efb8f3dc5fcdc965f2f5e411d8cf2353.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

“Born ASEAN”Project Module 31 Reverse Financials October, 2015 Advisor, Waseda University Dr. Takeru Ohe

Table of Contents 1. Drill Basic Math 2. Unit of Business 3. Reverse Financials (Revenue stream and cost structure) 4. Performance of the current business 5. Performance Requirements of new business 6. Performance Requirements of new business in relationship to the Main business 7. Profit Models Revenue stream and cost structure 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 2

1. DRILL BASIC MATH 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 3

2.UNIT OF BUSINESS 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 5
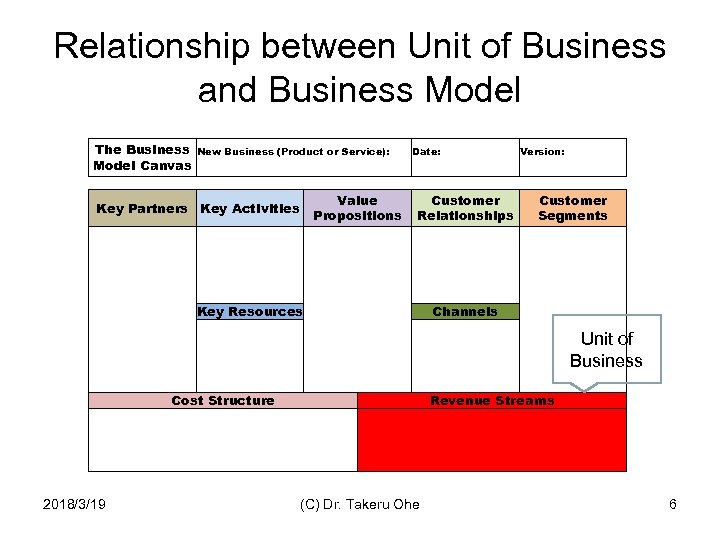
Relationship between Unit of Business and Business Model The Business Model Canvas New Business (Product or Service): Value Propositions Key Partners Key Activities Date: Version: Customer Relationships Customer Segments Key Resources 2018/3/19 Cost Structure Channels Revenue Streams (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe Unit of Business 6

Unit of Business • Unit of business is the fundamental thing that you sell. – For manufacturing companies, the traditional unit of business is literally a unit, typically of a Innovation product. – In services, the potential units of business are more varied. Typically, professional services firms (law firms, accountancies, consultants) charge for a unit of time, such as a billing day. Concept of “Unit of Business” is defined in Page 237, Rita Gunther Mc. Grath and Ian Mac. Millan 2000 The Entrepreneurial Mindset, Harvard Business School Press. 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 7

Unit of Business (Example 1) Changing the unit of business for growth • One way to growth is to change the rules by changing the unit. – One bicycle seller changes to bicycle-for-rent business and to bicycle-for-share business. 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 8

Unit of Business (Example 2) From car selling to car sharing (Forbes Asia Dec. 22, 2008) • The planet’s getting crowded and streets more congested. It might be time for carmakers to stop making cars-and sell transportation instead 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 9

Zipcar. com • We envision a future where car-sharing members outnumber car owners in major cities around the globe. • Zipcar is the world's largest car sharing and car club service. It is an alternative to traditional car rental and car ownership. Share Zipcars in Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, London, New York, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Portland, San Francisco, Seattle, Toronto, Vancouver and Washington DC. Zipcars also live on campus at universities across North America. 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 10

Unit of Business (Example 3) from hairdo to just haircut • A barbershop in Tokyo usually charges the 30 US$. It takes around 60 minutes for a hairdo including hair cut, shaving, shampoo, massage, and etc. The receipt describes as the charge of a hairdo. • QB Net Co. , Ltd. – Hair cut only: 10 minutes for 10 US$ – Started in 1996 and now it has 393 stores 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 11

QB Net Co. , Ltd. • QB" = "Quick Beauty" • "QB House" was born in Tokyo Japan since year of 1995. has revolutionized the way to cut your hair. Our innovative concept, combined with the latest technology and well trained and polished stylists, enables us to complete a haircut in just 10 minutes for SGD $10 / HKD $50 - only! QB offers high quality, seamless services to consumers on the move, who can now experience the innovative concept of SAVE your time & money –for everyday people! 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 12

New Business from Old Business • Select one of traditional business, and identify the current unit of business, then try to find a new unit of business Current Unit of Business New Unit of Business 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 13
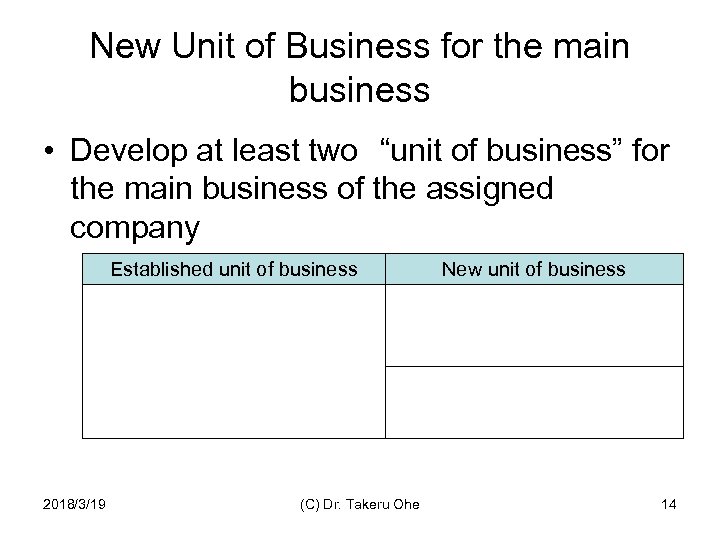
New Unit of Business for the main business • Develop at least two “unit of business” for the main business of the assigned company Established unit of business 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe New unit of business 14

3. REVERSE FINANCIALS (REVENUE STREAM AND COST STRUCTURE) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 15
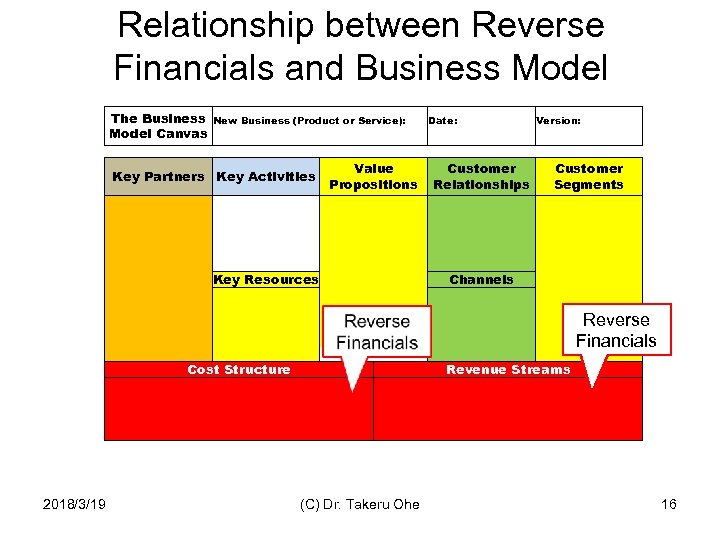
Relationship between Reverse Financials and Business Model The Business Model Canvas New Business (Product or Service): Value Propositions Key Partners Key Activities Date: Version: Customer Relationships Customer Segments Key Resources 2018/3/19 Cost Structure Channels (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe Reverse Financials Revenue Streams 16

Reverse Financial Statements • Do the financials from the bottom line up rather than from the top line down. • Start at the bottom line with target profits, target return on assets, and subsequent sales required. • Determine the required level of revenues and finally allowable costs and allowable investment. – Required profits= required revenue minus allowable costs – Required rerun on assets=required profits divided by allowable assets – Required unit volume=required revenue divided by allowable price The concept of Reverse Financials is developed by Prof. Ian Mac. Millan (The Entrepreneurial Mindset, HBR 2000) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 17

Is this return worth for risk and effort? 4. PERFORMANCE OF THE CURRENT BUSINESS 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 18
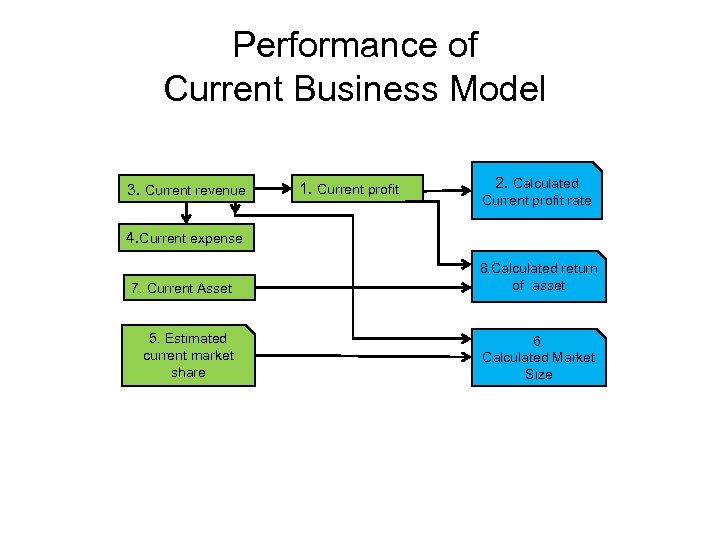
Performance of Current Business Model 3. Current revenue 1. Current profit 2. Calculated Current profit rate 4. Current expense 7. Current Asset 8. Calculated return of asset 5. Estimated current market share 6. Calculated Market Size
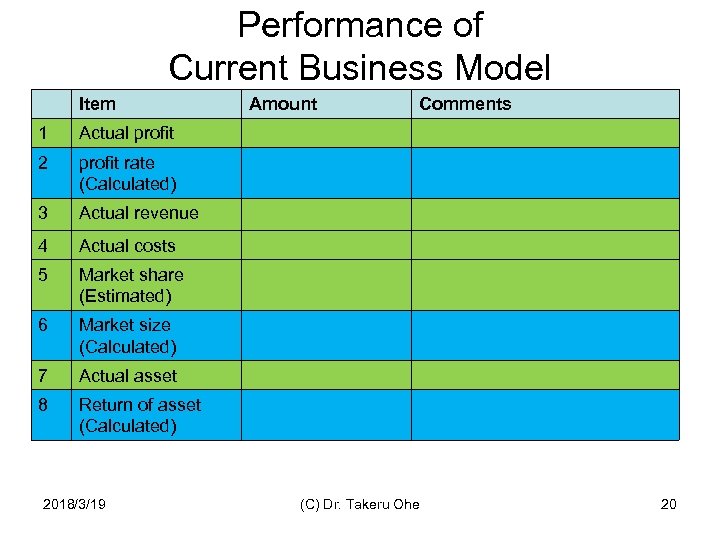
Performance of Current Business Model Item 1 profit rate (Calculated) 3 Actual revenue 4 Actual costs 5 Market share (Estimated) 6 Market size (Calculated) 7 Actual asset 8 Comments Actual profit 2 Amount Return of asset (Calculated) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 20

Is this return worth for risk and effort? 5. PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR NEW BUSINESS 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 21
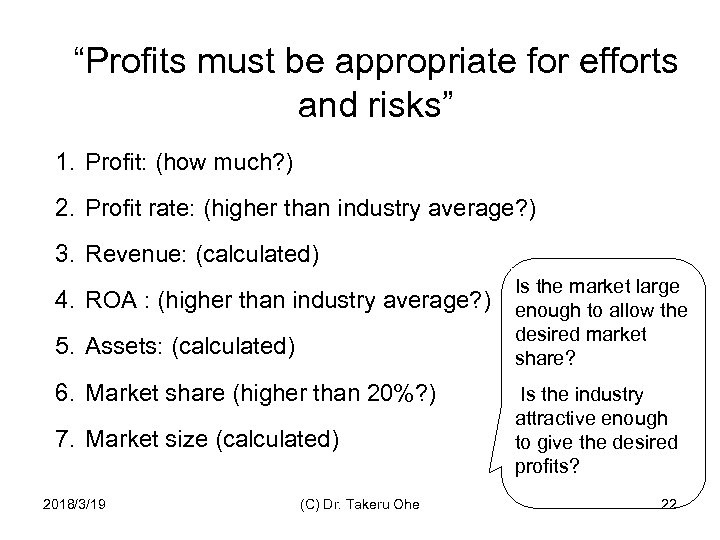
“Profits must be appropriate for efforts and risks” 1. Profit: (how much? ) 2. Profit rate: (higher than industry average? ) 3. Revenue: (calculated) 4. ROA : (higher than industry average? ) 5. Assets: (calculated) 6. Market share (higher than 20%? ) 7. Market size (calculated) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe Is the market large enough to allow the desired market share? Is the industry attractive enough to give the desired profits? 22
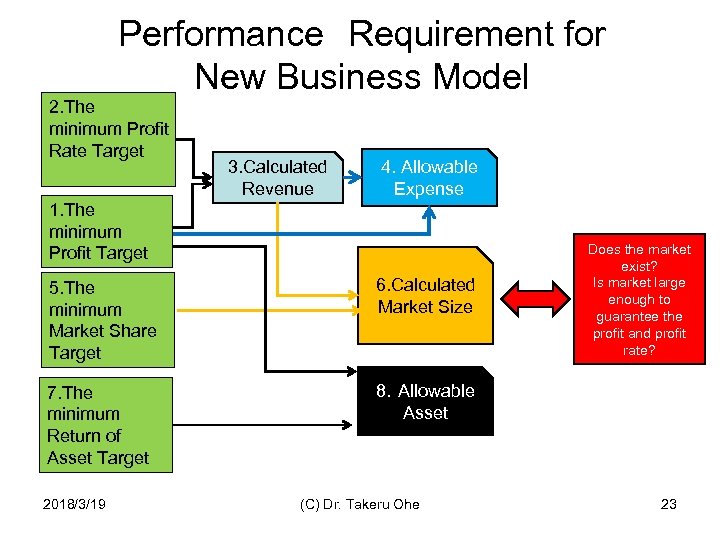
Performance Requirement for New Business Model 2. The minimum Profit Rate Target 3. Calculated Revenue 4. Allowable Expense 1. The minimum Profit Target 5. The minimum Market Share Target 6. Calculated Market Size 7. The minimum Return of Asset Target Does the market exist? Is market large enough to guarantee the profit and profit rate? 8.Allowable Asset 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 23
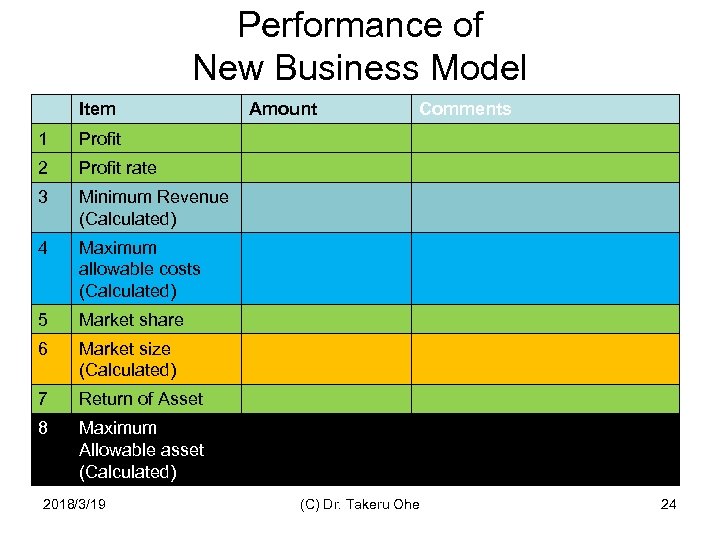
Performance of New Business Model Item 1 Profit rate 3 Minimum Revenue (Calculated) 4 Maximum allowable costs (Calculated) 5 Market share 6 Market size (Calculated) 7 Return of Asset 8 Comments Profit 2 Amount Maximum Allowable asset (Calculated) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 24

Exercise Return from New Business 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Estimate how much profit is the assigned firm is going to earn from this new business. Estimate the profit rate of this new business (at least equal to the industry average) Calculate the revenue from the profit and the profit rate. Estimate the market share of this new business (at least 20%) Calculate the total market size from the market share and the revenue of this business. Estimate the ROA for this new business (at least equal to the industry average). Calculate the allowable asset of this new business. . 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 25

Is this return worth for risk and effort? 6. PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS OF NEW BUSINESS (2) IN RELATIONSHIP TO Ohe THE MAIN 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru BUSINESS 26

Example: Is market large enough to guarantee the profit and profit rate? • • • Profit to be twice of your current business Profit Rate to be twice of your current business Revenue is calculated from profit and profit rate. Market share to be 20% Required market size is calculated from market share and calculated revenue • Calculated market size to be compatible to actual market size 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 27
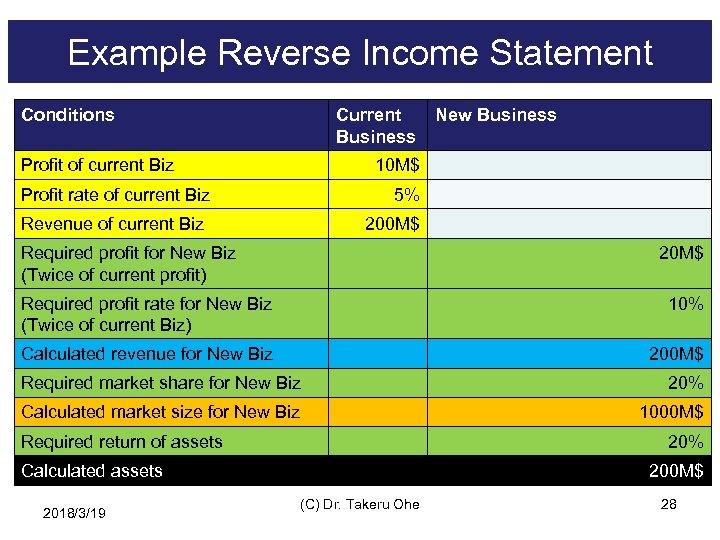
Example Reverse Income Statement Conditions Current Business Profit of current Biz New Business 10 M$ Profit rate of current Biz 5% Revenue of current Biz 200 M$ Required profit for New Biz (Twice of current profit) 20 M$ Required profit rate for New Biz (Twice of current Biz) 10% Calculated revenue for New Biz 200 M$ Required market share for New Biz 20% Calculated market size for New Biz 1000 M$ Required return of assets 20% Calculated assets 2018/3/19 200 M$ (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 28
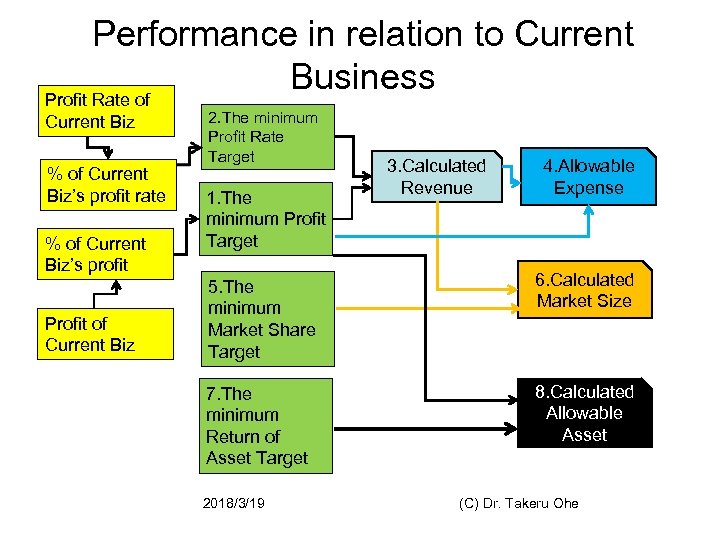
Performance in relation to Current Business Profit Rate of Current Biz % of Current Biz’s profit rate % of Current Biz’s profit Profit of Current Biz 2. The minimum Profit Rate Target 1. The minimum Profit Target 3. Calculated Revenue 4. Allowable Expense 5. The minimum Market Share Target 6. Calculated Market Size 7. The minimum Return of Asset Target 8. Calculated Allowable Asset 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe

Exercise Is this new business worth for the assigned company 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Estimate how much profit is the firm is going to earn from this business model. Estimate the profit rate of this business model (at least equal to the industry average) Calculate the revenue from the profit and the profit rate. Estimate the market share of this business model (at least 20%) Calculate the total market size from the market share and the revenue of the company. Estimate the ROA for this business model (at least equal to the industry average). Calculate the asset of this business model. 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 30
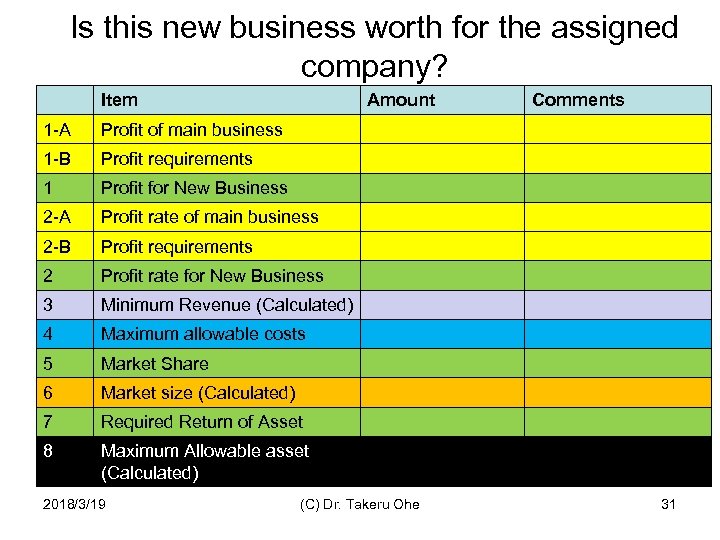
Is this new business worth for the assigned company? Item Amount 1 -A Profit of main business 1 -B Profit requirements 1 Profit for New Business 2 -A Profit rate of main business 2 -B Profit requirements 2 Profit rate for New Business 3 Minimum Revenue (Calculated) 4 Maximum allowable costs 5 Market Share 6 Market size (Calculated) 7 Required Return of Asset 8 Comments Maximum Allowable asset (Calculated) 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 31

7. PROFIT MODELS REVENUE STREAM AND COST STRUCTURE 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 32
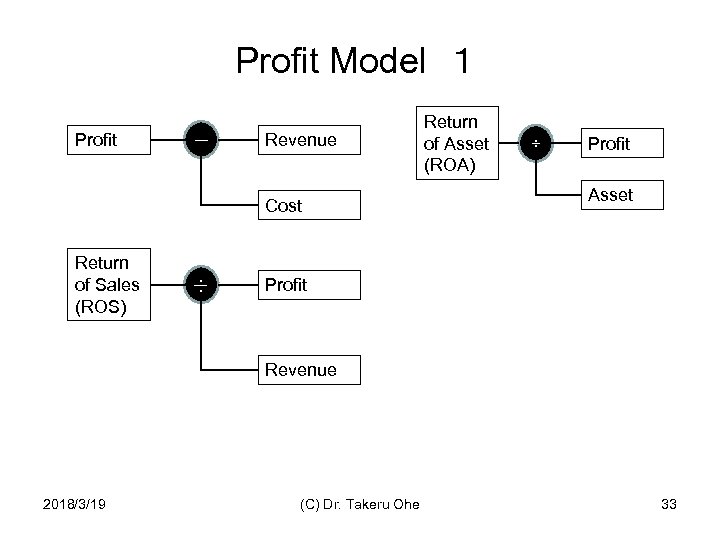
Profit Model 1 Profit - Revenue Cost Return of Sales (ROS) ÷ Return of Asset (ROA) ÷ Profit Asset Profit Revenue 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 33
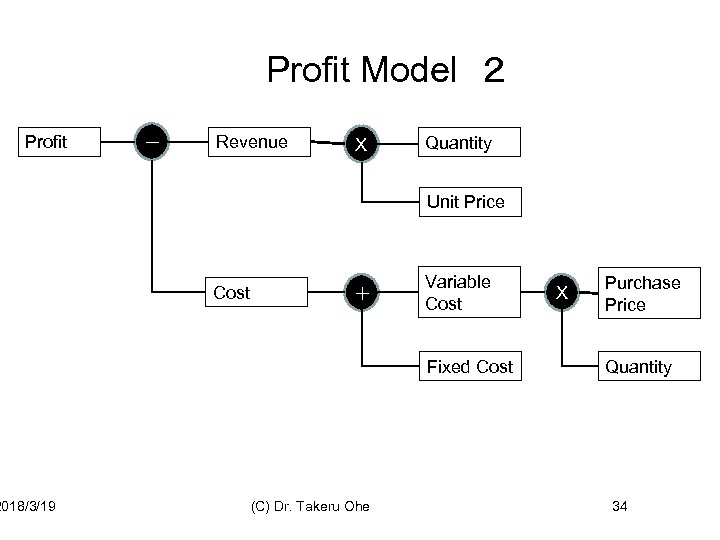
Profit Model 2 Profit 2018/3/19 - Revenue X Quantity Unit Price Cost + Variable Cost Fixed Cost (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe X Purchase Price Quantity 34
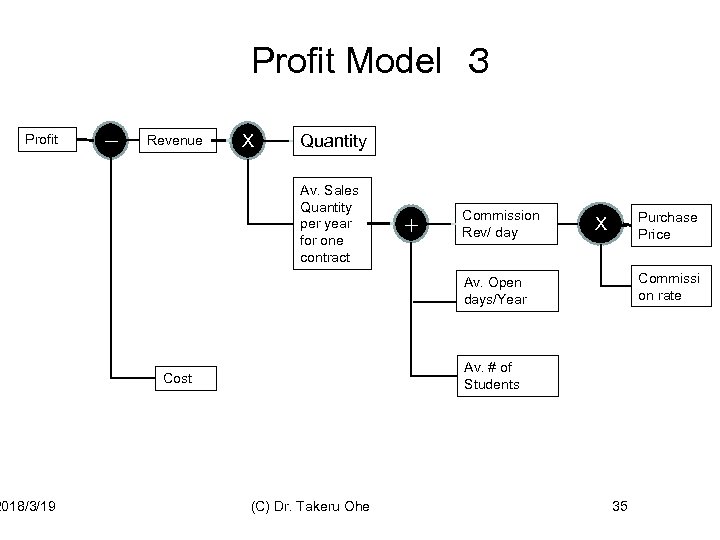
Profit Model 3 Profit 2018/3/19 - Revenue X Quantity Av. Sales Quantity per year for one contract + Commission Rev/ day Purchase Price X Commissi on rate Av. Open days/Year Av. # of Students Cost (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 35

Exercise 31 -6 Profit Model • Draw the profit model of the current business of the assigned firm 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 36

Exercise Write down a new business idea for the assigned firm • The idea must be satisfied your risk & return framework! • Who are the customers for your business? • What kind of problems do the customers have right now? • What kind of solutions which you are going to offer to the unsatisfied customers? • What are the difference from your competitors? 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 37

Exercise Profit Model of a new business idea for the assigned firm • Draw the profit model of the new business idea which you mentioned in Exercise 31 -7 2018/3/19 (C) Dr. Takeru Ohe 38
efb8f3dc5fcdc965f2f5e411d8cf2353.ppt