e4790a397ae6a0de6381befb212eb57a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

BRI Workshop, 2005. 10. 12 DEVELOPMENT OF TECHNICAL COOPERATION NETWORK FOR SEISMIC SAFETY OF HOUSES IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Dr. Taiki SAITO tsaito@kenken. go. jp Chief Researcher, IISEE Building Research Institute Tsukuba, Japan

INTERNATIONAL TRAINING PROGRAM ON SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING History 1960~ 1962~ 1963~ 1972~ 2005~ Training project started. IISEE was established in BRI. Joint project with UNESCO The project was continued by JAPAN. Master Degree for regular course participants. Training Courses Regular Course Field Seismology, Earthquake Engineering And Disaster Mitigation Global Seismological Observation Course Global Seismological Observation Individual Course Seismology Earthquake Engineering Period 12 months Arbitrary Max. Members 20 10 5
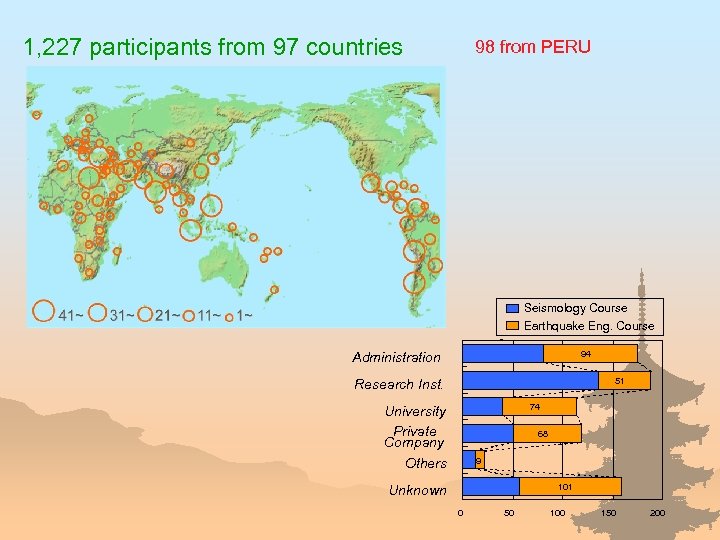
1, 227 participants from 97 countries 98 from PERU Seismology Course Earthquake Eng. Course 94 Administration 51 Research Inst. 74 University Private Company 68 9 Others 101 Unknown 0 50 100 150 200

Background Severe earthquake damage in developing countries Weak social and economical bases Lack of technical information for earthquake disaster mitigation In order to disseminate technical information Training for seismologists and earthquake engineers Transfer of technical information Algeria Earthquake 5/21, 2003, BBC News
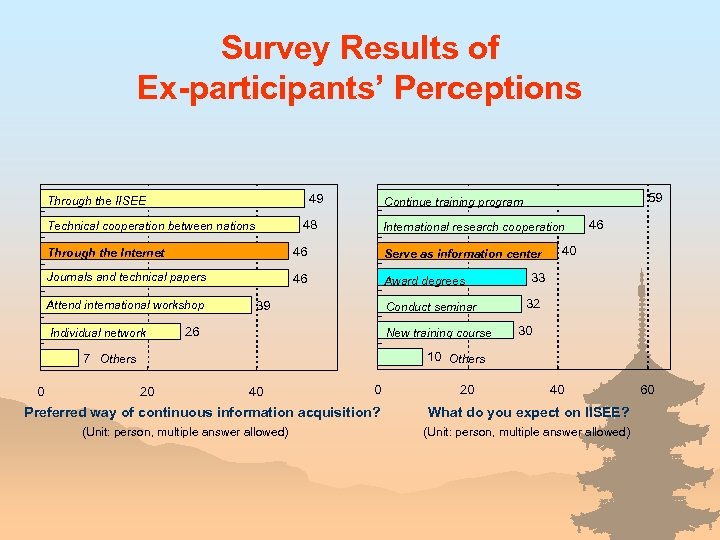
Survey Results of Ex-participants’ Perceptions 49 Through the IISEE 48 Technical cooperation between nations 59 Continue training program International research cooperation Through the Internet 46 Serve as information center Journals and technical papers 46 Award degrees Attend international workshop Individual network 39 Conduct seminar 26 New training course 40 33 32 30 10 Others 7 Others 0 46 20 40 0 Preferred way of continuous information acquisition? (Unit: person, multiple answer allowed) 20 40 What do you expect on IISEE? (Unit: person, multiple answer allowed) 60

IISEE-net http: //iisee. kenken. go. jp/net/index. htm | Internet-based system designed to disseminate a variety of technical information regarding seismology and earthquake engineering. | Free Web site to find technical information about seismic networks, the strong motion observatory network, seismic damage archives, seismic design codes, and microzonation data of developing countries. | Technical information on IISEE-net was obtained mainly through the International Training Program on Seismology and Earthquake Engineering and its ex-participants. | IISEE-net works not only as a system to disseminate technical information, but also as an forum for interactive information exchange among research institutes and researchers in developing countries.
IISEE-net
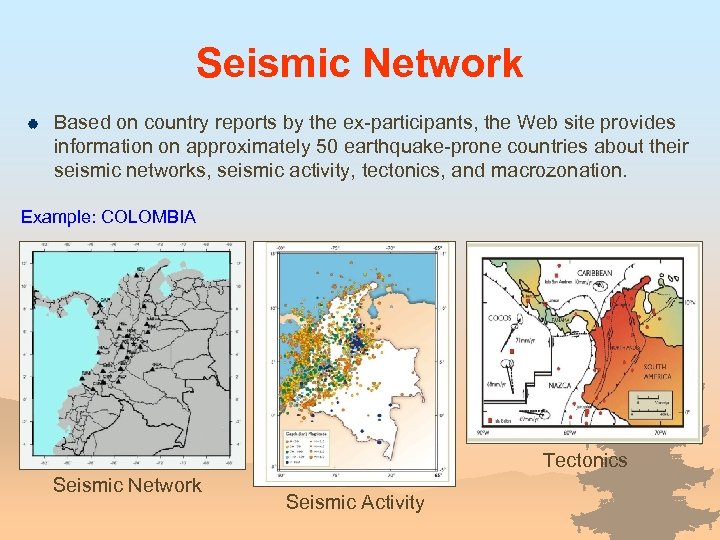
Seismic Network | Based on country reports by the ex-participants, the Web site provides information on approximately 50 earthquake-prone countries about their seismic networks, seismic activity, tectonics, and macrozonation. Example: COLOMBIA Tectonics Seismic Network Seismic Activity
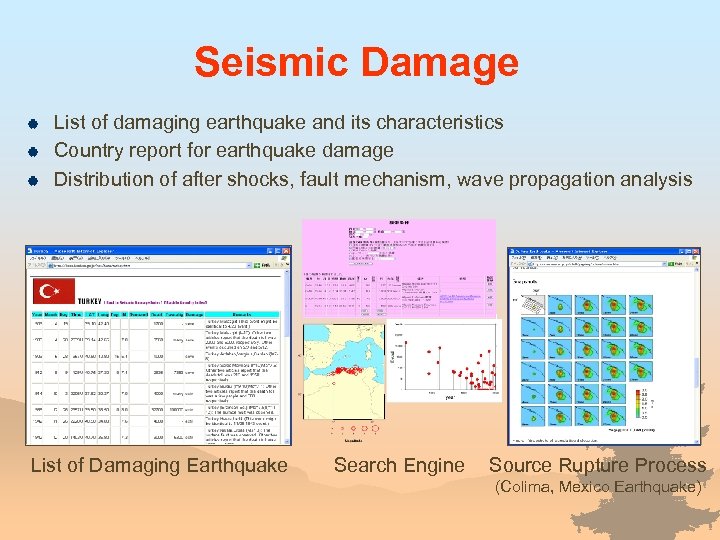
Seismic Damage | | | List of damaging earthquake and its characteristics Country report for earthquake damage Distribution of after shocks, fault mechanism, wave propagation analysis List of Damaging Earthquake Search Engine Source Rupture Process (Colima, Mexico Earthquake)

Seismic Design Code | | | Seismic design codes of approximately 45 developing countries. A summary of the Japanese Building Standard Law European code and ISO information. Example: MEXICO Seismic Design Force Design Spectrum Zone Factor
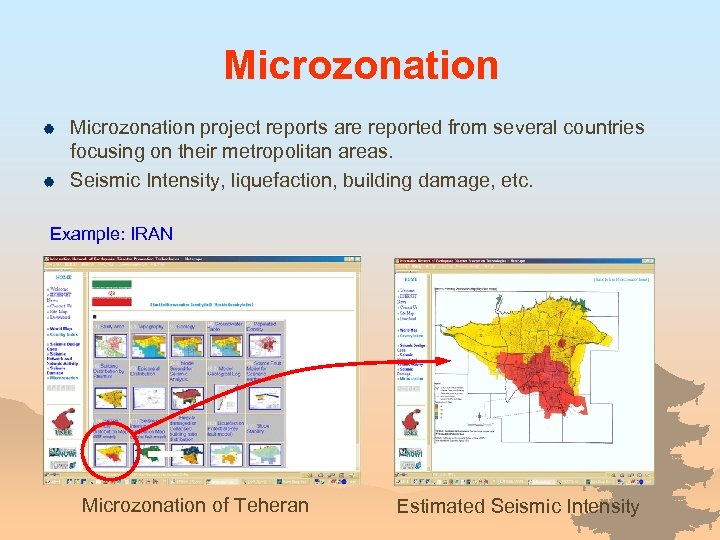
Microzonation | | Microzonation project reports are reported from several countries focusing on their metropolitan areas. Seismic Intensity, liquefaction, building damage, etc. Example: IRAN Microzonation of Teheran Estimated Seismic Intensity
IISEE-net http: //iisee. kenken. go. jp/net/index. htm
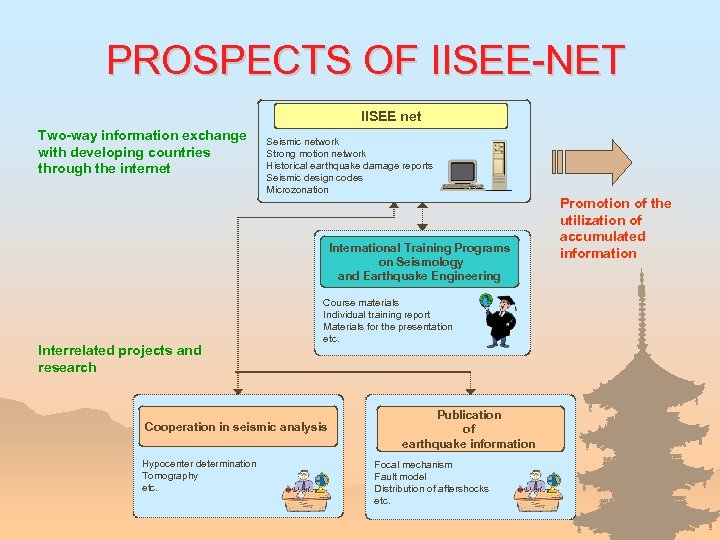
PROSPECTS OF IISEE-NET IISEE net Two-way information exchange with developing countries through the internet Seismic network Strong motion network Historical earthquake damage reports Seismic design codes Microzonation International Training Programs on Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Interrelated projects and research Course materials Individual training report Materials for the presentation etc. Cooperation in seismic analysis Hypocenter determination Tomography etc. Publication of earthquake information Focal mechanism Fault model Distribution of aftershocks etc. Promotion of the utilization of accumulated information
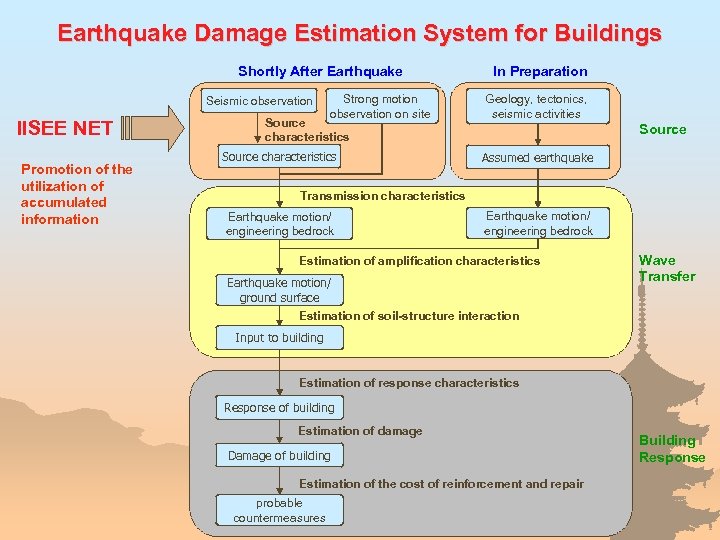
Earthquake Damage Estimation System for Buildings Shortly After Earthquake Seismic observation IISEE NET Promotion of the utilization of accumulated information Strong motion observation on site Source characteristics In Preparation Geology, tectonics, seismic activities Source Assumed earthquake Transmission characteristics Earthquake motion/ engineering bedrock Estimation of amplification characteristics Earthquake motion/ ground surface Wave Transfer Estimation of soil-structure interaction Input to building Estimation of response characteristics Response of building Estimation of damage Damage of building Estimation of the cost of reinforcement and repair probable countermeasures Building Response
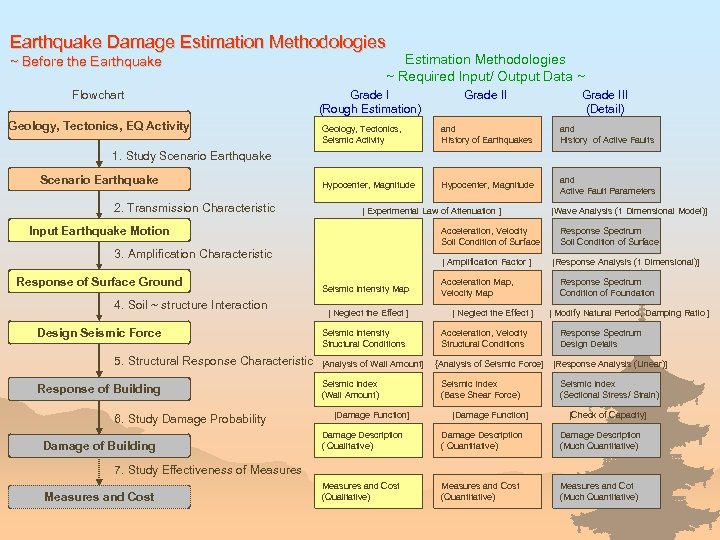
Earthquake Damage Estimation Methodologies ~ Required Input/ Output Data ~ ~ Before the Earthquake Flowchart Geology, Tectonics, EQ Activity Grade I (Rough Estimation) Grade III (Detail) Geology, Tectonics, Seismic Activity and HIstory of Earthquakes and History of Active Faults Hypocenter, Magnitude and Active Fault Parameters 1. Study Scenario Earthquake 2. Transmission Characteristic [ Experimental Law of Attenuation ] Input Earthquake Motion Acceleration, Velocity Soil Condition of Surface 3. Amplification Characteristic Response of Surface Ground 4. Soil ~ structure Interaction Design Seismic Force 5. Structural Response Characteristic Response of Building 6. Study Damage Probability Damage of Building [ Amplification Factor ] Seismic Intensity Map [ Neglect the Effect ] Seismic Intensity Structural Conditions [Analysis of Wall Amount] Seismic Index (Wall Amount) [Damage Function] Acceleration Map, Velocity Map [ Neglect the Effect ] Acceleration, Velocity Structural Conditions {Analysis of Seismic Force] Seismic Index (Base Shear Force) [Damage Function] [Wave Analysis (1 Dimensional Model)] Response Spectrum Soil Condition of Surface [Response Analysis (1 Dimensional)] Response Spectrum Condition of Foundation [ Modify Natural Period, Damping Ratio ] Response Spectrum Design Details [Response Analysis (Linear)] Seismic Index (Sectional Stress/ Strain) [Check of Capacity] Damage Description ( Qualitative) Damage Description ( Quantitative) Damage Description (Much Quantitative) Measures and Cost (Qualitative) Measures and Cost (Quantitative) Measures and Cot (Much Quantitative) 7. Study Effectiveness of Measures and Cost
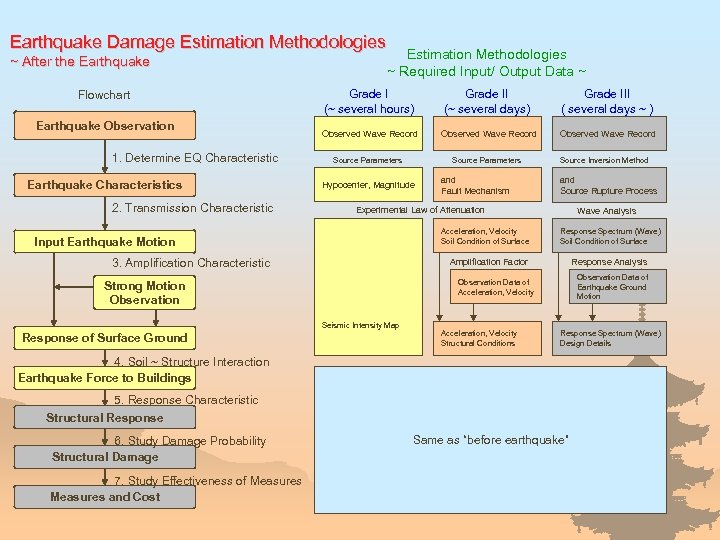
Earthquake Damage Estimation Methodologies ~ After the Earthquake Flowchart Earthquake Observation 1. Determine EQ Characteristic Earthquake Characteristics 2. Transmission Characteristic Estimation Methodologies ~ Required Input/ Output Data ~ Grade I (~ several hours) Grade II (~ several days) Grade III ( several days ~ ) Observed Wave Record Source Parameters Hypocenter, Magnitude and Source Rupture Process Experimental Law of Attenuation Acceleration, Velocity Soil Condition of Surface Input Earthquake Motion 3. Amplification Characteristic Wave Analysis Response Spectrum (Wave) Soil Condition of Surface Amplification Factor Response Analysis Observation Data of Earthquake Ground Motion Observation Data of Acceleration, Velocity Strong Motion Observation Seismic Intensity Map Response of Surface Ground and Fault Mechanism Source Inversion Method Acceleration, Velocity Structural Conditions Response Spectrum (Wave) Design Details 4. Soil ~ Structure Interaction Earthquake Force to Buildings 5. Response Characteristic Structural Response 6. Study Damage Probability Structural Damage 7. Study Effectiveness of Measures and Cost Same as “before earthquake”
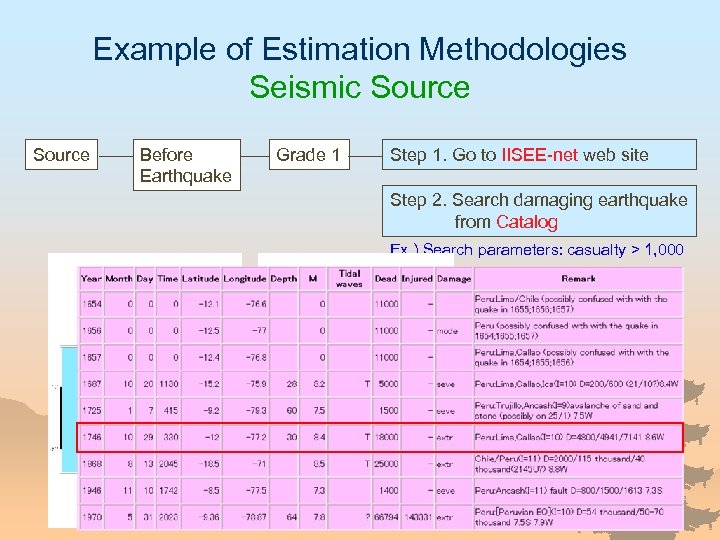
Example of Estimation Methodologies Seismic Source Before Earthquake Grade 1 Step 1. Go to IISEE-net web site Step 2. Search damaging earthquake from Catalog Ex. ) Search parameters: casualty > 1, 000
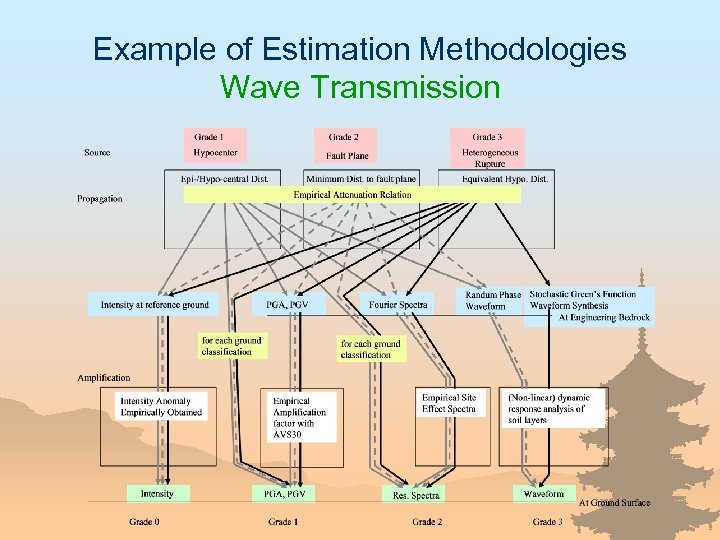
Example of Estimation Methodologies Wave Transmission
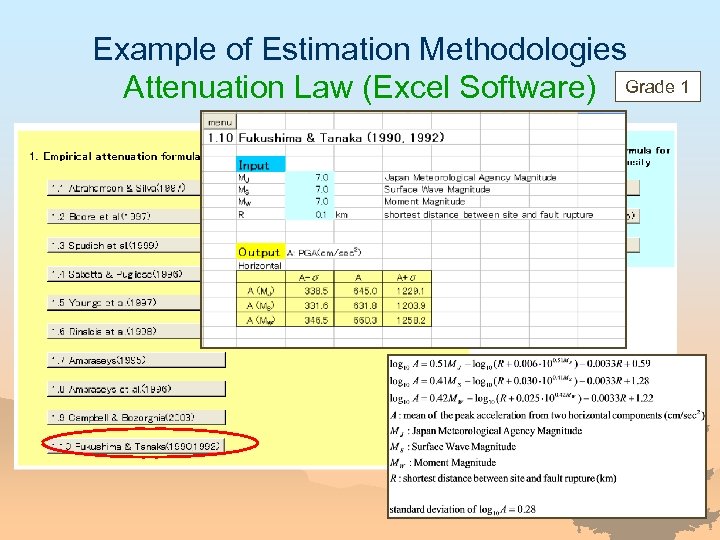
Example of Estimation Methodologies Attenuation Law (Excel Software) Grade 1
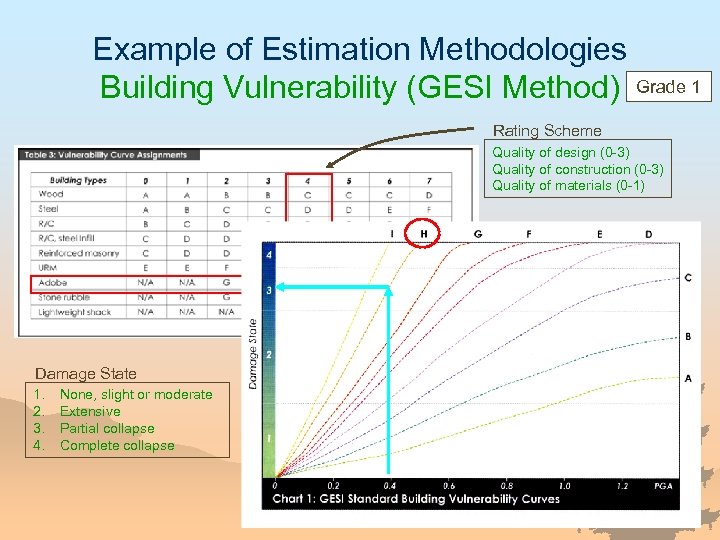
Example of Estimation Methodologies Building Vulnerability (GESI Method) Grade 1 Rating Scheme Quality of design (0 -3) Quality of construction (0 -3) Quality of materials (0 -1) Damage State 1. 2. 3. 4. None, slight or moderate Extensive Partial collapse Complete collapse
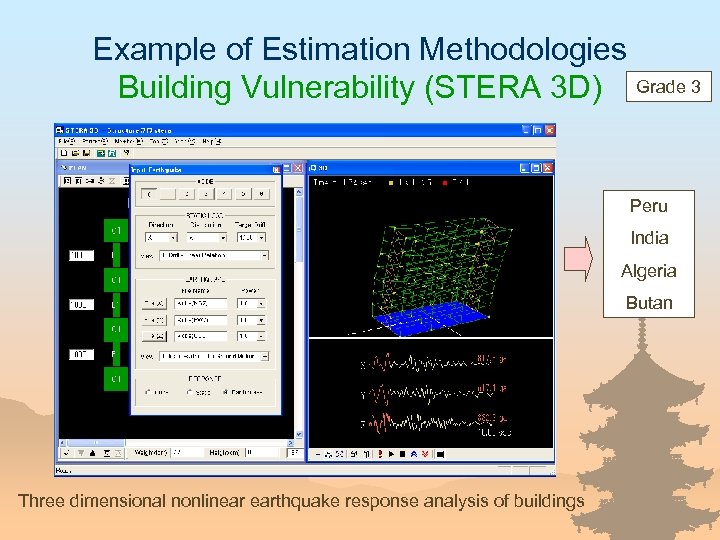
Example of Estimation Methodologies Building Vulnerability (STERA 3 D) Grade 3 Peru India Algeria Butan Three dimensional nonlinear earthquake response analysis of buildings
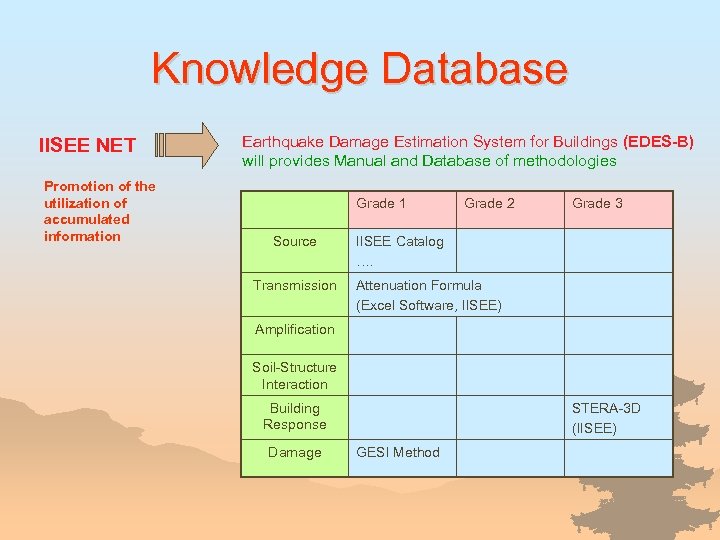
Knowledge Database IISEE NET Promotion of the utilization of accumulated information Earthquake Damage Estimation System for Buildings (EDES-B) will provides Manual and Database of methodologies Grade 1 Source Transmission Grade 2 Grade 3 IISEE Catalog …. Attenuation Formula (Excel Software, IISEE) Amplification Soil-Structure Interaction Building Response Damage STERA-3 D (IISEE) GESI Method
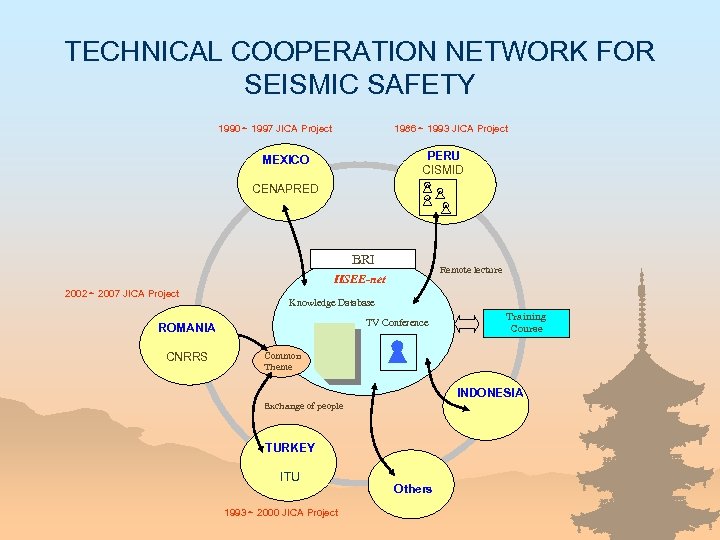
TECHNICAL COOPERATION NETWORK FOR SEISMIC SAFETY 1990~ 1997 JICA Project 1986~ 1993 JICA Project PERU CISMID MEXICO CENAPRED BRI Remote lecture IISEE-net 2002~ 2007 JICA Project Knowledge Database TV Conference ROMANIA CNRRS Training Course Common Theme INDONESIA Exchange of people TURKEY ITU 1993~ 2000 JICA Project Others
e4790a397ae6a0de6381befb212eb57a.ppt