ffeb45b5052ceb199ac0b1217d7900bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
Brain CT, MR Brain tumor, impaired blood flow Ágnes Nemeskéri 2014 Semmelweis University Department of Human Morpholgy and Developmental Biology Clinical Anatomy Research Laboratory nemeskeri. agnes@med. semmelweis-univ. hu
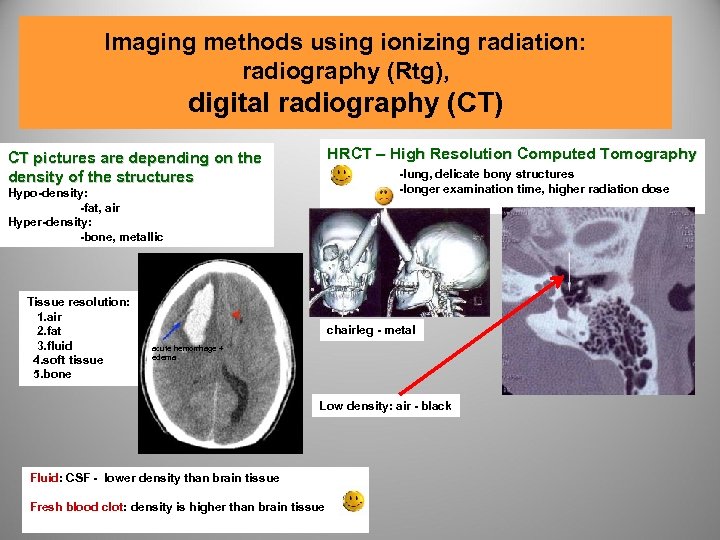
Imaging methods using ionizing radiation: radiography (Rtg), digital radiography (CT) CT pictures are depending on the density of the structures HRCT – High Resolution Computed Tomography -lung, delicate bony structures -longer examination time, higher radiation dose Hypo-density: -fat, air Hyper-density: -bone, metallic Tissue resolution: 1. air 2. fat 3. fluid 4. soft tissue 5. bone chairleg - metal acute hemorrhage + edema Low density: air - black Fluid: CSF - lower density than brain tissue Fresh blood clot: density is higher than brain tissue
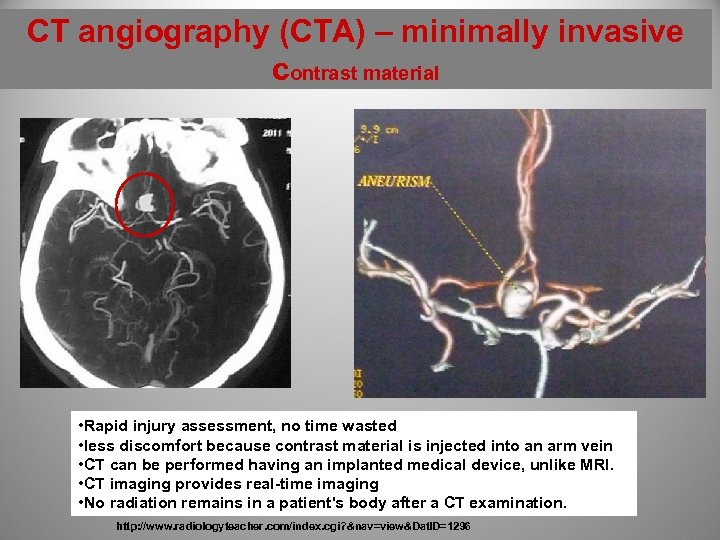
CT angiography (CTA) – minimally invasive contrast material • Rapid injury assessment, no time wasted • less discomfort because contrast material is injected into an arm vein • CT can be performed having an implanted medical device, unlike MRI. • CT imaging provides real-time imaging • No radiation remains in a patient's body after a CT examination. http: //www. radiologyteacher. com/index. cgi? &nav=view&Dat. ID=1296
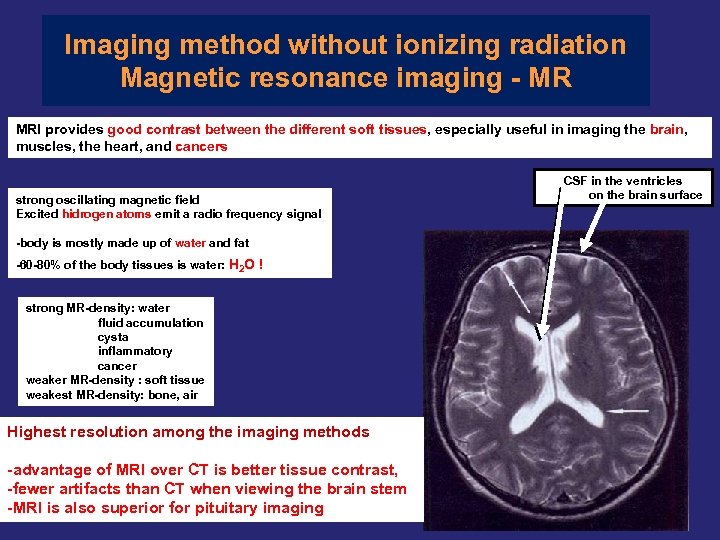
Imaging method without ionizing radiation Magnetic resonance imaging - MR MRI provides good contrast between the different soft tissues, especially useful in imaging the brain, muscles, the heart, and cancers strong oscillating magnetic field Excited hidrogen atoms emit a radio frequency signal -body is mostly made up of water and fat -60 -80% of the body tissues is water: H 2 O ! strong MR-density: water fluid accumulation cysta inflammatory cancer weaker MR-density : soft tissue weakest MR-density: bone, air Highest resolution among the imaging methods -advantage of MRI over CT is better tissue contrast, -fewer artifacts than CT when viewing the brain stem -MRI is also superior for pituitary imaging CSF in the ventricles on the brain surface
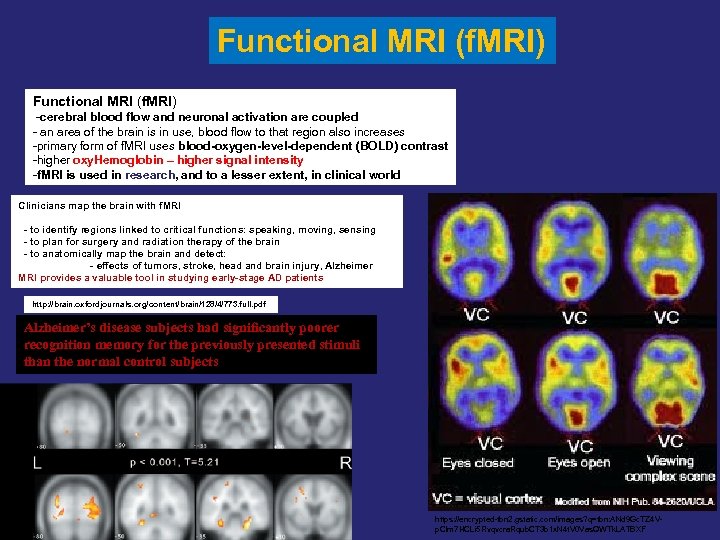
Functional MRI (f. MRI) -cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled - an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases -primary form of f. MRI uses blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) contrast -higher oxy. Hemoglobin – higher signal intensity -f. MRI is used in research, and to a lesser extent, in clinical world Clinicians map the brain with f. MRI - to identify regions linked to critical functions: speaking, moving, sensing - to plan for surgery and radiation therapy of the brain - to anatomically map the brain and detect: - effects of tumors, stroke, head and brain injury, Alzheimer MRI provides a valuable tool in studying early-stage AD patients http: //brain. oxfordjournals. org/content/brain/128/4/773. full. pdf Alzheimer’s disease subjects had significantly poorer recognition memory for the previously presented stimuli than the normal control subjects https: //encrypted-tbn 2. gstatic. com/images? q=tbn: ANd 9 Gc. TZ 4 Vp. Clm 7 HCLi 5 Rvqvcra. Rqub. CT 3 b 1 x. N 4 t. V 0 Vas. QWTk. LATBXF
Stroke (~bleeding? ischemia? ) Recently it was shown that the number of stroke events in Europe would increase from 1. 1 million per year in 2000 to more than 1. 5 million per year in 2025 1. Ischaemic stroke: 88% (most frequent) a. Thrombotic stroke b. Embolic stroke 2. Intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke: 9% 3. Subarachnoidal bleeding: 3%
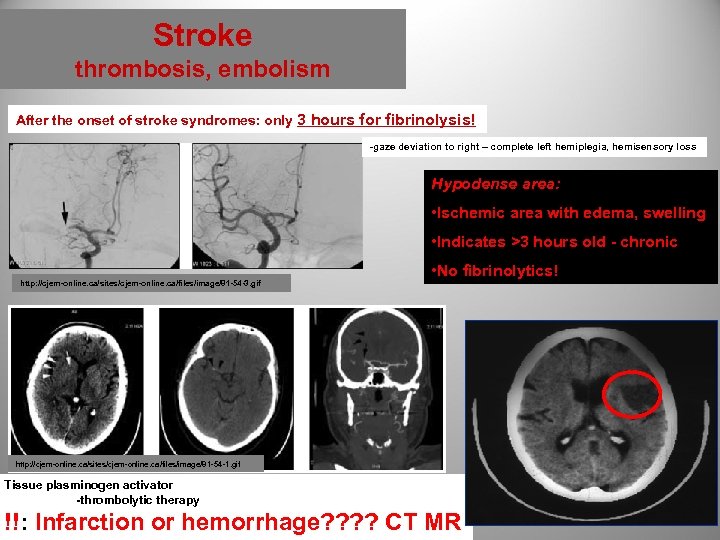
Stroke thrombosis, embolism After the onset of stroke syndromes: only 3 hours for fibrinolysis! -gaze deviation to right – complete left hemiplegia, hemisensory loss Hypodense area: • Ischemic area with edema, swelling • Indicates >3 hours old - chronic http: //cjem-online. ca/sites/cjem-online. ca/files/image/81 -54 -3. gif • No fibrinolytics! http: //cjem-online. ca/sites/cjem-online. ca/files/image/81 -54 -1. gif Tissue plasminogen activator -thrombolytic therapy !!: Infarction or hemorrhage? ? CT MR
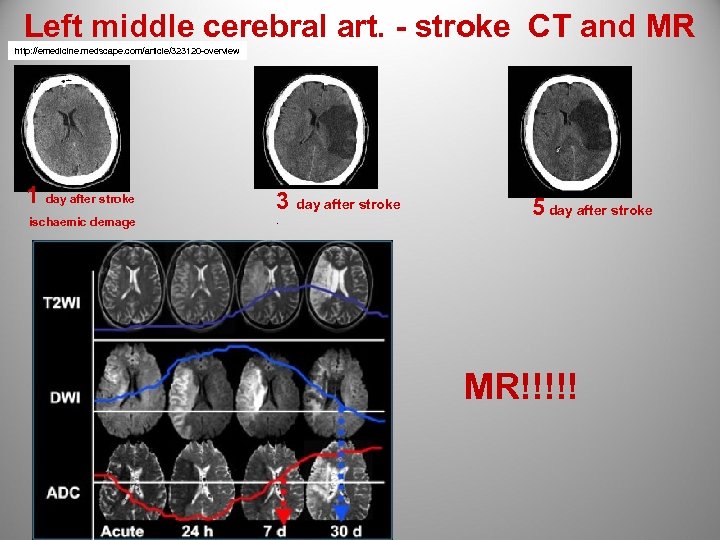
Left middle cerebral art. - stroke CT and MR http: //emedicine. medscape. com/article/323120 -overview 1 day after stroke ischaemic demage 3 day after stroke . 5 day after stroke MR!!!!!
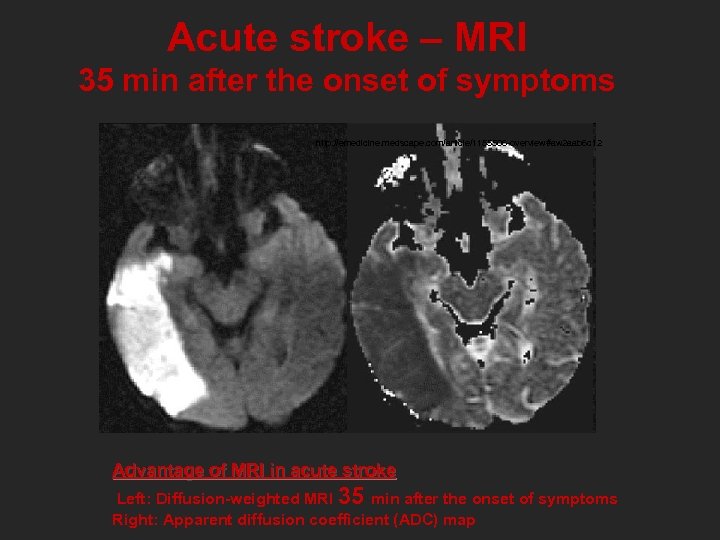
Acute stroke – MRI 35 min after the onset of symptoms http: //emedicine. medscape. com/article/1155506 -overview#aw 2 aab 6 c 12 Advantage of MRI in acute stroke Left: Diffusion-weighted MRI 35 min after the onset of symptoms Right: Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map
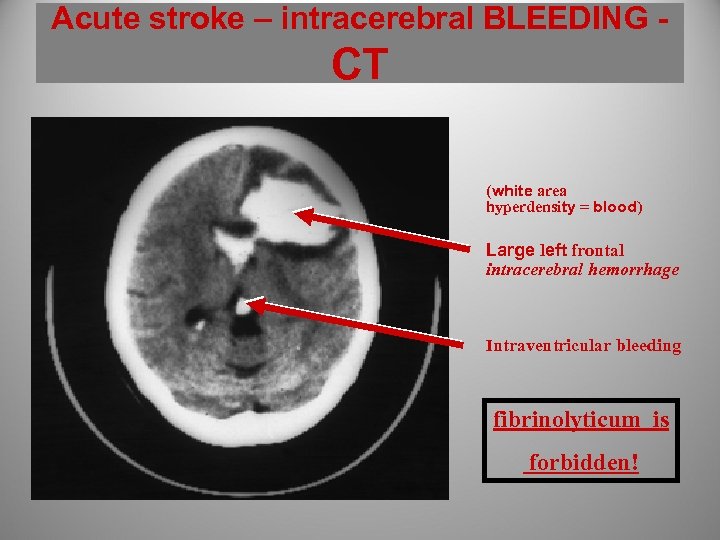
Acute stroke – intracerebral BLEEDING - CT (white area hyperdensity = blood) Large left frontal intracerebral hemorrhage Intraventricular bleeding fibrinolyticum is forbidden!
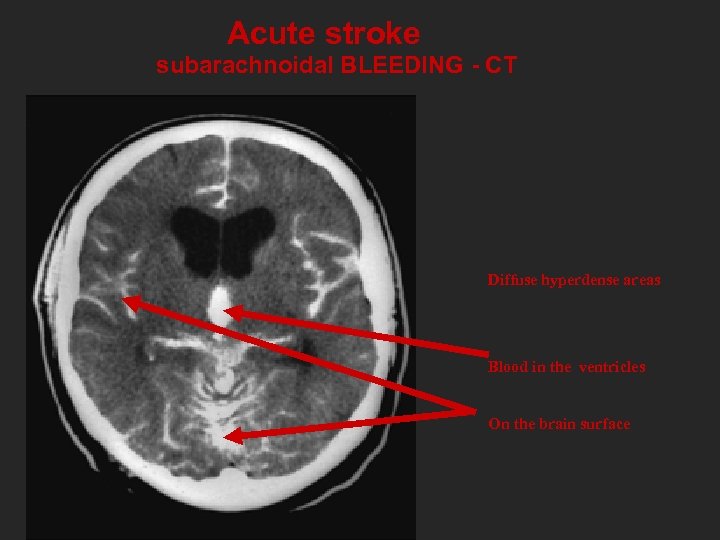
Acute stroke subarachnoidal BLEEDING - CT Diffuse hyperdense areas Blood in the ventricles On the brain surface

Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke • Subarachnoideal bleeding – neurosurgical intervention – Nimodipine – prevents the development of cerebral vasospasm and ischaemia • Intracerebral bleeding – treatment of increased intracranial pressure – neurosurgical decompression • Cerebellar – neurosurgical intervention – remove blood clot • Lobar – neurosurgical intervention
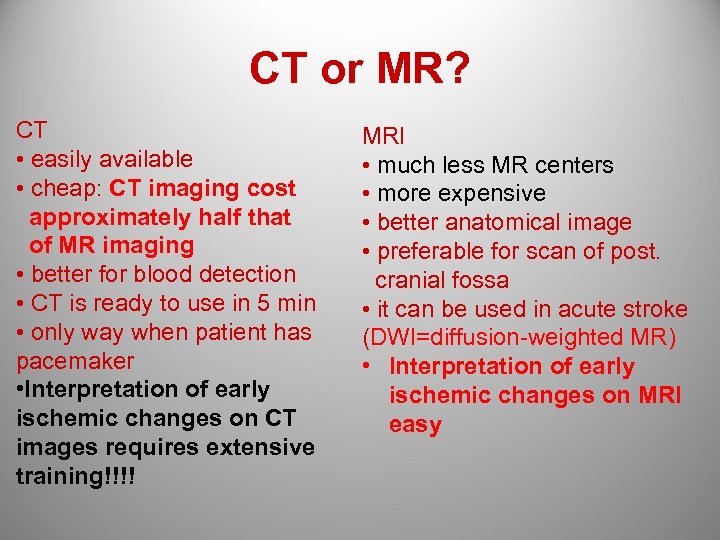
CT or MR? CT • easily available • cheap: CT imaging cost approximately half that of MR imaging • better for blood detection • CT is ready to use in 5 min • only way when patient has pacemaker • Interpretation of early ischemic changes on CT images requires extensive training!!!! MRI • much less MR centers • more expensive • better anatomical image • preferable for scan of post. cranial fossa • it can be used in acute stroke (DWI=diffusion-weighted MR) • Interpretation of early ischemic changes on MRI easy
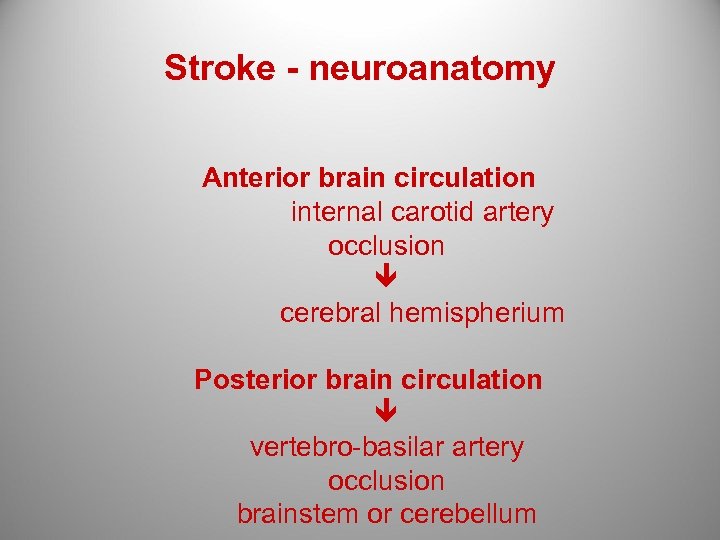
Stroke - neuroanatomy Anterior brain circulation internal carotid artery occlusion cerebral hemispherium Posterior brain circulation vertebro-basilar artery occlusion brainstem or cerebellum
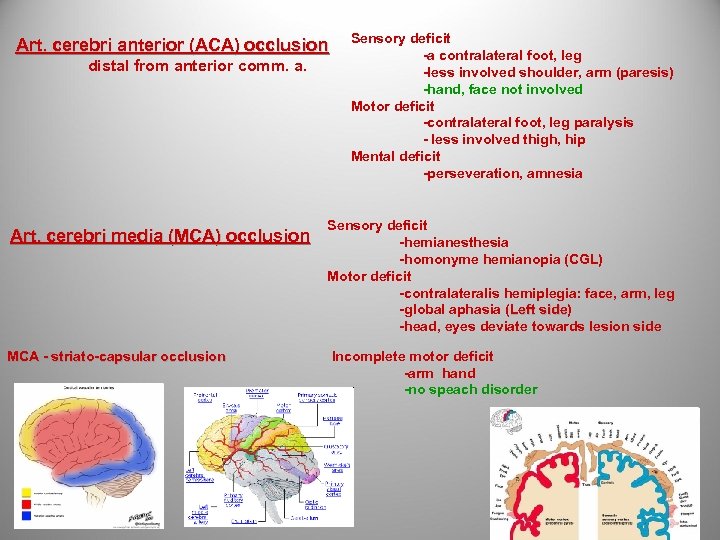
Art. cerebri anterior (ACA) occlusion distal from anterior comm. a. Art. cerebri media (MCA) occlusion MCA - striato-capsular occlusion Sensory deficit -a contralateral foot, leg -less involved shoulder, arm (paresis) -hand, face not involved Motor deficit -contralateral foot, leg paralysis - less involved thigh, hip Mental deficit -perseveration, amnesia Sensory deficit -hemianesthesia -homonyme hemianopia (CGL) Motor deficit -contralateralis hemiplegia: face, arm, leg -global aphasia (Left side) Left side -head, eyes deviate towards lesion side Incomplete motor deficit -arm hand -no speach disorder

Intracranial tumors
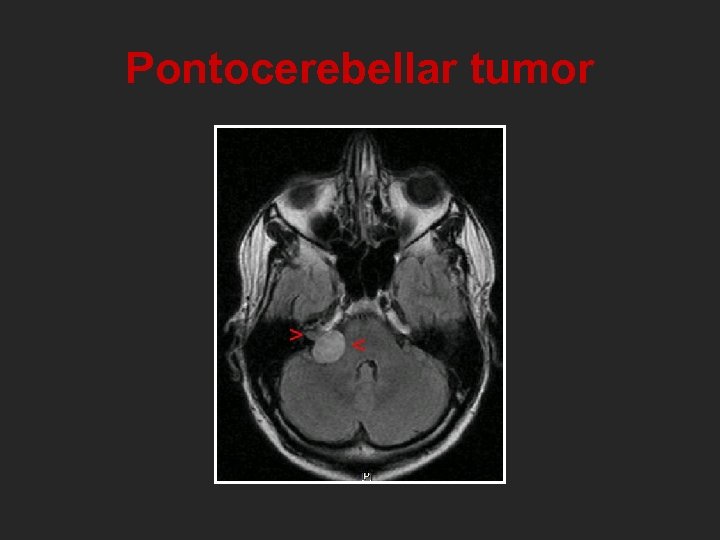
Pontocerebellar tumor
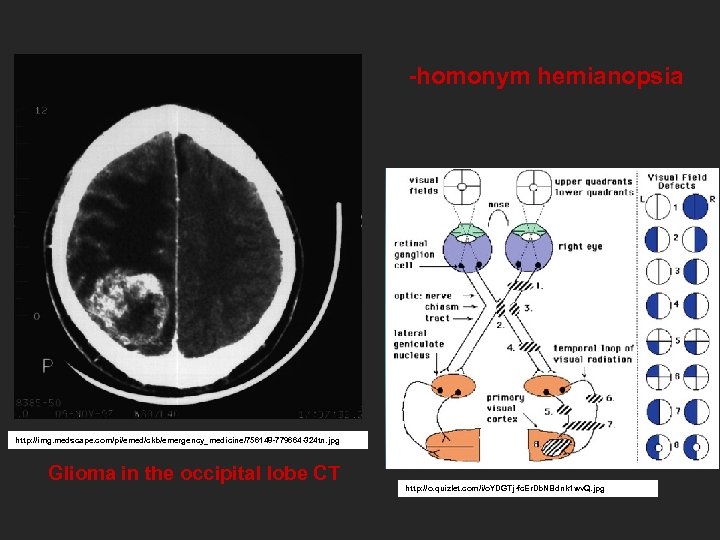
-homonym hemianopsia http: //img. medscape. com/pi/emed/ckb/emergency_medicine/756148 -779664 -324 tn. jpg Glioma in the occipital lobe CT http: //o. quizlet. com/i/o. YDGTj-fc. Er. Db. NBdnk 1 wv. Q. jpg
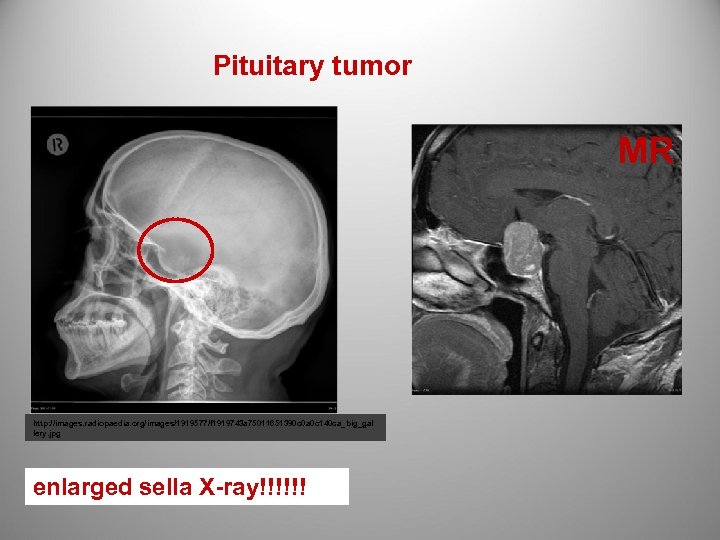
Pituitary tumor MR http: //images. radiopaedia. org/images/1919577/f 1919743 a 75011651390 c 0 a 0 c 140 ca_big_gal lery. jpg enlarged sella X-ray!!!!!!
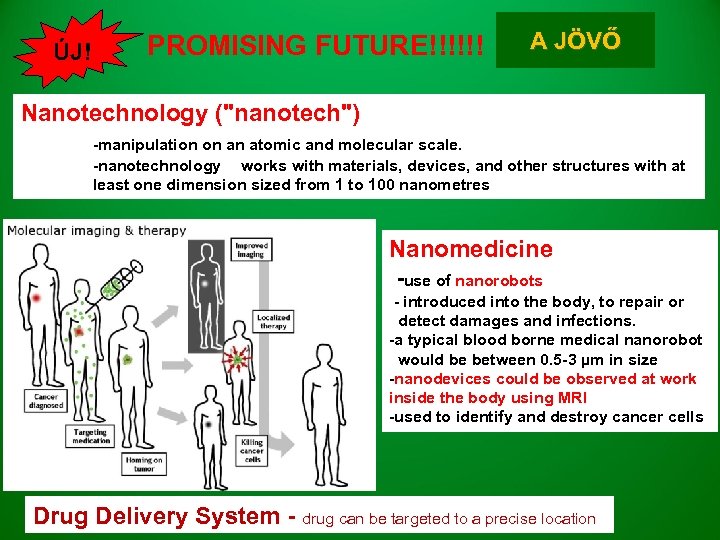
ÚJ! PROMISING FUTURE!!!!!! A JÖVŐ Nanotechnology ("nanotech") -manipulation on an atomic and molecular scale. -nanotechnology works with materials, devices, and other structures with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres Nanomedicine -use of nanorobots - introduced into the body, to repair or detect damages and infections. -a typical blood borne medical nanorobot would be between 0. 5 -3 µm in size -nanodevices could be observed at work inside the body using MRI -used to identify and destroy cancer cells Drug Delivery System - drug can be targeted to a precise location
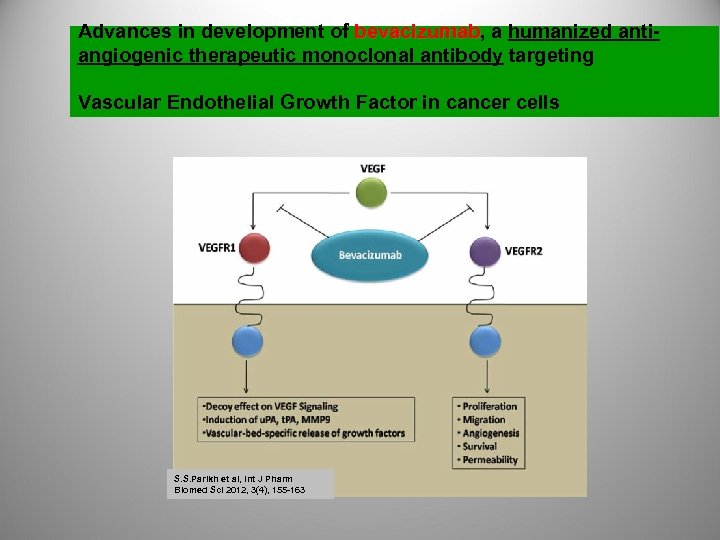
Advances in development of bevacizumab, a humanized antibevacizumab angiogenic therapeutic monoclonal antibody targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in cancer cells S. S. Parikh et al, Int J Pharm Biomed Sci 2012, 3(4), 155 -163
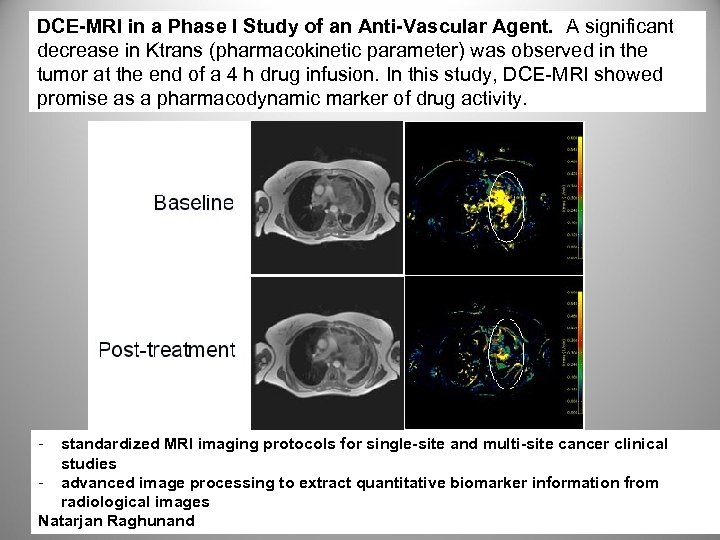
DCE-MRI in a Phase I Study of an Anti-Vascular Agent. A significant decrease in Ktrans (pharmacokinetic parameter) was observed in the tumor at the end of a 4 h drug infusion. In this study, DCE-MRI showed promise as a pharmacodynamic marker of drug activity. - standardized MRI imaging protocols for single-site and multi-site cancer clinical studies - advanced image processing to extract quantitative biomarker information from radiological images Natarjan Raghunand

ÚJ! Personalized molecular medicine Endoglin (CD 105) -a member of TGF-β family of receptors -required for endothelial cell proliferation -standard method for quantifying tumor angiogenesis is to assess microvessel density based on endoglin staining -“the visualization, characterization and measurement of biological processes at the molecular and cellular levels in humans”
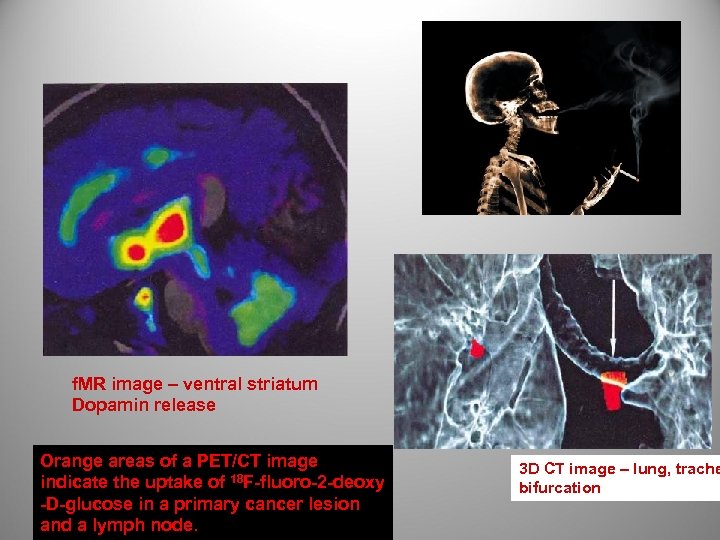
f. MR image – ventral striatum Dopamin release Orange areas of a PET/CT image indicate the uptake of 18 F-fluoro-2 -deoxy -D-glucose in a primary cancer lesion and a lymph node. 3 D CT image – lung, trache bifurcation
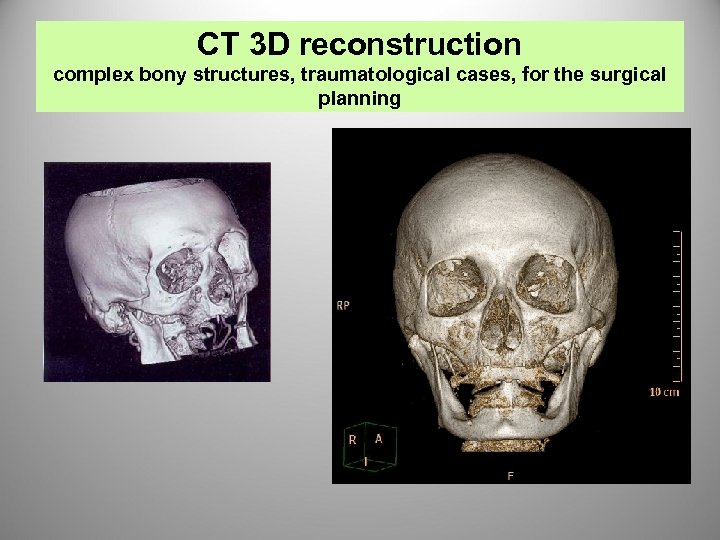
CT 3 D reconstruction complex bony structures, traumatological cases, for the surgical planning
References Lynn Wittwer, MD, MPD Clark County EMS Stroke ppp presentation http: //classes. midlandstech. com/carterp/courses/bio 210/chap 12/lecture 1. htm Nick Ward: Assessment and diagnosis in stroke DEPARTMENT OF HEADACHE, BRAIN INJURY, AND NEUROREHABILITATION NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY INSTITUTE OF NEUROLOGY UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON http: //emedicine. medscape. com/article/343207 -overview Hon-Man Liu: Basic interpretation of CT Scan
ffeb45b5052ceb199ac0b1217d7900bc.ppt