354e19a6e93c31bb3a38f20cb371db56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 126

Blown Film Extrusion Technology Presented by General Extrusion Technology (GET)


Blown Film Extrusion Technology • The future trend of extrusion technology is high speed, high output, less energy consumption at competitive cost • The following slides will provide you an overview of blown film extrusion technologies • Some of those technologies are proven and some of them represent the latest development from General Extrusion Technology Ltd. • The information contained in this presentation may be proprietary, confidential and privileged, and, therefore protected from disclosure

Blown Film Extrusion Technology • GET partners with some world best component/system suppliers

Blown Film Extrusion Technology • GET partners with some world best component/system suppliers Complete line control, gauge system, IBC control, Germany Extruder gearbox, Germany Extruder high torque motor, Germany AC motor and drive, ABB China Gear motor for extruder, winder, haul-off and bubble cage, SEW China

Blown Film Extrusion Technology • GET partners with some world best component/system suppliers PLC control system for winder, Autria All pneumatic web guide system, USA Control cabinet, low voltage components, Schneider China Solid state relay switch, Swiss Control cabinet, Rittal China

Blown Film Extrusion Technology • GET partners with some world best component/system suppliers Busbar system, Germany Bearing for all rollers, NSK China Brush spreader roller horizontal haul-off, Germany Heater band, Watlow China Melt pressure transducer, USA Barrel and screw, USA
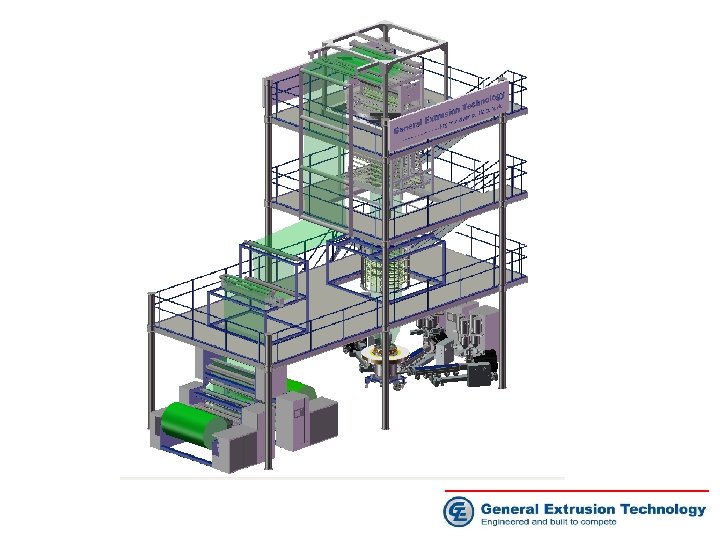

Blown Film Extrusion System • • • System ACS 5300 AS NAVIGATOR Gravimetric System Blown Film Extruder Screen Changer Blown Film Die Technology Bubble Cage Gauging System Collapsing Frame Haul-off System Winder Technology

System ACS 5300 AS NAVIGATOR 19” Color touch screen
System ACS 5300 AS NAVIGATOR • • • System ACS NAVIGATOR control principle Plant wide control concept Modular structure Machine control NAVIGATOR Temperature control

System ACS 5300 AS NAVIGATOR control principle
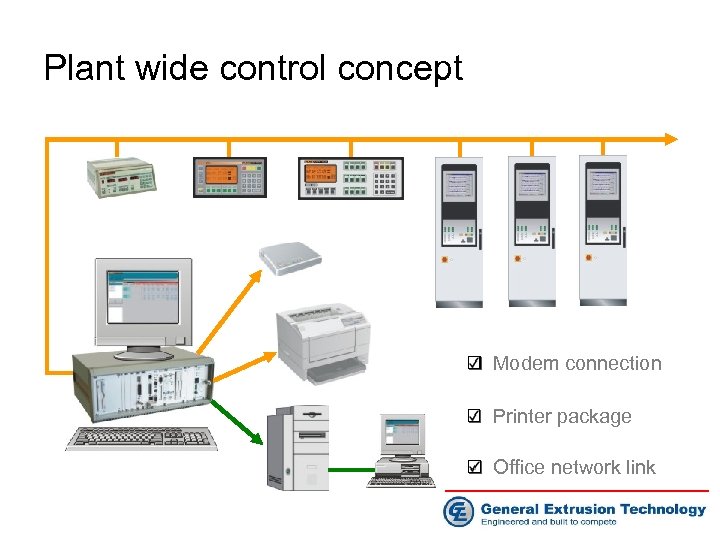
Plant wide control concept Modem connection Printer package Office network link
Modular structure
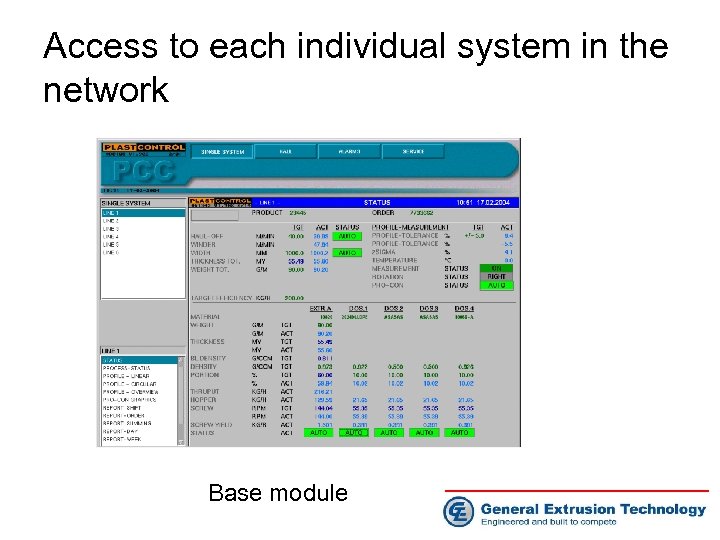
Access to each individual system in the network Base module
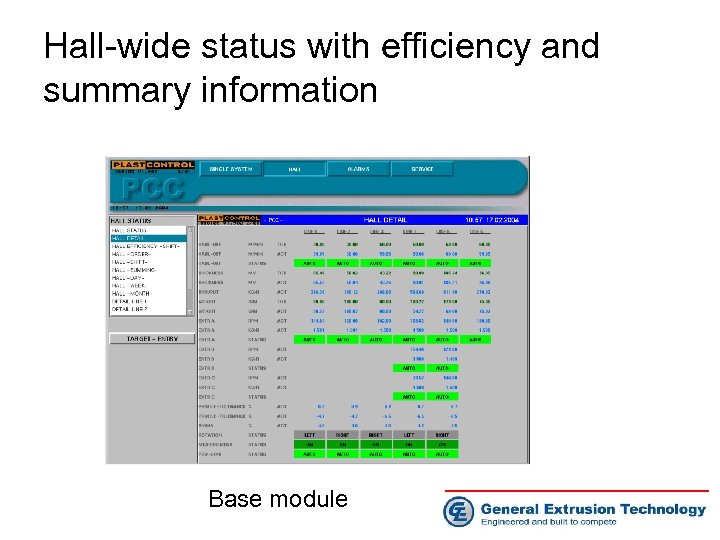
Hall-wide status with efficiency and summary information Base module
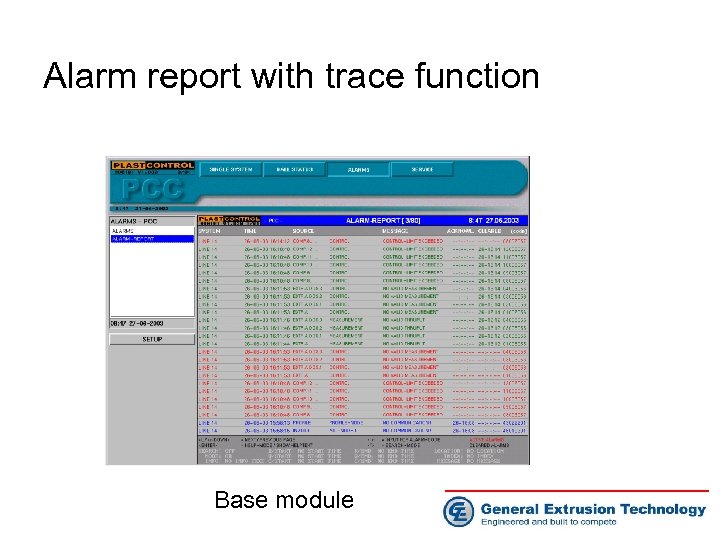
Alarm report with trace function Base module
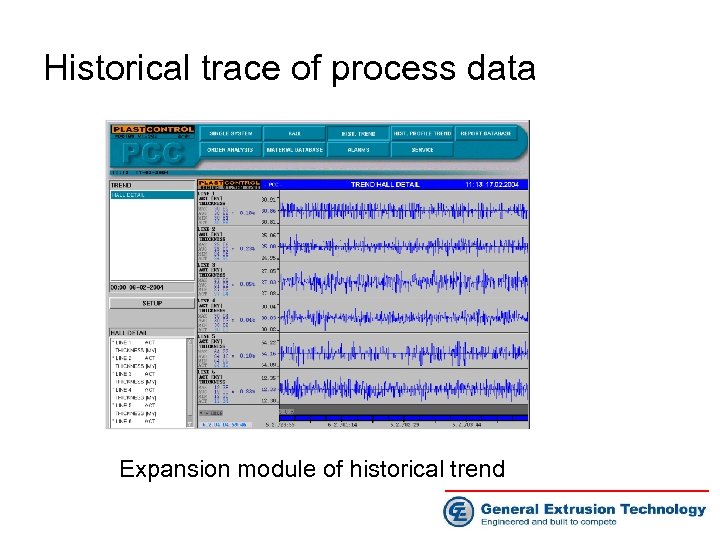
Historical trace of process data Expansion module of historical trend
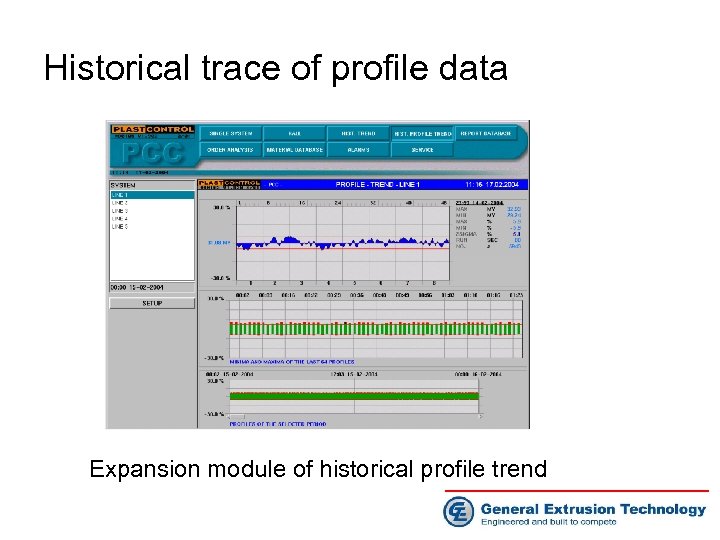
Historical trace of profile data Expansion module of historical profile trend
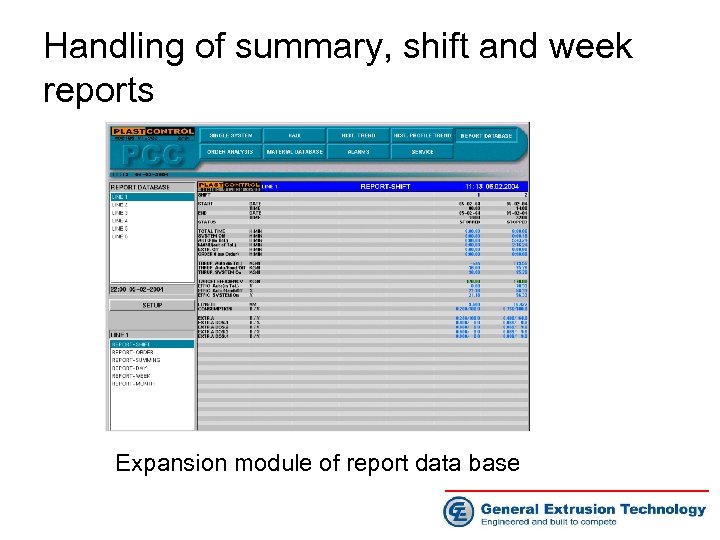
Handling of summary, shift and week reports Expansion module of report data base
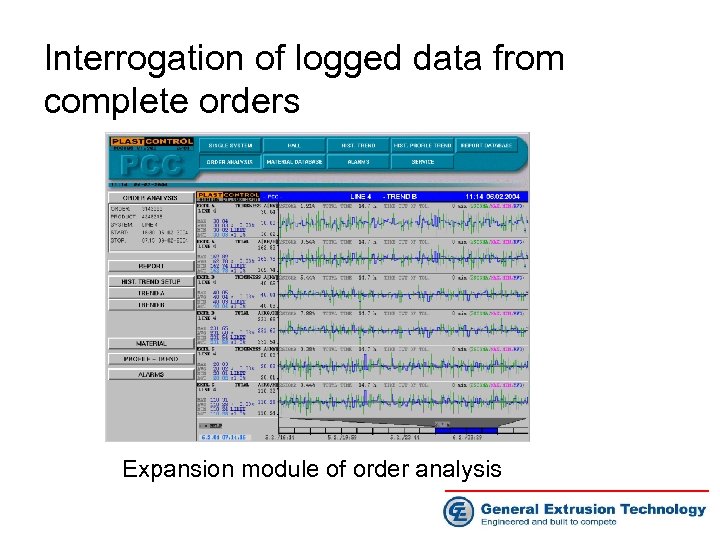
Interrogation of logged data from complete orders Expansion module of order analysis
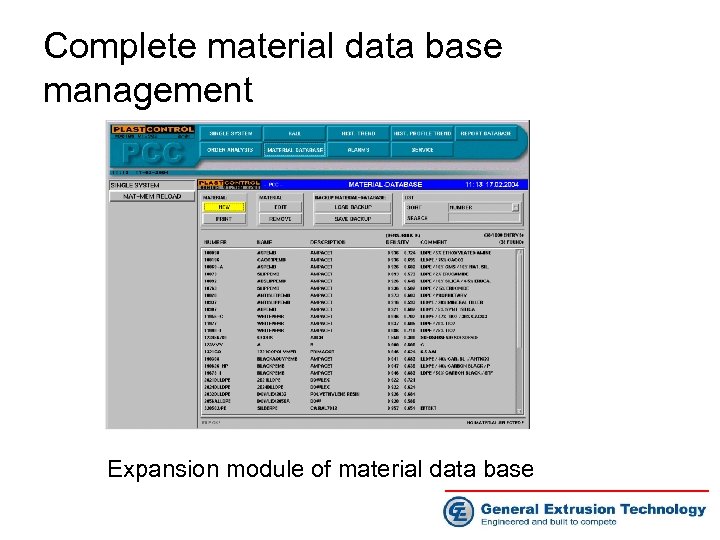
Complete material data base management Expansion module of material data base
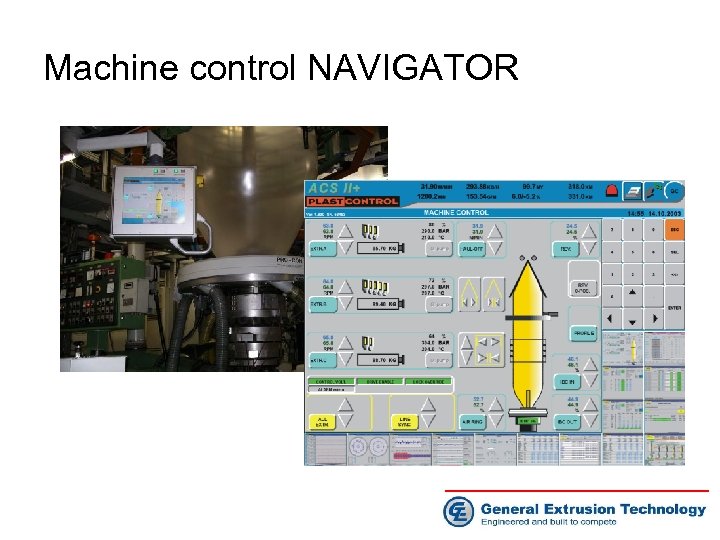
Machine control NAVIGATOR
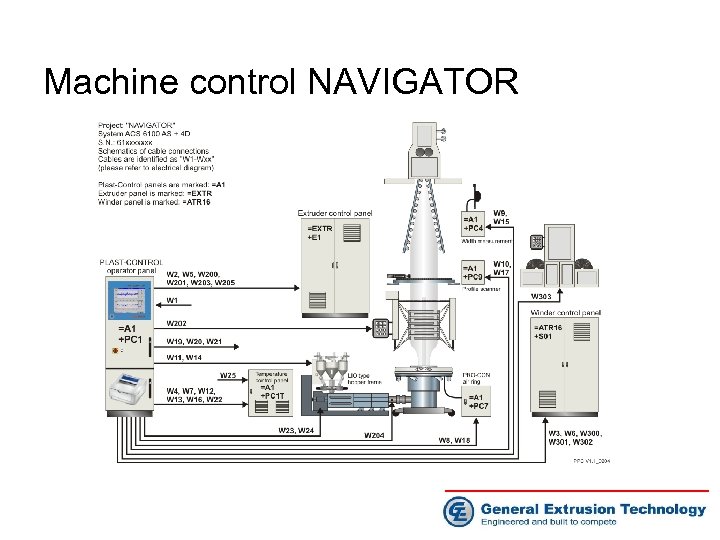
Machine control NAVIGATOR
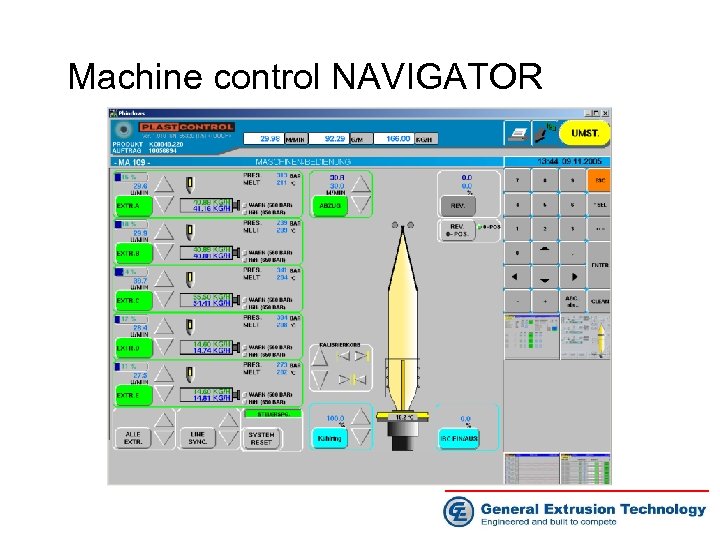
Machine control NAVIGATOR
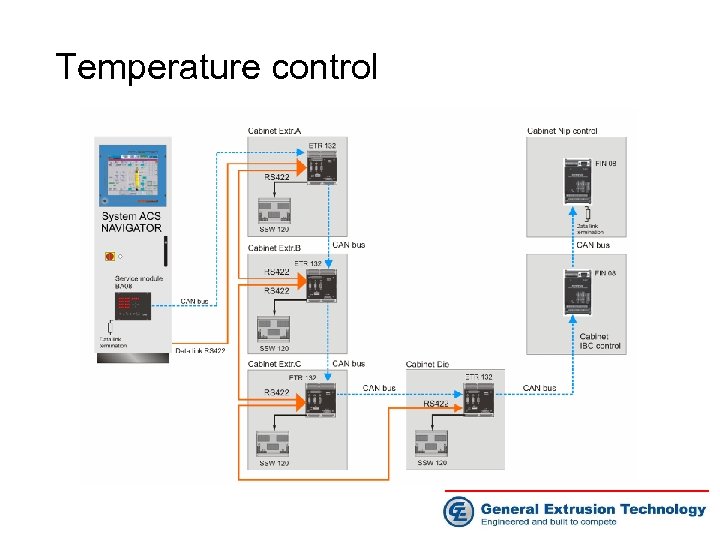
Temperature control
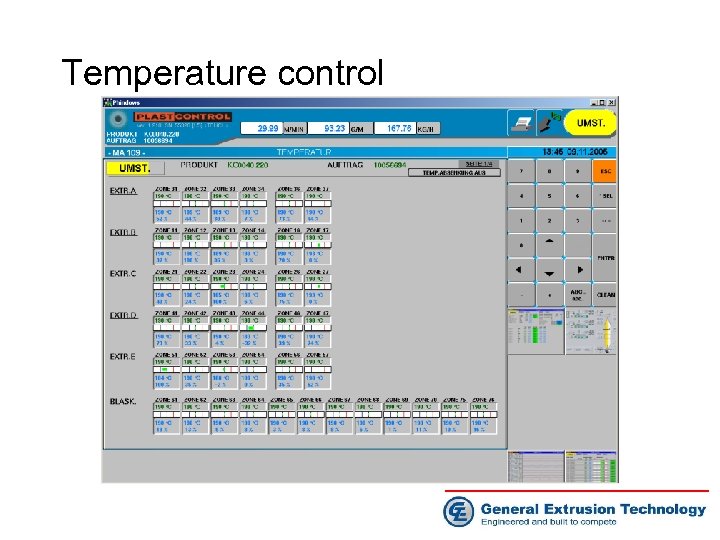
Temperature control
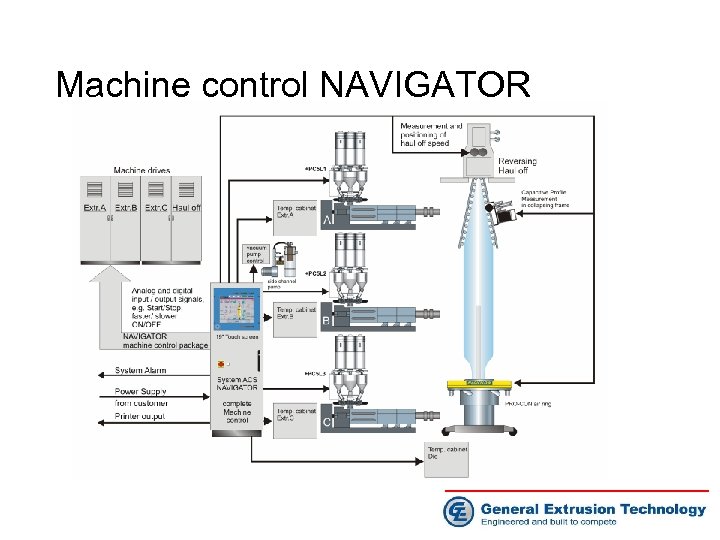
Machine control NAVIGATOR

Temperature control

Gravimetric batch blending system • Plast Control batch blender PB 422 • Mechanical advantages • Weighing hopper concept • Material conveyor PCH 400/PCH 800 • Pre-filter PCP 500

Gravimetric system advantages • Rugged mechanical design with easy refill possibility • Weighing device completely tested and calibrated • Density dependent hopper refill • Precise summing even during order changes • Easy understandable material conveying with clear text messages • Integration into existing central conveying systems • Overfill detection (e. g. after manual refill) • Fast thruput cycles • Intelligent error handling checks operator errors or mechanical vibrations • Synchronized ramping of each material component • Unified hopper sizes • Unified load cell types for 400 g/h up to 650 kg/h
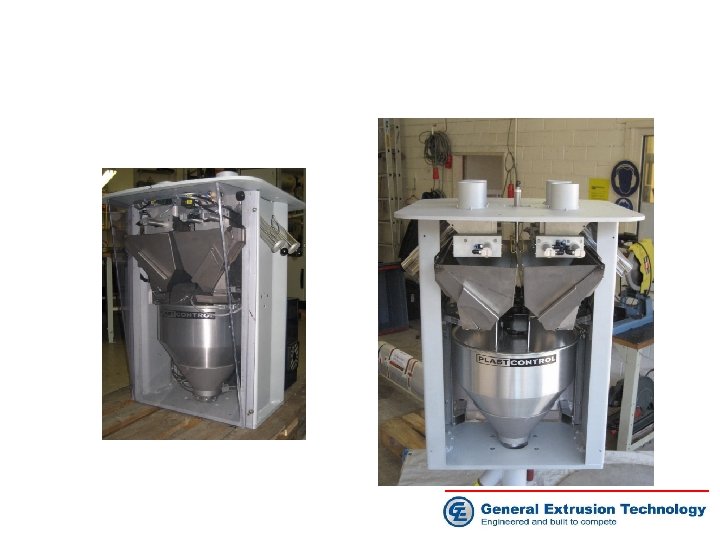

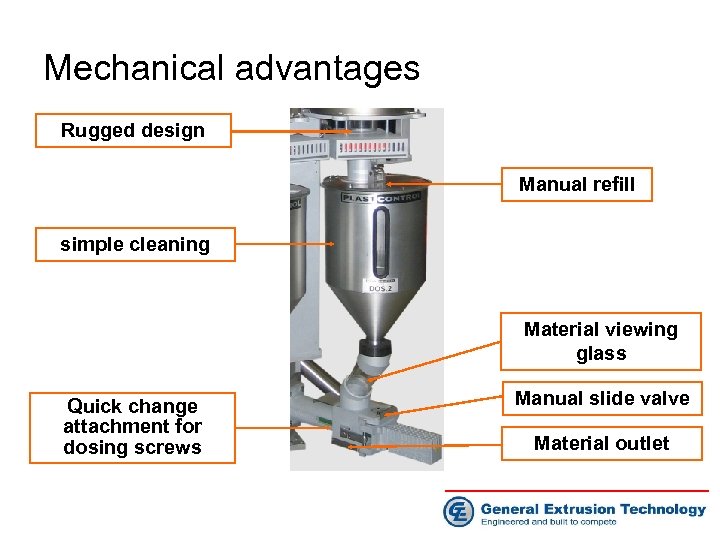
Mechanical advantages Rugged design Manual refill simple cleaning Material viewing glass Quick change attachment for dosing screws Manual slide valve Material outlet
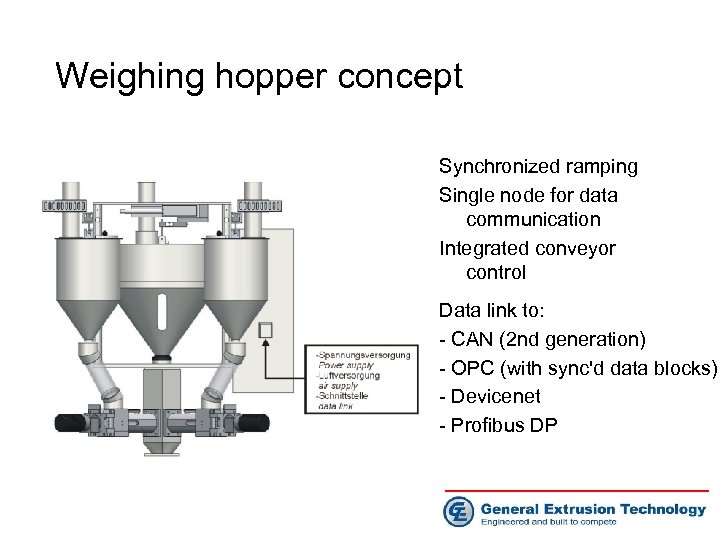
Weighing hopper concept Synchronized ramping Single node for data communication Integrated conveyor control Data link to: - CAN (2 nd generation) - OPC (with sync'd data blocks) - Devicenet - Profibus DP
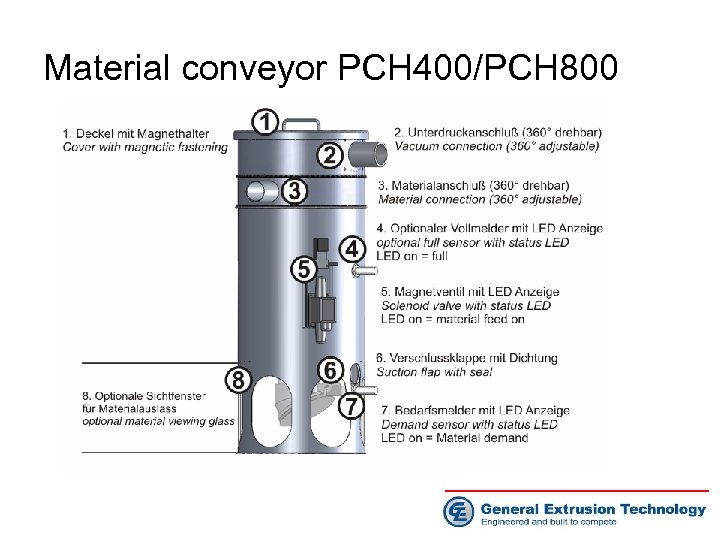
Material conveyor PCH 400/PCH 800

Material conveyor PCH 400/PCH 800 1) The metal filter is accessible without moving or disconnecting the hoses - Hoses don‘t get bent and leak 2) Variable position of connectors - each connector can be positioned independently 3) Each electrical function with status LED - LED display of material demand - LED display of vacuum status - Optional LED display demand sensor - Optional LED display full sensor 4) Optional viewing glasses in the area of material flap - Operator can always check for sufficient material - Fast service diagnosis
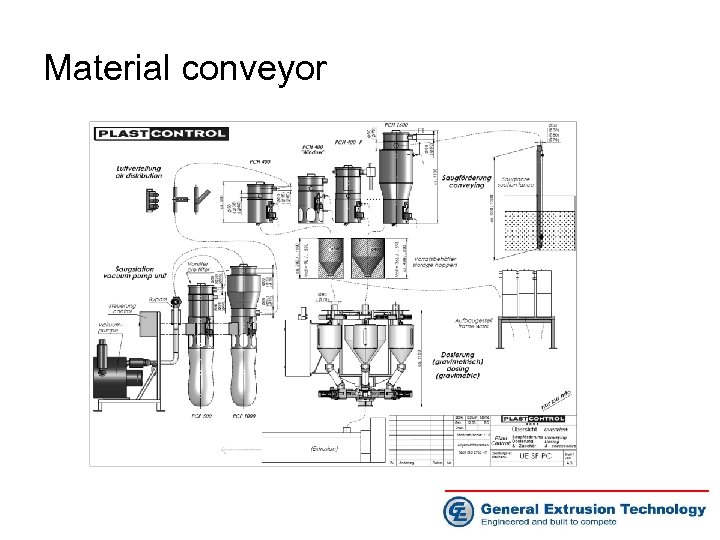
Material conveyor

Pre-filter PCP 500

Blown Film Extruder • Direct drive with torque motor(gearless) • Traditional drive motor with gearbox • Screw and Barrel Technology • Barrel cooling system

Direct drive with torque motor(gearless)

Torque motor benefits • 10 -20% less energy than a DC motor; 5 -10% less energy than a AC motor • High torque capability permits higher outputs • Virtually no vibration or noise and need no maintenance • Water-cooled and dust-free and use less oil-advantages for medical and foodpackaging films • Compact size, an advantage for coextrusion
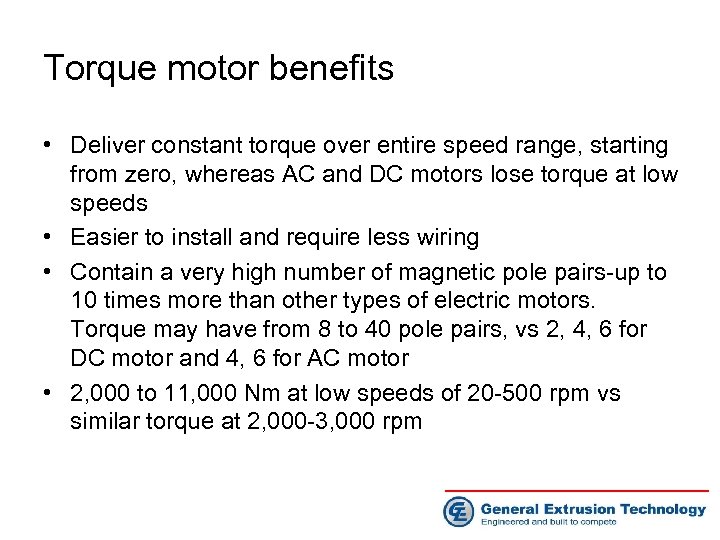
Torque motor benefits • Deliver constant torque over entire speed range, starting from zero, whereas AC and DC motors lose torque at low speeds • Easier to install and require less wiring • Contain a very high number of magnetic pole pairs-up to 10 times more than other types of electric motors. Torque may have from 8 to 40 pole pairs, vs 2, 4, 6 for DC motor and 4, 6 for AC motor • 2, 000 to 11, 000 Nm at low speeds of 20 -500 rpm vs similar torque at 2, 000 -3, 000 rpm

Traditional drive motor with gearbox

Traditional drive motor with gearbox • Directly coupled motor and gearbox for energy and space efficiency • Compact design with high power rating • Centerline to match application • Full length steel base frame • Maximum rigidity maintains alignment • Minimize screw wear

Screw and Barrel Technology • Some of the most important requirements are • Processability of mixtures with different sized and different shaped granules • High plastificating performance • Gentle but complete plastification • Good melt homogeneity • Controlled melt temperatures • Minimal change in the material through degradation or crosslinking • High level of versatility: ability to process a broad selection of raw materials with a wide range of throughput rates • Low performance-related investment and operating cost
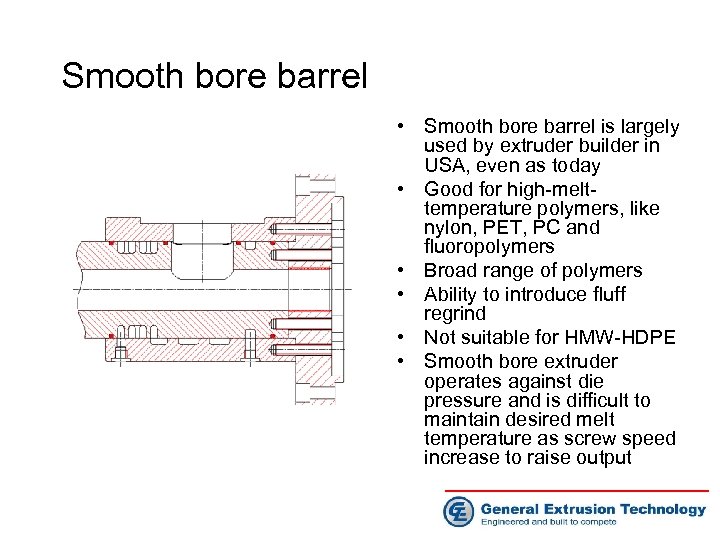
Smooth bore barrel • Smooth bore barrel is largely used by extruder builder in USA, even as today • Good for high-melttemperature polymers, like nylon, PET, PC and fluoropolymers • Broad range of polymers • Ability to introduce fluff regrind • Not suitable for HMW-HDPE • Smooth bore extruder operates against die pressure and is difficult to maintain desired melt temperature as screw speed increase to raise output
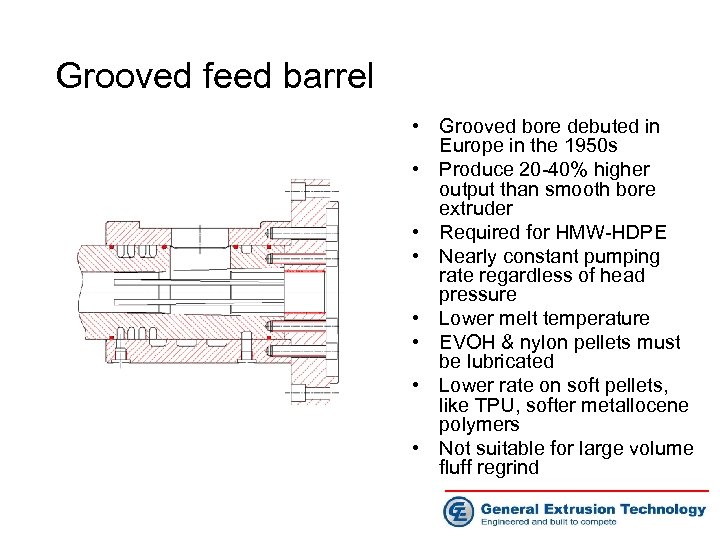
Grooved feed barrel • Grooved bore debuted in Europe in the 1950 s • Produce 20 -40% higher output than smooth bore extruder • Required for HMW-HDPE • Nearly constant pumping rate regardless of head pressure • Lower melt temperature • EVOH & nylon pellets must be lubricated • Lower rate on soft pellets, like TPU, softer metallocene polymers • Not suitable for large volume fluff regrind
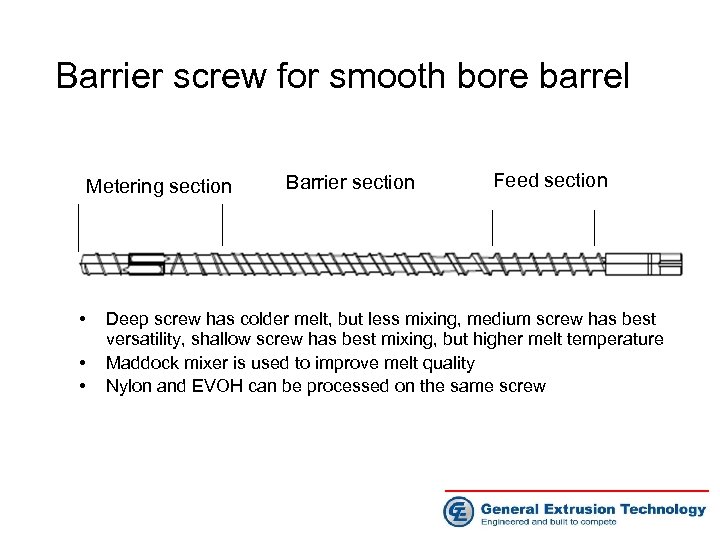
Barrier screw for smooth bore barrel Metering section • • • Barrier section Feed section Deep screw has colder melt, but less mixing, medium screw has best versatility, shallow screw has best mixing, but higher melt temperature Maddock mixer is used to improve melt quality Nylon and EVOH can be processed on the same screw

Barrier screw for grooved bore barrel Homogenizing section • • • Barrier section Feed section Good dispersive/distributive mixing effect Heat transfer to the barrel Low pressure loss Effective separation of solids from melt High homogenizing effect Good control of melt temperature Clear pressure build-up Melt throughput geared to homogenizing capacity Low pressure level Low torque Reduced wear and tear

Barrier screw for grooved bore barrel • Barrier screw with homogenizing elements Rhomboid mixing element Spiral shearing element
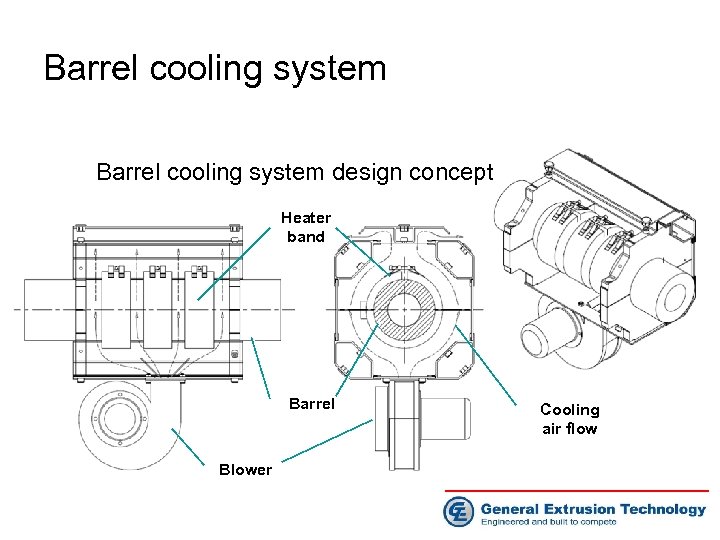
Barrel cooling system design concept Heater band Barrel Blower Cooling air flow
Barrel cooling system • The heat exchange surface area between the barrel and the cooling air flow is critical for the cooling efficiency • GET’s cooling system is designed for high speed extrusion with intensive cooling • Finned aluminum heat sink for intensive cooling • Finned ceramic heater band for intensive heating and cooling
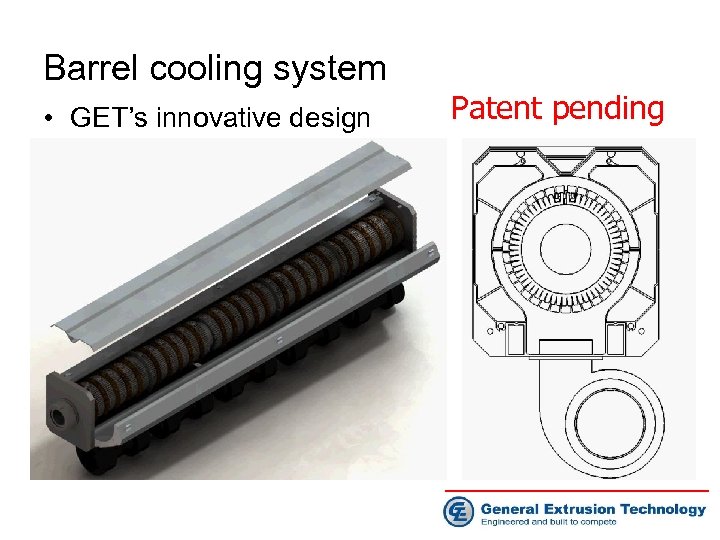
Barrel cooling system • GET’s innovative design Patent pending
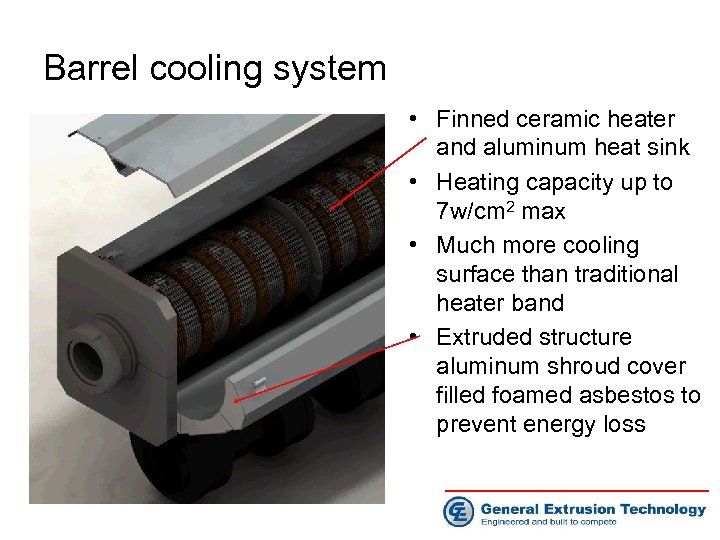
Barrel cooling system • Finned ceramic heater and aluminum heat sink • Heating capacity up to 7 w/cm 2 max • Much more cooling surface than traditional heater band • Extruded structure aluminum shroud cover filled foamed asbestos to prevent energy loss

Barrel cooling system

Choose a right solution • Production complexity and investment cost defines the solutions to be used • A modular cooling element is preferred, which can be adjusted to different barrel diameter and section length relatively easily • For best control of melt temperature, different cooling system may require for different temperature zone
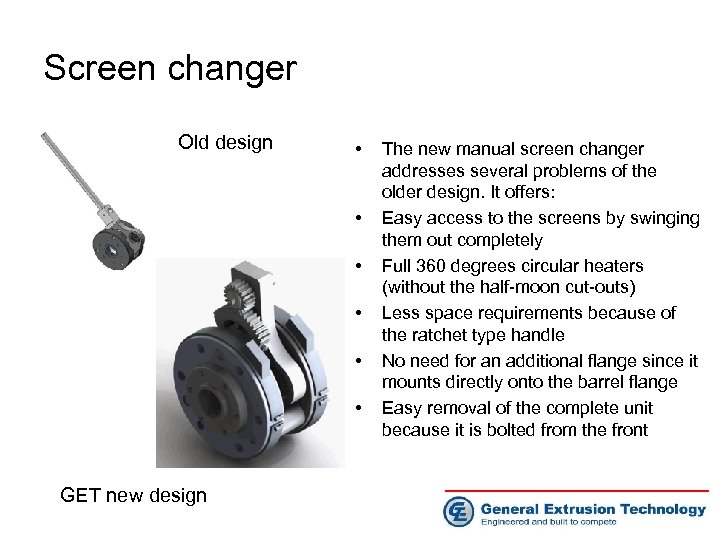
Screen changer Old design • • • GET new design The new manual screen changer addresses several problems of the older design. It offers: Easy access to the screens by swinging them out completely Full 360 degrees circular heaters (without the half-moon cut-outs) Less space requirements because of the ratchet type handle No need for an additional flange since it mounts directly onto the barrel flange Easy removal of the complete unit because it is bolted from the front

Blown film die system • Blown film die technology • Air ring cooling and die cart • Internal bubble cooling(IBC) system

Blown film die system Single air ring die system Double stack air ring die system
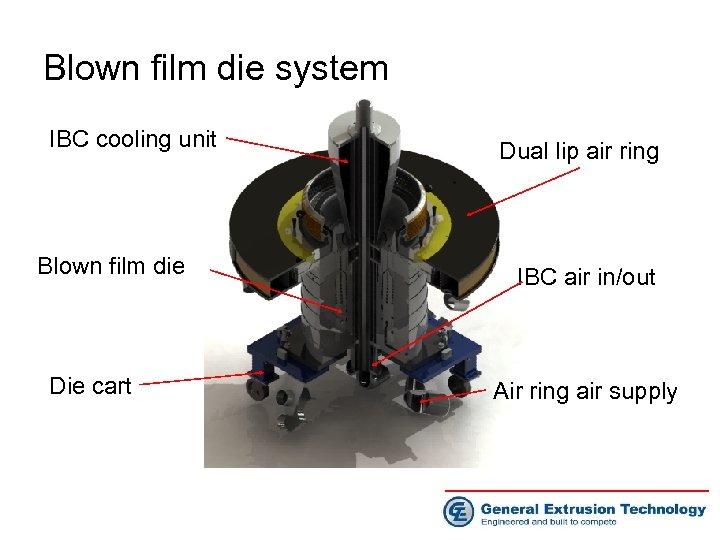
Blown film die system IBC cooling unit Blown film die Die cart Dual lip air ring IBC air in/out Air ring air supply

Blown film die technology • Spiral mandrel die Die pin Heater band Sizing ring Melt feed block Out layer Die cart Middle layer Die adjustment plate Inner layer Air supply

Blown die technology • Low profile die design • Single melt channel to dual channel melt channel distribution. Spiral mandrel • Short melt flow • No flow channel plug, no melt dead point • Short melt flow residence time • Strong self-cleaning, shortest purging time • No port lines • Low pressure drop • No layer leakage • Easy die assembly, easy die clean by customer

Blown die technology • Single to dual melt distribution and spiral mandrel die Spiral mandrel melt flow channel Binary pre-distribution)
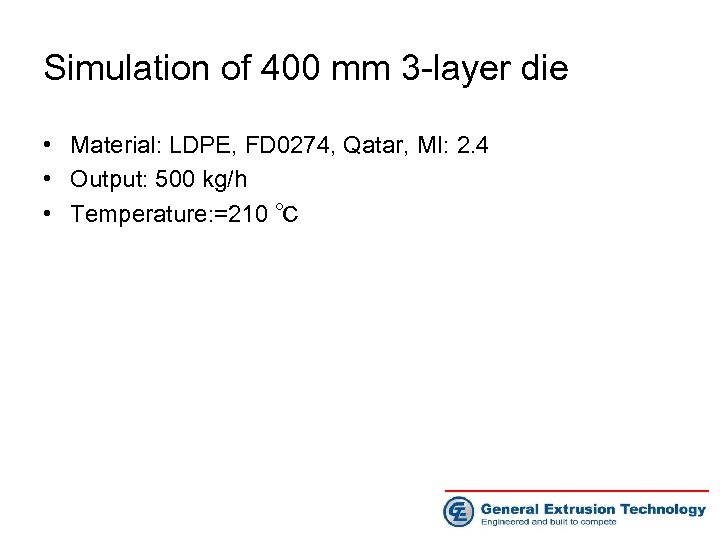
Simulation of 400 mm 3 -layer die • Material: LDPE, FD 0274, Qatar, MI: 2. 4 • Output: 500 kg/h • Temperature: =210 ℃
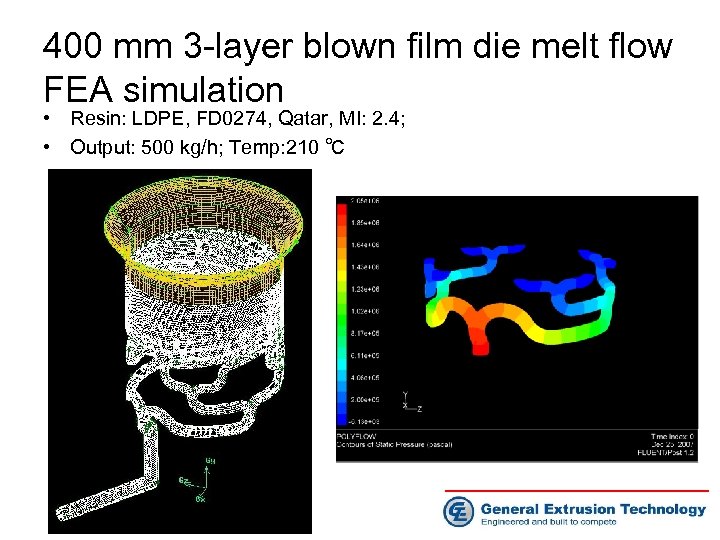

400 mm 3 -layer blown film die melt flow FEA simulation • Resin: LDPE, FD 0274, Qatar, MI: 2. 4; • Output: 500 kg/h; Temp: 210 ℃
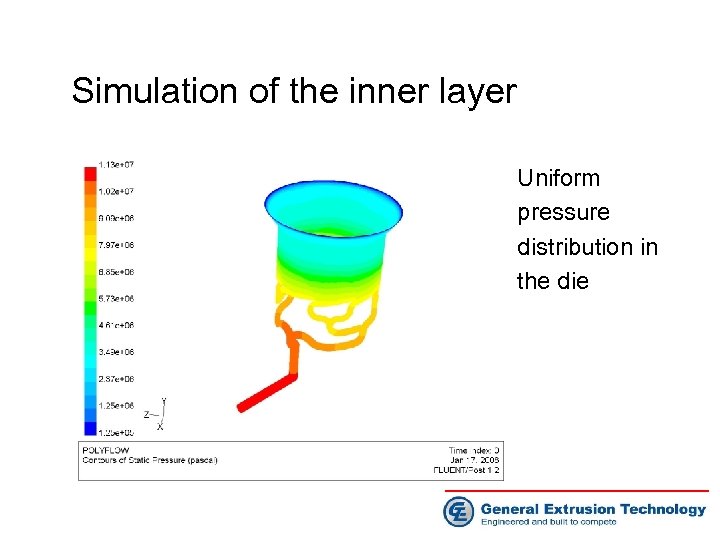
Simulation of the inner layer Uniform pressure distribution in the die
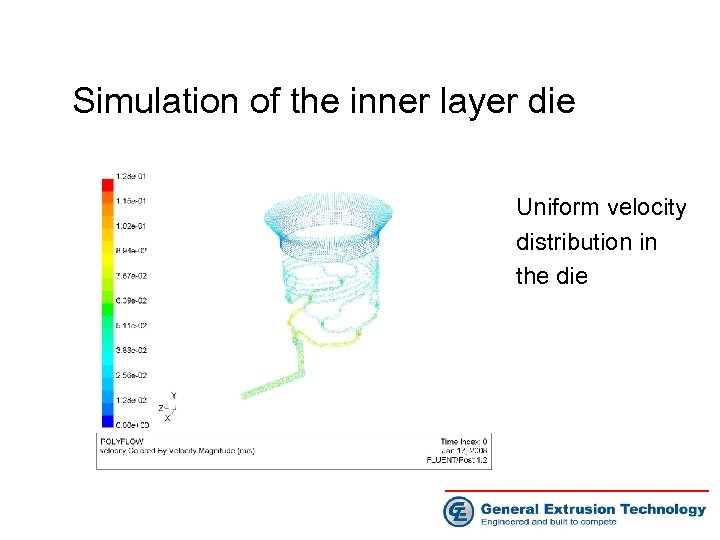
Simulation of the inner layer die Uniform velocity distribution in the die
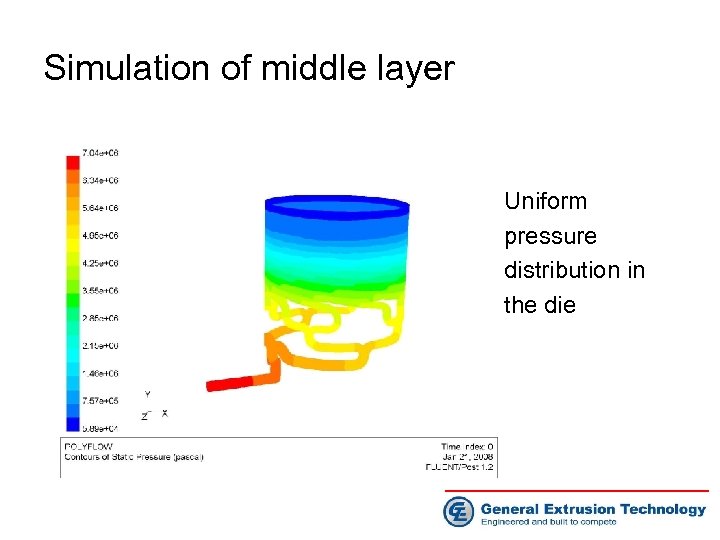
Simulation of middle layer Uniform pressure distribution in the die
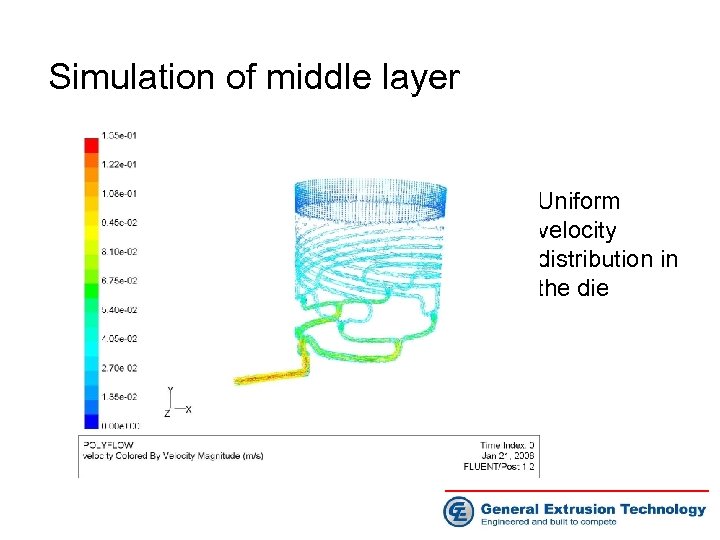
Simulation of middle layer • Uniform velocity distribution in the die
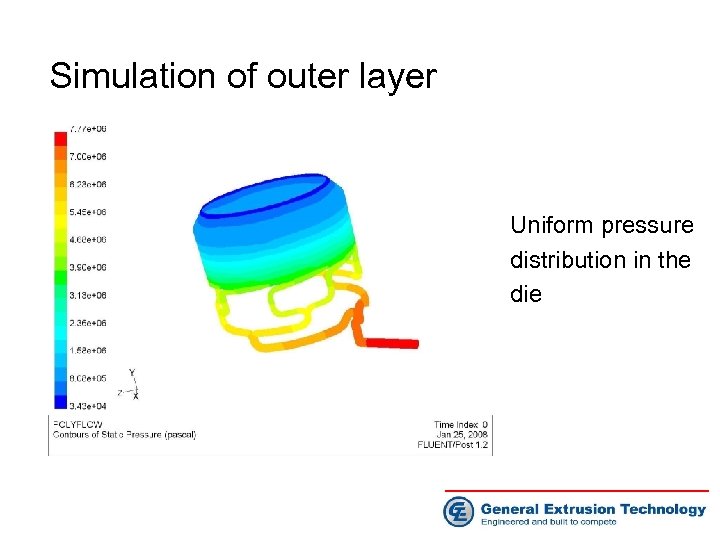
Simulation of outer layer Uniform pressure distribution in the die
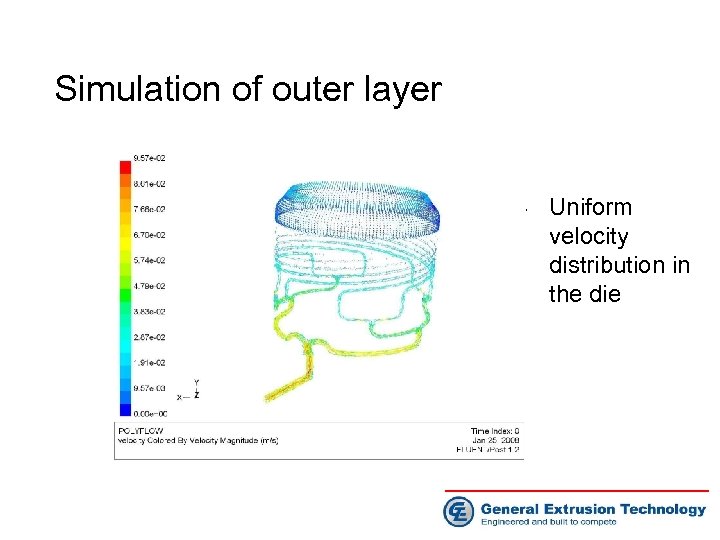
Simulation of outer layer • Uniform velocity distribution in the die

Air ring technology • • • External bubble cooling and forming Dual lip air ring type Perforated chimney dual lip air ring Double stack air ring Internal bubble cooling(IBC) system
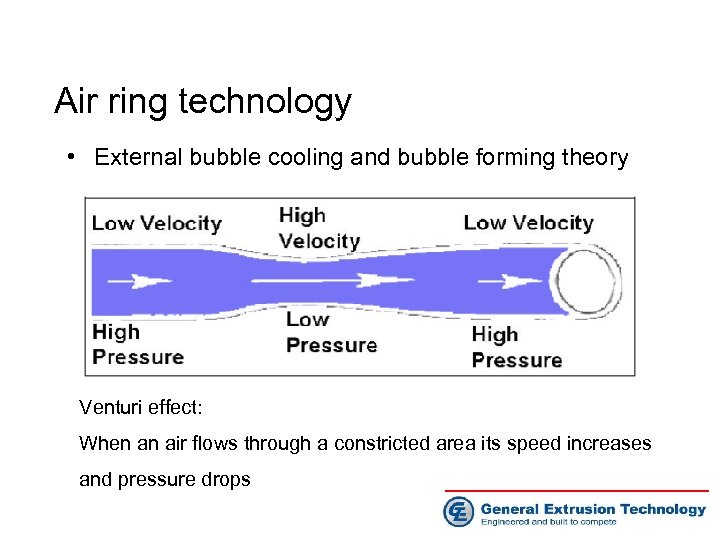
Air ring technology • External bubble cooling and bubble forming theory Venturi effect: When an air flows through a constricted area its speed increases and pressure drops
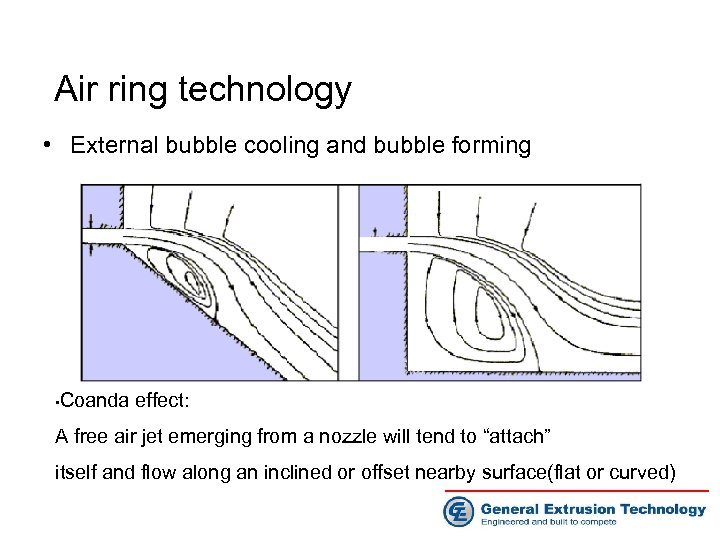
Air ring technology • External bubble cooling and bubble forming Coanda effect: • A free air jet emerging from a nozzle will tend to “attach” itself and flow along an inclined or offset nearby surface(flat or curved)
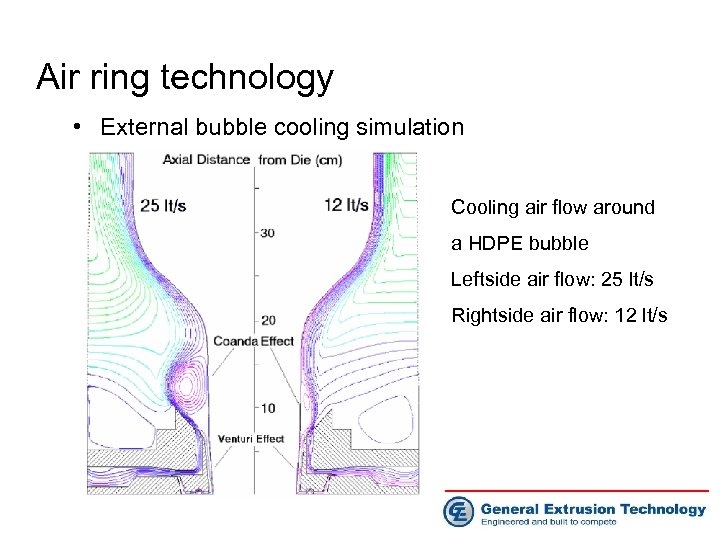
Air ring technology • External bubble cooling simulation Cooling air flow around a HDPE bubble Leftside air flow: 25 lt/s Rightside air flow: 12 lt/s
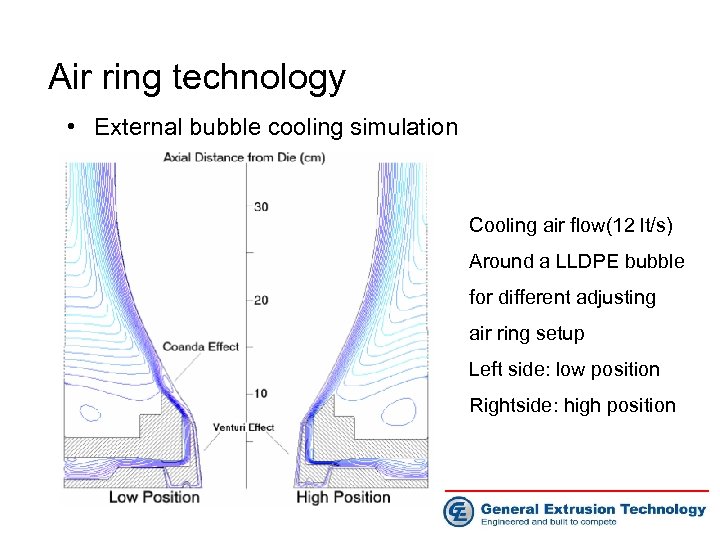
Air ring technology • External bubble cooling simulation Cooling air flow(12 lt/s) Around a LLDPE bubble for different adjusting air ring setup Left side: low position Rightside: high position
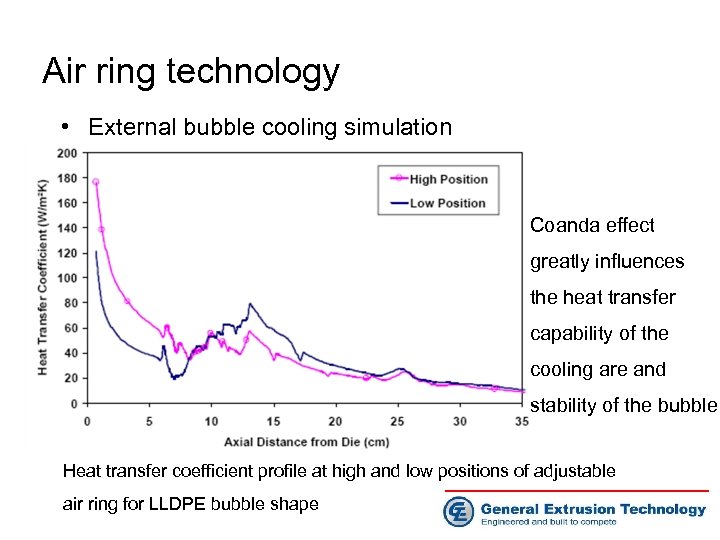
Air ring technology • External bubble cooling simulation Coanda effect greatly influences the heat transfer capability of the cooling are and stability of the bubble Heat transfer coefficient profile at high and low positions of adjustable air ring for LLDPE bubble shape
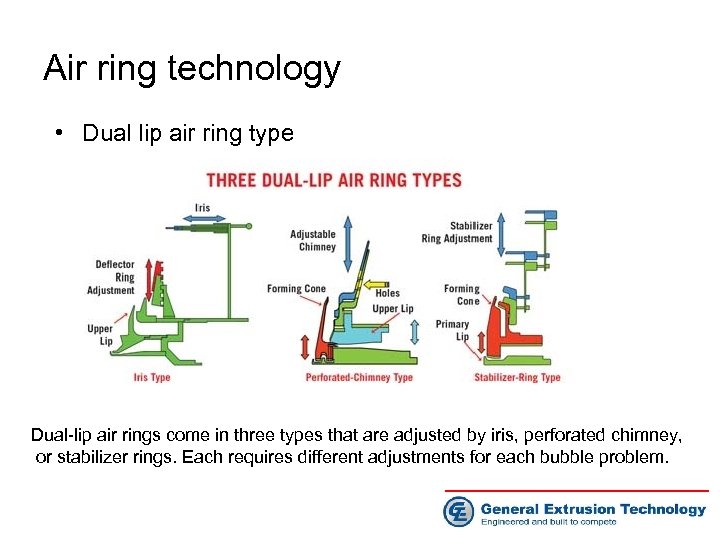
Air ring technology • Dual lip air ring type Dual-lip air rings come in three types that are adjusted by iris, perforated chimney, or stabilizer rings. Each requires different adjustments for each bubble problem.

Air ring technology • Perforated Chimney type dual lip air ring Forming cone and chimney manual adjustment
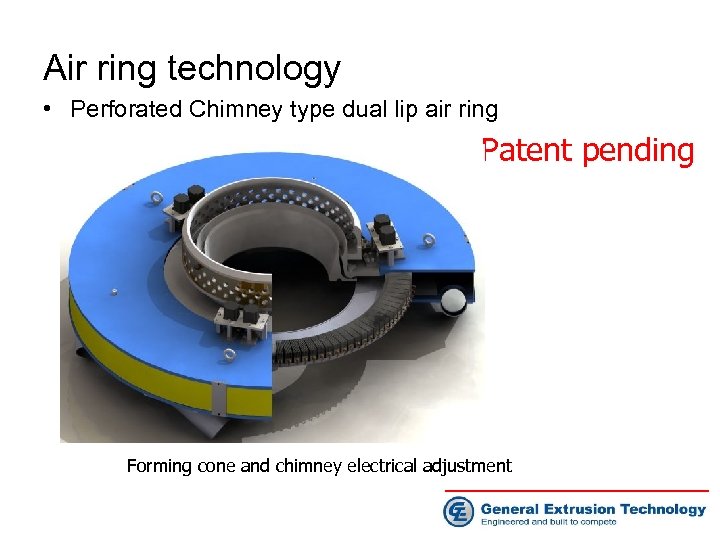
Air ring technology • Perforated Chimney type dual lip air ring Patent pending Forming cone and chimney electrical adjustment
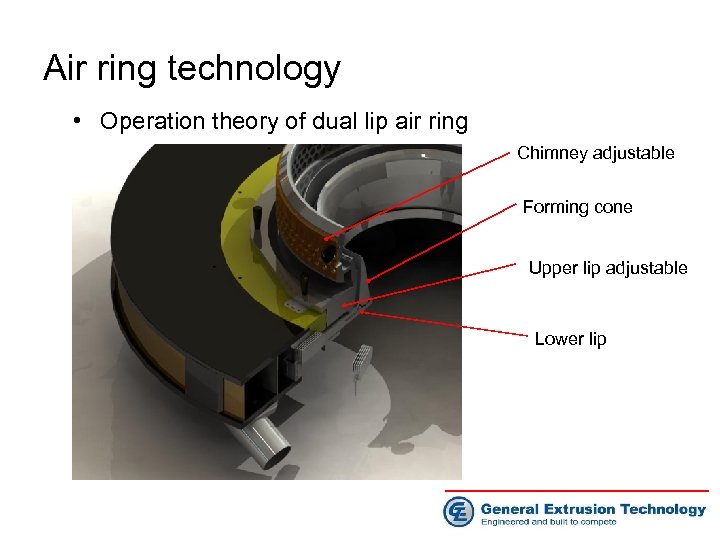
Air ring technology • Operation theory of dual lip air ring Chimney adjustable Forming cone Upper lip adjustable Lower lip

Air ring technology • Operation theory of dual lip air ring • Lower Lip: provides initial quenching to strengthen the melt provides venturi between bubble and cone to “set” the bubble • Forming Cone: guides lower lip air & supports bubble while in the ‘semi-solid’ state • Upper Lip: provides final “blast” of cooling air “adjustment” provides ability to vary volume & velocity of air -- to process wider variety of materials and BUR’s with same lip geometry • Chimney device: to further redirect the cooling air and increase the stability of the bubble

Air ring technology • Dual lip air ring • Adjustable upper lip design for wider BURs • +/- 0. 5% air flow consistency • Finished aluminum flow surfaces • Adjustable chimney ring for improved le bubble stability • Available from 75 to 2200 mm diameter

Air ring technology • Double stack air ring • Electrical actuator up/down adjustment • Suitable for high speed extrusion

Air ring technology • Autoprofile technology • • Autoprofile control principle Autoprofile air ring Autoprofile die Autoprofile benefits

Air ring technology • Autoprofile air ring adjusts according to data from ACS and scanner • Scanner monitors thickness sends data to ACS Autoprofile control principle

Air ring technology • Autoprofile technology • • • 3. 5 mmx 25 m air chamber Segmented air ring design 104 control zones for a 400 mm die 5 x 104= 520 x(3. 5 mm x 25 mm) air chamber A constant air flow blows through heater cartridge Air flow touches bubble at very fine area. More precise, more even Film thickness control more accurate
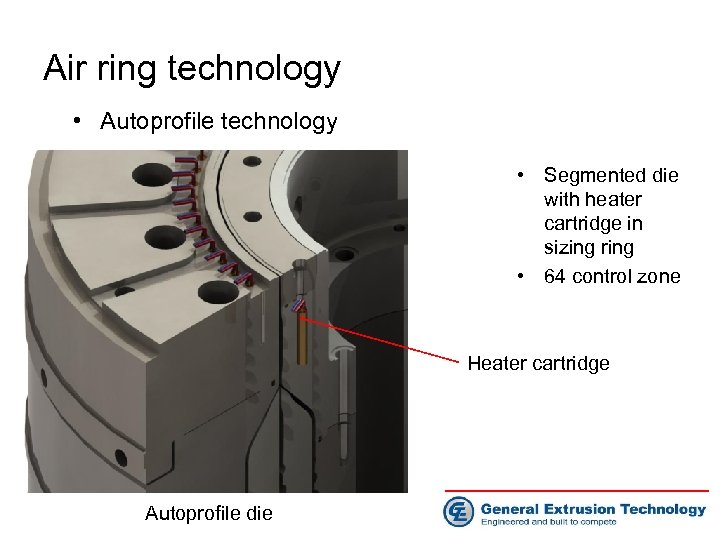
Air ring technology • Autoprofile technology • Segmented die with heater cartridge in sizing ring • 64 control zone Heater cartridge Autoprofile die

Air ring technology • Autoprofile benefits • Available in fixed or oscillating configuration • Utilizes Plast. Control ACS with any on-line thickness gage • Varies the cooling effect on specific bubble segments • Reduces long term repeatable film thickness variations • Retrofitable to almost any blown film die • Typical reduction of 30% of TD variation

Air ring technology • Air ring cooling air supply and die cart Die centering and up/down adjustment Air ring air supply

Internal Bubble Cooling (IBC) • Simulation of typical IBC system • IBC control principle • IBC cooling unit
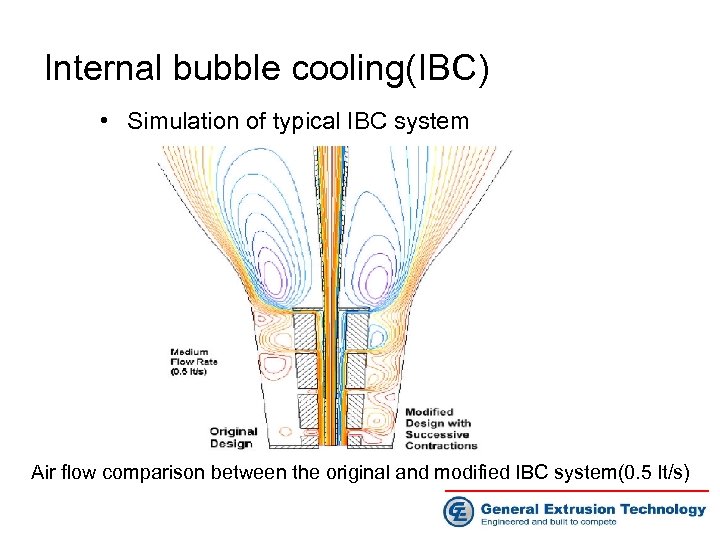
Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • Simulation of typical IBC system Air flow comparison between the original and modified IBC system(0. 5 lt/s)
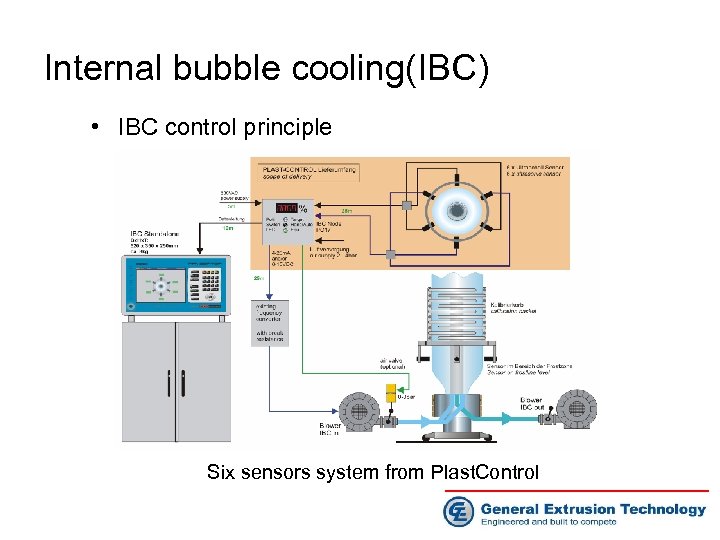
Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • IBC control principle Six sensors system from Plast. Control
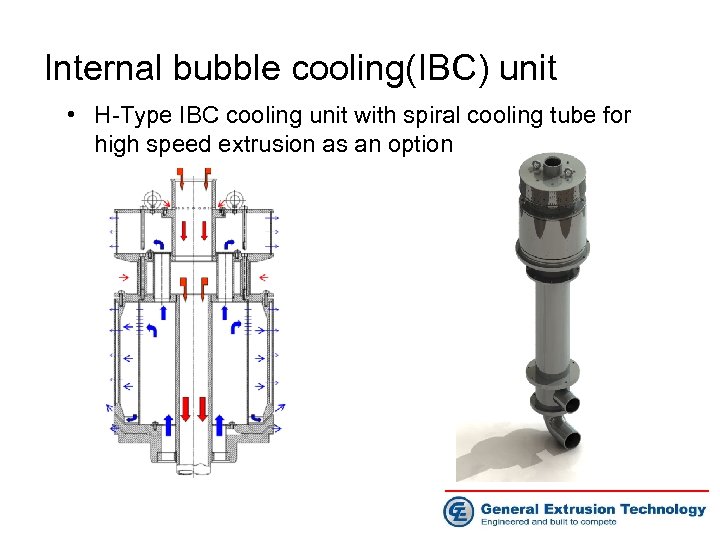
Internal bubble cooling(IBC) unit • H-Type IBC cooling unit with spiral cooling tube for high speed extrusion as an option

Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • V-Type IBC cooling unit with spiral cooling tube for high speed extrusion as an option

Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • Cooling area: 94 cm 2 • Heat venting area: 133 cm 2 • High cooling and venting efficiency. Suitable for high speed extrusion • IBC Cooling unit design more close to FEA simulation, more cooling capacity • IBC modular design, easy operation and maintenance • V-Type and H-Type cooling units interchangeable for different resin and different bubble shape
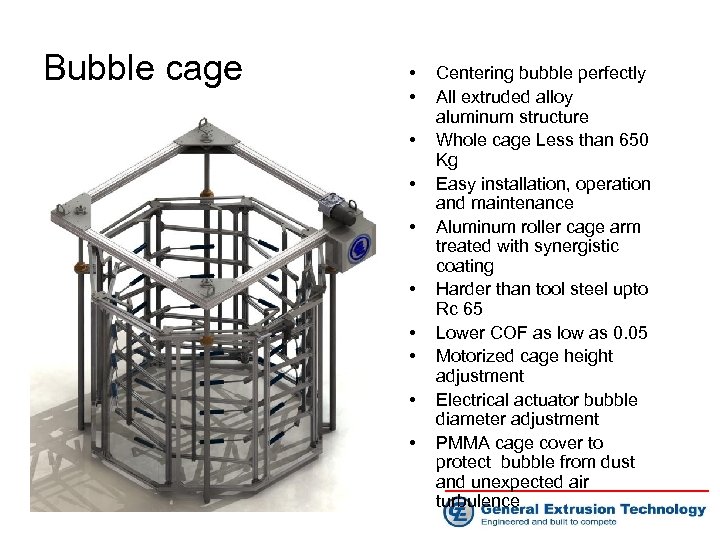
Bubble cage • • • Centering bubble perfectly All extruded alloy aluminum structure Whole cage Less than 650 Kg Easy installation, operation and maintenance Aluminum roller cage arm treated with synergistic coating Harder than tool steel upto Rc 65 Lower COF as low as 0. 05 Motorized cage height adjustment Electrical actuator bubble diameter adjustment PMMA cage cover to protect bubble from dust and unexpected air turbulence
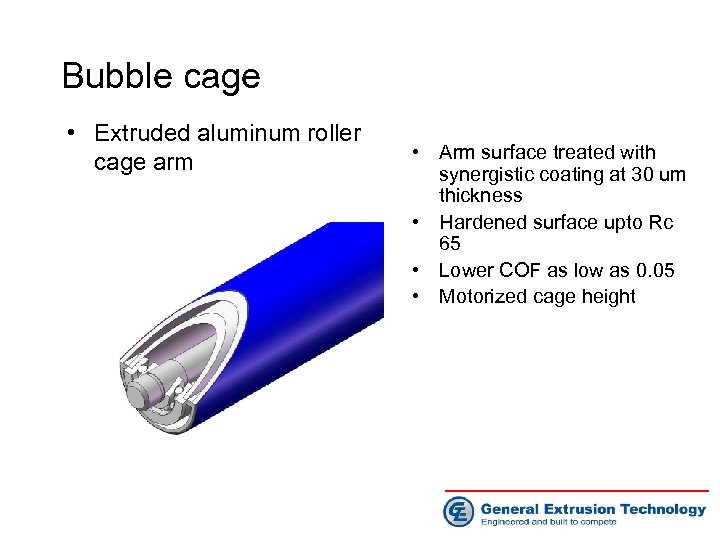
Bubble cage • Extruded aluminum roller cage arm • Arm surface treated with synergistic coating at 30 um thickness • Hardened surface upto Rc 65 • Lower COF as low as 0. 05 • Motorized cage height
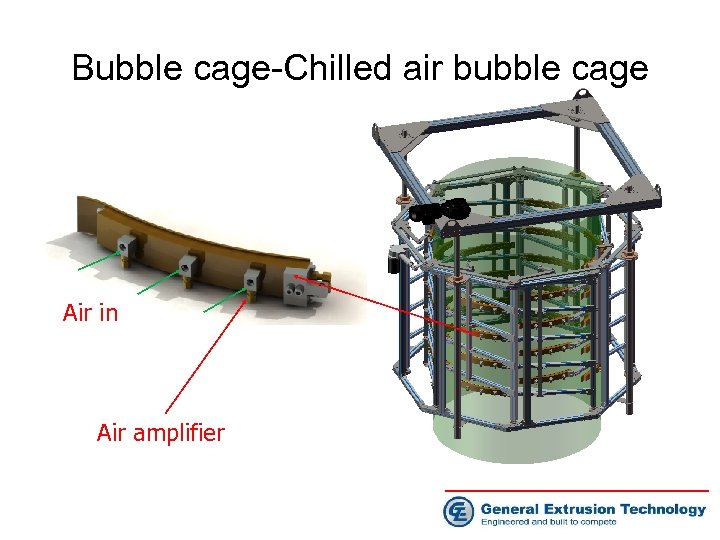
Bubble cage-Chilled air bubble cage Air in Air amplifier
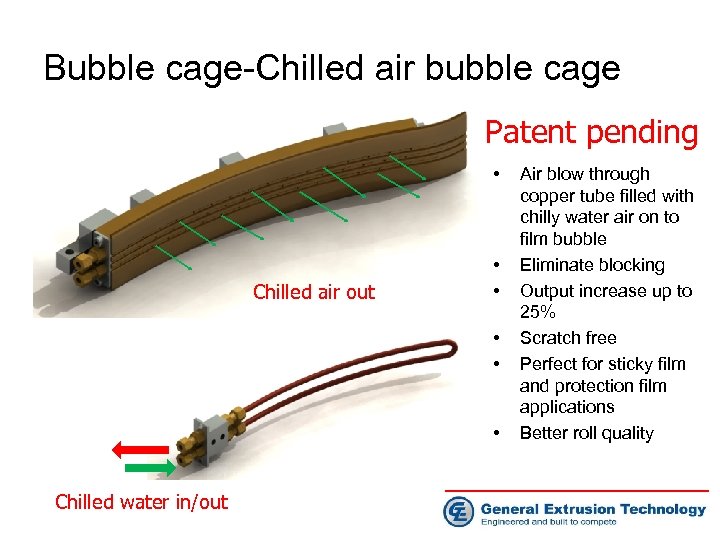
Bubble cage-Chilled air bubble cage Patent pending • Chilled air out • • • Chilled water in/out Air blow through copper tube filled with chilly water air on to film bubble Eliminate blocking Output increase up to 25% Scratch free Perfect for sticky film and protection film applications Better roll quality

Gauging system • Contact and non-contact capacitive rotating scanner

Gauging system
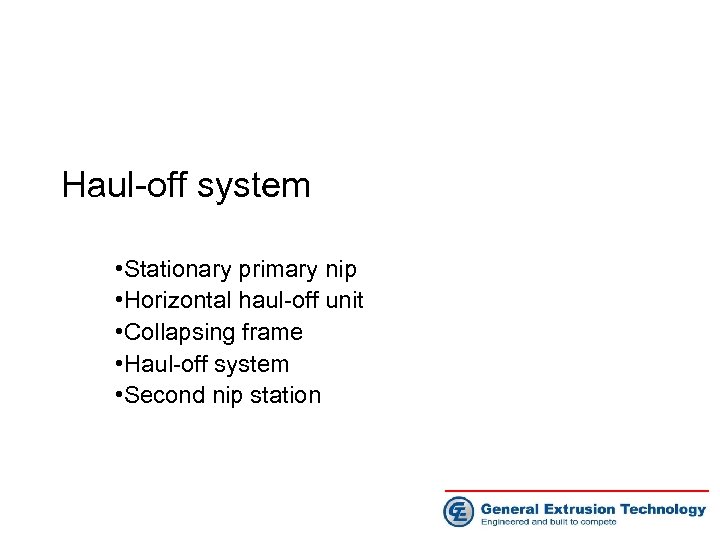
Haul-off system • Stationary primary nip • Horizontal haul-off unit • Collapsing frame • Haul-off system • Second nip station

Haul-off system • Haul-off system

Haul-off system – – – – – Equipped with Mink Web Spreader Brush Roll 10022, Germany Less scratcher due relative MD or TD film movement Low wear of nylon brushes Small contact surface to film and large non contact area Low heat transfer from film to brush No roll temperature increase No film bagging Less contamination Light weight, low height, easy installation
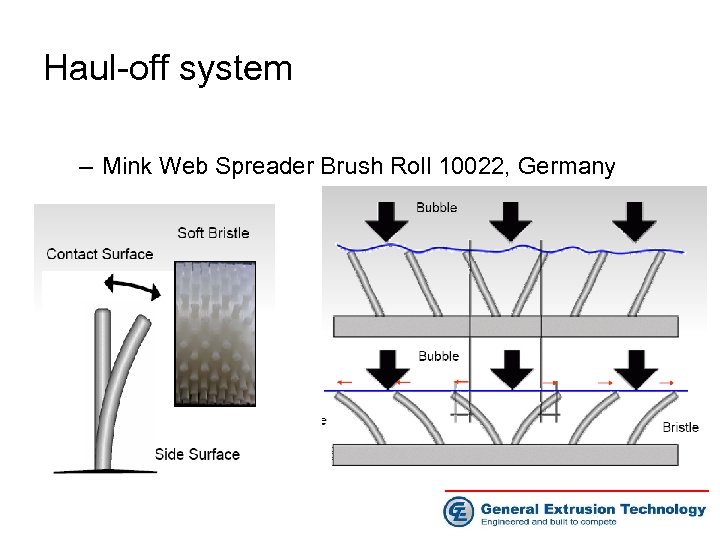
Haul-off system – Mink Web Spreader Brush Roll 10022, Germany

Haul-off system • Mink Web Spreader Brush Roll 10022, Germany
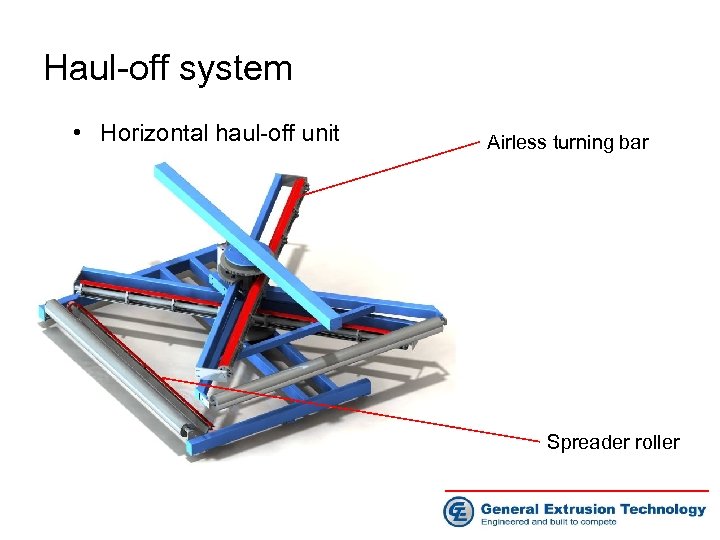
Haul-off system • Horizontal haul-off unit Airless turning bar Spreader roller

Haul-off system • Horizontal haul-off unit Synergistic surface coating Surface hardness: upto Rc 65 Surface COF as low as 0. 05 Heat resistance as high as 4600 C

Haul-off system • Stationary primary nip • Gearbox motor direct coupled to steel shaft. No pulley and belt • High quality HYPAl. ON rubber roll, long life, low wear • Easy access and maintenance • Optional water cooled steel roll
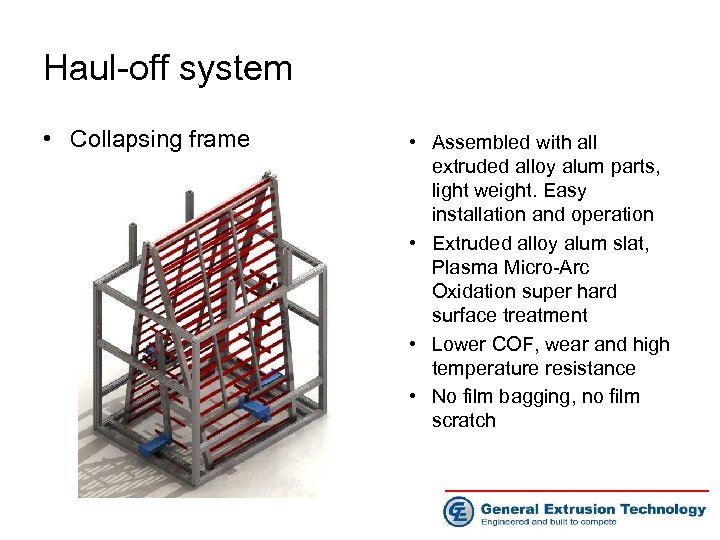
Haul-off system • Collapsing frame • Assembled with all extruded alloy alum parts, light weight. Easy installation and operation • Extruded alloy alum slat, Plasma Micro-Arc Oxidation super hard surface treatment • Lower COF, wear and high temperature resistance • No film bagging, no film scratch

Web guiding system • • • Coast Control all pneumatic web guide system, USA No motor, no electronics No hydraulic Easy installation Easy operation 10 years warranty on all parts
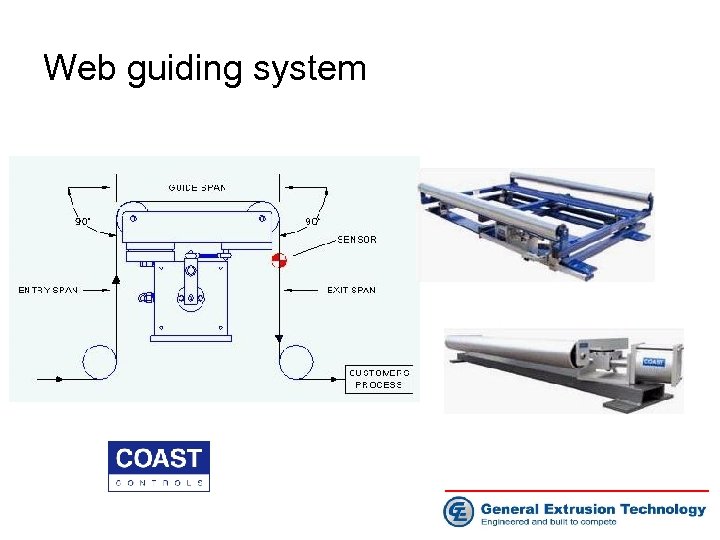
Web guiding system

Web guiding system
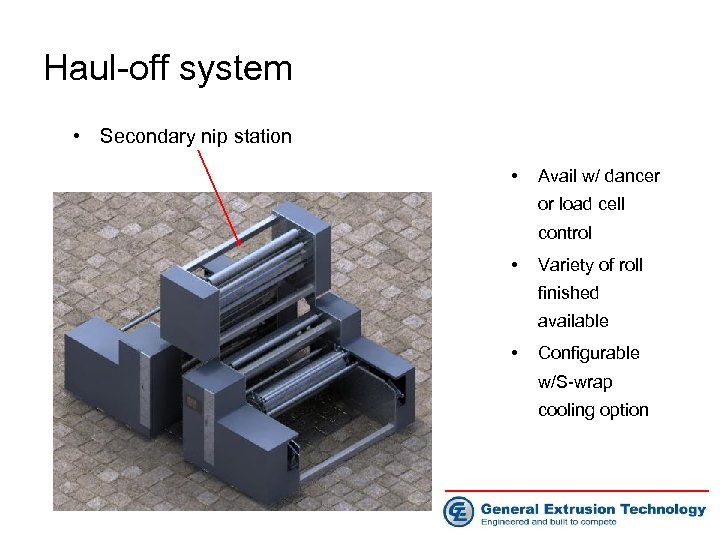
Haul-off system • Secondary nip station • Avail w/ dancer or load cell control • Variety of roll finished available • Configurable w/S-wrap cooling option

Winder Technology • Surface winder • Central surface winder
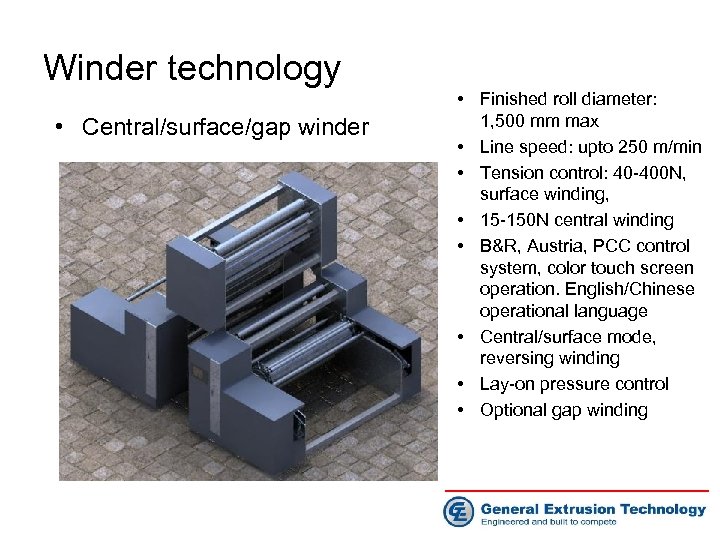
Winder technology • Central/surface/gap winder • Finished roll diameter: 1, 500 mm max • Line speed: upto 250 m/min • Tension control: 40 -400 N, surface winding, • 15 -150 N central winding • B&R, Austria, PCC control system, color touch screen operation. English/Chinese operational language • Central/surface mode, reversing winding • Lay-on pressure control • Optional gap winding
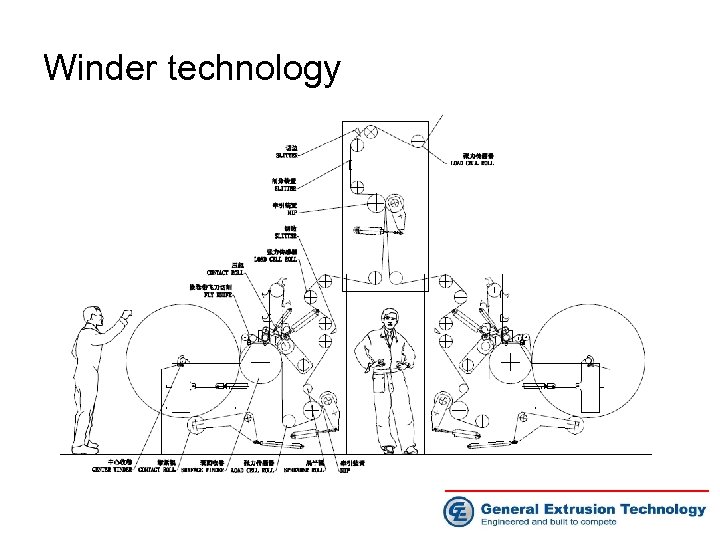
Winder technology
Film tower

Thank you for your attention!
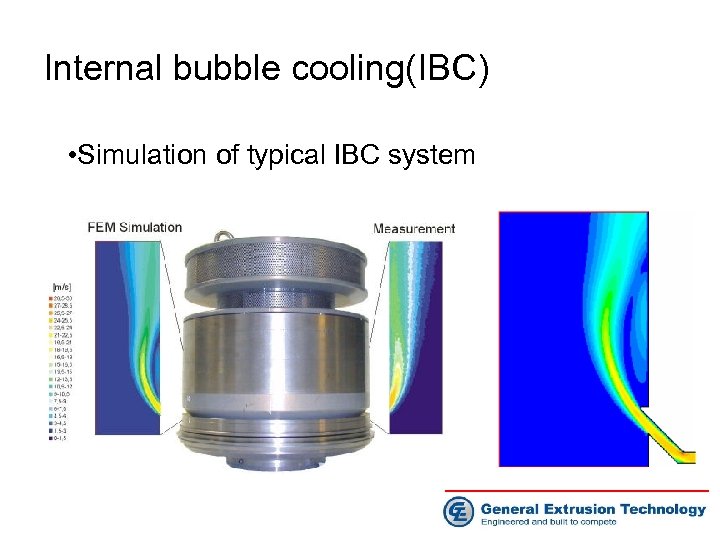
Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • Simulation of typical IBC system
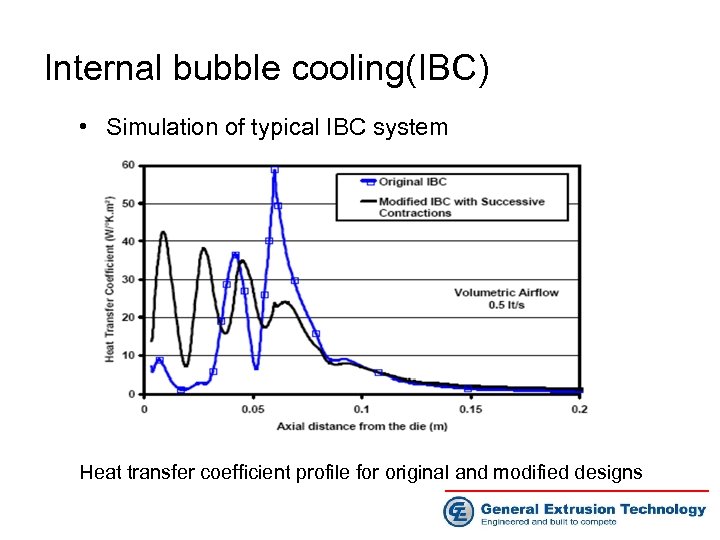
Internal bubble cooling(IBC) • Simulation of typical IBC system Heat transfer coefficient profile for original and modified designs
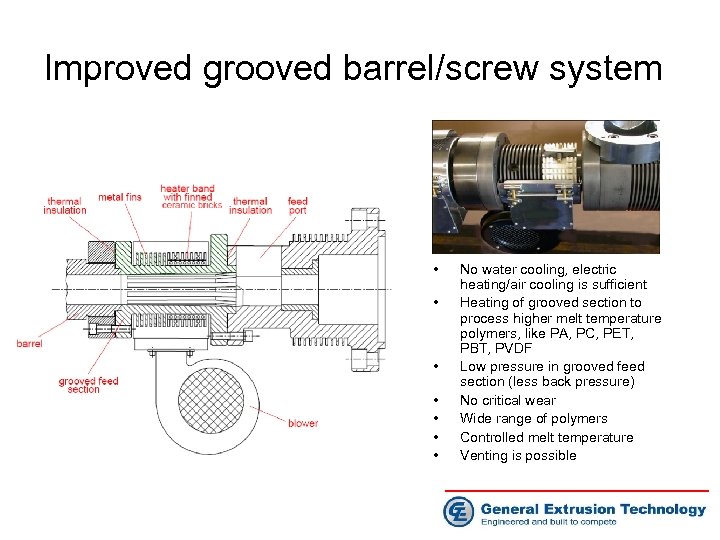
Improved grooved barrel/screw system • • No water cooling, electric heating/air cooling is sufficient Heating of grooved section to process higher melt temperature polymers, like PA, PC, PET, PBT, PVDF Low pressure in grooved feed section (less back pressure) No critical wear Wide range of polymers Controlled melt temperature Venting is possible
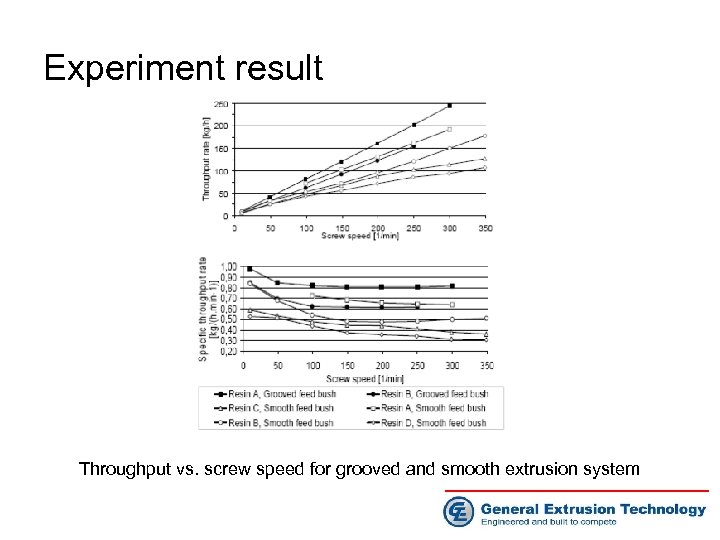
Experiment result Throughput vs. screw speed for grooved and smooth extrusion system
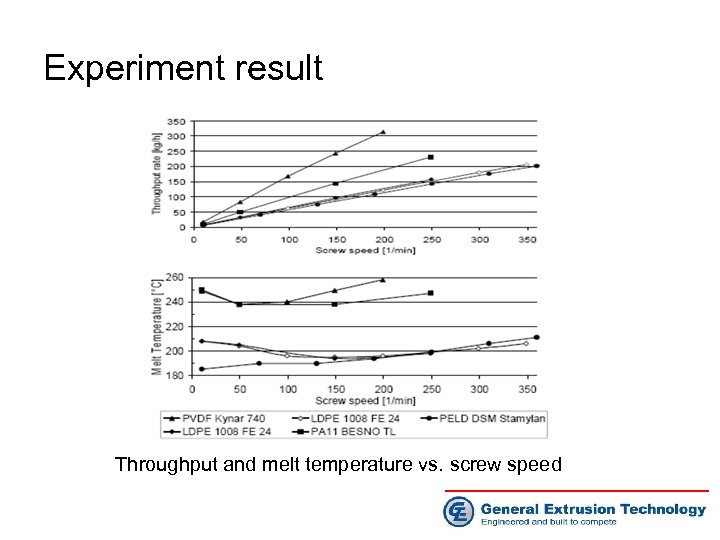
Experiment result Throughput and melt temperature vs. screw speed
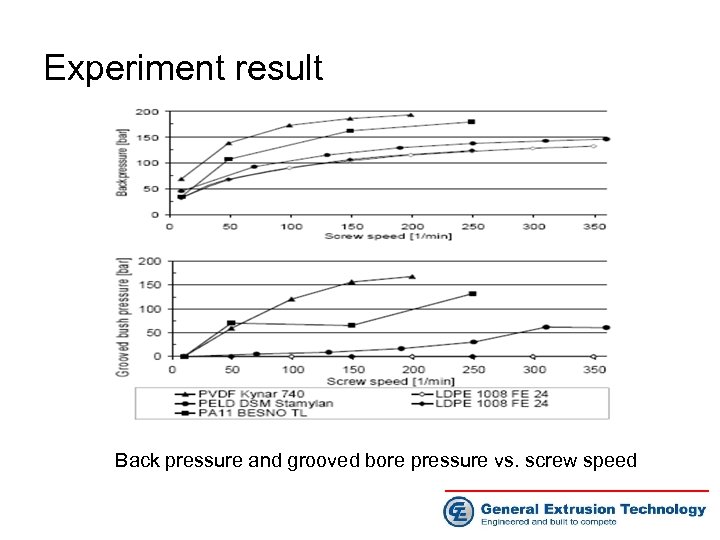
Experiment result Back pressure and grooved bore pressure vs. screw speed
354e19a6e93c31bb3a38f20cb371db56.ppt