fb76810f470b23a7f43c7d0416d97015.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

BOARD LEADERSHIP & GOVERNANCE - General Overview - Legal & Regulatory Framework By CS. CHARLES KANJAMA Managing Partner, Muma & Kanjama Advocates Certified Secretary (CPS(K)), Arbitrator (M. CIArb) Certified Accountant (CPA(K)) 9 th July 2015, Panafric Hotel, Nbi.

OUTLINE Introduction – Governance & Corporations 1. Legal & Regulatory Framework 2. Corporate/Board Governance – Concepts, Principles, Illustrations 3. Codes & Best Practices ¢ Conclusion ¢

INTRODUCTION – Governance & Corporations ¢ 1776, US Declaration of Independence “We hold these truths as self evident, that all men are created equal, and endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights, that among these are life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these ends, governments are formed among the people, deriving their just powers from the governed, and when any government becomes destructive of these ends, it is their right to alter and abolish it, and establish another one in its place…” The modern notion of governance: Democracy & Accountability

INTRODUCTION – History of Commercial Associations ¢ Medieval Period Merchant Guilds, l Partnerships or Societies, l Merchant Adventures/Joint Stock Companies, l Chartered/Monopoly Corporations - domestic l ¢ The South Sea Bubble (UK), 1711 -1720 Share dealing, Stock broking – combine the capitalist with the entrepreneur l Promoters, Speculators – boom, theft/misuse, bust l South Sea Company acquires most national debt; shares fall from 1000% to 125% in 6 mths (1720) l

INTRODUCTION – History of Commercial Associations ¢ 1720 -1844: The Bubble Act Unincorporated companies l Deed of settlement companies l Statutory regulation l ¢ Modern Company Laws (UK): 1844, 1857, 1948, 1967, 1985, 1989 Concept of limited liability l Transparency & Accountability rules – prospectus, audit, disclosure, etc. l The development of corporate governance – Board, Management, Meetings, Regulation l

1. LEGAL FRAMEWORK – Kenyan Law on Corporate Structures ¢ The Companies Act, 1962 Incorporated companies (private/non-private, limited/unlimited, shares/guarantee) l Securitisation: Share Capital, Debentures, Charges l Management: Registers, Members, Returns, Meetings, Accounts & Audit, Directors, Secretary l Winding Up, Liquidators, Receivers & Managers l ¢ Other Statutes Partnerships Act – Partnership, Limited Partnership l Registration of Business Names Act l Limited Liability Partnership Act (llp) l

1. LEGAL FRAMEWORK – Kenyan Law on Corporate Structures ¢ Other Statutes Societies Act, Building Societies Act, Co-operative Societies Act, SACCO Societies Act l Political Parties Act l NGO Co-ordination Act l Public Benefits Organizations Act l Trustee Act, Trustee (Perpetual Succession) Act l Education Act, Universities Act – Education Institutions l Labour Relations Act - Trade Unions l Ministry of Labour & Social Services: Community Based Organisations (CBO) - unincorporated l

1. LEGAL FRAMEWORK – Kenyan Law on Corporate Structures ¢ Commercial Entities Microfinance Act – Microfinance institutions l Capital Markets Act – Listed institutions l Banking Act – Registered banks l Insurance Act – Insurance companies l ¢ State Corporations Act, etc l Constitutional Commissions – Chap 15, Constitution of Kenya, 2010 l Independent Offices l ¢ County Government Entities

1. REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1 st Level - The Formation Authority - E. g. Registrar of Companies, Registrar of Business Names, Registrar of Lands (for Trusts), NGO Board, etc. 2 nd Level - The Operational Authority - E. g. Capital Markets Authority, Central Bank, Insurance Regulatory Authority, National Education Board, etc.

1. REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1. 2. 3. 4. The Constitution of Kenya, 2010 Art 10. National Values & Principles of Governance Chapter 4, Bill of Rights Chapter 6, Leadership & Integrity Art 232, Values & Principles of Public Service Legislative Framework 1. Financial Matters – Public Finance Management Act 2. Procurement Issues – Public Procurement & Disposal Act 3. Integrity – Leadership & Integrity Act, Public Officer Ethics Act -

What is good governance ü ü ü According to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and Pacific “governance” means the process of decision making and the process by which decisions are implemented (or not implemented) Governance can be used in several contexts such as corporate governance, international governance, national governance and local governance. Good governance ensures corruption is minimized, the views of minorities are taken into account and the voices of the most vulnerable in society are heard in decision making.

What is good governance ü ü According to the United Nations office of the High Commissioner for Human rights “good governance” is the process whereby public institutions conduct public affairs, manage public resources and guarantee the realization of human rights in a manner essentially free of abuse and corruption and with due regard to the rule of law. Key questions is are the institutions of governance that we work for effectively guaranteeing the right to health, clean and safe water in adequate quantities, adequate housing, sufficient food, quality education, fair justice and personal security?

Aims of Good Corporate Governance ¢ Enhance transparency, accountability and probity; ¢ Increased profitability, effectiveness and efficiency; ¢ Responsibility and responsiveness; ¢ Enhanced creation of wealth and employment; ¢ Sustainability and competitiveness; ¢ Increased capacity to attract investment ¢ Enhanced responsibility and responsiveness

Characteristics of good governance ü 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. UN ESCAP lists 8 major characteristics of good governance Transparency Accountability Public participation Rule of law Responsiveness Consensus oriented Equity and Inclusiveness Effectiveness and Efficiency

CGG-Transparency ü ü ü Transparency means that a reliable, relevant and timely information about activities of the county government is available to the public. Decisions taken and their enforcement are done in a manner that follows rules and regulations Information is freely available and directly accessible to those who will be affected by such decisions and their enforcement

CGG-Accountability ü ü ü Accountability is a key requirement for good governance It is not only applicable to institutions of Government but also the private sector, civil society organizations must be held accountable to the public and their respective institutional stakeholders The County Government is accountable to those who will be affected by its decisions and actions

CGG-Public Participation ü Participation by all members of the society is a key cornerstone of good governance ü The members may participate directly or through legitimate intermediary institutions or representatives including institutions and other elected public officers

CGG-Rule of law ü Good governance requires fair legal framework that is enforced impartially. ü It also requires full protection of human rights and especially the rights of minorities ü It presupposes an impartial Judiciary and Police force when enforcing the laws

CGG-Responsiveness ü ü ü Effective accountability demands responsiveness from institutions and organizations that hold power. Responsiveness implies the capacity to deliver public policies and programs in an effective, efficient and participatory manner It also entails the ability to respond to the various stakeholders, delivery of public service and goods in an effective and efficient manner while respecting and protecting human rights

CGG-Consensus oriented ü ü Good governance requires mediation of the different interests in society to reach a broad consensus on what is in the best interest of the whole community and how this can be achieved. It is important to take note that consensus can be achieved through the understanding of the historical and social context of a given society or county.

CGG-Equity and Inclusiveness ü The long-term cohesion of every society depends on ensuring that all its members feel that they have a stake in the society and not to feel excluded. ü Good governance advocates for according all groups an opportunity to improve their well being

CGG-Effectiveness and Efficiency ü Good governance exists when processes and institutions produce results that meet the needs of society while making the best use of resources at their disposal. ü It also covers the sustainable use of natural resources and protection of the environment.
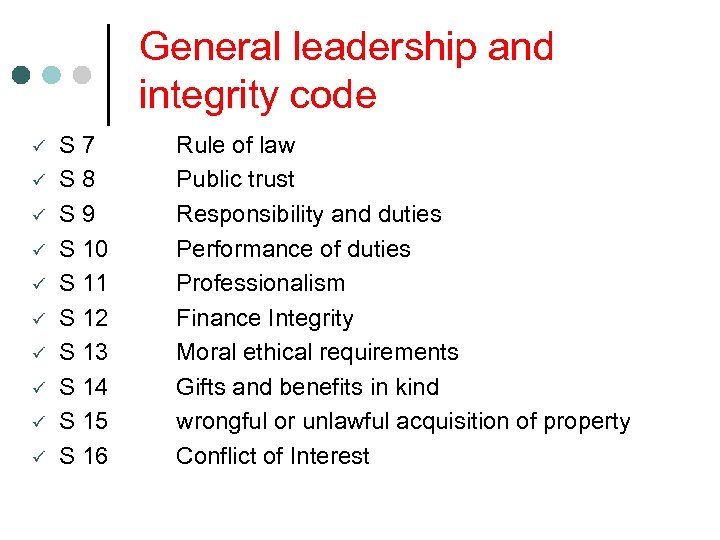
General leadership and integrity code ü ü ü ü ü S 7 S 8 S 9 S 10 S 11 S 12 S 13 S 14 S 15 S 16 Rule of law Public trust Responsibility and duties Performance of duties Professionalism Finance Integrity Moral ethical requirements Gifts and benefits in kind wrongful or unlawful acquisition of property Conflict of Interest
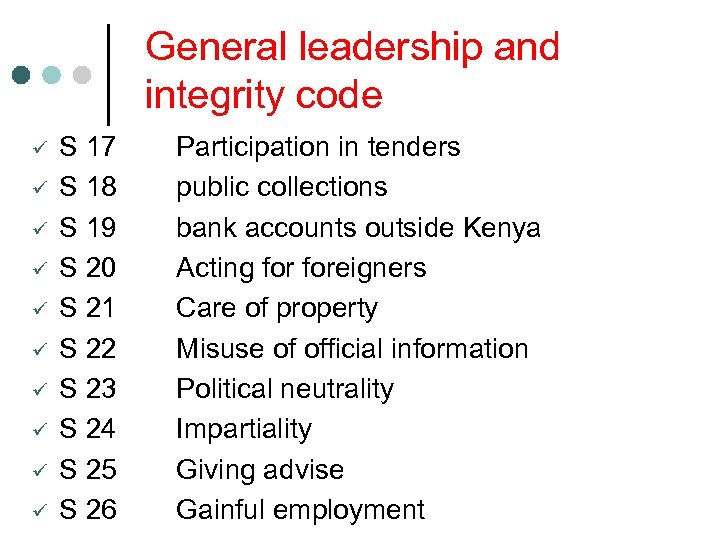
General leadership and integrity code ü ü ü ü ü S 17 S 18 S 19 S 20 S 21 S 22 S 23 S 24 S 25 S 26 Participation in tenders public collections bank accounts outside Kenya Acting foreigners Care of property Misuse of official information Political neutrality Impartiality Giving advise Gainful employment
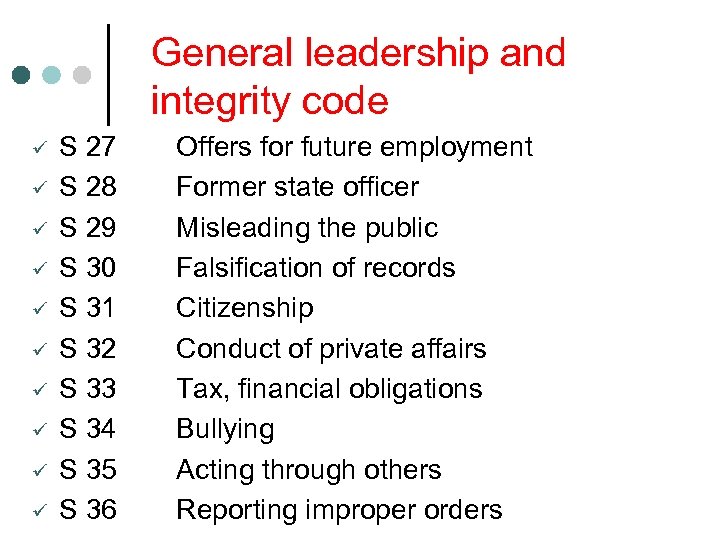
General leadership and integrity code ü ü ü ü ü S 27 S 28 S 29 S 30 S 31 S 32 S 33 S 34 S 35 S 36 Offers for future employment Former state officer Misleading the public Falsification of records Citizenship Conduct of private affairs Tax, financial obligations Bullying Acting through others Reporting improper orders

3. CODES, BEST PRACTICES ¢ ICPSK, Code of Governance for Private Organisations in Kenya Mwongozo Code of Governance for State Corporations ¢ CMA, Guidelines on Corporate Governance Practices by Public Listed Companies ¢ IFC, Corporate Governance Charter ¢ UK 1992, Cadbury Report ¢ US 2002, Sarbanes Oxley Act ¢ CMA 2014, Draft CG Blueprint ¢

3. BEST PRACTICE - Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Board of Directors Transparency & Disclosure Accountability, Risk & Internal Controls Ethical Leadership & Corporate Citizenship Shareholder Rights & Obligations Stakeholder Relationships Sustainability & Performance Management Compliance with Laws & Regulations

CONCLUSION The Board must identify strategic goals & focus on them ¢ Case Examples ¢ Appointment of CEO l Board Evaluation l Strategic Plan of the Organisation l Nomination/Recruitment of Board Members l THANK YOU
fb76810f470b23a7f43c7d0416d97015.ppt