5.Физиология ствола мозга.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Brain stem.
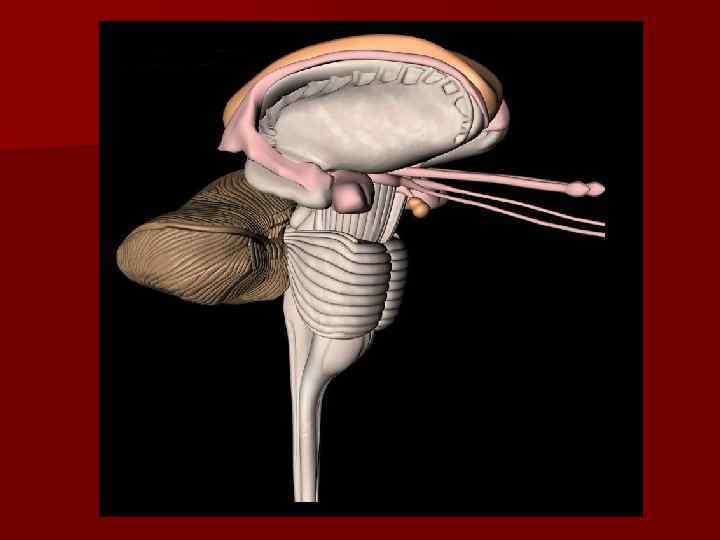
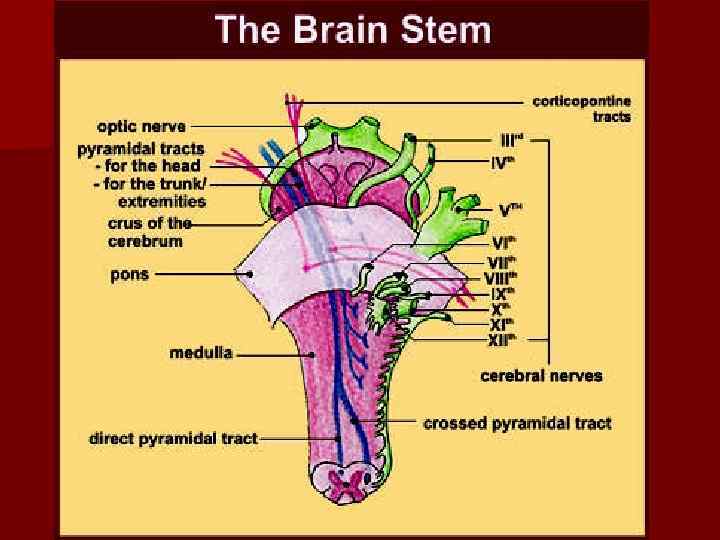

Hindbrain n 1. 2. Hindbrain is composed of two regions: Metencephalon Myelencephalon METENCEPHALON is composed of the pons and cerebellum. MYELENCEPHALON is composed of only one structure – the medulla oblongata or medulla.

Medulla oblongata About 3 cm long, the medulla is continuous with the pons superiorly and the spinal cord inferiorly. n All of the descending and ascending fiber tracts that provide communication between spinal cord and the brain pass through the medulla. Many of these tracts (for example, descending pyramidal and ascending fasciculus gracilis and f. cuneatus) cross to the contralateral side in elevated triangular structures called pyramids. Medulla relates by olives with spinal cord, cerebellum and extrapyramidal system, and also the reticular formation’s neurons. n

Medulla oblongata n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Many important nuclei are contained within the medulla which are involved in motor control through the cranial nerves VIII, IX, X, XI and XII. VIII – vestibulocochlear – sensory-equilibrium, hearing IX – glossopharyngeal – motor- innervates the larynx (phonation) and pharynx (swallowing), salivation sensory -sens. imp. from pharynx and taste buds X – vagus–motor-parasympathetic regulation of many visceral functions and sensory-proprioception from visceral muscles, general visceral sensation XI –accessory motor--movements of head, neck, shoulders, sensory-proprioception from these muscles XII –hypoglossal– motor-innervation of tongue, sensoryproprioception from tongue.
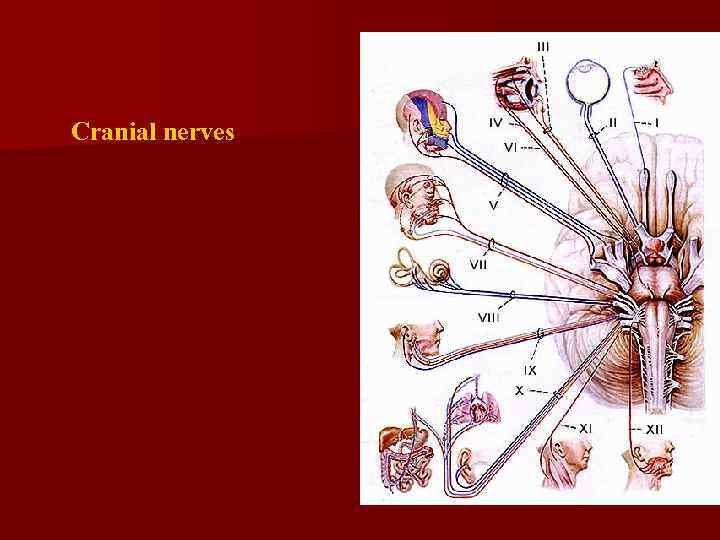
Cranial nerves

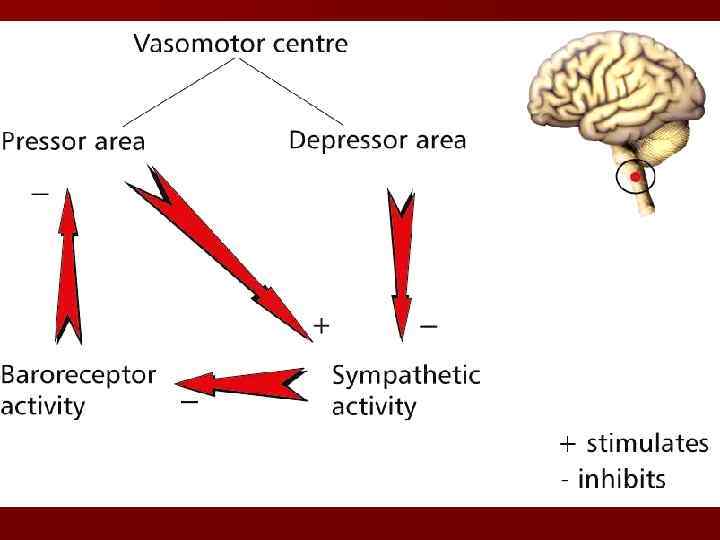
Vital centers of the medulla 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Respiratory Vasomotor and cardiac Mastication Swallowing Regurgitation Salivation Sneezing Cough Twinkle Sucking

Reflexes of the medulla oblongata n Medulla oblongata contains groupings of neurons required, mainly, for maintaining the pose or tonus of skeletal muscles, related with vestibular organ and semicircular canals. Medulla controls the two motor reflexes so called static and kinetic reflexes.

Static reflexes were subdivided to reflexes, which relate with making a correct pose for concrete moment. 1. Static reflexes ensure the alteration of muscle tonus due to the changing of the head position comparatively to the body position. 2. The reflexes of unbending are due to the redistribution of muscle tonus, which leads to the restitution of natural correct pose. Note! The static reflexes may be ensured under the control of the spinal cord alone, while the unbending reflexes need the participation of the medulla oblongata. n

n Kinetic reflexes ensure the maintaining of concrete pose and the moving in the space during the acceleration or deceleration. n For example, lift reflex.

Midbrain n The mesencephalon, or midbrain, as a medulla oblongata and pons, belong to the brain stem. n Midbrain is located between the diencephalon and the pons. Midbrain is composed of two main parts: – dorsal part - tectum and ventral peduncles.
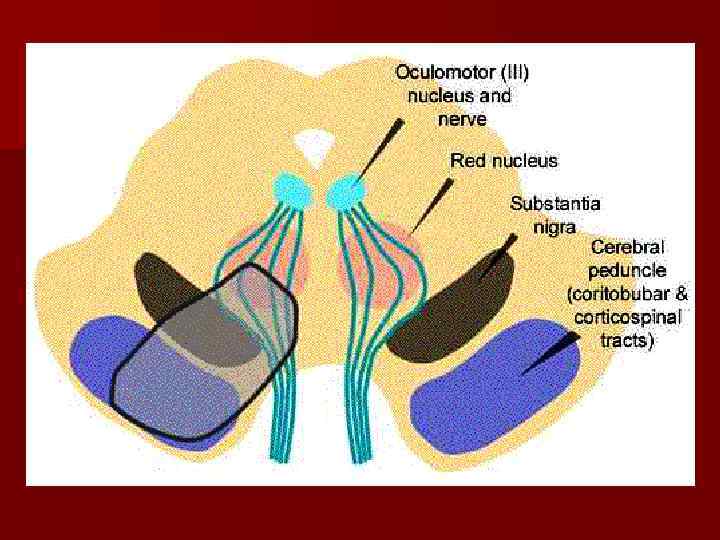

n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The most important departments of the midbrain are: Red nucleus Corpora quadrigemina Nuclei of ascending and descending tracts Substantia nigra Neurons of the reticular formation
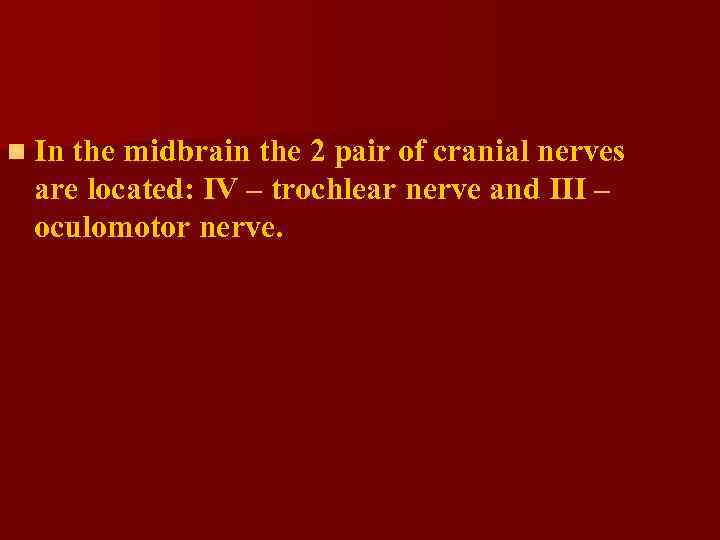
n In the midbrain the 2 pair of cranial nerves are located: IV – trochlear nerve and III – oculomotor nerve.

n The two upper mounds of the corpora quadrigemina – superior colliculi – are the primary visual center, while the inferior colliculi, immediately below, are primary or relay center for auditory information. n These centers participate in the formation of the orientation visual and auditory reflexes.

The main motor functions of the midbrain is ensured by red nucleus and substantia nigra. 1. Red nucleus, an area of gray matter deep in the midbrain, maintains connections with the cerebrum and cerebellum and is involved in motor coordination (it’s control a tonus of extensors). 1. Substantia nigra is located in the pedancles, its ensures the such physiological acts, as mastication, swallowing and exact movements of the fingers. It’s neurons can synthesized the dopamine, which is delivered to the basal ganglia by the axoplasm transport. The lost or deficiency of the dopamine leads to the Parkinson’s disease. n

n Rigidity is a sharp increasing of the extensors tonus due to the cutting of brain stem beneath the red nucleus. It’s leads to the interruption of the signalling through the cortical and rubro-spinal tracts to the motomeurons (alpha- and gamma). Hence, the activity of the vestibular-spinal centers will be predominate, which enhance the extensor’s tonus. Another words, the rigidity is due to disappearance of inhibitory impulses from the motor cortex and red nucleus.
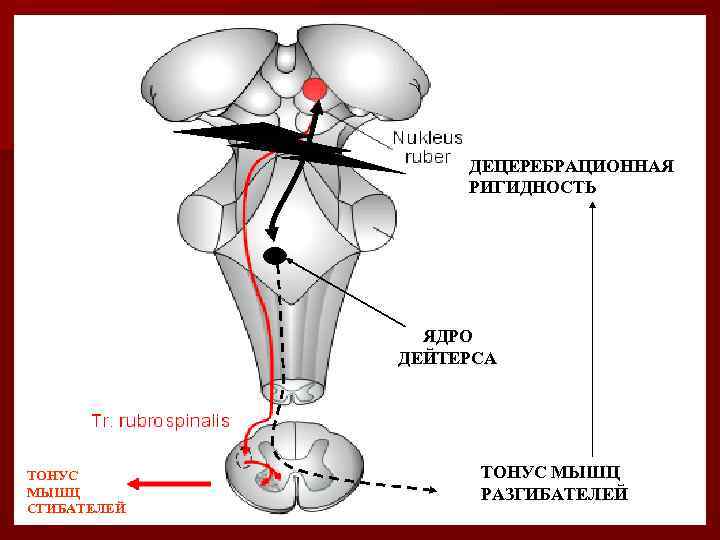
ДЕЦЕРЕБРАЦИОННАЯ РИГИДНОСТЬ ЯДРО ДЕЙТЕРСА ТОНУС МЫШЦ СГИБАТЕЛЕЙ ТОНУС МЫШЦ РАЗГИБАТЕЛЕЙ
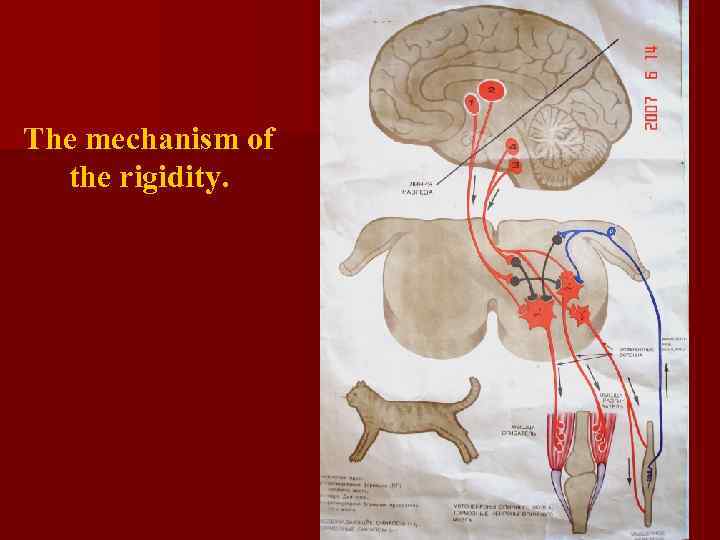
The mechanism of the rigidity.

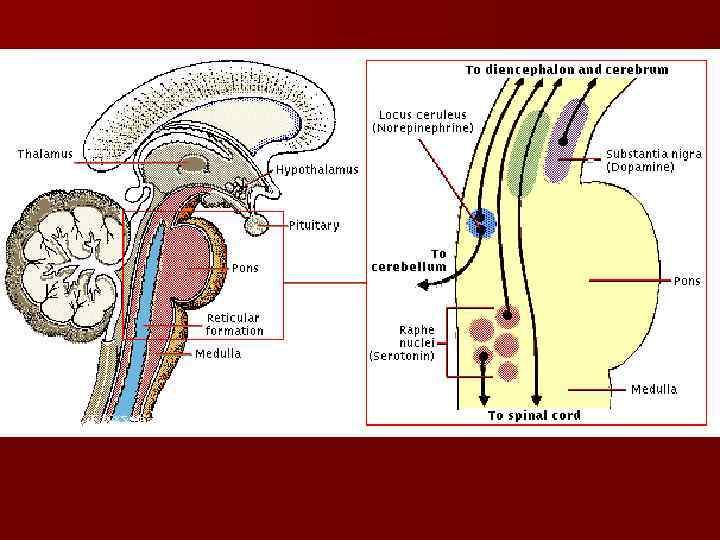
The nigrostriatal system. The midbrain has two systems of dopaminergic (dopaminereleasing) neurons that project to other areas of the brain. n 1. The nigrostriatal system – projects from the substantia nigra to the corpus striatum of the basal nuclei. This system is need for exact, complicated movements of fingers, for example. The degeneration of these fibers or dopaminergic neurons leads to Parkinson‘s disease. n 2. Other dopaminergic neurons are the part of mesolimbic system project from nuclei near S. N. to the limbic system. Of the forebrain. This system is involved in behavior and reward system, related with sense of pleasure. The releasing of dopamine from these neurons is promoted by abused drugs. n

Thank you for attention.
5.Физиология ствола мозга.ppt