a0f57b17487d0953a8eb3476539ae00d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35


BP 105 Installing and Administering the IBM Lotus Sametime Gateway Chris Miller, Director of Messaging & Collaboration, Connectria Kyungae Lim| Senior Software Engineer, Lotus Software, IBM Software Group

Agenda Gateway Overview Requirements Installation and Configuration of single and clustered deployments Connecting to External Communities Connecting to public IM providers Connecting to external Sametime Communities Connecting to external XMPP Communities SSL, DNS, Network placement and network address translation (NAT) New in the Sametime Gateway 8. 0 Troubleshooting
What is the Sametime Gateway? A Websphere J 2 EE application that allows Sametime users to share presence and chat sessions with users of the public Instant Messaging services as well as other Sametime communities Replaces and enhances Sametime 7. 0 SIP Gateway Supports multiple protocols – SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) – VP (Virtual Places) protocol – XMPP (e. Xtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) Federates the local Sametime community with external IM communities such as AOL ® AIM ®, Yahoo! ® Messenger, Google Talk (tm), Jabber (tm) user communities Acts as an server application (SA) to local Sametime Community Access Proxy to external IM providers
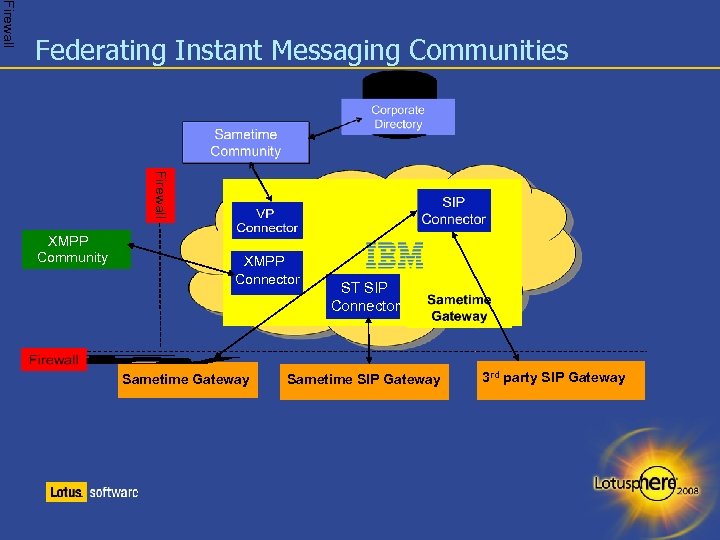
Firewall Federating Instant Messaging Communities Firewall XMPP Community XMPP Connector Sametime Gateway ST SIP Connector Sametime SIP Gateway 3 rd party SIP Gateway

What does the Sametime Gateway provide: Secure message routing between communities Protocol translation – VP<->SIP – VP<->XMPP SSL or built in encryption Management of connection to communities Policy Management Who can access which community – users, groups, or all (“*”) Blacklisting domains, enabling/disabling route to a community Activity logging, chat logging through extensions Capacity management – Global and local settings of maximum session limits – current session count monitoring Extensible platform Programming extension points and SDK available to additional functionality
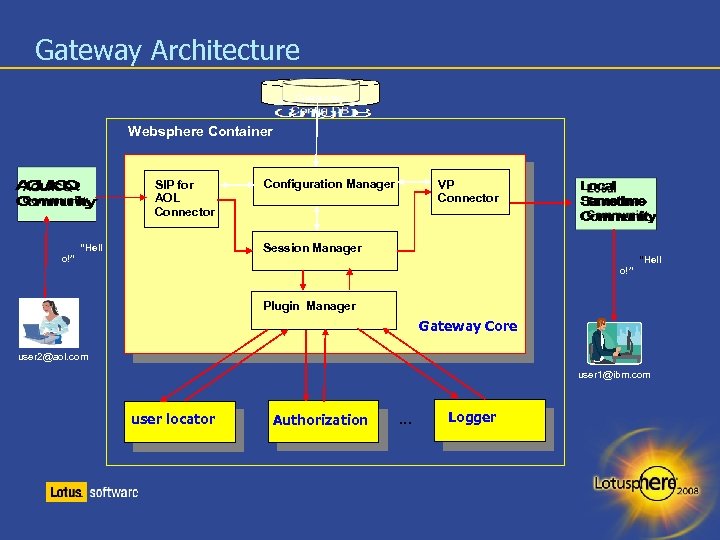
Gateway Architecture Websphere Container SIP for AOL Connector o!” Configuration Manager VP Connector Session Manager “Hell o!” “Hell Plugin Manager Gateway Core user 2@aol. com user 1@ibm. com user locator Authorization . . . Logger
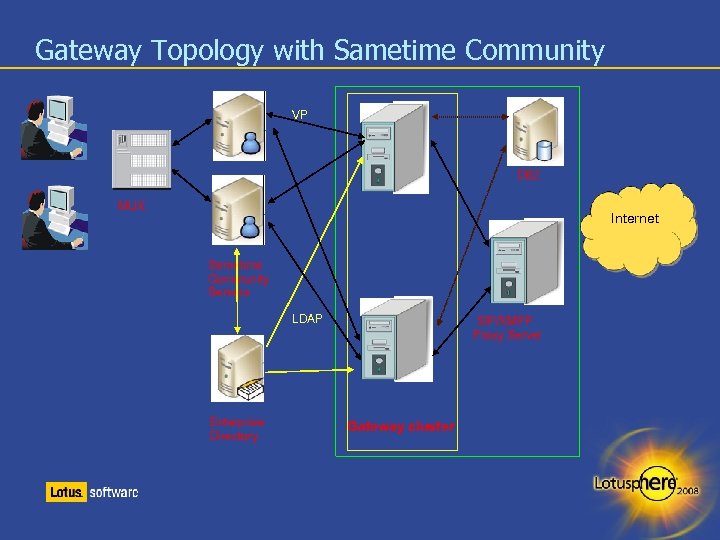
Gateway Topology with Sametime Community VP DB 2 MUX Internet Sametime Community Servers LDAP Enterprise Directory SIP/XMPP Proxy Server Gateway cluster
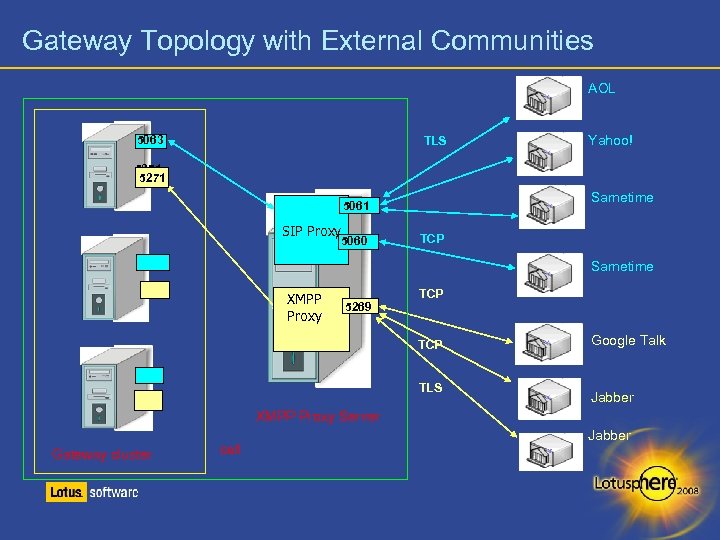
Gateway Topology with External Communities AOL 5063 TLS Yahoo! 5271 Sametime 5061 SIP Proxy 5060 TCP Sametime XMPP Proxy 5269 TCP TLS Google Talk Jabber XMPP Proxy Server Gateway cluster cell Jabber

Resources Sametime 8. 0 infocenter http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/sametime/v 8 r 0/index. jsp Web. Sphere infocenter http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/wasinfo/v 6 r 1/index. jsp Deployment Wiki coming to you http: //www. ibm. com/developerworks/wikis/display/sametime/Home Sametime Support Forum http: //www-10. lotus. com/ldd/stforum. nsf System Requirement http: //www. ibm. com/support/docview. wss? rs=477&uid=swg 27010738 Installing and Administrating the Sametime Gateway guide http: //www. lulu. com/content/609639
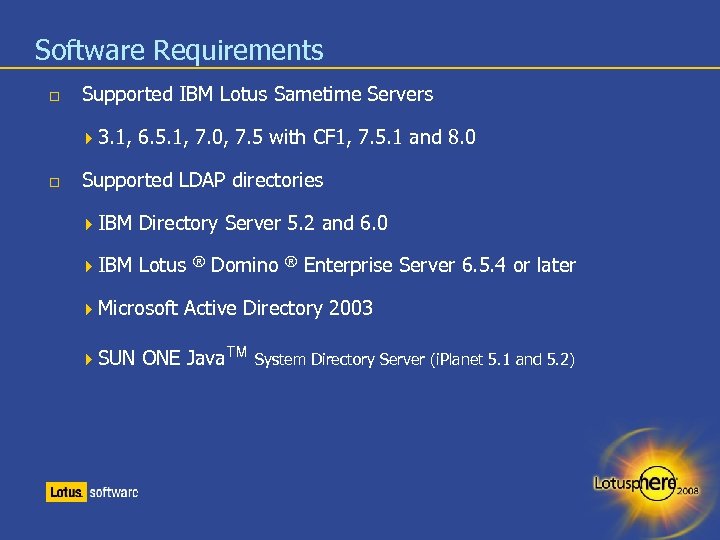
Software Requirements Supported IBM Lotus Sametime Servers 3. 1, 6. 5. 1, 7. 0, 7. 5 with CF 1, 7. 5. 1 and 8. 0 Supported LDAP directories IBM Directory Server 5. 2 and 6. 0 IBM Lotus ® Domino ® Enterprise Server 6. 5. 4 or later Microsoft Active Directory 2003 SUN ONE Java System Directory Server (i. Planet 5. 1 and 5. 2)
Deployment Topologies Standalone deployment A single-server Gateway and DB 2 install, or DB 2 on a separate machine Clustered deployment Two-machine installation ● DM (Deployment Manager), DB 2 and primary on machine 1 ● Secondary node with proxy servers on machine 2 Three-machine installation ● DM and primary on machine 1 ● Secondary node and DB 2 on machine 2 ● Proxy servers on machine 3 Four or more machine installation ● ● DB 2 or DM on a separate machines Additional secondary nodes for load balancing Place proxy servers on a separate machine whenever possible
Configuration Topologies There are different ways to configure the connection to external IM communities. Establish a direct, separate connection to each of AOL AIM ®, Yahoo! Messenger, Google Talk. TM, Jabber XCP™ and Sametime communities ® ® Use a single secure SIP connection to AOL Clearinghouse – AOL Clearinghouse connects to ● AOL/AIM community ● AOL EFP (Enterprise Federation Partner) participants such as LCS, i. Chat, Sametime, and Jabber XCP™ communities You can not connect to Google Talk and Yahoo! Messenger via AOL Clearinghouse You can connect Sametime or Jabber XCP communities via AOL Clearinghouse, or via direct connection

Direct Connection vs. Clearinghouse Direct connection One connection per community – SSL certificate exchange required for each connection – External firewall must allow each community server to access Gateway – Finer-grained policy control ● Gateway can reject requests to unknown domains ● Access rights can be set to grant per community ● Can disable/enable route or set the connection limit to each community Connection via Clearinghouse One connection serving multiple communities – Single SSL connection from the Lotus Sametime Gateway to AOL Clearinghouse – Connection from AOL Clearinghouse to a target community is encrypted using a different SSL certificate negotiated between AOL Clearinghouse and the participating community

Direct Connection vs. Clearinghouse (cont'd) A Single IP connection through firewall Ability to reach other IM providers such as OCS or i. Chat Access control is coarser – Sametime users can either access all the Clearinghouse communities or none – Gateway will not be able to filter requests to a user of unknown domain ● Domain resolution is done by the AOL Clearinghouse You can mix and match – select the topology according to your enterprise needs

Connecting to XMPP Communities In 8. 0, Jabber XCP is supported in addition to Google Talk Support for Jabber XCP Server 5. 2 A TCP connection is available for both Google Talk and Jabber TLS is available for Jabber connectivity only If both Google Talk and Jabber XCP are configured, port 5269 is shared between SSL connection and a non-SSL connection Connection via XMPP Proxy Server on cluster The Proxy handles load balancing, affinity and node failover Port 5271 used for communication between the and the proxy – To change the port, go to ISC and edit ● Application Servers->XMPP Proxy Server->Ports->XMPP_INTERNAL_PORT

SSL configuration considerations Naming your gateway for SSL is an important consideration The name chosen should be portable in your environment The name chosen should not equal the hostname or STGW Choosing a certificate provider Not every certificate provider is supported by all the public instant messaging providers – For example, if you choose to only connect to AOL, you may choose any vendor AOL supports – Verify your chosen vendor has support of both communities via the online Sametime Gateway documentation as they may change Google does not require a certificate from a provider and relies on SRV entries in DNS

DNS considerations Once you have established a portable DNS name, a few standard DNS entries are required First is a standard A or CNAME entry for your GATEWAY – For example imgateway. company. com Second is a proper SRV entry for Google communication – For example _xmpp-server. _tcp. lotus. com. IN SRV 5 0 5269 imgateway. company. com. – The first 5 listed is the priority when using a cluster. The lower number is utilized first, much like MX records are in DNS – The weight (listed as 0) is how often the SRV entry is queried. The higher number the more often the server is queried – The port is the standard XMPP port of 5269 – The last part of the entry is the hostname you have established in DNS
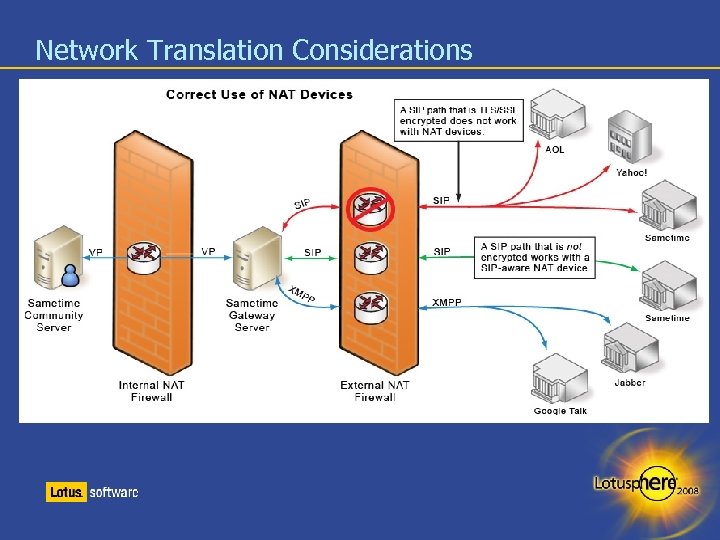
Network Translation Considerations
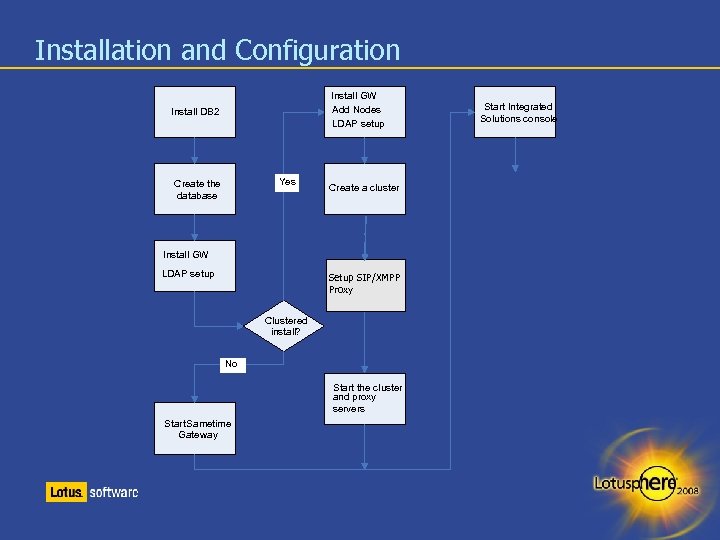
Installation and Configuration Install GW Add Nodes to makesetup LDAP a cluster Install DB 2 Yes Create the database Install GW Install the Sametime LDAP setup gateway Create aacluster Create cluster Setup SIP/XMPP Proxy Clustered install? No No Start the cluster and proxy and SIP servers server Start Sametime Gateway Start Integrated Solutions console

New in 8. 0 Installation Simplified installation and configuration The wizards populate values with information detected from the operating system – Less administrator input is required – More input validation checking has been added The DB 2 client no longer needs to be installed on the Lotus Sametime Gateway machine – Migration from 7. 5. x will also upgrade the JDBC driver to type 4 to make the use of DB 2 client obsolete Application security is enabled automatically – no separate step to enable security A LDAP Configuration Wizard is launched from Install – Discovery of LDAP servers is based on DNS SRV A Cluster Configuration Wizard launches to automate cluster creation Proxy Server installation is offered as an Install Wizard option Adding primary/secondary cluster node is an Install Wizard option The upgrade of the Gateway automatically upgrades the Websphere version (6. 1. 0. 11)
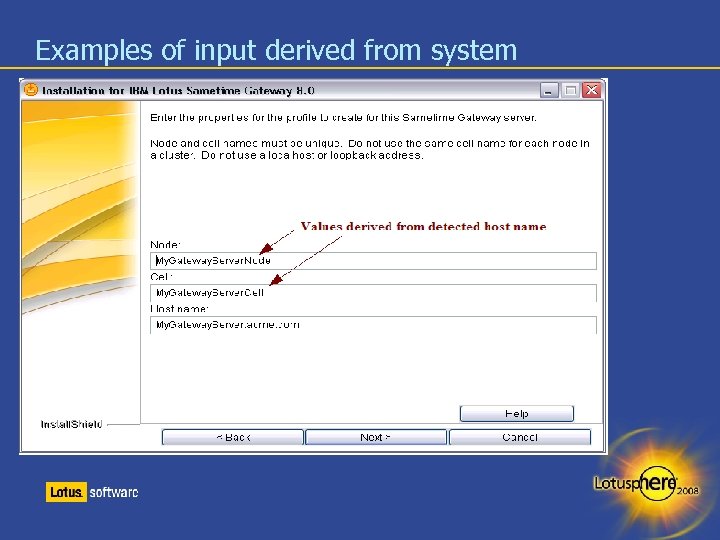
Examples of input derived from system
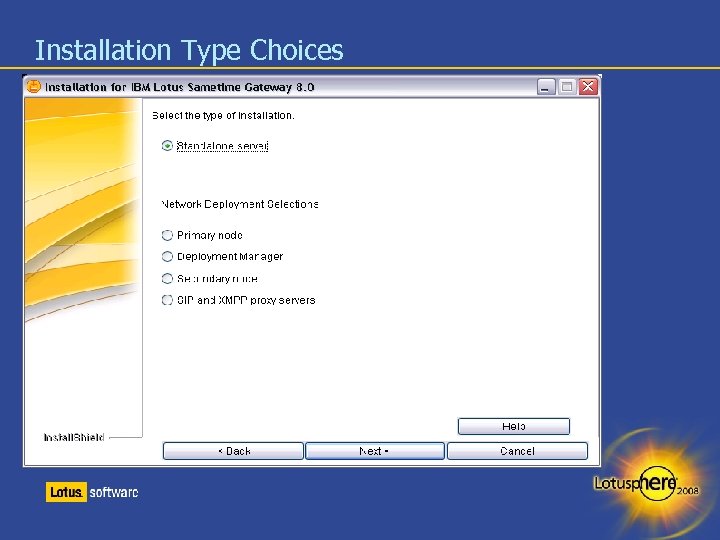
Installation Type Choices

Understanding Installation Tasks The installation wizards performs the following tasks in the order: Installation of the Web. Sphere Application Server shared binaries Configuration of the profile using the Profile Management Tool Sametime Gateway files are copied to the file system Generation of the system specific scripts and execution of them to configure the server. The script will: – Deploy Gateway Applications, JDBC providers, data sources and related components to WAS – Configure the DB 2 database – Provide optional LDAP configuration When an install error occurs, the wizard rolls back to a clean system prior to install, leaving the logs and folders only for debug purposes.
Where to look if Installation fails Gateway install log files are found in: <user temp dir>stgwlogsinstalllog. txt <stgw_server_root>lo gsinstalllog. txt <user temp dir>stgwdb. Conn. Text. t xt <stgw_server_root>lo gsconfigwizard. log <WAS HOME>logsinstall <WAS HOME>logsmanagepr ofiles

Checklist to clean previous installations after failure Locate the VPD (Vital Product Database) registry used by the installation procedure from stgw_server_root/logs/installlog. txt Search for “using VPD registry at “ in the log file On Windows system, VPD is found in Program FilesCommon FilesInstall. ShieldUniversalCommonGen 2 Back up, and delete the Gen 2 folder NOTE: backup is recommended, since the 'Gen 2' folder may contain installation/upgrade information used by other applications Delete the registry files On Windows system, c: Windows. nifregistry On Unix systems, /opt/ibm/. nifregistry Delete the installation directory Start the installation again

Preserving SSL certificates between installations If you decide to uninstall 7. 5. x and then perform a fresh install of 8. 0, be sure to preserve your CA certificates before beginning. Back up the following files: Single server – <stgw_profile_root>configcells<cellname>nodes<nodename>key. p 12 – <stgw_profile_root>configcells<cellname>nodes<nodename>trust. p 12 Cluster – <stgw_profile_root>configcells<cellname>key. p 12 – <stgw_profile_root>configcells<cellname>trust. p 12 Backup is not necessary for upgrades Upgrade scripts preserve the trust/keystores from the previous versions

Troubleshooting – Gateway startup To verify that the Servers have started successfully: On clustered deployments, start the ISC on the Deployment Manager, check the status indicator on SIP Proxy, XMPP Proxy and the application server on each cluster node – ISC -> Servers -> Proxy Servers for SIP Proxy – ISC -> Servers -> Application Servers for XMPP Proxy and the cluster member servers On the application server on each cluster member, verify that the Gateway J 2 EE applications have started successfully – ISC -> Applications -> Enterprise Applications: Application Status indicator should be green View log files for failures FFDC (First Failure Data Capture) in <stgw_profile_root>/ffdc JVM logs under stgw_profile_root/logs/RTCGW_Server
Troubleshooting – adding an external buddy Verify that Gateway connects to the local Sametime server Trust the IP address of the Sametime Gateway inside the Sametime Community server Check the Sametime server policy Verify the Gateway has started Verify the Community Connection Status is green If connecting to the Sametime server of 3. 1, 6. 5. 1, or 7. 0, disable the old SIP Gateway Verify there are not multiple Gateways connecting to the local Sametime community Use Sametime Connect Client 7. 5. 1 or above to add a buddy from public IM providers
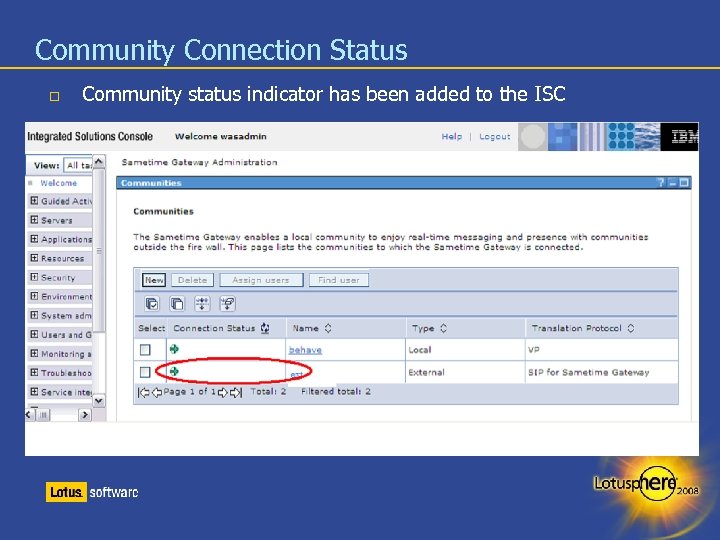
Community Connection Status Community status indicator has been added to the ISC

Troubleshooting – SSL configuration Host and Port consideration The hostname should not be STGW (changes to DB 2 must be made) The FQHN should match the certificate name specified when requesting the SSL certificate – If it is a clustered installation, it should reflect the SIP/XMPP Proxy server hostname The port specified in the provisioning application should match the SIP transport and the port in the Connection Settings of the external community in ISC – Check the SIP Proxy transport chain if clustered. Check the SIP Containter transport chain if single-server deployment – Default SSL port is 5061, but this port number changes if the port conflict is detected during cluster configuration Valid CA-signed personal certificate and the signer certificate, root or intermediate, must exist in the key/truststores. http: //publib. boulder. ibm. com/infocenter/sametime/v 8 r 0/index. jsp? topic=/com. ib m. help. sametime. gateway. doc/i_rtc_t_install_settingupsecuresocketslayerprotocol. html

Turning on diagnostic tracing From the ISC, Troubleshooting -> Logs and Trace -> RTCGWServer -> Change Log Detail Levels – by components and by levels ● com. ibm. rtc. gateway. *, com. ibm. ws. sip. *, com. ibm. ws. ssl. *, etc. ● Fine, finer, finest – Select 'runtime' tab to dynamically turn on/off tracing – Diagnostic messages go to <stgw_profile_root>/logs/RTCGWServer/trace. log Diagnostic tracing for SSL handshakes: – Servers -> Application Servers -> RTCGWServer -> Java and Process Management -> Process Definition -> Java Virtual Machine, add JVM argument, -Djavax. net. debug=ssl

Where to find your presenters Chris Miller HND 302 – Hands-on Setup and Administration of the Sametime Gateway @Lotusphere or @Ido. Notes on Twitter this week Kyungae Lim Meet the Developers Lab

Questions?

© IBM Corporation 2007. All Rights Reserved. The information contained in this publication is provided for informational purposes only. While efforts were made to verify the completeness and accuracy of the information contained in this publication, it is provided AS IS without warranty of any kind, express or implied. In addition, this information is based on IBM’s current product plans and strategy, which are subject to change by IBM without notice. IBM shall not be responsible for any damages arising out of the use of, or otherwise related to, this publication or any other materials. Nothing contained in this publication is intended to, nor shall have the effect of, creating any warranties or representations from IBM or its suppliers or licensors, or altering the terms and conditions of the applicable license agreement governing the use of IBM software. References in this presentation to IBM products, programs, or services do not imply that they will be available in all countries in which IBM operates. Product release dates and/or capabilities referenced in this presentation may change at any time at IBM’s sole discretion based on market opportunities or other factors, and are not intended to be a commitment to future product or feature availability in any way. Nothing contained in these materials is intended to, nor shall have the effect of, stating or implying that any activities undertaken by you will result in any specific sales, revenue growth or other results. All customer examples described are presented as illustrations of how those customers have used IBM products and the results they may have achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics may vary by customer. IBM, the IBM logo, Lotus Notes, Domino, Quickr, Sametime, Web. Sphere, UC 2, Partner. World and Lotusphere are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. Unyte is a trademark of Web. Dialogs, Inc. , in the United States, other countries, or both. Java and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both. Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both. Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
a0f57b17487d0953a8eb3476539ae00d.ppt