b4f5619cceda5a0a4870890727509145.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Boulder’s Carbon Tax: History & Implementation Jonathan Koehn Environmental Affairs Manager, City of Boulder, Colorado GRA 2007 Research Conference August 7, 2007

Climate Change? Can cities really make a difference?

What we’ll talk about: l l l Orient you to Boulder Development of Boulder’s Climate Action Plan The Carbon Tax 2007 Implementation Plans What will the future hold?





Boulder’s Political Context l l l smart policy decisions over the decades have created a solid foundation from which to build financial resources, community support, and political will to be an innovator and leader “powerful” municipal image in Colorado

Climate Change in the News

Boulder’s Climate Action Plan: How we got here Sustainability is about problem solving …………………. think out here

Boulder’s Climate Action Plan: How we got here l l May 2002: Boulder City Council adopts Kyoto Protocol goals for the city: “Reduce community-wide greenhouse gas emissions to 7% below 1990 levels by 2012. ” 2003: volunteer group develops framework for Climate Action Plan; city spends $100, 000 developing a detailed GHG inventory

Boulder’s Climate Action Plan: How we got here l l November 2004: City Council appropriates $258, 000 annually in 2005 and 2006 for GHG reduction programs and development of a Climate Action Plan (CAP), including longterm funding options 2005: Council, staff, and key stakeholders develop overarching strategies for the CAP and explore funding options; staff begins ramping up limited programs

Boulder’s Climate Action Plan: How we got here 2006: l Climate Action Plan Committee shepherds CAP toward completion; adopted by city council in June l Council determines carbon tax is best revenue source for implementation, places tax on November ballot l Measure passes, 60. 5% in favor, 39. 5% opposed
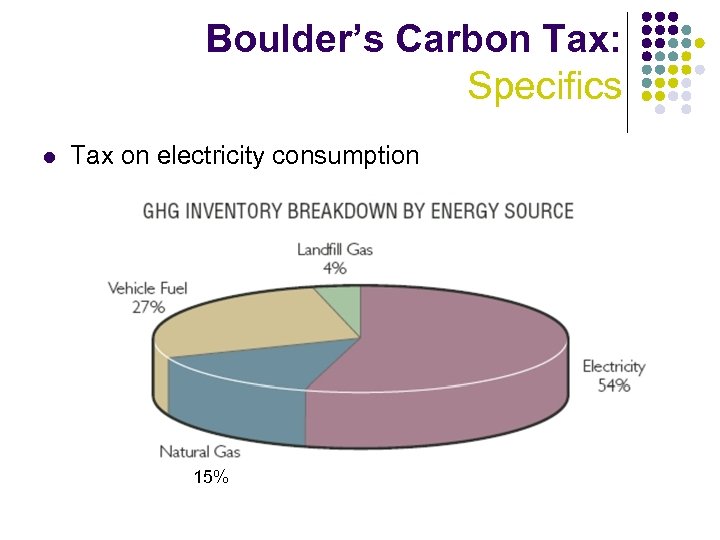
Boulder’s Carbon Tax: Specifics l Tax on electricity consumption 15%

Boulder’s Carbon Tax: Specifics l Maximize voluntary emissions reductions through: l Education, outreach and marketing l Reducing barriers to energy efficiency and renewable energy l Connecting residents and businesses with available rebates and tax credits

Boulder’s Carbon Tax: Specifics l l l l Applies to all electricity customers in the city No tax charged for green power customers Rates set in direct proportion to expected program sector expenditures Rates can be re-set depending on program needs Rates can be increased by 20% Sunsets in 2012 Will raise approximately $1 million per year
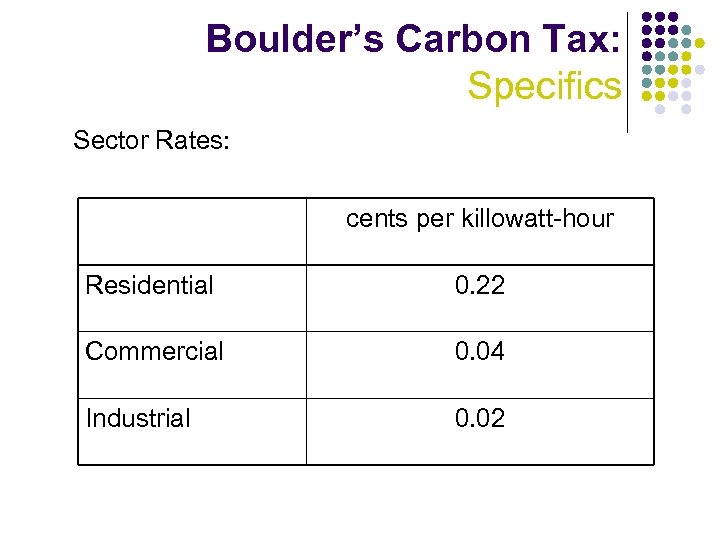
Boulder’s Carbon Tax: Specifics Sector Rates: cents per killowatt-hour Residential 0. 22 Commercial 0. 04 Industrial 0. 02

Climate Action Plan Strategies Increase energy efficiency Switch to renewable energy and vehicle fuels Reduce vehicle miles traveled 1. 2. 3. Maximize voluntary emissions reductions through: l l l Education, outreach and marketing Connecting residents and businesses with available rebates and tax credits Providing services not offered in the Boulder market
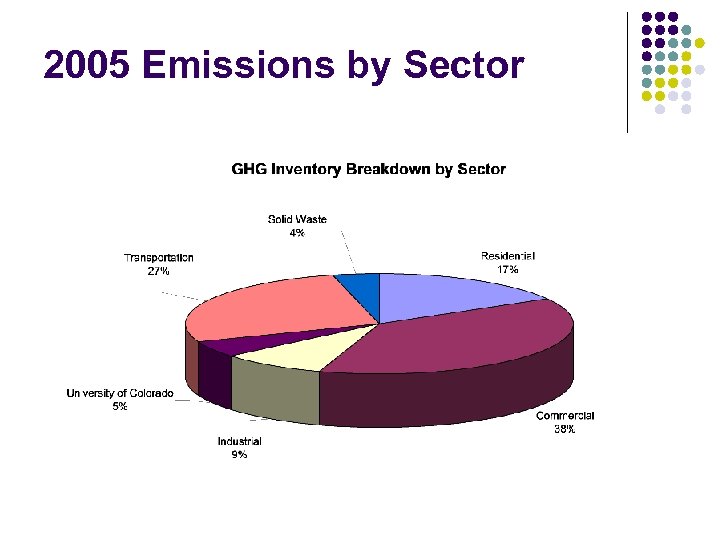
2005 Emissions by Sector

Residential Sector Characteristics l l l 17% of total GHG emissions Approximately 51, 030 residential units, 45% single-family and 55% multi-family dwellings Roughly half of housing units are rental properties
Energy Efficiency Current Programs Income – Qualified Weatherization l 2007 Budget: $40, 000, for 20 homes l Increased income guidelines to 78. 5% of AMI (HUD + 10%) and opened to renters l Measures include: l l l l Insulation Furnace replacement Refrigerator replacement Programmable thermostat Duct sealing CFLs Considering evaporative cooling

Energy Efficiency Current Programs Residential Energy Audit Program l l l 2007 Budget: $33, 450 218 homes in the city of Boulder Homeowner pays $100 of the audit cost

Energy Efficiency Current Programs Boulder Energy Brigade l 2007 budget $30, 000 l 2006 pilot targeted 550 homes with kits, and conducted 63 1 hour audits l Program highlights: l Deliver kits with low-cost, no-cost efficiency measures and educational literature
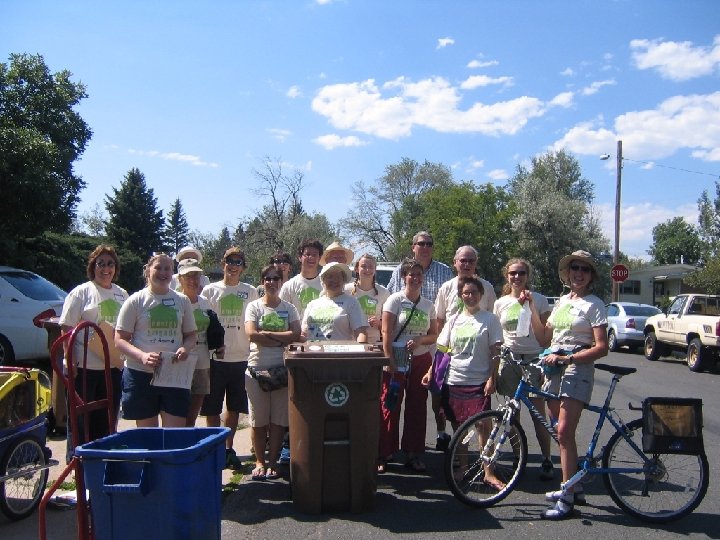


Energy Efficiency Current Programs Multi-Family Unit Audits l l 4 MFUs audited in 2006 2007 budget - $25, 000 Water conservation matching budget 2007 Goal – 15 buildings as well as working with property owners to implement recommendations

Energy Efficiency Current Programs Home Performance w/ ENERGY STAR (HPw. ES) l l 2007 budget: $20, 000 Intensive contractor training aimed to transform market CFL giveaway/buy down l l 2007 budget: $9, 000 focus on buy-down and coupon program in conjunction with Xcel’s buy down Conserv. ED: 100 th Human Initiative l l 2007 pilot budget: $3, 000 Energy Impact Analyses for 30 homes

Energy Efficiency Residential Programs to be developed in 2007 l l l Home Energy Makeover Refrigerator Round-up Insulation Buy-down Public Housing Retrofits Updated Lighting Program Integrate Green Building Programs – Training and Education

Commercial Sector Characteristics Context: l l l 1, 600+ Commercial Buildings 30 million sq ft of space 38% of Boulder’s emissions Goals through 2012: l l l 20% reduction in electricity use 5% reduction in natural gas consumption Reach 1/3 of commercial building stock

Commercial Sector 2007 Work Plan Energy Efficiency l l l Budget: $128, 000 Goal: 500, 000 k. Wh reductions implemented Strategies: l Establish Trade Ally network l Focused and robust training for property owners, managers, and contractors on building energy efficiency and Xcel Energy rebates

Commercial Sector Xcel Energy Commercial rebates and other programs l l l l Cooling efficiency Compressed Air efficiency Custom Efficiency Energy Design Assistance Energy Management System Lighting Efficiency Motor Efficiency Recommissioning

Renewable Energy Programs l l Boulder Wind Challenge Solar promotion Ideas: l Neighborhood renewable energy competitions l Bulk purchases of solar equipment l Collaborate with local RE suppliers and nonprofits to maximize visibility and promotion

Industrial Sector l l Just 13 industrial customers in Boulder 9% of GHG emissions Focus will be on leveraging Xcel Energy programs Looking into industrial “self-direct” approach

Transportation l l l 27% of total GHG emissions Goal: Reduce emissions by 40, 000 tons by 2012 Focus of CAP will be on promoting and increasing access to renewable fuels and promoting highly-efficiency and flex-fuel vehicles
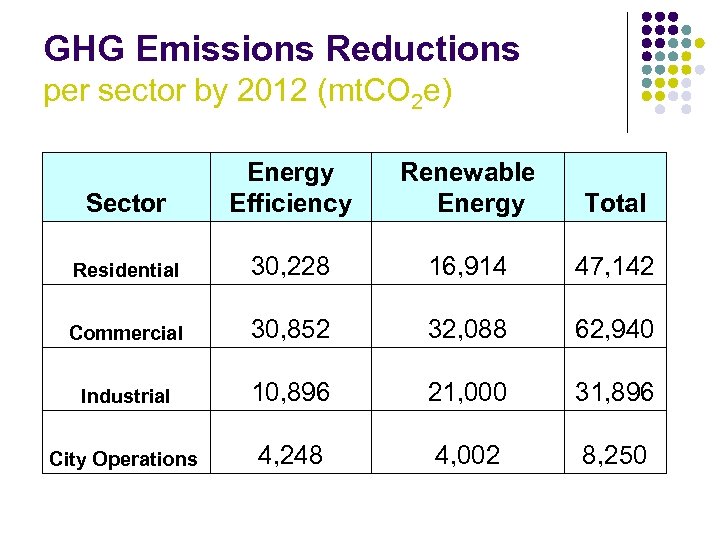
GHG Emissions Reductions per sector by 2012 (mt. CO 2 e) Sector Energy Efficiency Renewable Energy Total Residential 30, 228 16, 914 47, 142 Commercial 30, 852 32, 088 62, 940 Industrial 10, 896 21, 000 31, 896 City Operations 4, 248 4, 002 8, 250
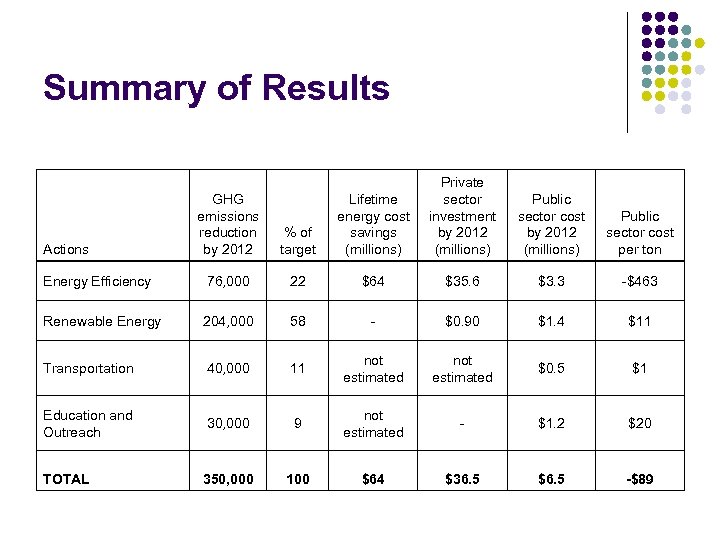
Summary of Results Private sector investment by 2012 (millions) Public sector cost per ton GHG emissions reduction by 2012 % of target Lifetime energy cost savings (millions) Energy Efficiency 76, 000 22 $64 $35. 6 $3. 3 -$463 Renewable Energy 204, 000 58 - $0. 90 $1. 4 $11 Transportation 40, 000 11 not estimated $0. 5 $1 Education and Outreach 30, 000 9 not estimated - $1. 2 $20 TOTAL 350, 000 100 $64 $36. 5 $6. 5 -$89 Actions

Next Steps Climate Action Plan efforts: • Program branding • Awards programs • CAP Symposium Other policy efforts: • Solar rebates and municipal solar installations • Building energy codes • Renewable Energy investments • Municipalization

Boulder’s Carbon Tax: What we’ve learned l l City council and city management leadership and commitment is critical Involve your residents in designing your plan and approach Engage your key community stakeholders – and listen to what they have to say Keep the issue in front of your community

Contact Information: Jonathan Koehn Environmental Affairs Manager, City of Boulder Colorado 303 -441 -1915 koehnj@bouldercolorado. gov www. environmentalaffairs. com
b4f5619cceda5a0a4870890727509145.ppt