0276bc54125ae143d9f8cd384a2dceb6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Breakout Session 2(II): Development Summary W. Rance Cleaveland II, Ph. D CEO, Reactive Systems Inc. -and. Dept. of Comp. Sci. , SUNY at Stony Brook November 17, 2004 Planning Meeting for HCMDSS Workshop
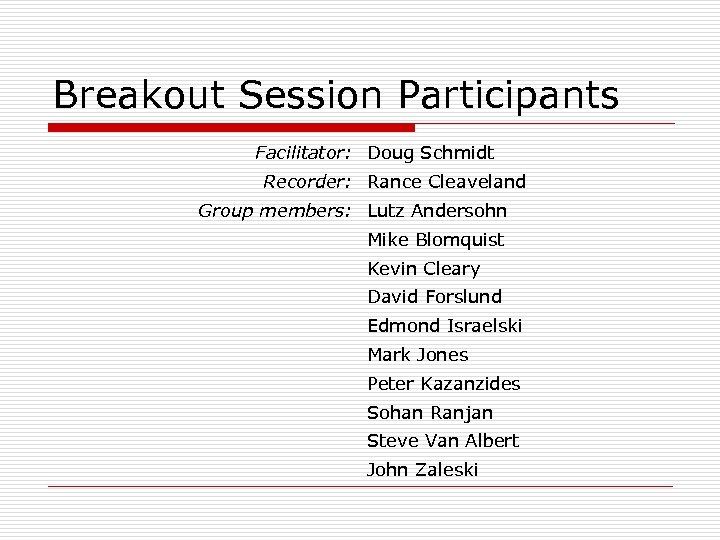
Breakout Session Participants Facilitator: Doug Schmidt Recorder: Rance Cleaveland Group members: Lutz Andersohn Mike Blomquist Kevin Cleary David Forslund Edmond Israelski Mark Jones Peter Kazanzides Sohan Ranjan Steve Van Albert John Zaleski

Session Remit “We ask this breakout to discuss current practice and improvements in available technologies and approaches needed for high-confidence system and software development. What are the challenges in developing highly reliable software for medical devices and systems, yet achieving reasonable time-to-market and profitability? For the spring meeting, what questions should we be asking, and who should be participating in the discussion? For example: How might end products of development steps need to include information for certification or V&V that can enable this? How solid is the current technology base upon which medical devices and systems are built (e. g. , real-time operating systems and networking technologies)? What are the security issues? Are reusable IT technologies (e. g. , middleware, frameworks) in use? Is system code generated from mathematical control design frameworks such as Mat. Lab and Simulink? How do critical decision support and highly-automated systems become trusted? ”

Challenges and Opportunities o o o Validation / testing costs Certification costs Distribution and data sharing Design technology Automated process support Open source

Existing Solutions o o o V&V costs: use-cases, manual testing Certification: certification-centered processes, attention to certification issues up-front Distribution: Syngo, reference architectures Design technology: simulation (for GUIs), user-centered design, rapid iteration Automated process support: Rational Open source: Linux, ACE/TAO
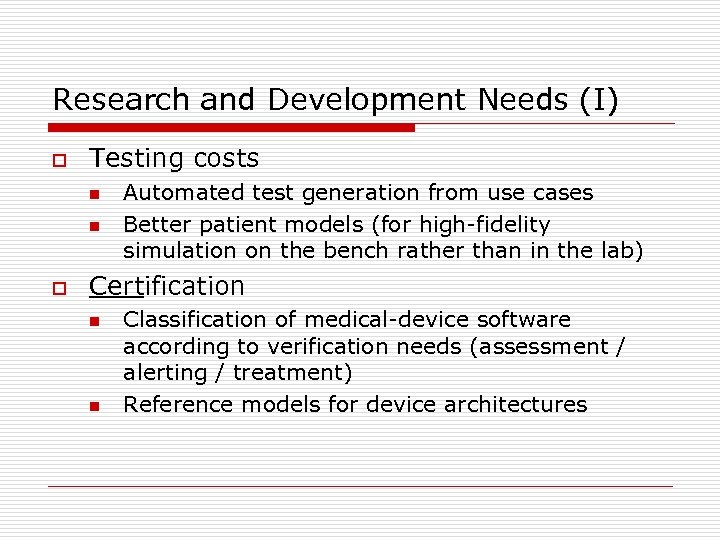
Research and Development Needs (I) o Testing costs n n o Automated test generation from use cases Better patient models (for high-fidelity simulation on the bench rather than in the lab) Certification n n Classification of medical-device software according to verification needs (assessment / alerting / treatment) Reference models for device architectures

Research and Development Needs (II) o Distribution and data sharing n n n o Network Qo. S Patient / device authentication protocols Network trouble-shooting tools Secure data sharing for remote devices Side-effect reasoning Design technology n n n Techniques for mathematical analysis of specification completeness, consistency High-fidelity simulation support Standardized modeling languages (cf. VHDL for hardware design)

Research and Development Needs (III) o Automated process support n n n o Knowledge bases (remembering what we used to know, “software paperclip”) Cost estimation models for requirements changes Reference standard processes Open source n n n Open-source modeling tools Role of open-source tools in software development Third-party certification for FDA compliance

Logistics To Meet Needs o o o Consortia for standards Tech-transfer vehicles for software technology Funding!

Roadmap o o o Processes vis a vis tools (both important) Standards issues addressable by govt. , industrial consortia “Co-operate on platforms, compete on devices”

Recommendations for Full Workshop o Invite representation from n Professional organizations INCOSE, IEEE, Advi. Med, AAMI, OMG n Tool vendors IBM, National Instruments, Math. Works n Other device makers (implantable, etc. ) Medtronic, Guidant, GE n Other industries Auto, aero, telecom o o Experience reports on n Current practices in device software n Certification Overview of FDA certification processes (maybe from FDA compliance side? )
0276bc54125ae143d9f8cd384a2dceb6.ppt