54a2a71338e1bd1dec51f0c18fd11890.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 83

Blood and Marrow Transplantation Francisco F. Lopez, MD Hematology and Medical Oncology Bone Marrow Transplantation

1 st BMT Reunion (January 2004)

Outline • • History Definition Rationale Procedure Indications Our data Summary
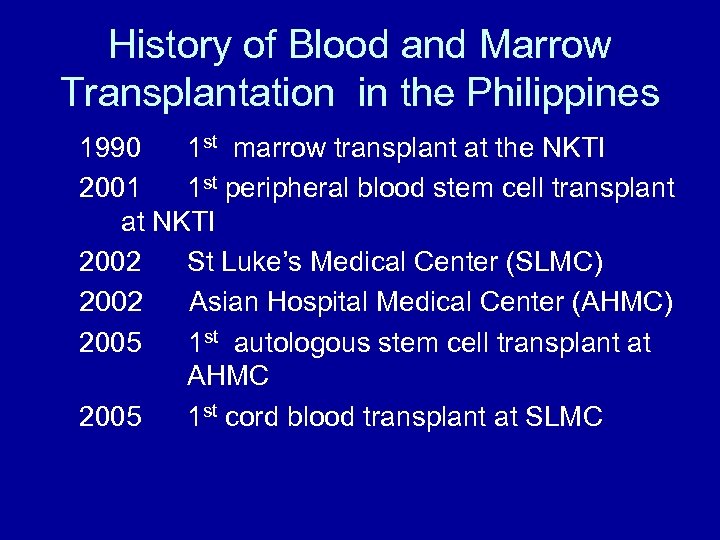
History of Blood and Marrow Transplantation in the Philippines 1990 1 st marrow transplant at the NKTI 2001 1 st peripheral blood stem cell transplant at NKTI 2002 St Luke’s Medical Center (SLMC) 2002 Asian Hospital Medical Center (AHMC) 2005 1 st autologous stem cell transplant at AHMC 2005 1 st cord blood transplant at SLMC

The transfusion of the immature progenitor stem cells derived from a donor to the recipient (allogeneic); OR stem cells previously harvested from the patient (autologous). It is NOT an operation / surgical procedure.
“Let’s crack your bones wide open!”

Stem cells • Young immature cells that make up 0. 5% to 5% of the marrow cells. • Express CD 34+ • Progenitor cells: self-renew and divide to become red and white cells, and platelets.
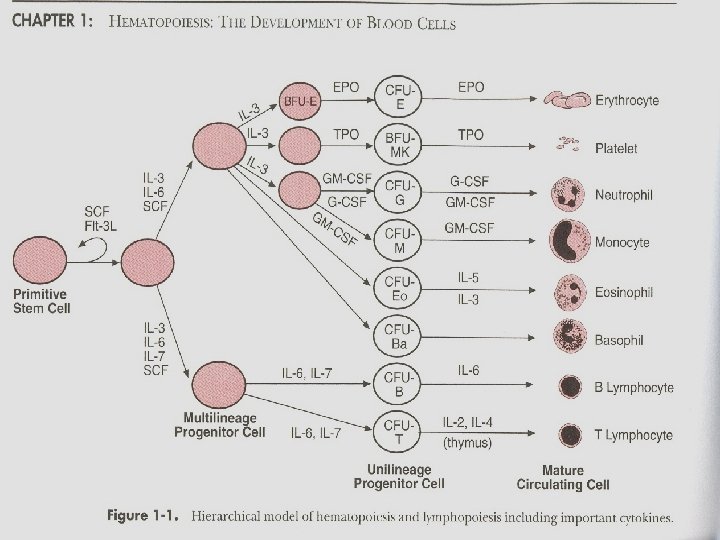

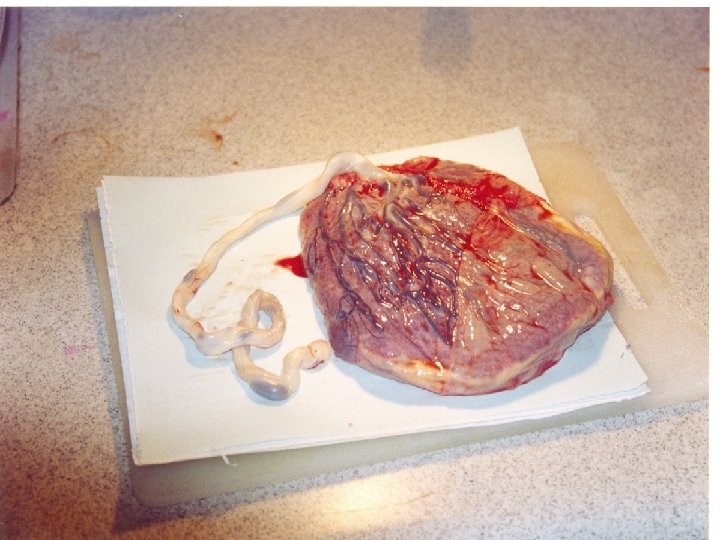
Stem cells Bone marrow 2 to 5 x 108 TNC/kg weight of recipient with the maximum volume dictated by the weight of the donor (20 ml BM aspirate/kg) can be stored at room temperature for up to 24 hrs until infusion into the recipient or cryopreserved Peripheral blood 2. 0 to 5. 0 x 106 CD 34+ cells/kg for auto/allo transplants can be stored at 4 C overnight or cryopreserved with dimethyl sulfoxide (DSMO) Umbilical cord 3. 7 x 106 TNC/kg recipient body weight can be stored at 4 C or 25 C for up to three days or cryopreserved with DSMO

Rationale

Two kinds • Allogeneic: Donor – Matched or partially mismatched sibling – Unrelated – Cord blood • Autologous: No donor – Stem cells are harvested from patient

Allogeneic transplant • involves the transfer of stem cells from donor to recipient to permanently replace all hematopoietic cells • eradicate malignant cells with high dose chemotherapy +/- radiotherapy • sufficient immunosuppression of the host to allow growth of the allograft • immune mediated graft vs leukemia/lymphoma or graft vs tumor effect
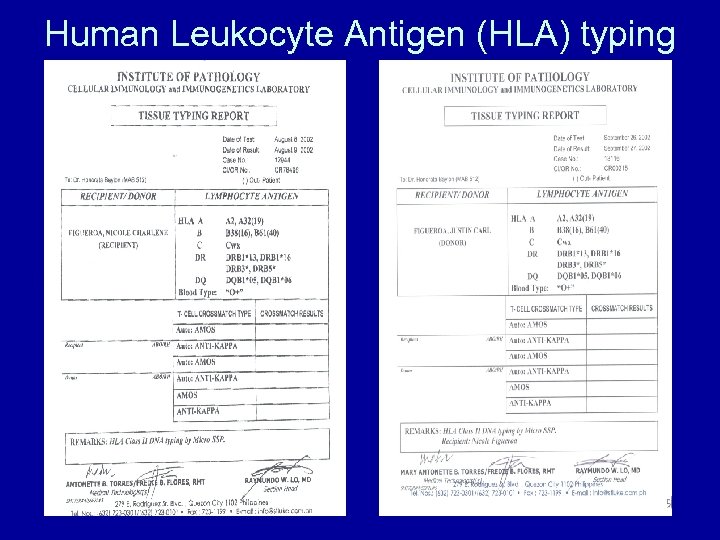
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) typing

Autologous transplant • Increasing the dose of some chemotherapeutic agents may result in large increase in tumor cell kill • Transfusing previously harvested stem cells of the patient will guarantee bone marrow recovery

Procedure Allogeneic transplant
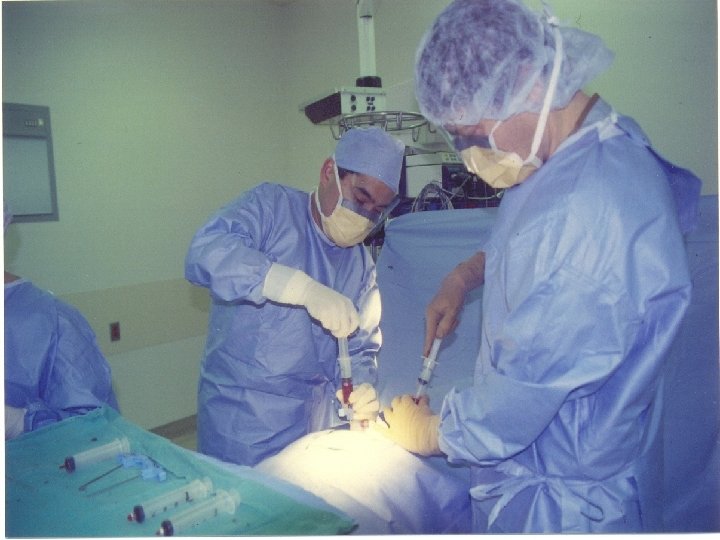

Schema -8 admit to hospital -7 Total body Irradiation -6 Total body Irradiation -5 Total body Irradiation -4 Total body Irradiation; Donor starts GCSF -3 Cytoxan (60 mg/kg) -2 Cytoxan (60 mg/kg) -1 Rest day and start cyclosporine IV 0 Harvest and infusion of stem cells +1 Methotrexate 15 mg/mm +3 Methotrexate 10 mg/mm +6 Methotrexate 10 mg/mm +11 Methotrexate 10 mg/mm

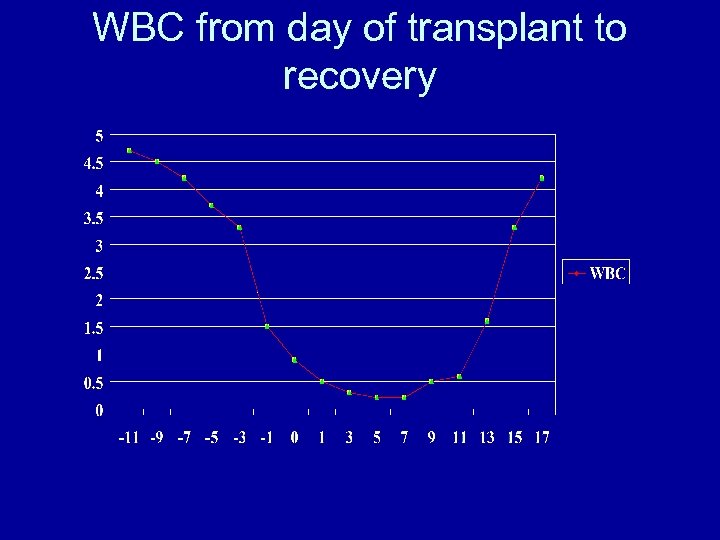
WBC from day of transplant to recovery

Procedure Autologous transplant

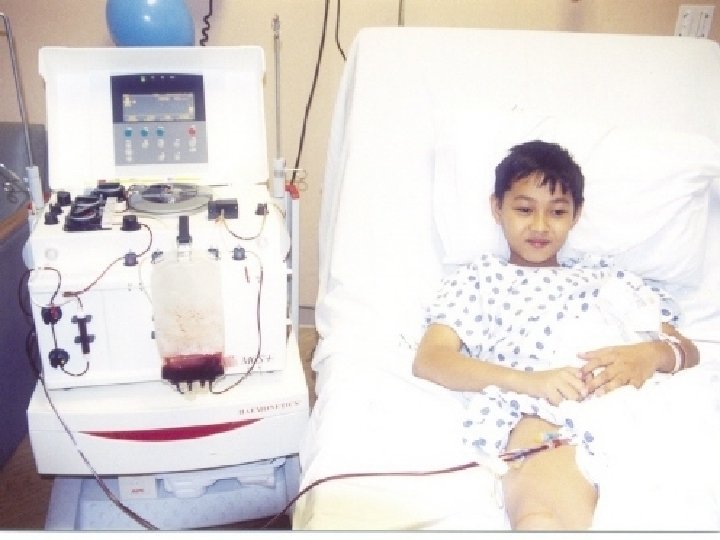
Procedure: The Harvest D – 10 Cyclophosphamide 1. 5 gm/mm D – 7 Start GCSF 10 mcg/kg D– 6 D– 5 D– 4 D– 3 D– 2 D– 1 D 0 Harvest using apheresis machine (collect 2. 5 x 106 / kg. BW CD 34+ cells)
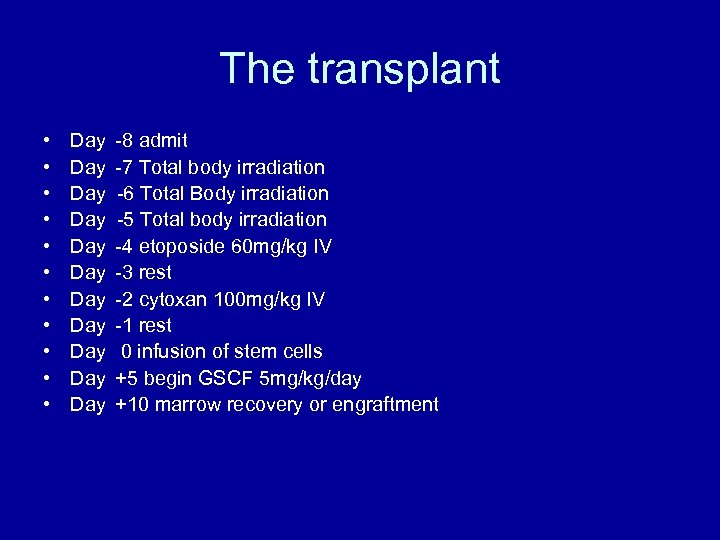
The transplant • • • Day Day Day -8 admit -7 Total body irradiation -6 Total Body irradiation -5 Total body irradiation -4 etoposide 60 mg/kg IV -3 rest -2 cytoxan 100 mg/kg IV -1 rest 0 infusion of stem cells +5 begin GSCF 5 mg/kg/day +10 marrow recovery or engraftment
Transfusion of stem cells
Indications and Timing of Transplant

Allogeneic Transplant Malignant • Acute and chronic leukemias – AML, ALL, CML • • Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) Lymphomas (failed chemotherapy) Multiple myeloma Myeloproliferative diseases

Allogeneic Transplant Non malignant • • Aplastic anemia Thalassemia Immune disorders Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)

Autologous Transplant • • • Multiple Myeloma Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma Hodgkins Disease Solid Tumors Autoimmune diseases (multiple sclerosis)
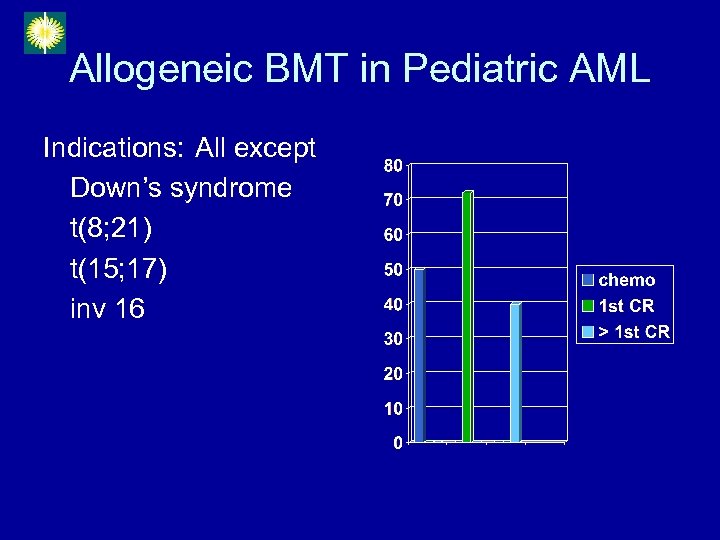
Allogeneic BMT in Pediatric AML Indications: All except Down’s syndrome t(8; 21) t(15; 17) inv 16
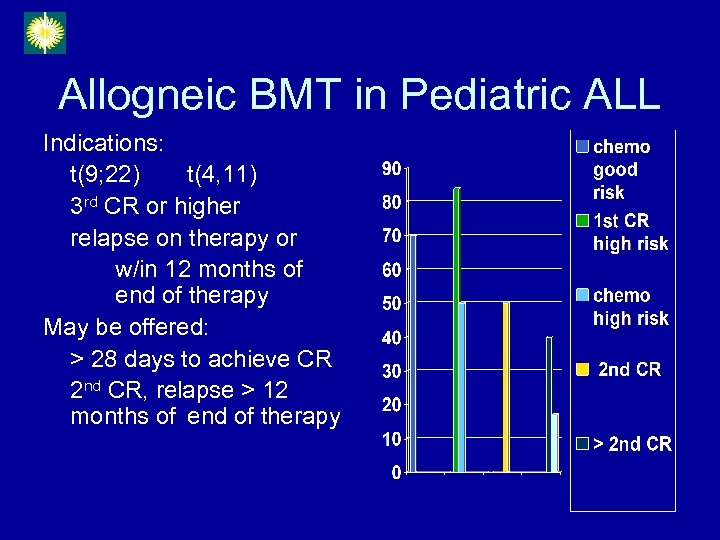
Allogneic BMT in Pediatric ALL Indications: t(9; 22) t(4, 11) 3 rd CR or higher relapse on therapy or w/in 12 months of end of therapy May be offered: > 28 days to achieve CR 2 nd CR, relapse > 12 months of end of therapy
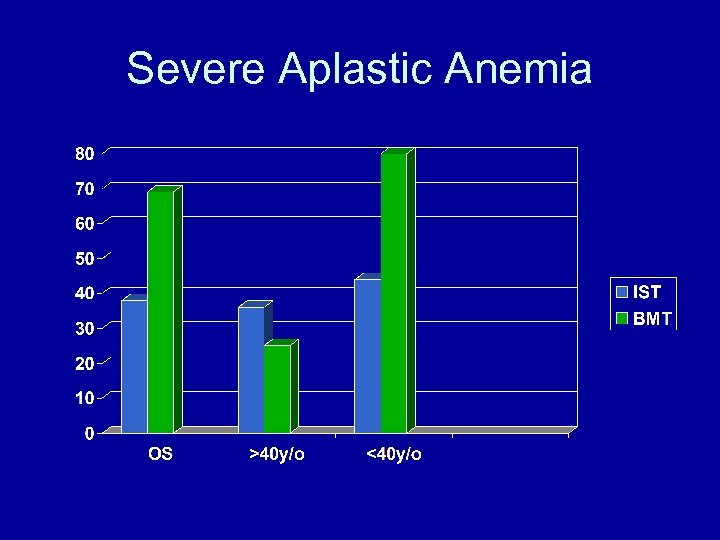
Severe Aplastic Anemia
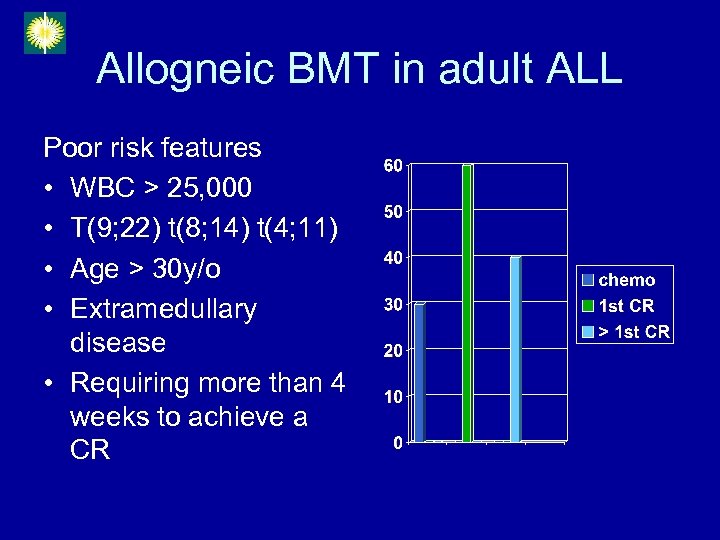
Allogneic BMT in adult ALL Poor risk features • WBC > 25, 000 • T(9; 22) t(8; 14) t(4; 11) • Age > 30 y/o • Extramedullary disease • Requiring more than 4 weeks to achieve a CR
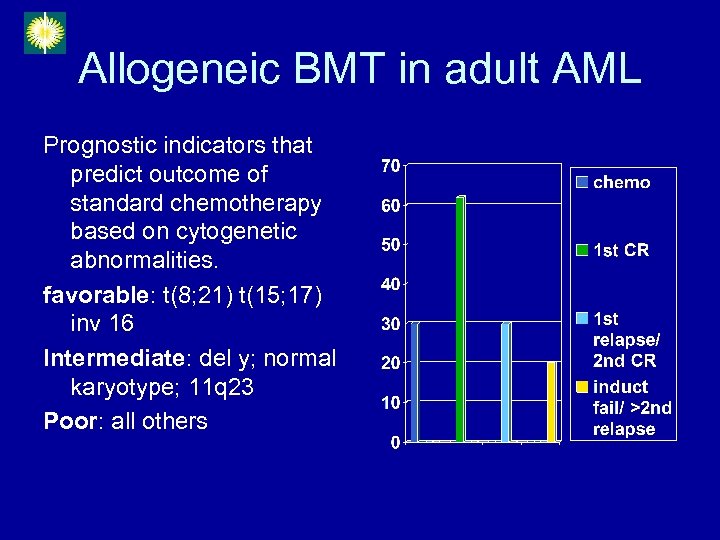
Allogeneic BMT in adult AML Prognostic indicators that predict outcome of standard chemotherapy based on cytogenetic abnormalities. favorable: t(8; 21) t(15; 17) inv 16 Intermediate: del y; normal karyotype; 11 q 23 Poor: all others

2 nd BMT Reunion (January 2005)

Complications During BMT

• • • • Nausea and Vomiting Nutrition Mouth Sores Diarrhea Infection Renal complications Veno-Occlusive disease of the liver (VOD) Pancytopenia Graft Rejection Acute Graft vs Host Disease Rash Pulmonary complications Death

• Nausea and Vomiting – More common during the early part of transplant – Round the clock anti emetic medications – During the recovery phase, nausea / vomiting / abdominal pain (cramps) / diarrhea, the patient may have graft vs host disease (GVHD).

• Nutrition – Low bacteria diet: no fresh fruit and vegetables; served hot; no left over; tray should be clean; – Appetite diminishes after chemotherapy – Total parenteral nutrition until patient can eat.

• Mouth Sores – Mouth wash (nystatin and biotene) – Morphine pushes or drip when severe (face will be swollen) – Thrush

• Diarrhea – Chemotherapy induced (Cuclophosphamide) – Infection: Clostridium Defficile – GVHD (graft vs host disease) – Food induced (avoid creamy, milk, oily food)

• Bacterial Infections – Gram negative – Gram positive (central line or skin); patient should shower or sponge bath daily. – Antibiotics: third generation cephalosporin and vancomycin • Fungal – Pulmonary (aspergillus) – Yeast – Amphoteric B prophylaxis • Viral – Herpes zoster – Acyclovir IV

Prevention • • Isolation room : positive pressure Strict hand washing Mask No need for gown or gloves unless patient is positive for clostridum defficile

• Renal Complications – Renal insufficiency – Drugs: cyclosporine, vancomycin, amphotericin B) – Monitor I & 0 accurately every 12 hours. Balance fluid I & 0. lasix IV given prn.
• Liver Complications – Veno-Occlusive disease of the liver (VOD) • Water retention • Tender liver • Elevated bilirubin • Elevation in bilirubin and SGPT and SGOT – Medications: cyclosporine, TPN – GVHD

• Pancytopenia – Blood and platelet transfusion – Platelet apheresis is always used – Blood and platelets should always be available, filtered and irradiated.

• Graft rejection – Engraftment occurs between two to three weeks after transfusion of stem cells – Recipient develops antibodies against the HLA antigen of the donor. – Incidence increases in heavily transfused patients. – Prior transfusions without filter and random donor platelets used

• Graft versus host disease – Occurs when donor stem cells recognizes the body of the recipient as foreign and attacks the body. – Acute GVHD occurs during engraftment: diarrhea, elevated bilirubin and rash – GVHD prophylaxis: cyclosporine IV, methotrexate IV

• Rash – Drug – GVHD – infection
• Pulmonary complications – Pneumonia – Pulmonary congestion • Total fluid per day 3 L to 4 L – Engraftment syndrome

• Mortality – Infection – GVHD – Relapse

3 rd BMT Reunion (January 2006)

Bone Marrow Transplant Data
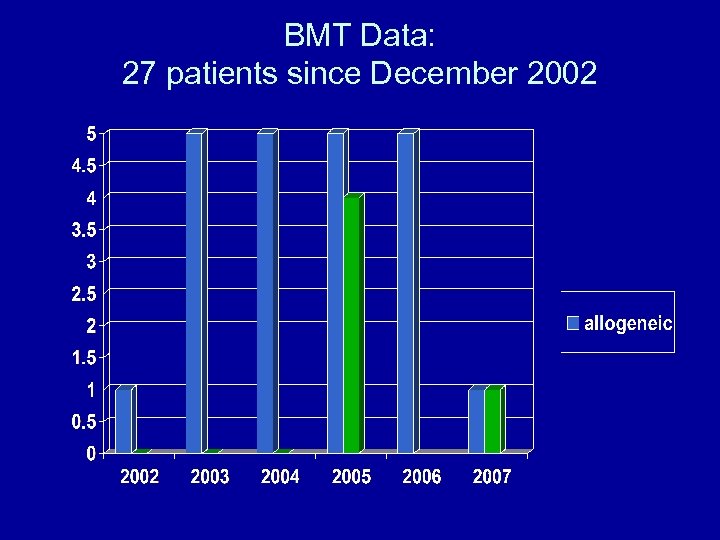
BMT Data: 27 patients since December 2002

BMT Data • December 2002 to April 2007 • 27 stem cell transplants – 22 allogeneic – 5 autologous • Ages: 8 months to 66 years old • Sex: 17 M and 10 F • Transplant Regimen: – Chemotherapy only: 21 – Fractionated total body irradiation + chemo: 6 • GVHD prophylaxis: – CSA + Methotrexate 17 – CSA + Cellcept 5

BMT Data: Donor • Sex – Same sex: 10 – Opposite sex: 12 • HLA match – Full sibling: 21 – Mismatch: 1(HLA 4/6 from father)
BMT Data • 22 allogeneic – Acute myelogenous Leukemia 10 • 1 st CR 7 • 2 nd CR 1 • Induction failure 2 – Acute lymphoblastic leukemia 4 • 1 st CR 1 • > 1 st CR 3 – – – Myelodysplastic syndrome 4 Chronic myelogenous leukemia 1 Severe aplastic anemia 1 Thalassemia 1 Metastatic (lung & bones) renal cell cancer 1

BMT Data • 5 Autologous – 3 multiple myeloma – 1 relapsed hodgkin’s disease – 1 acute myelogenous leukemia in 2 nd CR
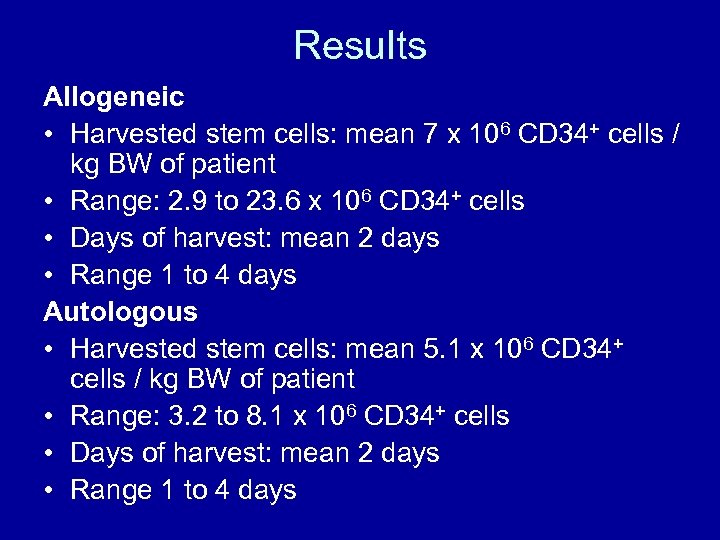
Results Allogeneic • Harvested stem cells: mean 7 x 106 CD 34+ cells / kg BW of patient • Range: 2. 9 to 23. 6 x 106 CD 34+ cells • Days of harvest: mean 2 days • Range 1 to 4 days Autologous • Harvested stem cells: mean 5. 1 x 106 CD 34+ cells / kg BW of patient • Range: 3. 2 to 8. 1 x 106 CD 34+ cells • Days of harvest: mean 2 days • Range 1 to 4 days

Results • Engraftment (allo and auto) – Mean 13 days – Range: 10 to 18 days

Morbidity

Rejection Acute: Patient with AML 1 st CR did not engraft at all. Positive antibodies against HLA. Was salvaged with a second transplant using same donor. Currently doing well and off immuno drugs Delayed: Patient with thalassemia. Graft rejection after 1 year. Autologous recovery of marrow. Transfusion dependent.

Acute Graft Vs Host Disease (AGVHD) in BMT • Manifestation of alloreactivity and occurs when mature T cells are transferred to hosts expressing histocompatibility differences • Donor CD 4+ and CD 8+ target major tissues of the skin, liver and intestinal tract
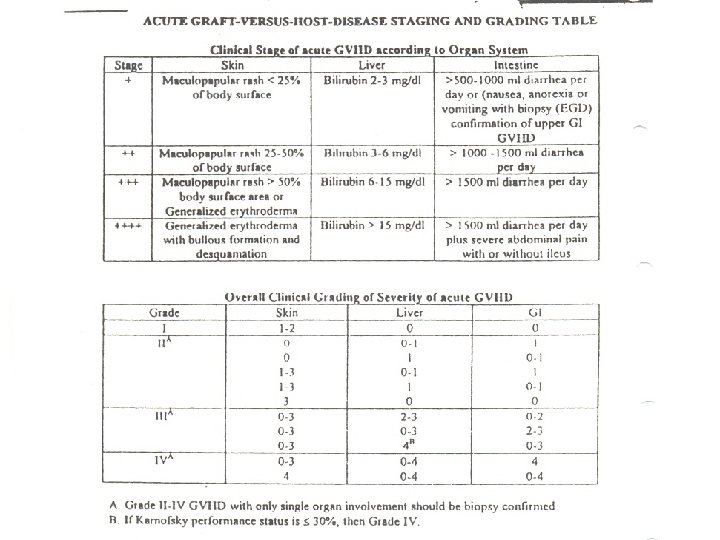
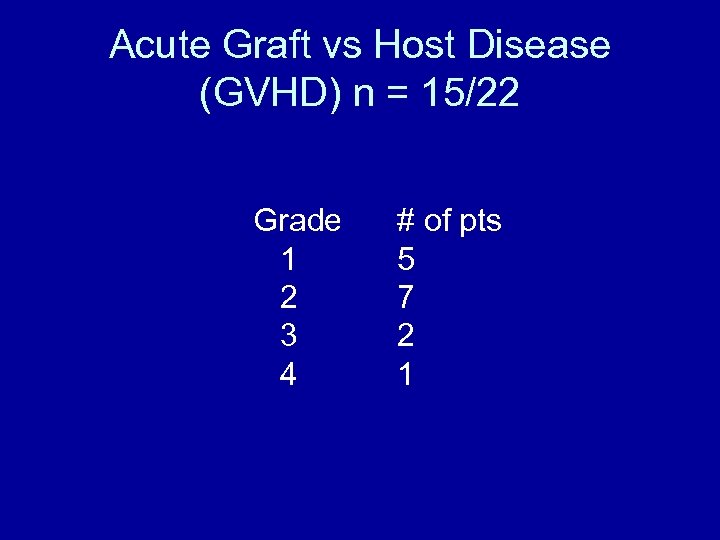
Acute Graft vs Host Disease (GVHD) n = 15/22 Grade 1 2 3 4 # of pts 5 7 2 1

Causes of GVHD Causes • HLA disparity • Conditioning regimen • Sex mismatch • Age • Parous donor • Peripheral blood vs marrow

Infection • 8 had either gram (+) or gram (-) bacterial infection • 1 had recurrence of PTB during transplant. He was an auto transplant patient with relapsed hodgkin’s disease, (+) history of treated PTB • 4 had herpes zoster, months after • 1 had anal warts, months after
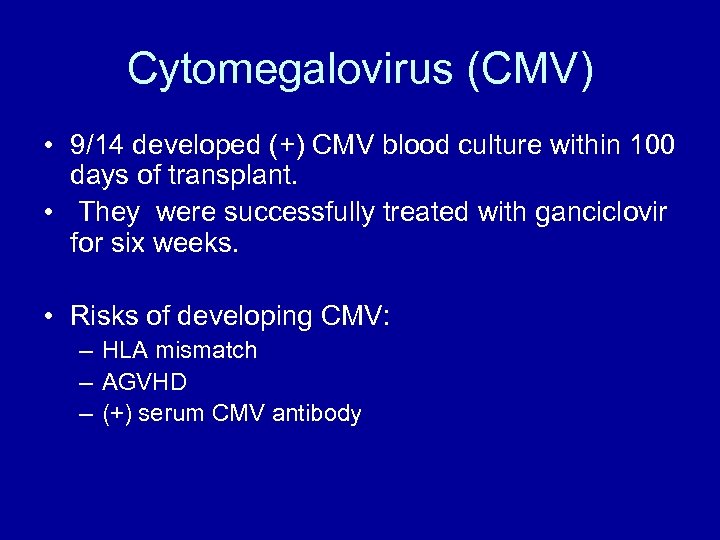
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) • 9/14 developed (+) CMV blood culture within 100 days of transplant. • They were successfully treated with ganciclovir for six weeks. • Risks of developing CMV: – HLA mismatch – AGVHD – (+) serum CMV antibody

Mortality n = 11 • Infection (Gm negative septic shock) 2 – 10 and 11 days post transplant – history of prior infections – poor performance status • Severe AGVHD of the GIT 1 • Relapse disease 8 – – – 2 ALL > 1 st CR 3 myelodysplastic syndrome 1 AML induction failure 1 AML auto 1 multiple myeloma auto

survival • • Allogeneic: 13/22 Autologous: 3/5 16/27 survivors 1 st patient transplanted is now 4 yrs and 5 months post transplant • Data may change in time – wait for 2 to 3 years
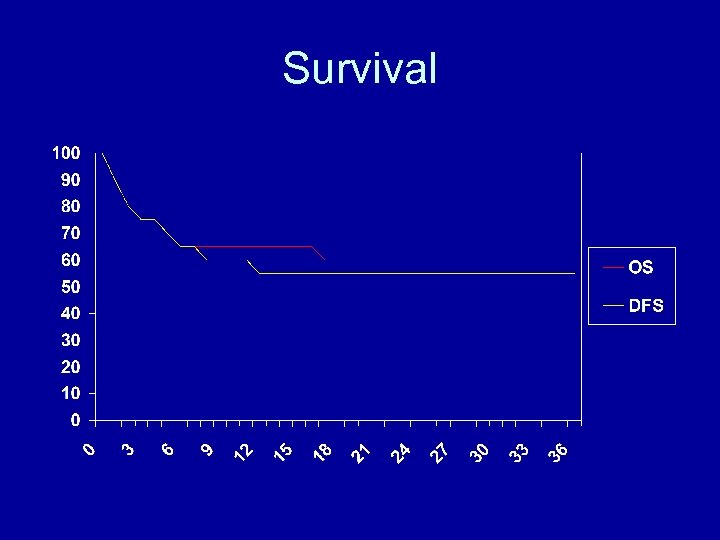
Survival

Improve outcome • Education and information – Can be done in our country – Dispel myths • • Not a surgical procedure Harvesting stem cells is not a painful procedure Maximum hospital stay 6 weeks Live a normal life • Screen candidates • Early transplant and not later on (not a last resort)

Burst my bubble!

Kicking leukemia away!
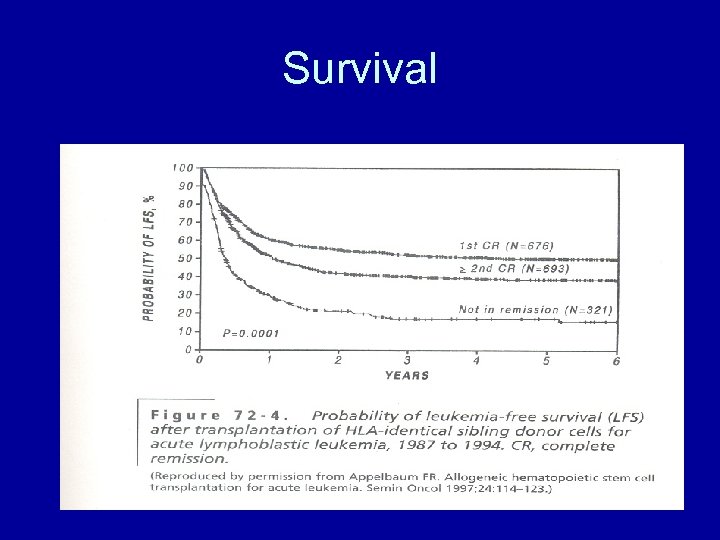
Survival

Cost

Cost Factors – Age – Disease and status of disease – Weight – Complications – Regimen used

Cost • Range (Php 0. 8 M to Php 3 M) – Adult (Php 1. 7 M) – Pediatric (Php 1. 4 M) • Beyond what most Filipinos can afford • The cost of BMT abroad is more expensive – Israel US$ 100, 000 – USA $250, 000 to $500, 000

4 rd BMT Reunion (February 2007)
54a2a71338e1bd1dec51f0c18fd11890.ppt