297d3e7b4ec261c8f0c9028197951663.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
Bo. M / CAWCR. Text Generation in the Next-Gen Forecast System (GFE) J Bally & T Leeuwenburg

Background & Drivers. . Next-Gen Forecast System Better use of NWP models Systematic forecast process Temporal and spatial detail Can verify everything Efficiency gains Many new services: grids, graphics and text all from the same weather database
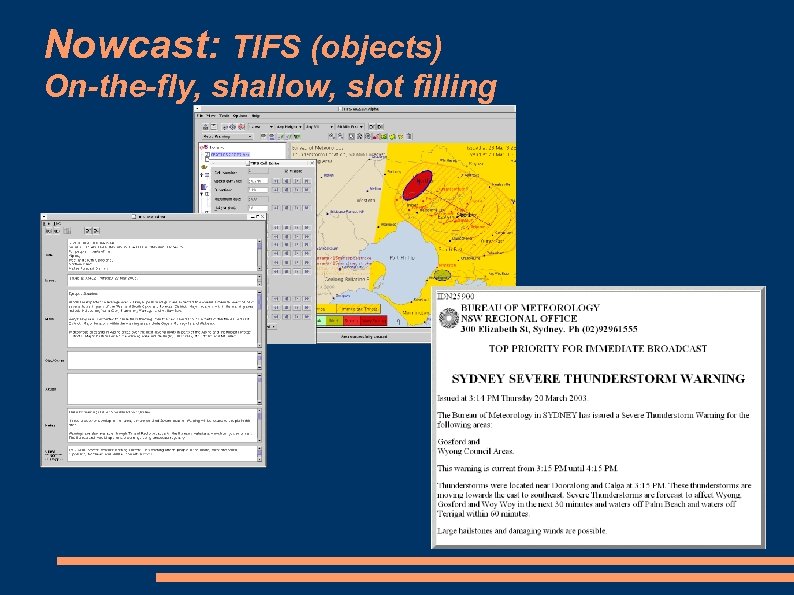
Nowcast: TIFS (objects) On-the-fly, shallow, slot filling
Text Generation… introduction Most sophisticated meteorological text generation system ? ? ? Large jump from “slot filling” systems (TIFS, TC, Scribe etc) Text as a network of nodes Goal directed multi-pass processing 64, 000 lines of python - > 15 p-yr development

Text Generation : example goals Try for <= three weather sub-phrases (2 for wind etc. ) Describe the weather trends, rather than a sequence Describe changes in weather only if the impact differs substantially Try for elegant sentence structure; split out unusual weather types if they are not part of the trend Must-goals (guarantees) vs should-goals ………. etc
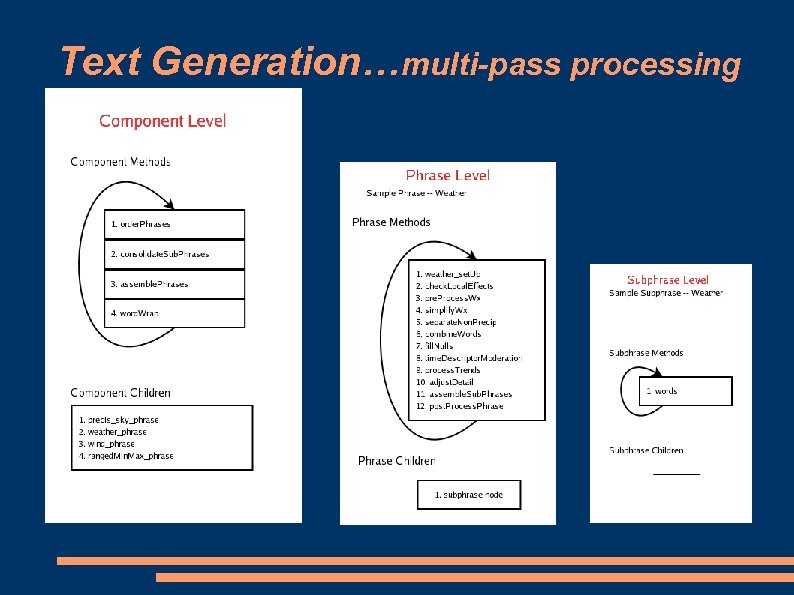
Text Generation…multi-pass processing
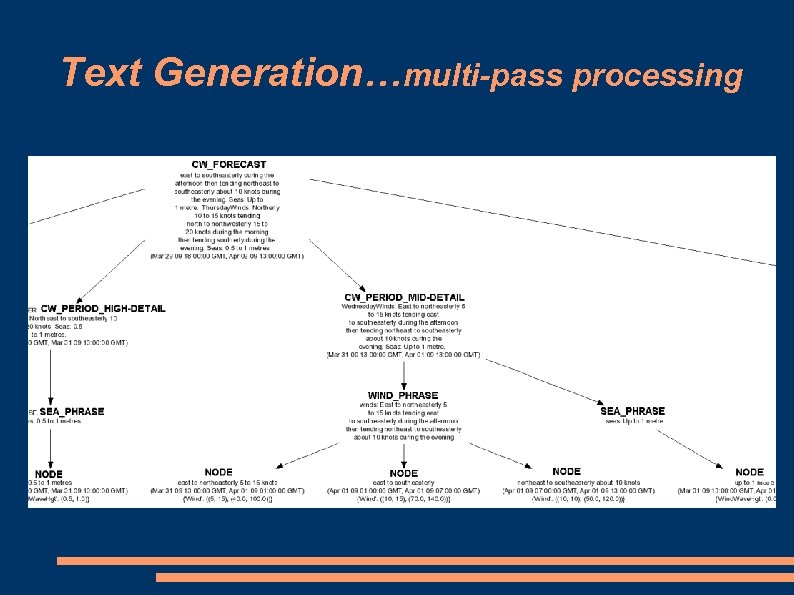
Text Generation…multi-pass processing
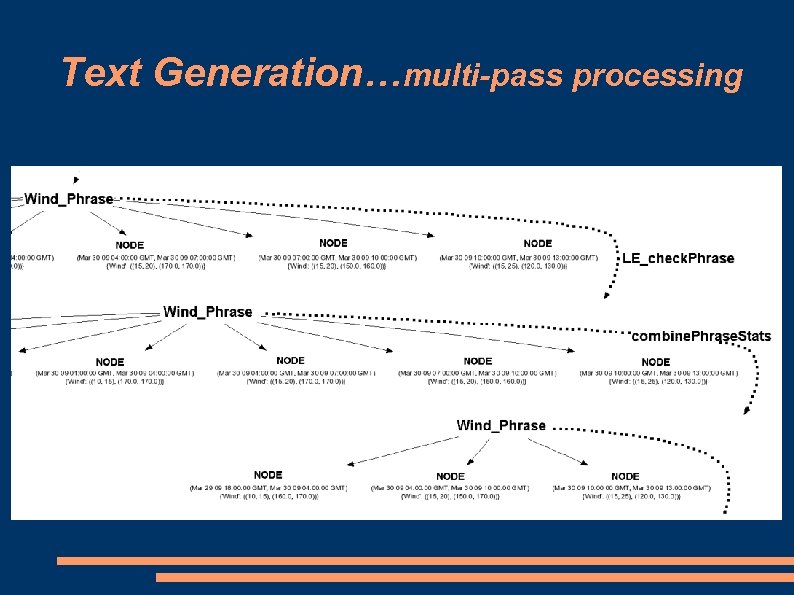
Text Generation…multi-pass processing

Text Generation. . overview Information representation Data Gathering Information Processing and Document Planning Mapping to Words ( Surface Realisation ) Post Processing
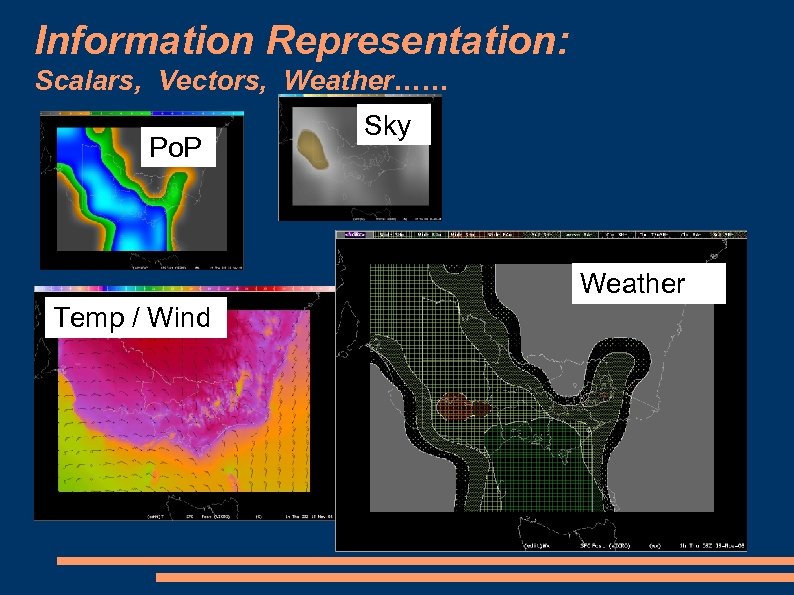
Information Representation: Scalars, Vectors, Weather…… Po. P Sky Weather Temp / Wind
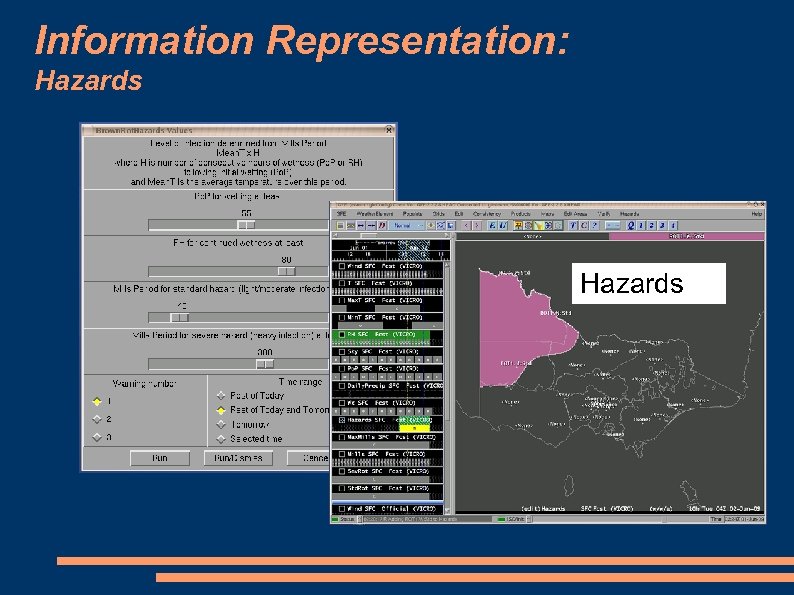
Information Representation: Hazards
Text Generation. . Information representation Data Gathering Information Processing and Document Planning Mapping to Words ( Surface Realisation ) Post Processing
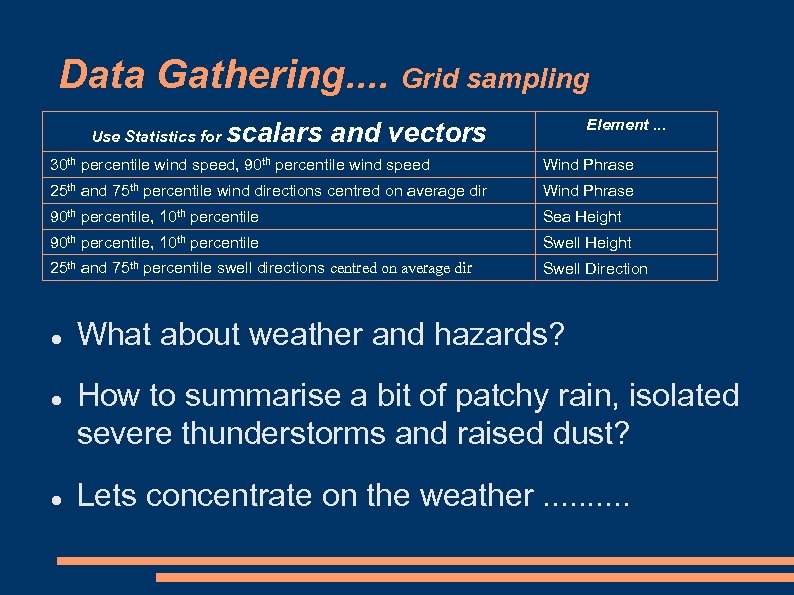
Data Gathering. . Grid sampling Use Statistics for Element. . . scalars and vectors 30 th percentile wind speed, 90 th percentile wind speed Wind Phrase 25 th and 75 th percentile wind directions centred on average dir Wind Phrase 90 th percentile, 10 th percentile Sea Height 90 th percentile, 10 th percentile Swell Height 25 th and 75 th percentile swell directions centred on average dir Swell Direction What about weather and hazards? How to summarise a bit of patchy rain, isolated severe thunderstorms and raised dust? Lets concentrate on the weather. .
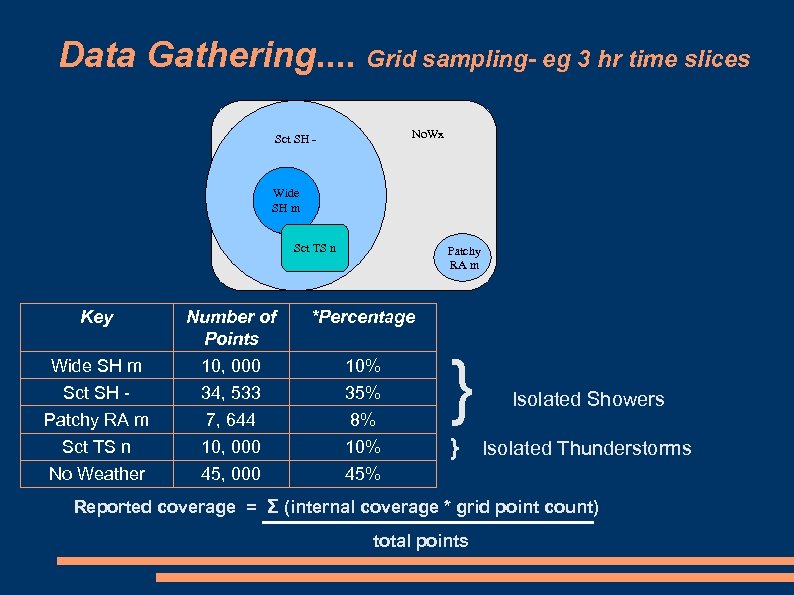
Data Gathering. . Grid sampling- eg 3 hr time slices No. Wx Sct SH - Wide SH m Sct TS n Patchy RA m Key Number of Points *Percentage Wide SH m 10, 000 10% Sct SH - 34, 533 35% Patchy RA m 7, 644 8% } Sct TS n 10, 000 10% } Isolated Thunderstorms No Weather 45, 000 45% Isolated Showers Reported coverage = Σ (internal coverage * grid point count) total points
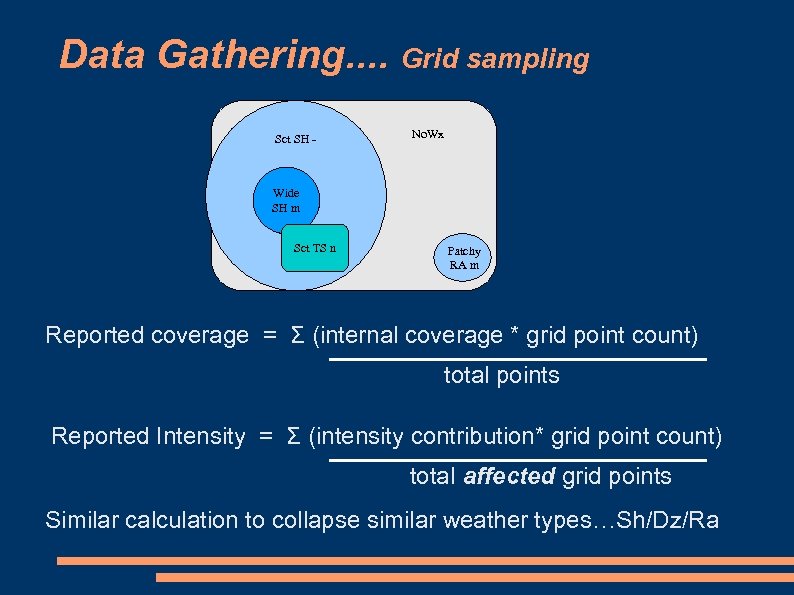
Data Gathering. . Grid sampling Sct SH - No. Wx Wide SH m Sct TS n Patchy RA m Reported coverage = Σ (internal coverage * grid point count) total points Reported Intensity = Σ (intensity contribution* grid point count) total affected grid points Similar calculation to collapse similar weather types…Sh/Dz/Ra
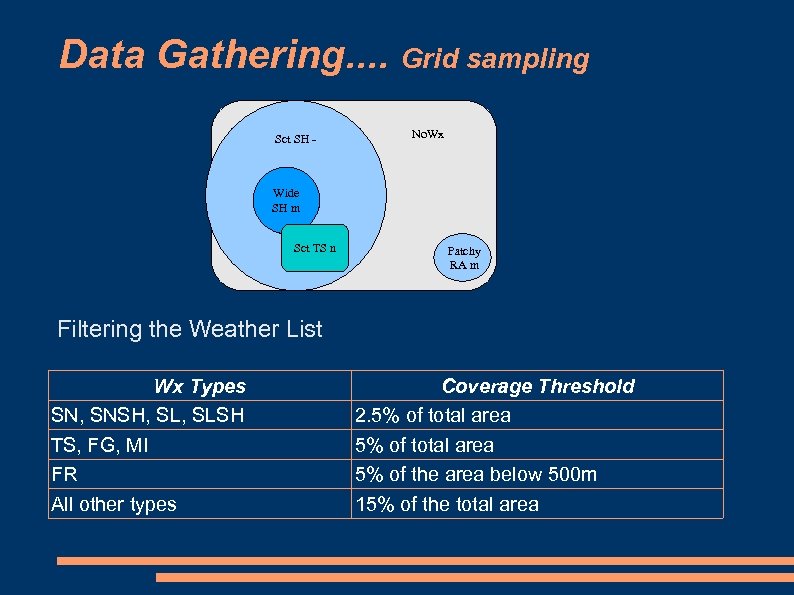
Data Gathering. . Grid sampling Sct SH - No. Wx Wide SH m Sct TS n Patchy RA m Filtering the Weather List Wx Types SN, SNSH, SLSH TS, FG, MI FR All other types Coverage Threshold 2. 5% of total area 5% of the area below 500 m 15% of the total area

Text Generation. . Information representation Data Gathering Information Processing and Document Planning Mapping to Words ( Surface Realisation ) Post Processing

Information Processing. . Embedded Local Effect > Winds: Easterly 10 to 20 knots decreasing to 10 to 15 knots around midday then increasing to 15 to 20 knots during the afternoon, locally up to 30 knots in the east. Seas: Below 0. 5 metres increasing to 0. 5 to 1 metres by early evening, locally up to 1. 5 metres in the east. Forecast-Split Local Effect > In the east: Winds: Easterly 10 to 20 knots increasing to 20 to 30 knots during the afternoon. Seas: 0. 5 to 1 metres, increasing up to 1. 5 metres by early evening. Elsewhere: Easterly 10 to 20 knots decreasing to 10 to 15 knots around midday then increasing to 15 to 20 knots during the afternoon. Seas: Below 0. 5 metres increasing to 0. 5 to 1 metres by early evening.
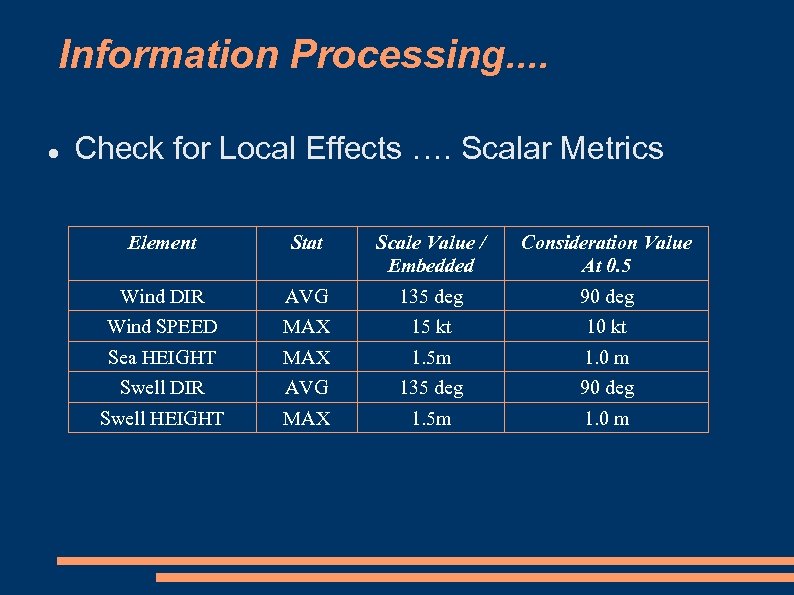
Information Processing. . Check for Local Effects …. Scalar Metrics Element Stat Scale Value / Embedded Consideration Value At 0. 5 Wind DIR AVG 135 deg 90 deg Wind SPEED MAX 15 kt 10 kt Sea HEIGHT MAX 1. 5 m 1. 0 m Swell DIR AVG 135 deg 90 deg Swell HEIGHT MAX 1. 5 m 1. 0 m
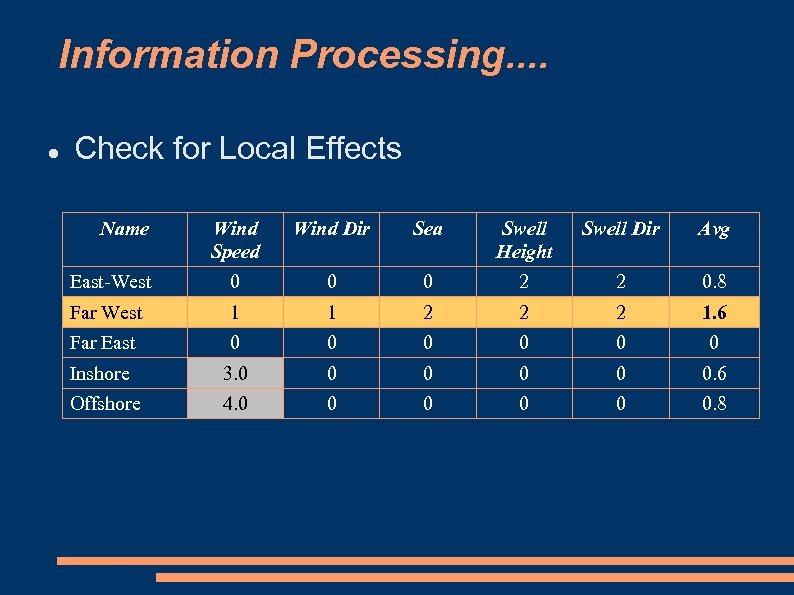
Information Processing. . Check for Local Effects Name Wind Speed Wind Dir Sea Swell Height Swell Dir Avg East-West 0 0 0 2 2 0. 8 Far West 1 1 2 2 2 1. 6 Far East 0 0 0 Inshore 3. 0 0 0. 6 Offshore 4. 0 0 0. 8
Text Generation…multi-pass processing
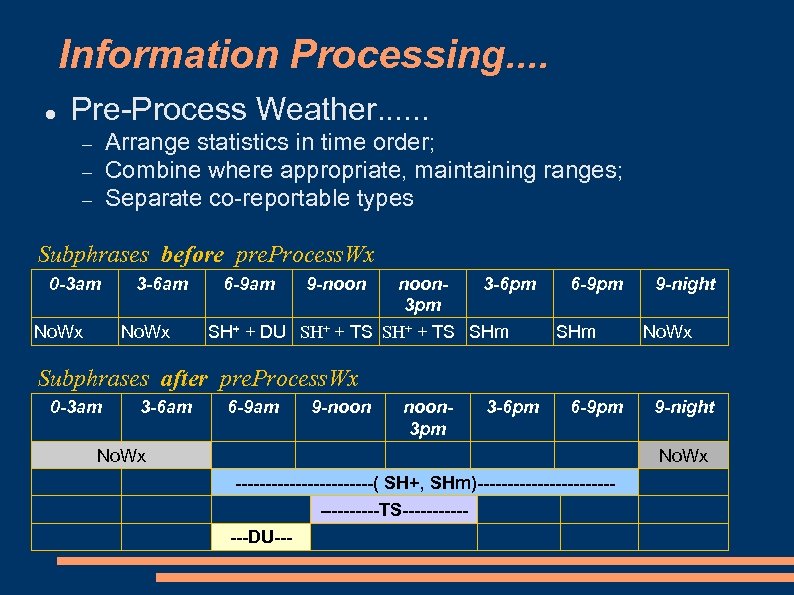
Information Processing. . Pre-Process Weather. . . Arrange statistics in time order; Combine where appropriate, maintaining ranges; Separate co-reportable types Subphrases before pre. Process. Wx 0 -3 am No. Wx 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am 9 -noon 3 -6 pm 3 pm SH+ + DU SH+ + TS SHm 6 -9 pm SHm 9 -night No. Wx Subphrases after pre. Process. Wx 0 -3 am 3 -6 am 6 -9 am 9 -noon 3 pm 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm No. Wx 9 -night No. Wx ------------( SH+, SHm)----------------TS-------DU---
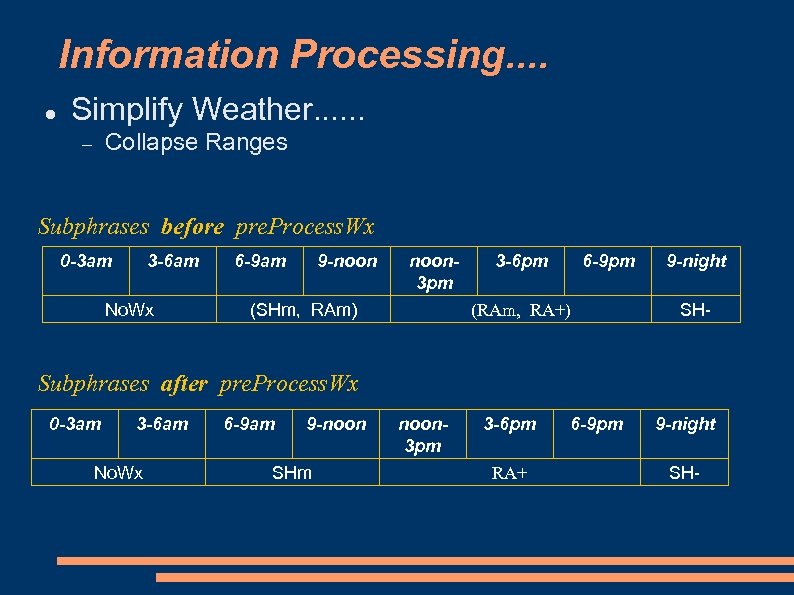
Information Processing. . Simplify Weather. . . Collapse Ranges Subphrases before pre. Process. Wx 0 -3 am 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am 9 -noon 3 pm (SHm, RAm) 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm (RAm, RA+) 9 -night SH- Subphrases after pre. Process. Wx 0 -3 am 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am 9 -noon SHm noon 3 pm 3 -6 pm RA+ 6 -9 pm 9 -night SH-
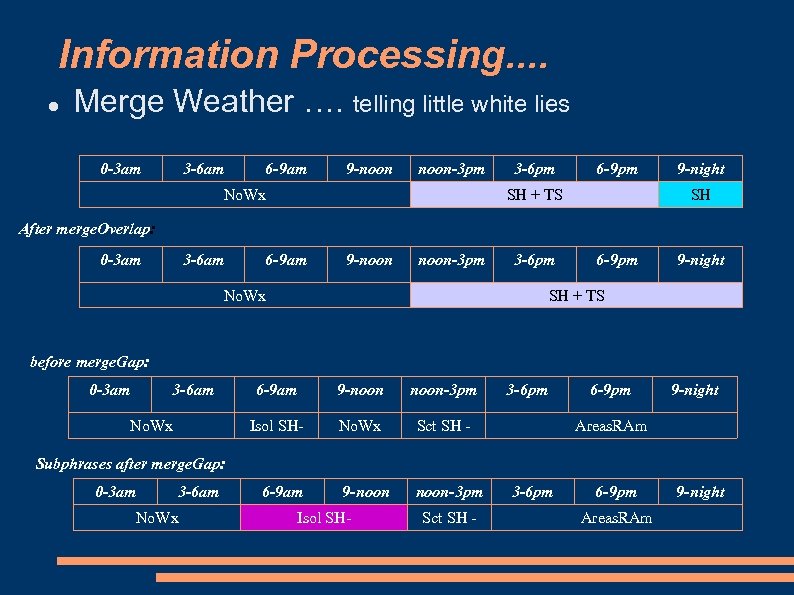
Information Processing. . Merge Weather …. telling little white lies 0 -3 am 3 -6 am 6 -9 am 9 -noon-3 pm No. Wx 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm SH + TS 9 -night SH After merge. Overlap: 0 -3 am 3 -6 am 6 -9 am 9 -noon-3 pm 3 -6 pm No. Wx 6 -9 pm 9 -night SH + TS before merge. Gap: 0 -3 am 3 -6 am 9 -noon-3 pm Isol SH- No. Wx 6 -9 am No. Wx Sct SH - 9 -noon-3 pm 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm 9 -night Areas. RAm Subphrases after merge. Gap: 0 -3 am 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am Isol SH- Sct SH - 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm Areas. RAm 9 -night
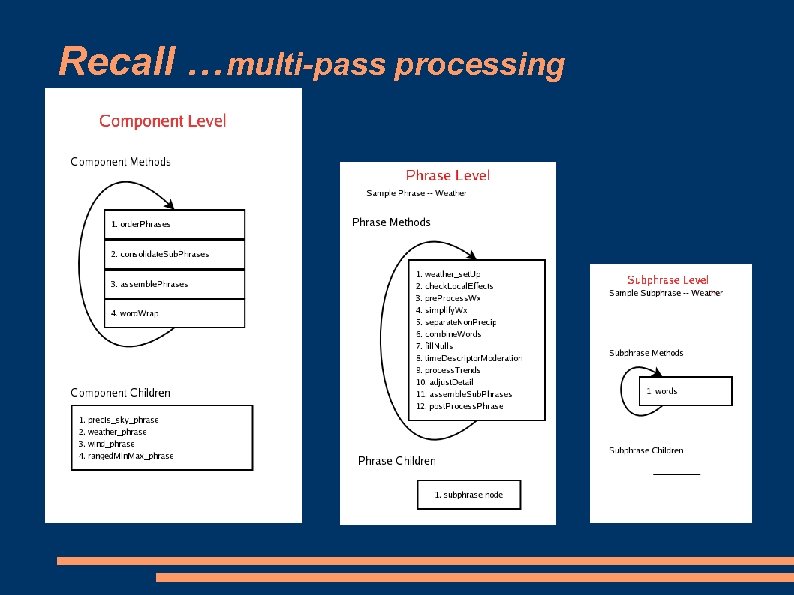
Recall …multi-pass processing

Information Processing. . Have we tried every processing step enough? Have we achieved our goals for level of detail? Can Adjust Detail by…. . More aggressive sub-phrase combining Looking for more local effects? . . Split forecast? Coarser sampling strategy Start again !

Text Generation. . Information representation Data Gathering Information Processing and Document Planning Mapping to Words ( Surface Realisation ) Post Processing

Mapping to words. . Process Trends…. Recognise and Summarise trends Subphrases before Process. Trends 0 -3 am No. Wx 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am No. Wx 9 -noon SH- noon 3 pm SHm 3 -6 pm RAm 6 -9 pm RAm 9 -night RAm Subphrases after Process. Trends 0 -3 am 3 -6 am No. Wx 6 -9 am 9 -noon 3 pm 3 -6 pm 6 -9 pm 9 -night SH- developing >. . skip. . > increasing to Ram

Mapping to words. . Connectors Increasing / Decreasing Becoming / Tending Developing / Clearing Winds W to. NW’y at 15 to 25 knots tending W to SW’ly then increasing to 30 knots. Isolated showers developing during the morning then increasing to heavy widespread rain…. .

Mapping to words. . Time reporting Transition (change verbs) Over-time (nouns) Mixed (trend verbs) Winds W to NW’y at 15 to 25 knots tending W to SW’ly around noon then increasing to 30 knots. Morning Fog. Isolated showers developing during the afternoon then increasing to widespread rain…

Text Generation. . Information representation Data Gathering Information Processing and Document Planning Mapping to Words ( Surface Realisation ) Post Processing

Post Processing. . Post-Process Phrases - string replacements to cover limitations - “band-aid”… eg Early frost. Early fog. >> Early frost and Fog. Remove repeated words eg W to NW’y winds becoming NW’ly
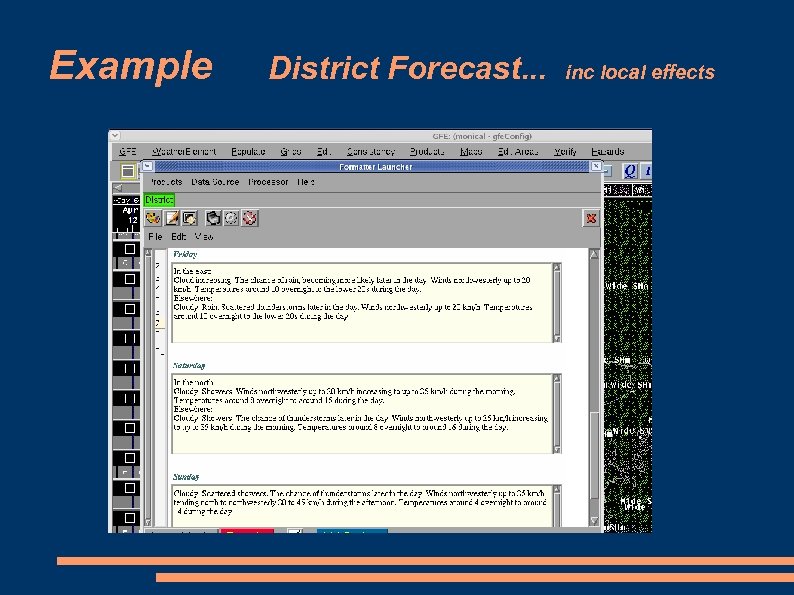
Example District Forecast. . . inc local effects
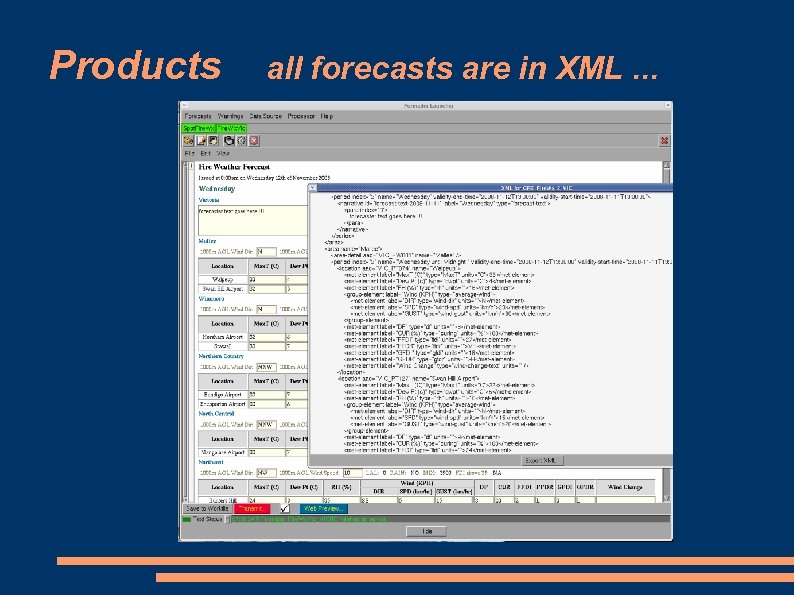
Products all forecasts are in XML. . .
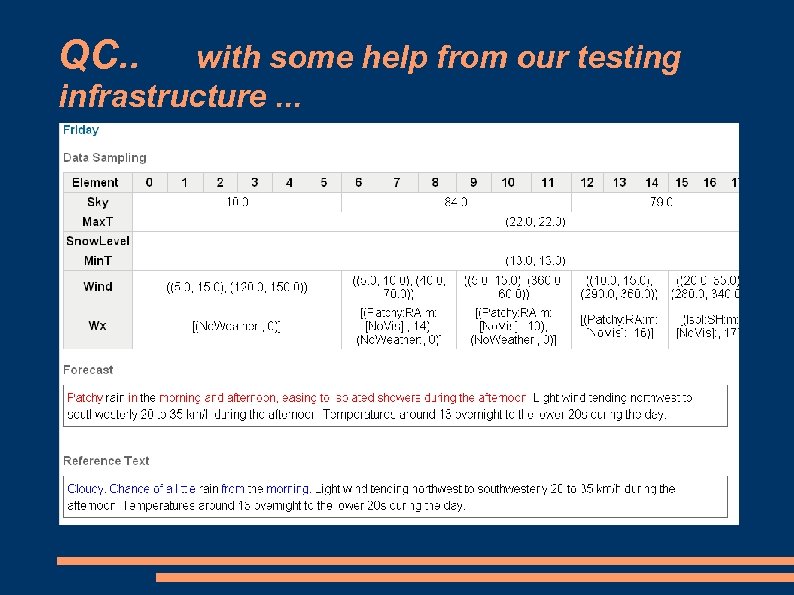
QC. . with some help from our testing infrastructure. . .

Change Management. . Importance of specifications Agreed? policies Big change in the role of forecasters Forecaster edits for style and/or substance Change management

The End Text Generation in the GFE
297d3e7b4ec261c8f0c9028197951663.ppt