may be inclusive of Constructive and Deconstructive Argumentation simultaneously Evaluation and outlining of critical issues in the debate Highlight relation of arguments to opposing arguments and relation of issues to the proposition

Whip Speeches Organization of a Whip Speech: 1. 2. 3. What is required to determine the truth of the motion? How does the other side fail to meet this requirement? How do our efforts meet this requirement?

Taboos Things not to be done during the round: a) “knifing” – abandoning opening teams b) “burnt turf” – situation in which opening team covered “all” possible arguments and/or ideas/points c) “”squirrelling” - misinterpretation or unjustified interpretation of the motion.
British Parliamentary Format.pptx