Литература Англии.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14

British Literature
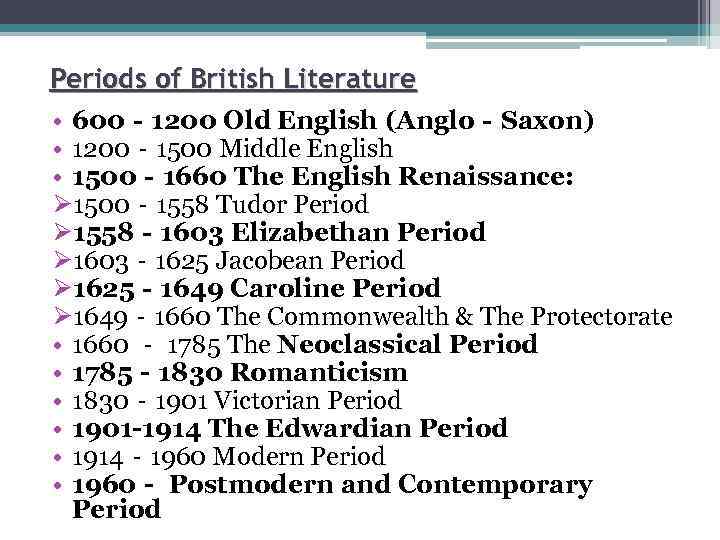
Periods of British Literature • 600‐ 1200 Old English (Anglo‐Saxon) • 1200‐ 1500 Middle English • 1500‐ 1660 The English Renaissance: Ø 1500‐ 1558 Tudor Period Ø 1558‐ 1603 Elizabethan Period Ø 1603‐ 1625 Jacobean Period Ø 1625‐ 1649 Caroline Period Ø 1649‐ 1660 The Commonwealth & The Protectorate • 1660 ‐ 1785 The Neoclassical Period • 1785‐ 1830 Romanticism • 1830‐ 1901 Victorian Period • 1901 -1914 The Edwardian Period • 1914‐ 1960 Modern Period • 1960‐ Postmodern and Contemporary Period
600‐ 1200 Old English (Anglo‐Saxon) • Beowulf

1200‐ 1500 Middle English • Geoffrey Chaucer ( 1343 – 1400), known as the Father of English literature, is widely considered the greatest English poet of the Middle Ages and was the first poet to have been buried in Poet's Corner of Westminster Abbey • The Canterbury Tales, which is a collection of stories told by fictional pilgrims on the road to the cathedral at Canterbury; these tales would help to shape English literature. • the anonymous Sir Gawain and the Green Knight is a late 14 th-century Middle English alliterative romance. It is one of the betterknown Arthurian stories, of an established type known as the "beheading game" • Thomas Malory (1405 – 14 March 1471) was an English writer, the author or compiler of Le Morte d'Arthur. The legend of King Arthur and the knights of the Round Table is the most powerful and enduring in the western world. King Arthur, Guinevere, and Sir Lancelot did not really exist, but their names conjure up a romantic image of gallant knights in shining armour, elegant ladies in medieval castles, heroic quests for the Holy Grail in a world of honour and romance, and the court of Camelot at the centre of a royal and mystical Britain.

1500‐ 1660 The English Renaissance 1500‐ 1558 Tudor Period • Sir Thomas More (/ˈmɔr/; 1478 – 1535), known to Catholics as Saint Thomas More since 1935, was an English lawyer, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist • Utopia (completed and published in 1516) is a novel in Latin. In it a traveller, Raphael Hythlodeaus (in Greek, his name and surname allude to archangel Raphael, purveyor of truth, and mean "speaker of nonsense"), describes the political arrangements of the imaginary island country of Utopia. Sir Thomas Wyatt (1503 – 1542) was a 16 thcentury English ambassador and lyrical poet. Wyatt was one of the earliest poets of the Renaissance. He was responsible for many innovations in English poetry. He, along with Henry Howard, Earl of Surrey, introduced the sonnet from Italy into England. His lyrics show great tenderness of feeling and purity of diction. He is one of the originators of the convention in love poetry according to which the mistress is painted as hard-hearted and cruel.
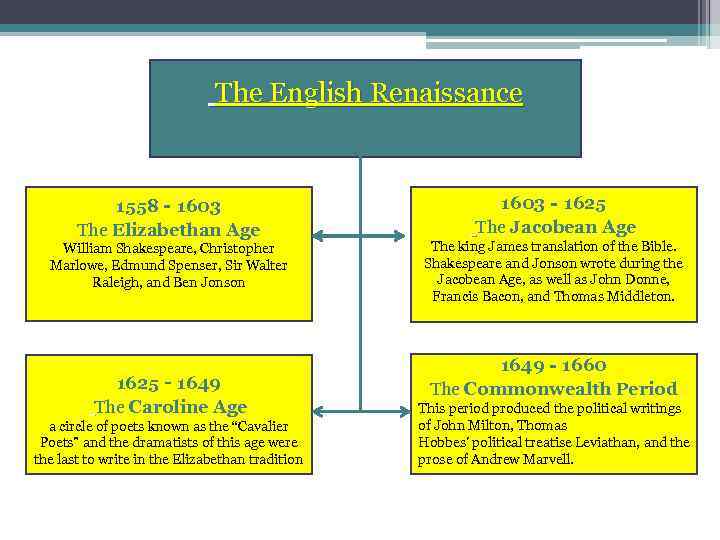
The English Renaissance 1558‐ 1603 The Elizabethan Age William Shakespeare, Christopher Marlowe, Edmund Spenser, Sir Walter Raleigh, and Ben Jonson 1625‐ 1649 The Caroline Age a circle of poets known as the “Cavalier Poets” and the dramatists of this age were the last to write in the Elizabethan tradition 1603‐ 1625 The Jacobean Age The king James translation of the Bible. Shakespeare and Jonson wrote during the Jacobean Age, as well as John Donne, Francis Bacon, and Thomas Middleton. 1649‐ 1660 The Commonwealth Period This period produced the political writings of John Milton, Thomas Hobbes’ political treatise Leviathan, and the prose of Andrew Marvell.

The Neoclassical Period can be divided into three subsets: üthe Restoration üthe Augustan Age üthe Age of Sensibility.

1660‐ 1700 The Restoration • John Milton 1608 – 1674) was an ( English poet. Milton's poetry and prose reflect deep personal convictions, a passion for freedom and self-determination • Paradise Lost (1667) The poem concerns the Biblical story of the Fall of Man: the temptation of Adam and Eve by the fallen angel Satan and their expulsion from the Garden of Eden. Milton's purpose, stated in Book I, is to "justify the ways of God to men". Paradise Lost is often considered one of the greatest literary works in the English language • Paradise Regained (1671)It is connected by name to his earlier and more famous epic poem Paradise Lost, with which it shares similar theological themes. It deals with the subject of the temptation of Christ.

The Augustan Age 1700‐ 1745 • Jonathan Swift (1667 – 1745) was an Anglo -Irish satirist, essayist, political pamphleteer • Gulliver's Travels (1726) Part I: A Voyage to Lilliput Part II: A Voyage to Brobdingnag Part III: A Voyage to Laputa, Balnibarbi, Luggnagg, Glubbdubdrib, and Japan Part IV: A Voyage to the Country of the Houyhnhnms • Alexander Pope (1688 – 1744) was an 18 th-century English poet, best known for his satirical verse • Daniel Defoe (1659– 1661 - 1731) was an English trader, writer, journalist, pamphleteer and spy • Robinson Crusoe (1719) tells of a man's shipwreck on a deserted island his subsequent adventures

The Age of Sensibility • Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 1784), often referred to as Dr Johnson, was an English author who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer • After nine years of work, Johnson's A Dictionary of the English Language was published in 1755; it had a farreaching effect on Modern English and has been described as "one of the greatest single achievements of scholarship. " This work brought Johnson popularity and success. • Johnson's dictionary was not the first, nor was it unique. It was, however, the most commonly used and imitated for the 150 years between its first publication and the completion of the Oxford English Dictionary in 1928

1785‐ 1830 The Romantic Period • William Wordsworth (1770 – 1850) was a major English Romantic poet • The Prelude (1850) • Jane Austen (1775 – 1817) was an English novelist whose works of romantic fiction, set among the landed gentry, earned her a place as one of the most widely read writers in English literature. • Sense and Sensibility (1811) • Pride and Prejudice (1813) and Emma (1816) • Lord Byron (1788 – 1824) was a British poet and a leading figure in the Romantic movement • Don Juan and Childe Harold's Pilgrimage He is regarded as one of the greatest British poets and remains widely read and influential

The Victorian Period 1830‐ 1901 • Charles Dickens ( 1812 – 1870) was an English writer and social critic who is generally regarded as the greatest novelist of the Victorian period and the creator of some of the world's most memorable fictional characters. • The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club (Monthly serial, April 1836 to November 1837) • The Adventures of Oliver Twist (Monthly serial in Bentley's Miscellany, February 1837 to April 1839) • Charlotte Brontë ( /ˈbrɒnti/1816 – 1855) was an English novelist and poet, the eldest of the three Brontë sisters who survived into adulthood, whose novels are English literature standards • Jane Eyre (1847) It tells the story of a plain governess (Jane) who, after early life difficulties, falls in love with her employer, Mr Rochester. They eventually marry, but only after Rochester's mad first wife (whom Jane initially had no knowledge of) dies in a dramatic house fire. • George Eliot Mary Anne Evans (1819 – 1880), better known by her pen name George Eliot, was an English novelist, journalist and translator, and one of the leading writers of the Victorian era. She is the author of seven novels, including Adam Bede (1859), The Mill on the Floss (1860) and Daniel Deronda (1876), most of them set in provincial England known for their realism and psychological insight.

1901‐ 1914 The Edwardian Period • George Bernard Shaw • H. G. Wells • Rudyard Kipling
Литература Англии.pptx