MMM_ACNS2012.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 12

Blind 384 -bit Digital Signature Scheme Nikolay Moldovyan 1, Alexandr Moldovyan 1 and Evgenia Novikova 2 1 Laboratory 2 Laboratory of Cryptology, St. Petersburg Institute for Informatics and Automation (SPIIRAS) of Computer Security Problems, St. Petersburg Institute for Informatics and Automation (SPIIRAS) Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Blind Digital Signature Schemes User anonymity is required in electronic voting system e-commerce … => blind digital signature • • the signer cannot read the document during process of signature generation; the signer cannot correlate the signed document with author of the message Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Digital Signature Scheme (DSS) with Short Signature Length DSS with short signature length are useful in mobile environments For L-bit security: 4 L bit signature (DSS based on discrete logarithm problem) ? ? bit signature (DSS based on factorization problem) constructively impossible to use them for blind DSS as they use two level exponentiation operation 3 L bit signature (DSS based on discrete logarithm problem modulo composite integer) Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Preliminary: hard computational problem multiplicative group R*n of finite ring Rn n = q*p, p, q - strong primes, |q| |p| 1232 bits p = Npr 2 + 1 , q = Nqr 2 + 1, Np , Nq - even integers, |r |= 128 bits - subgroup of r 2 , - basis elements of the order r Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Preliminary: Generation of the Basis Elements (variant #1 ) Choose random positive integer b (1 ≤b≤ n). 2. Compute values = L(n)/r and z = b mod n. 3. If z 1 holds then take z as (or ) else repeat steps 1 -3. 1. Probability that and belong to one subgroup: For |r| = 128 bits → Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012
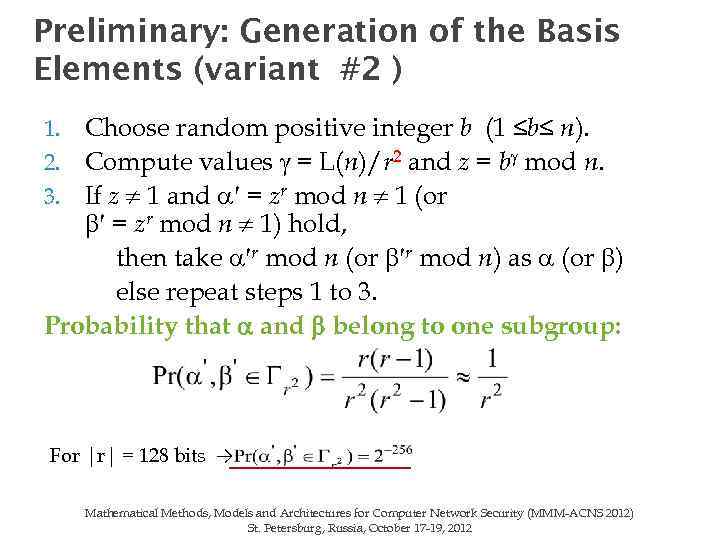
Preliminary: Generation of the Basis Elements (variant #2 ) Choose random positive integer b (1 ≤b≤ n). Compute values = L(n)/r 2 and z = b mod n. If z 1 and = zr mod n 1 (or = zr mod n 1) hold, then take r mod n (or r mod n) as (or ) else repeat steps 1 to 3. Probability that and belong to one subgroup: 1. 2. 3. For |r| = 128 bits → Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Key Construction Scheme Possible variants: p, q – secret key n – public key n – secret key (p, q are destroyed after computation of the n) (p, q, x, w) - secret key p, q – divisors of the n x, w – random 128 bit numbers (x < r, w < r) (n, r, , , y) – public key Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Basic Digital Signature Scheme Signature generation procedure to the message M The signer 1. generates pair of random numbers k and t (1 < k < r and 1 < t < r) 2. computes parameter 3. calculates H = FH(M) and E = F H(R||M) mod r, where FH and F H - secure hash-functions having size 256 and 128 bits, respectively; M – message to be signed. 3. calculates S = (k + x. E) mod r and U = (t + w. E) mod r. => (E, S, U) – signature to message M |E| = |S| = |U| = 128 bits → signature length = 384 bits Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Blind Digital Signature Scheme Signature generation procedure to message M Signer: 1. generates random disposable secret key (k, t), (1 < k < r and 1 < t < r) 2. computes 3. sends to the requester. Requester: 1. calculates H = FH(M). 2. generates random “blinding” parameters ( , , ) that lie in the interval (1, q) 3. calculates 4. if E = 0, repeats step 1 -3 5. sends to the signer. Signer: 1. computes 2. sends to requester Requester: 1. “unblinds” parameters (E, S, U) – signature to message M Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Blind Digital Signature Scheme Signature verification procedure M – signed message, (E, S, U) – signature to message M Verifier: 1. computes the values 2. compares E and 3. if → (E, S, U) is valid. Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Proof of the Correctness To prove the correctness of the proposed scheme substitute in verification equation: Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012

Discussion of the Anonymity (E, S, U) random Mathematical Methods, Models and Architectures for Computer Network Security (MMM-ACNS 2012) St. Petersburg, Russia, October 17 -19, 2012
MMM_ACNS2012.pptx