5e08621808d5742ea9863494d2b1994b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Bright. Water® – A Step Change in Sweep Improvement - What is it? - What isn’t it? - Where did it come from? -Where can it go?
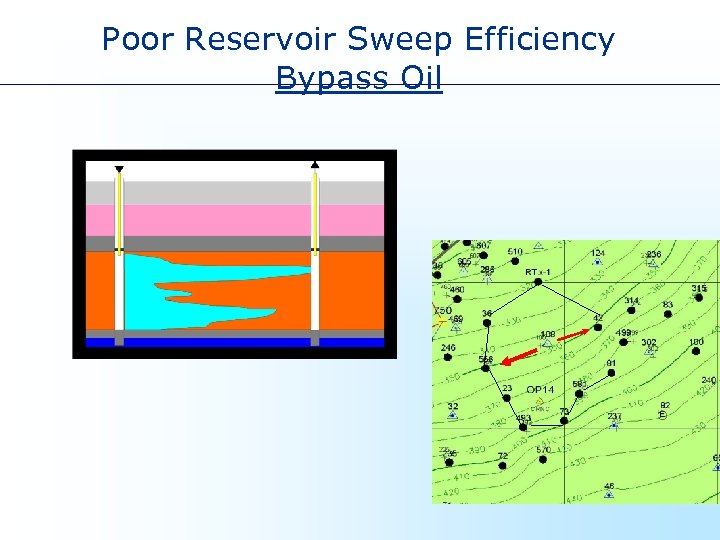
Poor Reservoir Sweep Efficiency Bypass Oil
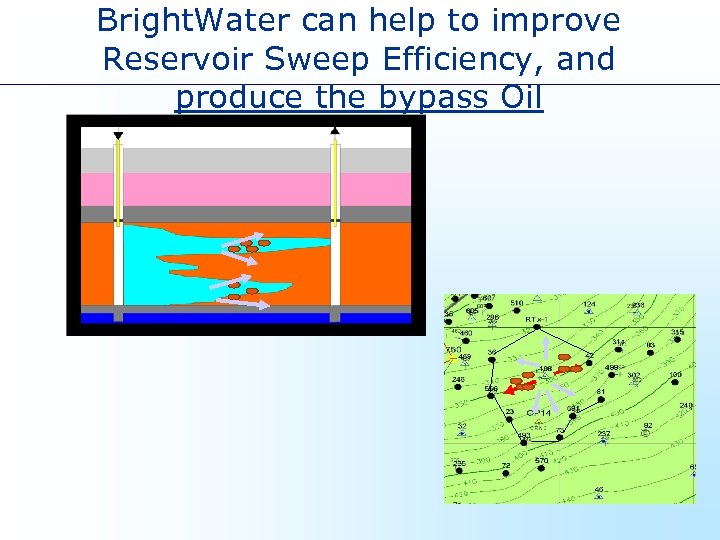
Bright. Water can help to improve Reservoir Sweep Efficiency, and produce the bypass Oil

Outline • • What is Bright. Water? How does Bright. Water improve waterflood? Any field success? How to use in mature fields? • Candidate selection • Tests • Implementation. • Conclusions

What is Bright. Water® • Bright. Water is a technology that improve the sweep efficiency of water flood by using a Novel robust particulate system for in–depth waterflood conformance control • Designed to overcome injectivity and cost limitations of classical polymer treatments. (i. e. , injected as small particles then can become larger with time in the presence of a “trigger” - temperature)

Bright. Water® History Contributor Involvement Bright. Water®, as a BP project, started in 1997 It was considered as a speculative, but high-reward project, and was proposed as a Joint Venture project to the “Mo. BPTe. Ch” consortium which has now disbanded. Nalco was identified as best potential development/supply partner, and joined as equal contributors. 1997 1998 Now: BP Mobil, BP, Texaco, Chevron BP, Chevron, Nalco + Nalco

Bright. Water® – what it’s not • Bright. Water material is NOT a classic viscous polymer • During injection it has viscosity very close to water • It cannot be damaged by shear during injection • It is not active initially • Totally different from conventional gel jobs. • No CAPEX – Simple to deploy
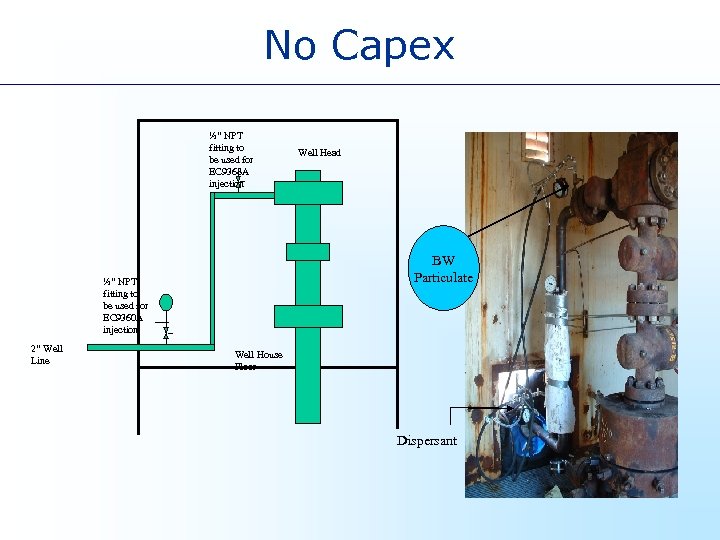
No Capex ½” NPT fitting to be used for EC 9368 A injection BW Particulate ½” NPT fitting to be used for EC 9360 A injection 2” Well Line Well Head Well House Floor Dispersant

What is Bright. Water® • Bright. Water is particles • The median of the particle size distribution is about 0. 3 to 0. 5 microns • Bright. Water particle is supplied as a dispersion in hydrocarbon solvent • The active content in the dispersion is about 30%
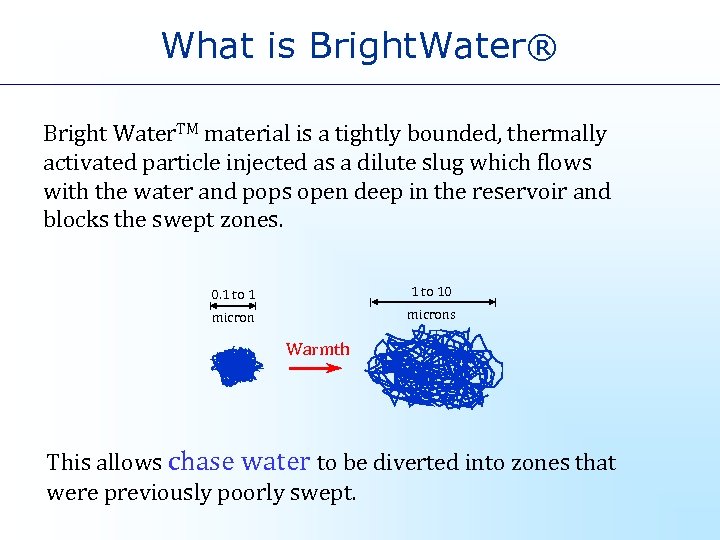
What is Bright. Water® Bright Water. TM material is a tightly bounded, thermally activated particle injected as a dilute slug which flows with the water and pops open deep in the reservoir and blocks the swept zones. 0. 1 to 10 microns Warmth This allows chase water to be diverted into zones that were previously poorly swept.

Inert Bright. Water Material

Bright. Water Particles Pre-activated – Activated This magnification is 10 x greater than this one Before Expansion After Expansion Scale bar is 500 nanometers Scale bar is 5000 nanometers A polymer particle which is able to propagate through rock pores without injectivity loss Under the influence of heat the particle expands to a size which can block rock pore throats.
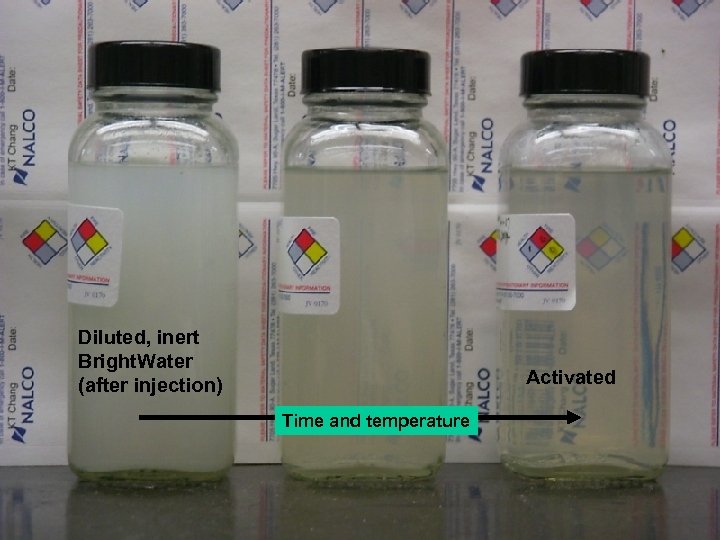

Diluted, inert Bright. Water (after injection) Activated Time and temperature
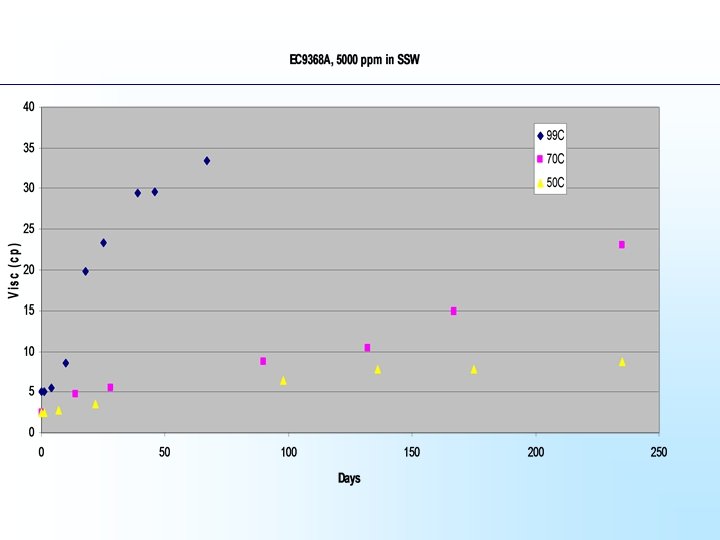
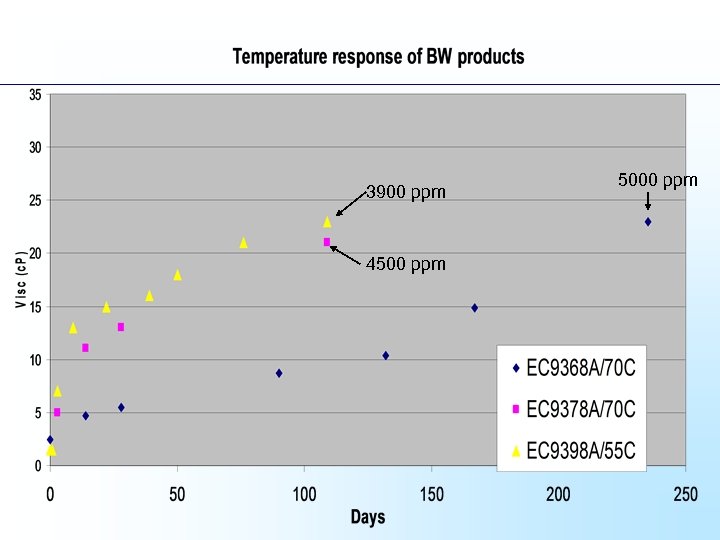
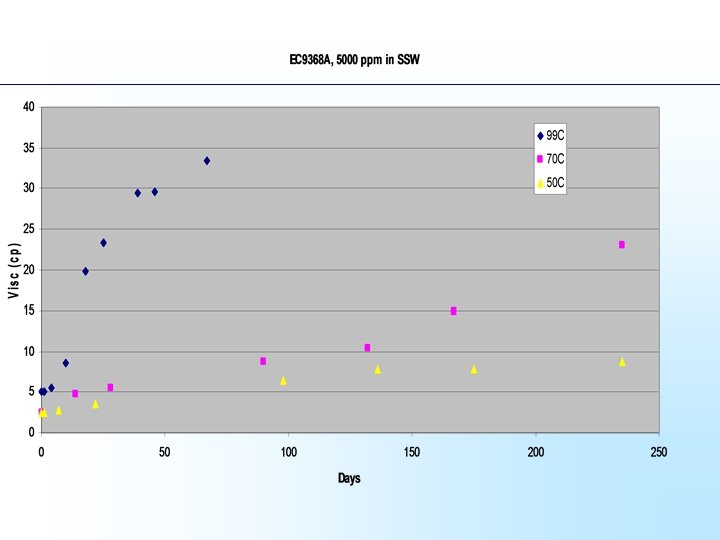
3900 ppm 4500 ppm 5000 ppm

What is Bright. Water® • The injected sub-micron particles are inert - they give virtually no viscosity or adsorption - they are far smaller than the pores they move through • The expanded particles are “sticky” - they have increased solution viscosity, showing they now interact with each other - they act to restrict water flow rate in the reservoir - the restriction can be permanent showing they are interacting with the porous rock
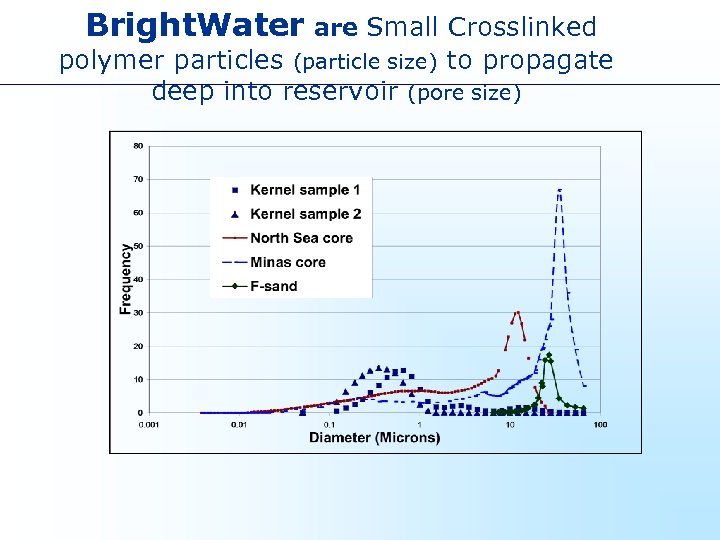
Bright. Water are Small Crosslinked polymer particles (particle size) to propagate deep into reservoir (pore size)

What is Bright. Water® • The time before activation can be selected • The strength of the block can be selected • A complete block is not usually the aim or necessary

So how does Bright. Water work in the reservoir?
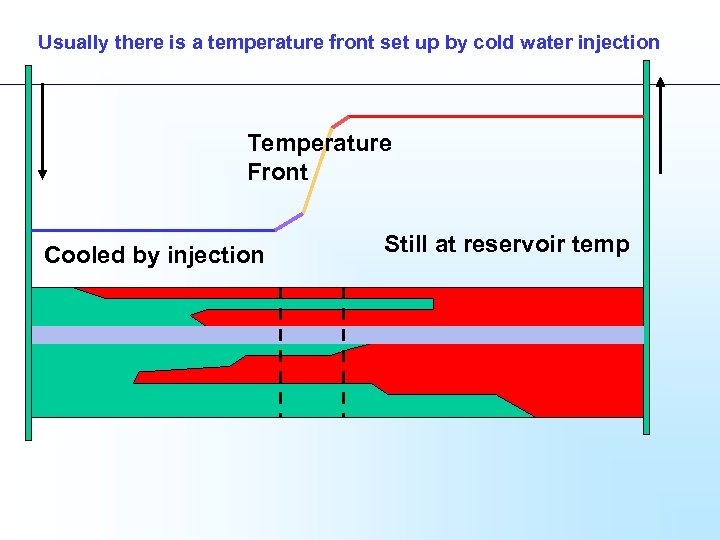
Usually there is a temperature front set up by cold water injection Temperature Front Cooled by injection Still at reservoir temp
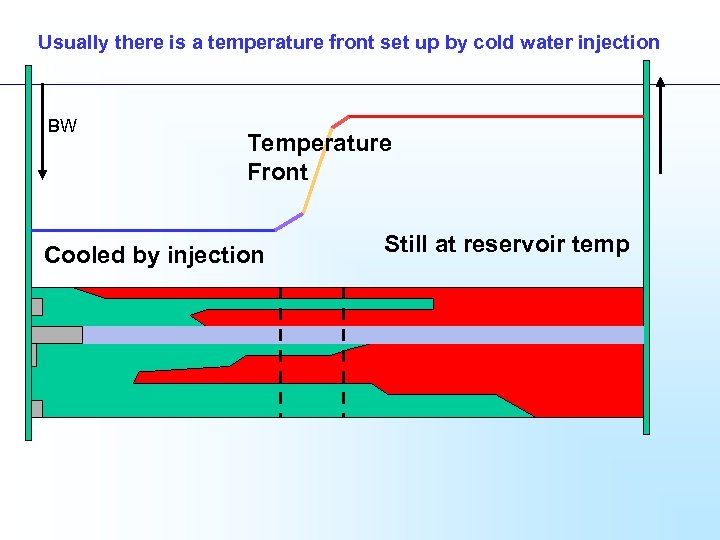
Usually there is a temperature front set up by cold water injection BW Temperature Front Cooled by injection Still at reservoir temp
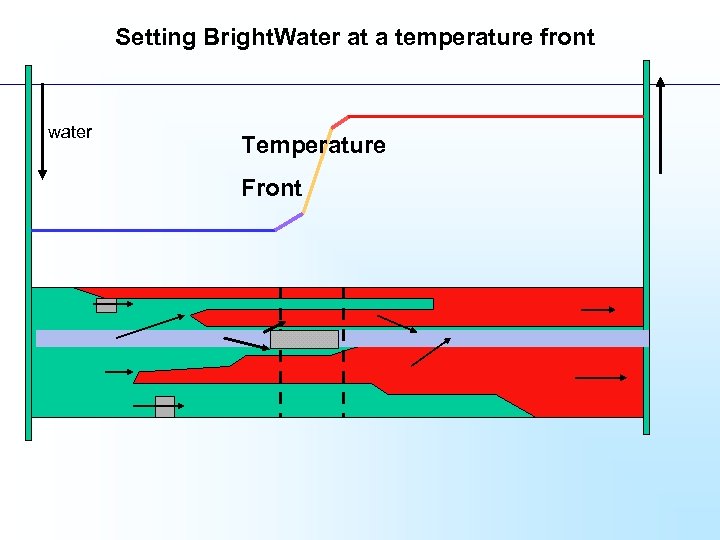
Setting Bright. Water at a temperature front water Temperature Front

• Setting at a temperature front can be very convenient and is the ideal and usual mode for hot reservoirs • But we may not need a temperature front • We can select the grade to control the setting time, and set at any temperature up to 80 -90 C
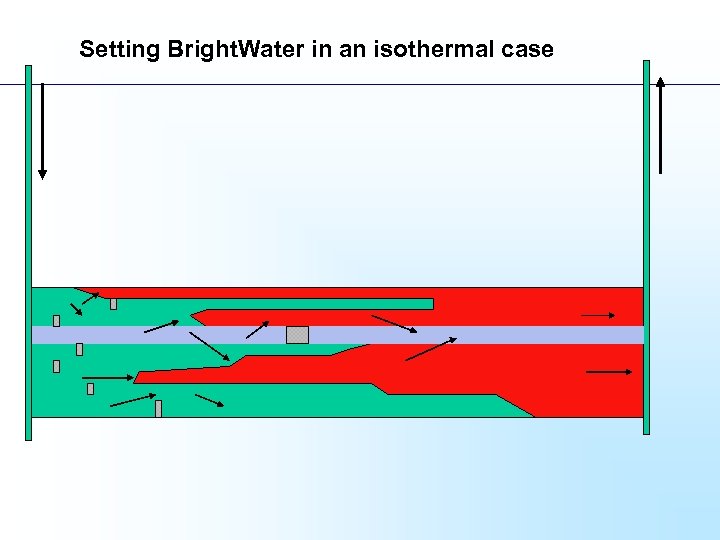
Setting Bright. Water in an isothermal case

Typical treatment objectives: • Vertical conformance improvement by diverting water from a thief layer • Vertical and horizontal sweep improvement by diverting water from a channel • Slow down water cycling - allow use of increased injection pressure - allow use of increased drawdown at producers

Bright. Water List of Field Trials • Minas, Indonesia (Chevron, 2001) • Arbroath, North Sea, UK (BP, 2002) • Milne Point and Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, USA (BP) (several, 2004 -5) • • • Strathspey field, North Sea, UK (Chevron, 2006) Argentina (several, 2006) Pakistan (BP, 2006 -7) Alaska (several, 2007) Being considered: more treatments in Indonesia Australia, Alaska and Gulf of Mexico, USA
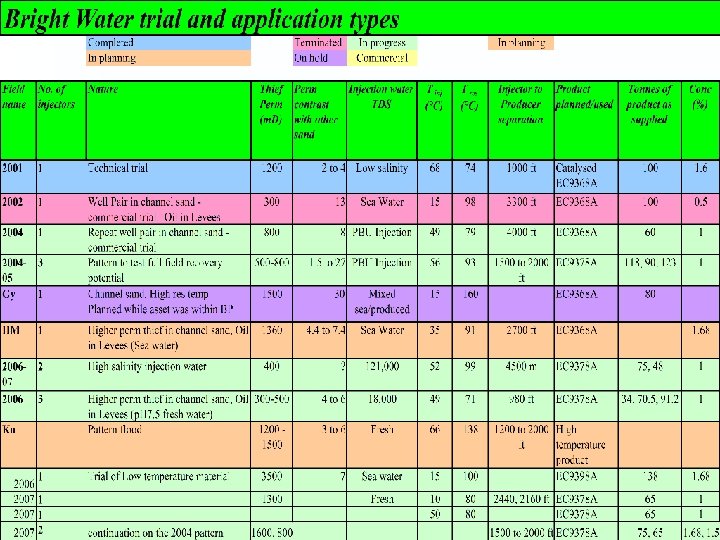
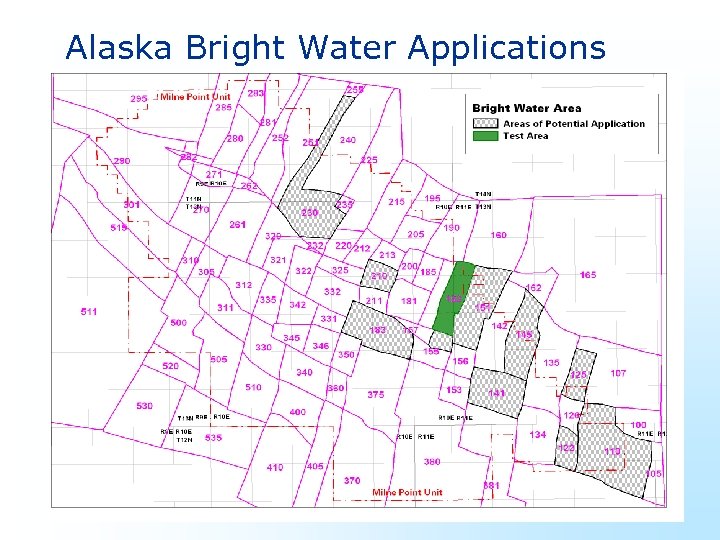
Alaska Bright Water Applications
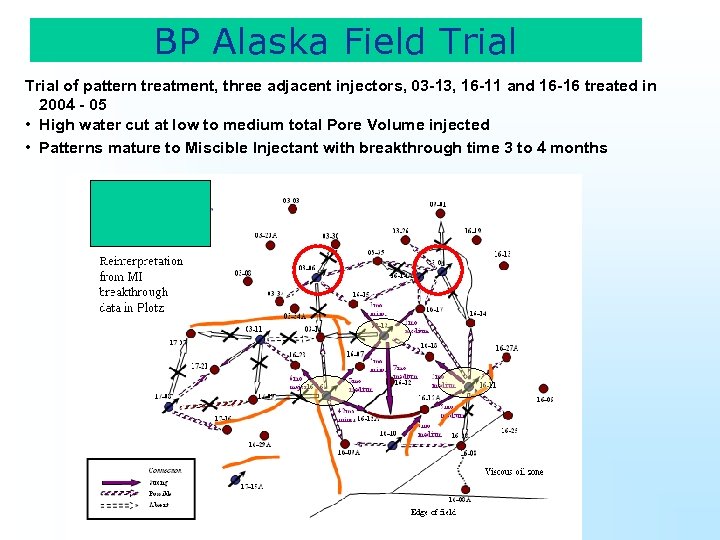
BP Alaska Field Trial of pattern treatment, three adjacent injectors, 03 -13, 16 -11 and 16 -16 treated in 2004 - 05 • High water cut at low to medium total Pore Volume injected • Patterns mature to Miscible Injectant with breakthrough time 3 to 4 months
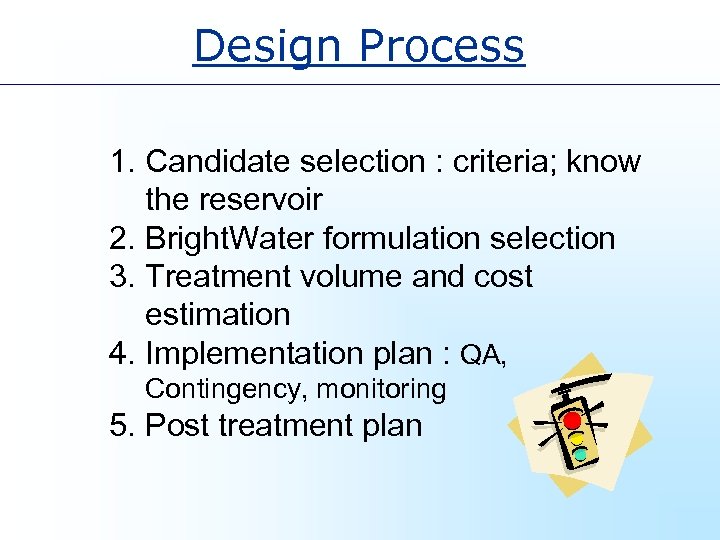
Design Process 1. Candidate selection : criteria; know the reservoir 2. Bright. Water formulation selection 3. Treatment volume and cost estimation 4. Implementation plan : QA, Contingency, monitoring 5. Post treatment plan
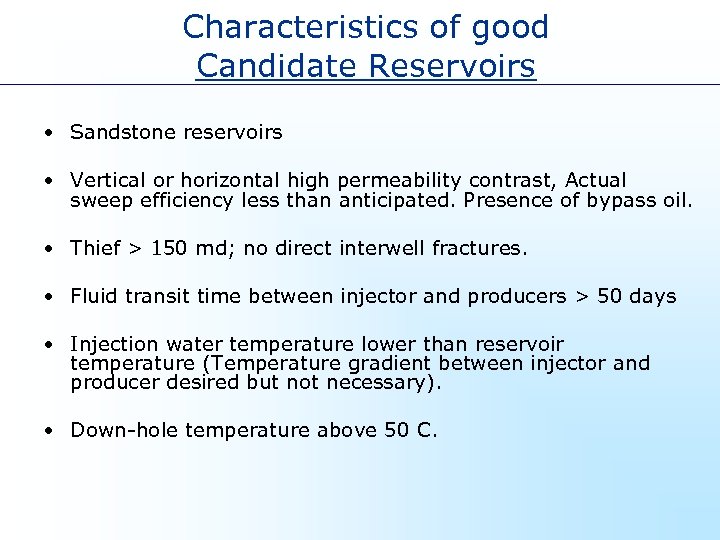
Characteristics of good Candidate Reservoirs • Sandstone reservoirs • Vertical or horizontal high permeability contrast, Actual sweep efficiency less than anticipated. Presence of bypass oil. • Thief > 150 md; no direct interwell fractures. • Fluid transit time between injector and producers > 50 days • Injection water temperature lower than reservoir temperature (Temperature gradient between injector and producer desired but not necessary). • Down-hole temperature above 50 C.
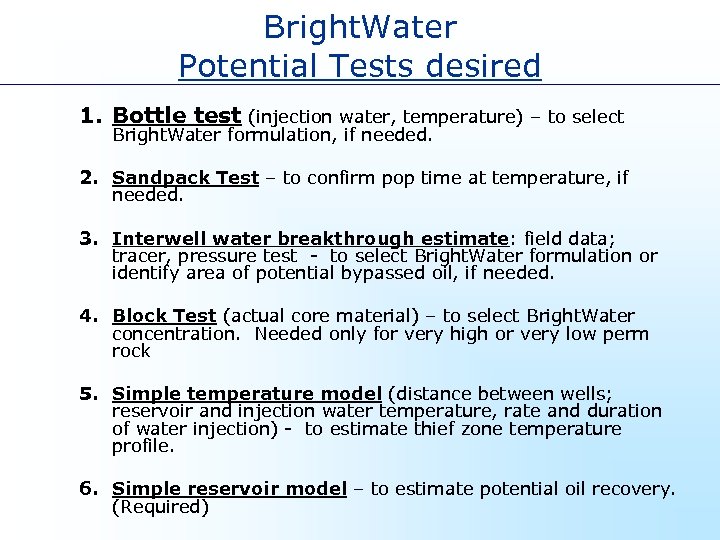
Bright. Water Potential Tests desired 1. Bottle test (injection water, temperature) – to select Bright. Water formulation, if needed. 2. Sandpack Test – to confirm pop time at temperature, if needed. 3. Interwell water breakthrough estimate: field data; tracer, pressure test - to select Bright. Water formulation or identify area of potential bypassed oil, if needed. 4. Block Test (actual core material) – to select Bright. Water concentration. Needed only for very high or very low perm rock 5. Simple temperature model (distance between wells; reservoir and injection water temperature, rate and duration of water injection) - to estimate thief zone temperature profile. 6. Simple reservoir model – to estimate potential oil recovery. (Required)
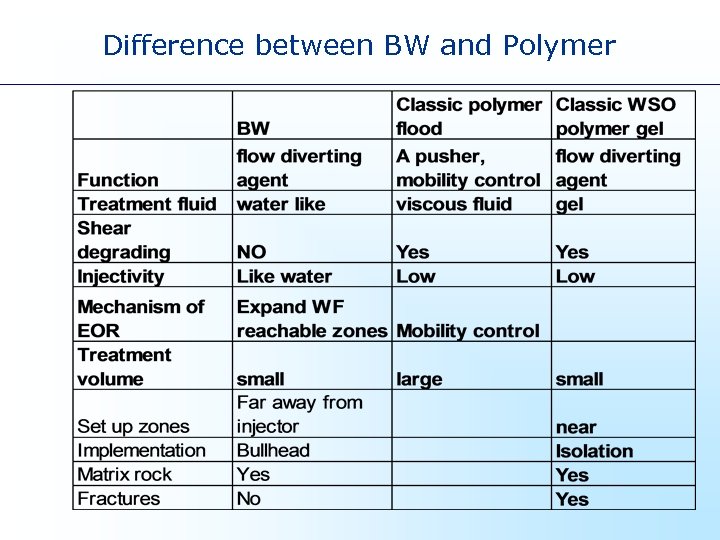
Difference between BW and Polymer

Conclusions • Bright. Water is a new robust pre-crosslinked polymer particle that can expand in size at design temperature and time. • There are successful field implementations (onshore and offshore) • Increase oil production and recovery. • Bullhead into injection line easily, even from a great distance or into subsea completion. • No facilities upset.

The Early stage Research team members BP Nalco Energy Services K. T. Chang Dennis Williams Harry Frampton Jim Morgan Chevron. Texaco Steve Cheung Rick Ng Billy Surles Les Munson

Thank you ! Questions?
5e08621808d5742ea9863494d2b1994b.ppt