4db255404aa5a6fc0b8a4985aaed52fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Botnets Dr. Neminath Hubballi IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Introduction § Bot: A program performing automated task § A bot itself is not bad § A botnet is a collection of computers, which are connected and work under the instruction of a master in order to accomplish something § Typically botnets are used for committing computer crimes § A botnet is controlled by a person or a group of people § Usually has monetary interests § Advertisement companies § Spam sending companies: outsource the work to bots IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Motivation § A report from Dhamballa, 2010 – number of infections increased at the rate of 8% per week § Almost every botnet newly created overtaking the previous largest § Financial profits § § § User credential stealing Click fraud Political interests § § § DDo. S attacks Spamming Traffic sniffing Spreading malware Port scanning Key loggers etc. . § Illegal activity include IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Components of a Botnet Infrastructure § Command Control Infrastructure § Centralized § Client server model § Distributed § Works more autonomously § Also called as peer to peer botnets § Crucial § Have to maintain a stable connectivity § Robust § Stable § Reaction time § Communication protocol IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
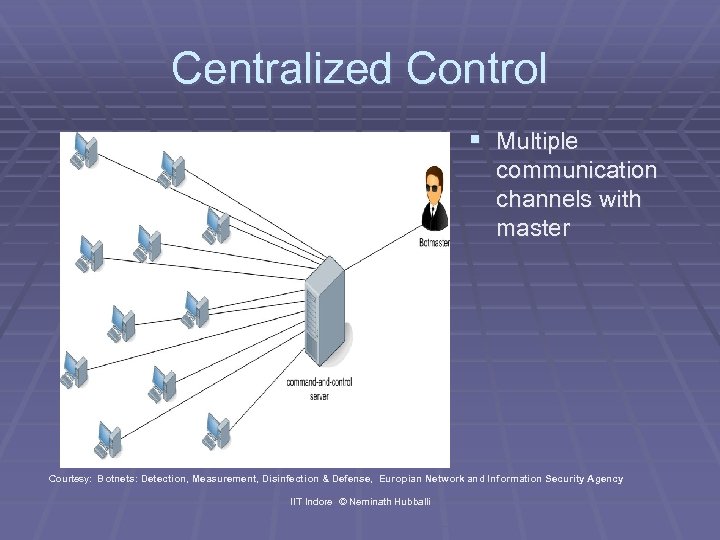
Centralized Control § Multiple communication channels with master Courtesy: Botnets: Detection, Measurement, Disinfection & Defense, Europian Network and Information Security Agency IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
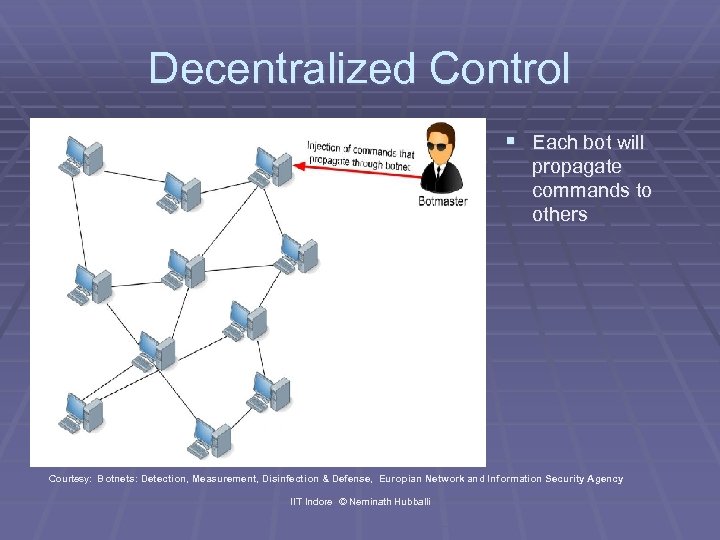
Decentralized Control § Each bot will propagate commands to others Courtesy: Botnets: Detection, Measurement, Disinfection & Defense, Europian Network and Information Security Agency IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Botnets Types § There are 2 types of botnets § Operate through IRC § Operate through web server § Operate as Peer-to-Peer network IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Internet Relay Chat (IRC) based § Uses a Push model of communication § Master pushes commands for execution to the Bots § All Bots receive commands through IRC PRIVMSG, understand the instruction and execute the command send back results § In order to issue commands Botmaster first authenticates herself with a username and password § Advantages § Open source § Easy for modification § Two way communication § Real-time connectivity § Public and private mode interaction § Disadvantages § § Single point of failure Easily detectable IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Communication Over IRC § Sequence of Events § Master authenticates § Master queries info about § § § botnet –version number Master queries system information Issue instruction to scan other potentially vulnerable machines Bot replies with scan results Courtesy: Botsniffer: Detecting Botnet Command Control Channels in Network Traffic IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
HTTP based § This type of Botnet uses HTTP as a communication medium § Uses a pull method of interaction § Bots periodically poll the master requesting new commands to be issued § Through a HTTP post method Bots connect to the master § Usually used form submissions § Advantage of using HTTP § It becomes difficult to detect § Port 80 is open in all firewalls § Normally encryption is used to avoid detection and eavesdropping IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Role of DNS in Botnet § DNS has an important role to play in Botent networks § It allows changes to be done to the Botnet infrastructure transparently § Fast Flux Networks § § § Create a domain evil. com Authoritative DNS server for the network evil. com is owned by attacker Attacker has multiple infected machines in her possession The RR mapping is changed at a very high frequency Each time the client connects to a different infected machine or Bot machine § All of these machines or Bots act as a proxy to the Bot server § Increases the resiliency of Botnet infrastructure IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
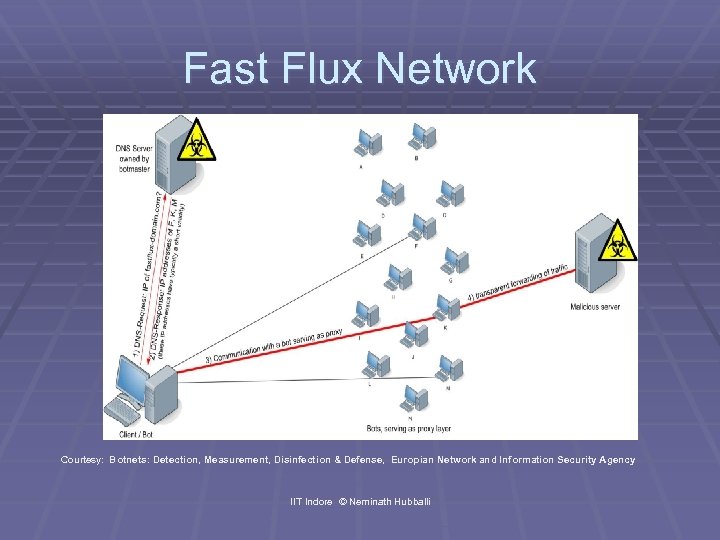
Fast Flux Network Courtesy: Botnets: Detection, Measurement, Disinfection & Defense, Europian Network and Information Security Agency IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Who Suffers from Botnet § Three entities § § § Victim – suffers directly ISP – have to carry lot of malicious traffic Third party – effect of malware § Defense § § § Victim- corporates have to protect their IT assets ISP – detect malicious traffic Third party – keep the machine clean IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Threat Characterization § Botnet Size and Origin § Footprint- Number of infected machines indicates scaling factor § Live Population – How many of infected machines are able to interact using CC infrastructure currently § Spam throughput: Received spam emails per unit of time § Freshness of IP address in spam emails –fresh one is better § Bandwidth usable for DDo. S attacks § Harvested personal data – more data approximately leads to more financial gain IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Botnet Detection § There are two types of detection mechanisms § Passive techniques § Activity can be tracked without interfering with environment § No disturbance § Active techniques § Blocking malicious domains and identifying infected machines IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Source of Data for Passive Detection § Packet analysis § Shell code detection § Protocol filed § Combination of some fields etc. § Drawbacks § § Full packet inspection is difficult Scaling is a factor Only known patterns are detected If the attack code is split across multiple packets, streams it is far more difficult to detect IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Source of Data for Passive Detection § Flow Record Analysis § Flow is a summary of what transpired in communication § Typical attributes are: § Source and destination address § Related port numbers § Protocol used inside the packets § Duration of the session § Cumulative size and § Number of transmitted packets. § Drawbacks § Payload is ignored § Keep track of all sessions § Switches and routers do it for you Courtesy: Bot. Grep IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Source of Data for Passive Detection § Use of DNS Data § Identify Fast Flux Networks § Collect DNS queries and responses and do an offline analysis § Identify “typo squatting” domain names in the data § Ex. Goggle. com § Malicious domain name can be blocked by domain registrars § Currently not happening § If a domain is identified as a malicious domain § In all likelihood the queries to that domain are from infected machines § It helps to track down even those machines IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
Source of Data for Passive Detection § Use of spam email analysis § Botnets often run spam campaigns § All spam emails will have similarity § In contents § Pattern § Length of mail § Source IP address used (often they reuse the IP addresses) § Antivirus software feedback § Collect information from many sensors IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
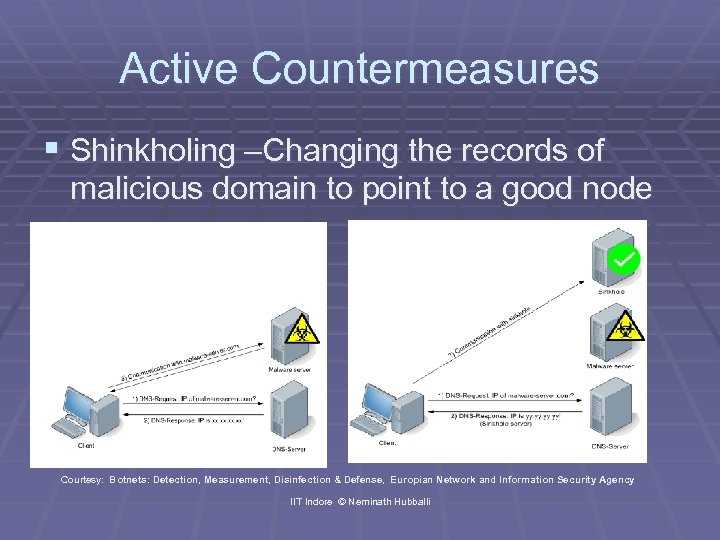
Active Countermeasures § Shinkholing –Changing the records of malicious domain to point to a good node Courtesy: Botnets: Detection, Measurement, Disinfection & Defense, Europian Network and Information Security Agency IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi

Active Countermeasures § Identifying infected Machines through DNS Cache Snooping § This will help identify whether any machines in the local network are part of a malicious domain § Issue a query to a DNS server for a domain which is suspicious § Verify the TTL value § If any other machine has already visited that domain, it is likely that TTL value has decreased w. r. t the default TTL value given by authoritative name server § Another variation is through by setting RD flag off IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
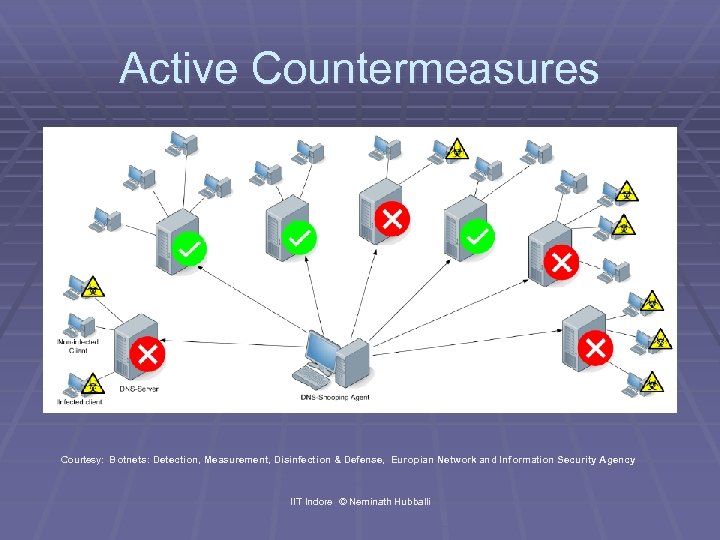
Active Countermeasures Courtesy: Botnets: Detection, Measurement, Disinfection & Defense, Europian Network and Information Security Agency IIT Indore © Neminath Hubballi
4db255404aa5a6fc0b8a4985aaed52fe.ppt