baeba9479f755fd218fd310009d6762d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Branches of Government Legislative, Executive and Judicial

Article 1 Graphic Organizer n When you finish the quiz, begin working independently on the graphic organizer. n Refer to Ch. 10 -11, as well as the text of the US Constitution (pg. 760)


Congress n n n Lawmaking body National government Bicameral legislature = 2 houses q q Senate (upper house) House of Representatives (lower house) 115 th Congress- 1 st session (2017 -2018)

Congress: Important facts n n n Meet for terms = 2 years Divide terms into 2 one-year sessions Term begins January 3 of odd numbered years Meet from January until November/December Recesses for holidays and vacations Members must vote to adjourn or take a break
No Warm-up Get out your graphic organizer about the Legislative Branch from yesterday.

Lawmaking Game

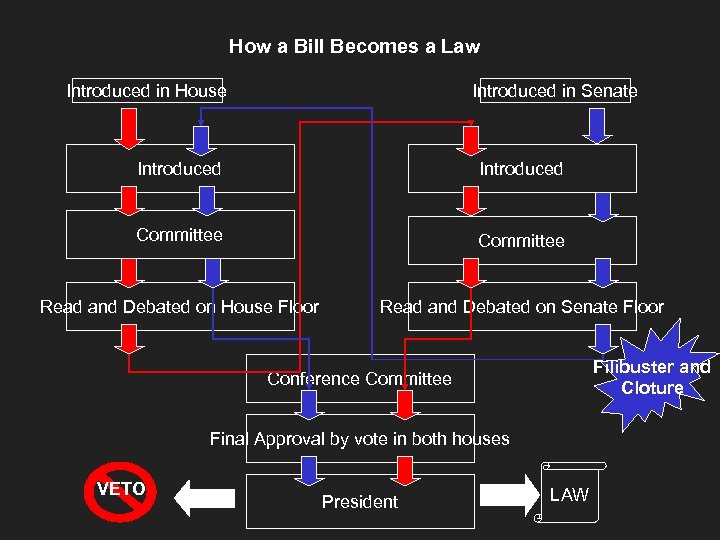
How a Bill Becomes a Law Introduced in House Introduced in Senate Introduced Committee Read and Debated on House Floor Read and Debated on Senate Floor Filibuster and Cloture Conference Committee Final Approval by vote in both houses VETO President LAW

In your groups, each person proposes a bill. Round 1: Introduction and Committee - Read the proposal and roll three dice to see if it gets out of committee (need a roll of 12+ to pass). - If it does not pass the first time, change at least one word of the bill and roll again, reducing the # needed by 2 to 10+. - Repeat up to 5 times until the bill passes. If you don’t succeed after 5 attempts, the bill fails and voting ends.

Vote on the Bill in Congress Round 2: Full vote in one house of Congress - Roll two dice to see if it passes (need a roll of 6+ to pass). - If it does not pass, go back to the committee, change a word/phrase, and roll again using the same # needed as when it passed the committee. - Repeat up to 5 times until the bill passes. If you don’t succeed after 5 attempts, the bill fails and voting ends.

Send the bill to the other house Round 3: House-Senate Conference Committee and vote - Roll one dice to see if it passes the other house (need a roll of 4+ for it to pass) - If it does not pass, go back to the first house and roll again using the same # needed as when it passed the committee. - Repeat up to 5 times until the bill passes. If you don’t succeed after 5 attempts, the bill fails and voting ends.

Send the bill to the President Round 4: Send the bill to the President to sign or veto - Roll one dice to see if the President signs the bill (need a roll of 3+ for him/her to sign it) - If it does not pass, roll three dice twice (one for each house of Congress) to see if they can override the veto by a 2/3 rds majority. Each house needs to roll a 12+ to pass it now.

Members of Congress n Average = white male; fifties n Major duties: q q Pass laws Represent what is best for their constituents Oversee the workings of the federal government Help constituents solve problems with the federal government

Senate: Qualifications n 30 years old Citizen for at least 9 years Live in the state from which he/she is elected n Term of Office: 6 years n Salary: $174, 000 n n

House of Representatives: Qualifications n 25 years old U. S. citizen for at least 7 years Live in the state from which he/she is from n Term of office: 2 years n Salary: $174, 000 n n

Members of Congress: Privileges and benefits n n Tax deduction (homes in their district and Washington, D. C. ) Members’ Representational Allowance (MRA) to support work in their district q q Average MRA $1, 268, 520/representative FY 2017 appropriations- $562. 6 million n Free postage for all official business franking privilege n Free printing of speeches and newsletters n Low-cost health and life insurance

Members of Congress: Duties n n Serve on committees Help constituents as they interact with the federal government

Duties of Each House of Representatives q q Propose revenue laws (tax laws) Elect president in the event of a tie Senate q q Confirm or reject presidential nominees Confirm or reject treaties with other nations

Representation n n Determined by The Great Compromise Senate = equal representation q n Two per state 100 total House of Representatives = population q q Use census to determine number of state representatives 435 total Reapportionment = seats are reassigned after census (taken every 10 years) n Based on gains or losses in state’s population

Redistricting n n n Occurs when a states gain or lose seats in the House of Representatives Must redraw districts Political party in power (state-level) will sometimes set up districts to help its members win elections q q Creates funny shaped districts gerrymandering

House of Representatives: Leadership n Speaker of the House member of majority party q q n n Most important and powerful member: presiding officer Chosen by a caucus (closed meeting) of the majority party and approved by the full House Maintain order Lead majority party Appoint members to committees Schedule bills for votes and send bills to committees Salary- $223, 500

House of Representatives: Leadership n Majority leader (2 nd most powerful) q q n Minority leader q q n Help the speaker Guide party’s agenda through the House Main spokesperson for his/her party in the House Salary $193, 400 Determine how their party will react to the majority party’s programs Salary $193, 400 Whips q q q Assistants to the party leaders Job is to make sure members vote as leadership desires Political position not official positions

Senate: Leadership n Vice president: presiding officer of Senate q n President pro tempore: presiding officer for daily sessions q q q n n Votes only in event of tie Usually senior member of majority party Elected by whole Senate Position lacks the power of the Speakers of the House Majority Leader- Salary $193, 400 Minority Leader- Salary $193, 400 Salary- $223, 500

House of Representatives: Committees n n n Most of the work is done in committees Committees = small groups of representatives Chairperson belongs to the majority party Majority of members in a committee will always be from the majority party Review and discuss bills

House of Representatives: Rules Committee n n n Powerful committee Only in the House Know as the “traffic cop” Must issue a rule = decision on how quickly or slowly a bill will be voted on Can keep a bill from reaching the House floor May limit how long the House has to debate a bill and the number of amendments can be added

Senate: Committees n n n Bills are introduced by any member Majority leader has power to decide what happens to the bill Less formal More flexible = allows senators more time to discuss, think about issues and repeat Debate may run weeks q n Unlimited debate = filibuster Senators may express their views on the issues before the entire Senate

Committees: Four types n Standing Committees permanent n n q n n Subcommittees = small working groups of members of the standing committees Select temporary; created for special purposes q n House of Representatives = 19 Senate = 18 Study one topic or issue (i. e. : Watergate scandal) Joint permanent or temporary; comprised of members from House and Senate (i. e. : Printing) Conference temporary; members from both houses

Creating Laws n n n n Bill is written and submitted Introduced by Senator or Representative Sent to committee for study: collect information, hold hearings, suggest changes Read and debated on the floor Proceeds through the other house of Congress Conference Committee resolves differences Final approval by a vote in both houses Sent to the President to be signed

How a Bill Becomes a Law Introduced in House Introduced in Senate Introduced Committee Read and Debated on House Floor Read and Debated on Senate Floor Filibuster and Cloture Conference Committee Final Approval by vote in both houses VETO President LAW

Create a Bill n In groups of two: Create a bill to be introduced in the House. The bill is going to address an issue in education. (ex. . standardized testing, school start times, college scholarships, vocational training, and curriculum) Include: q Title –catch the attention of representatives and introduce the bill q Sponsors’ names-authors of legislation q Purpose-explain the goals of the bill n n n Why should your bill become a law? How does it meet the needs of your constituents? Will it benefit every American citizen or the people of a single state? *Your bill will attempt to make its way through Congress. *

The President The Executive Branch

Executive Branch: The president n Qualifications q q q Native-born citizen of the United States 35 years old Lived in the U. S. for at least 14 years

President: Terms of office n n n Serve a term of 4 years May serve two terms (8 years) A vice president who becomes president and serves two years or less of the president’s term may be elected for two full terms. (22 nd amendment)

President: Salary and benefits $400, 000 salary n $100, 000 travel allowance n 50, 000 expense allowance n Free health care n Living rent-free in the White House n Retirement pension n

President: Privileges n n Use Air Force One Use of Camp David (presidential retreat)

Roles of the President n Chief Executive q q p. 174 Ensure that laws are carried out Issue executive orders, pardons or reprieves (postponement of a punishment) n Head of State q q n Living symbol of the nation; represents the U. S. to the world Ceremonial duties Chief Diplomat q q Represents the nation when dealing with other nations Directs foreign policy of the U. S. ; make treaties

Roles of the President n Commander in Chief q q n Legislative Leader q q n Propose legislation to help Americans Proposes annual budget Economic Leader q q n Leader of the military Use military force to support foreign policy goals Attempts to help the country’s economy prosper Proposes a federal budget Party Leader q q Head of his political party Make speeches to help fellow party members running for office

Powers of the President n n n Power to veto Make treaties Create Executive Agreements q n Informal document made with other nations Issue executive orders n n Grant pardons n n Excuses a person from being punished for a criminal offense Commute sentences n n Statement carrying the force of law Shorten the time someone must spend in prison for a crime Offer reprieves n Delay the implementation of a sentence…usually for new evidence

The State of the Union n n Report to Congress “from time to time” Outlines what he wants Congress to do in the coming year 1790 - 1 st State of the Union by President Washington

Vice President In this I am nothing, but I may become everything. -- John Adams n Qualifications: Same as President. n Constitution lists only two duties. President of the Senate. Becomes president if the president is unable to carry out presidential duties. n n n Live at the Naval Observatory

Presidential Succession n Order of who becomes president if the current president can’t serve Presidential Succession Act 1947 Twenty-fifth Amendment n 1967 1. Vice President Speaker of the House President pro tempore 2. 3. Presidential portrait of Harry Truman pushed through the Presidential Succession Act of 1947.

Removing a president n Must violate the Constitution n Impeachment q q q House impeaches (President, VP, or “civil officers of the US”) Doesn’t mean they are guilty or will be removed Trial takes place in the Senate 2/3 of Senate must vote to remove person from office Andrew Johnson and Bill Clinton- neither convicted

President’s Cabinet Blue = Exec. Departments Red = Inner Cabinet n n n Secretary of State Secretary of Treasury Secretary of Defense Attorney General (Justice Department) Secretary of the Interior Secretary of Agriculture Secretary of Commerce Secretary of Labor White House Chief of Staff Director, Office of Management and Budget Director, Environmental Protection Agency n n n n n Secretary of Health and Human Services Secretary of Transportation Secretary of Energy Secretary of Housing and Urban Development Secretary of Education Secretary of Veterans Affairs Secretary of Homeland Security United States Trade Representative Director, Office of National Drug Control Policy VP

Executive Departments n State q n Treasury q n FBI, ATF and DEA Homeland Security q q n Military Justice q n Secret Service, IRS (Internal Revenue Service) and taxes Defense q n Foreign countries and U. S. citizens abroad Newest department (2001) PATRIOT Act- allows government officials extended power to protect the U. S. against terrorism Health and Human Services q Distribute monies and handle issues dealing with welfare, Medicaid and Social Security

Judicial Branch n n Federal Courts Supreme Court
baeba9479f755fd218fd310009d6762d.ppt