46ba47c52a0344380897663e575a6ace.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Black Holes And Spacetime The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory: a Caltech/MIT collaboration supported by the National Science Foundation Gregory Mendell, LIGO Hanford Observatory, on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 050374 -00 -W LIGO-G 050635 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Einstein • Einstein, age 26, working at a Swiss Patent Office, published papers in 1905: §Sparked the quantum theory of light §Showed that atoms were real §Introduced a theory of space and time, called Special Relativity §Discovered E=mc 2. • Einstein worked 10 years to generalize Special Relativity and Newton’s Theory of Gravity, resulting in General Relativity. • Others contributed: Lorentz, Poincaré, Minkowski, Grossmann, Hilbert, … • Einstein revolutionized our concepts of space and time! LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Some Far Out Ideas • • The faster you go the slower time goes. Nothing can go faster than light. Gravity disappears when you free fall. Sources of gravity warp space and time; gravity slows down time. • Black holes really are like holes in space. • Worm holes through space and time could exist within our universe or to other universes. • Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime. LIGO is searching for these waves, with black holes as one possible source. LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
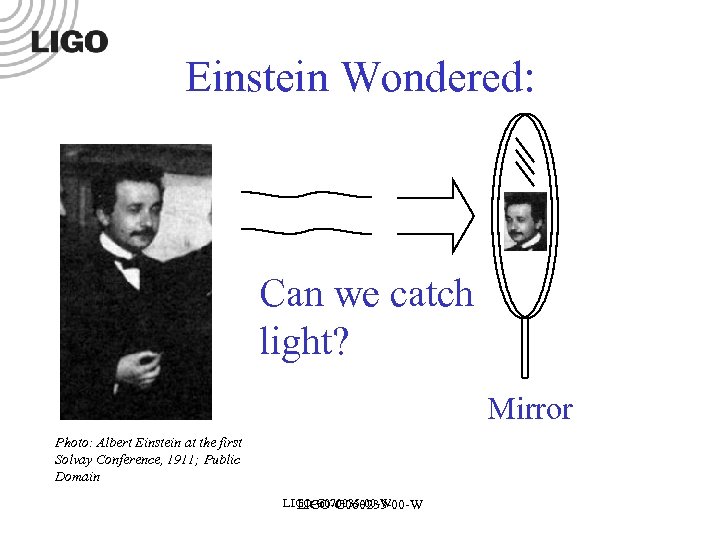
Einstein Wondered: Can we catch light? Mirror Photo: Albert Einstein at the first Solvay Conference, 1911; Public Domain LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Einstein’s Key Idea, 1905 • Galileo & Newton: motion is relative; speeds are additive. • Newton thought light was made of particles. • Sound is a wave moving through the air or some material. The speed of sound (741 mph) is fixed to the rest frame of the air. We can catch sound. • By analogy, in 1905 light was thought to be a wave moving through the “aether”. Experiments could not measure the aether or detect changes in the speed of light due to relative motion. • Einstein: we cannot catch light; no experiment can detect absolute motion; there is no aether; the speed of light is the same for all observers. LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
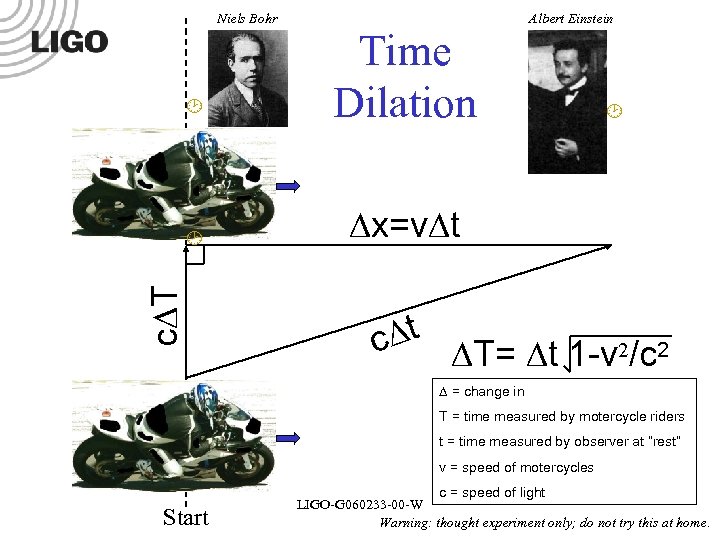
Niels Bohr x=v t c T Time Dilation Albert Einstein t c T= t 1 -v 2/c 2 = change in T = time measured by motercycle riders t = time measured by observer at “rest” v = speed of motercycles Start c = speed of light LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Warning: thought experiment only; do not try this at home.

v t T Car 60 mph 1 day -. 35 nanoseconds Plane 600 mph 1 day – 35 nanoseconds Shuttle 17, 000 mph 1 day – 28 microseconds Voyager 38, 000 mph 1 day – 140 microseconds Andromeda 300, 000 mph 1 day – 8. 7 milliseconds Electrons 99% c 1 day 3. 4 hours The faster you go the slower time goes! Nothing can go faster than light! LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Photo: Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC); Public Domain The Speed of Light c = 186, 000 miles/s = 670, 000 miles/hr

Length Contraction http: //www. anu. edu. au/Physics/Searle/paper 2. html; Web page for "The Physicist" Paper "Visualising special relativity", C. M. Savage and A. C. Searle, The Physicist, vol. 36, pg. 141, July/August 1999. LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
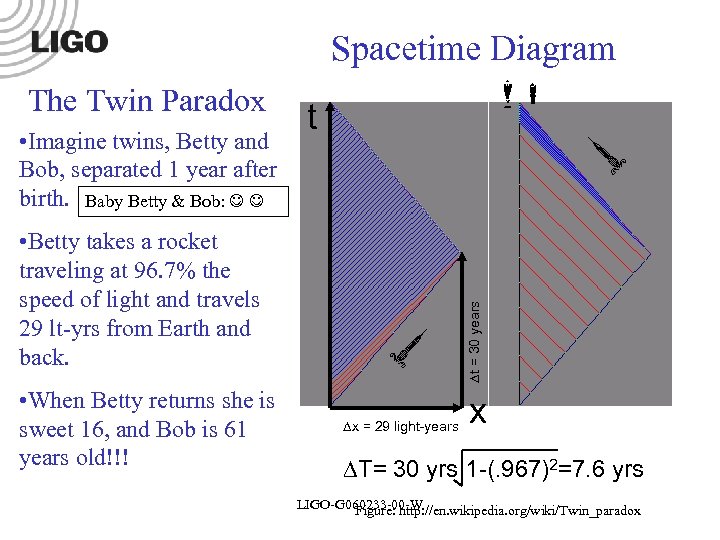
Spacetime Diagram • Betty takes a rocket traveling at 96. 7% the speed of light and travels 29 lt-yrs from Earth and back. • When Betty returns she is sweet 16, and Bob is 61 years old!!! t • Imagine twins, Betty and Bob, separated 1 year after birth. Baby Betty & Bob: x = 29 light-years t = 30 years The Twin Paradox x T= 30 yrs 1 -(. 967)2=7. 6 yrs LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Figure: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Twin_paradox

The Problem With Gravity Credit: Portrait of Isaac Newton painted in 1689 by Sir Godfrey Kneller (Farleigh House, Farleigh Wallop, Hampshire) http: //www. huntington. org/Library. Div/Newtonexhibit. htm Sir Isaac Newton invented theory of gravity and much of the math needed to understand it. LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Einstein’s Happiest Thought: Gravity Disappears When You Free Fall Video: NASA; http: //ksnn. larc. nasa. gov Photo: NASA http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Leaning_ Tower_of_Pisa LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Warning: thought experiment only; do not try this at home.

A new wrinkle on gravity: General Relativity arrives in 1915. Figure: Focus Mar 95 p 30 Not only the path of matter, but even the path of light is affected by gravity from massive objects. Gravity is the curvature of space and time! http: //www. geocities. com/Omegaman_UK/relativity. html: Photo credit: NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) A massive object shifts apparent position of a star LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Black Holes http: //antwrp. gsfc. nasa. gov/apod/ap 060528. html; GRO J 1655 -40: Evidence for a Spinning Black LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W Hole; Drawing Credit: A. Hobart, CXC LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
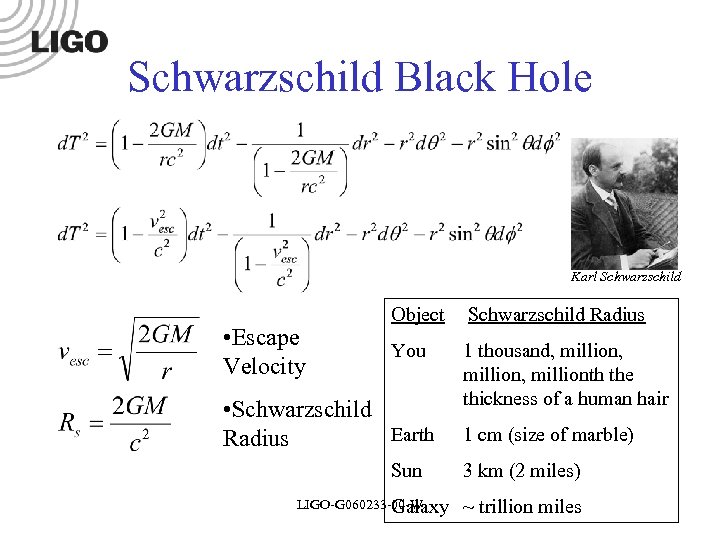
Schwarzschild Black Hole Karl Schwarzschild • Escape Velocity Object Schwarzschild Radius You 1 thousand, million, millionth the thickness of a human hair • Schwarzschild Earth Radius Sun LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Galaxy 1 cm (size of marble) 3 km (2 miles) ~ trillion miles

Gravitational Time Dilation Gravity slows time down! Clock_Photos: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wik Photo: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Lea LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -Wi/Cuckoo_clock ning_Tower_of_Pisa

Relativity and GPS • Due to the orbital speed, clocks on the satellite lose 7 microseconds per day • Due to the weaker gravitational field, clocks on the satellite gain 45 microseconds per day • Satellite clocks gain a net of 38 microsecond per day • Distance error = c*38 microseconds; c = 186, 000 miles per second. • Without calibrating clocks to account for Relativity, GPS distance would be off by 7 miles after one day! See Scientific American, Sept. 1994 Illustration: NASA Clock_Photos: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cuckoo_clock LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
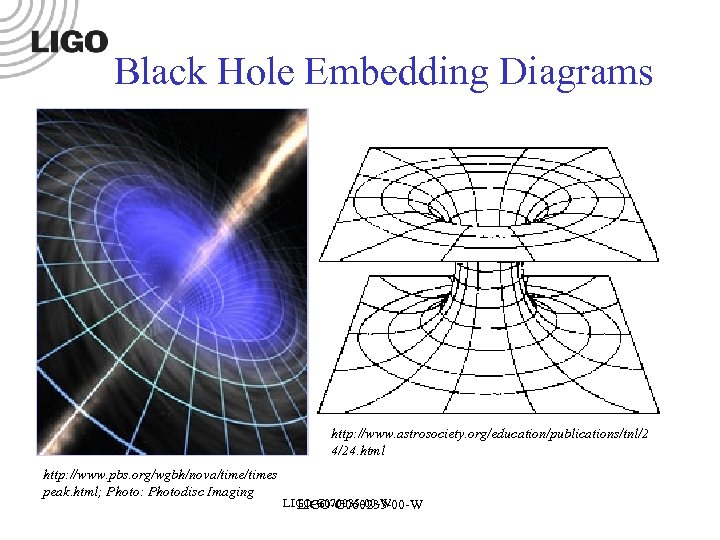
Black Hole Embedding Diagrams http: //www. astrosociety. org/education/publications/tnl/2 4/24. html http: //www. pbs. org/wgbh/nova/times peak. html; Photo: Photodisc Imaging LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
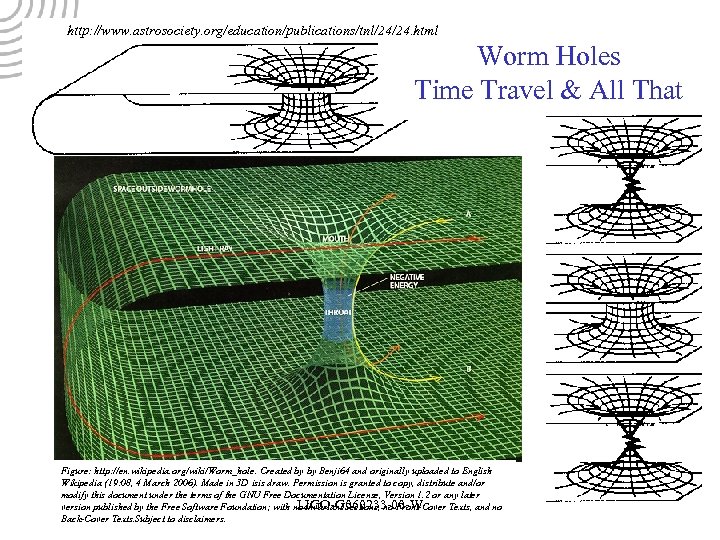
http: //www. astrosociety. org/education/publications/tnl/24/24. html Worm Holes Time Travel & All That Figure: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Worm_hole. Created by by Benji 64 and originally uploaded to English Wikipedia (19: 08, 4 March 2006). Made in 3 D isis draw. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1. 2 or any later LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. Subject to disclaimers.

Stellar Collapse To Form A Black Hole Singularity LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Black Holes And LIGO Credit: Henze, NASA; http: //www. nasa. gov/vision/universe/starsgalaxies/gwave. html LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

The End LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
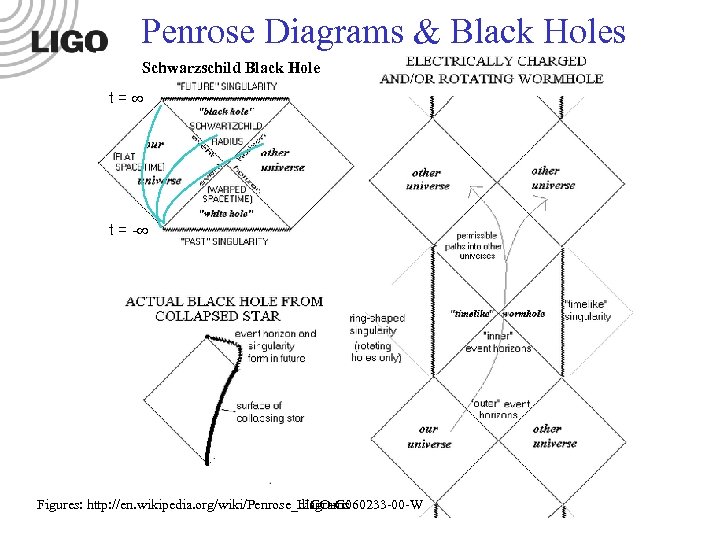
Penrose Diagrams & Black Holes Schwarzschild Black Hole t= t = - LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W Figures: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Penrose_diagrams LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Equivalence Principle: Objects fall with the same acceleration in a gravitational field. There is an equivalence between gravity and acceleration. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Leaning_ Tower_of_Pisa http: //www. physics. fsu. edu/Courses/Sp ring 98/AST 3033/Relativity/General. Rel LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W ativity. htm

Tests Of General Relativity 1. Bending of starlight by the Sun 2. Shift of Mercury’s Perihelion by 43’’ per century Sun and Mercury Figures: http: //www. astro. cornell. edu/academics/courses/astro 201/ast ro 201. html; http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Leaning_ http: //www. astro. cornell. edu/academics/courses/astro 201/to Tower_of_Pisa pics. html; pages designed by Martha Haynes and Stirling Churchman 3. LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Gravitational Redshift of Light
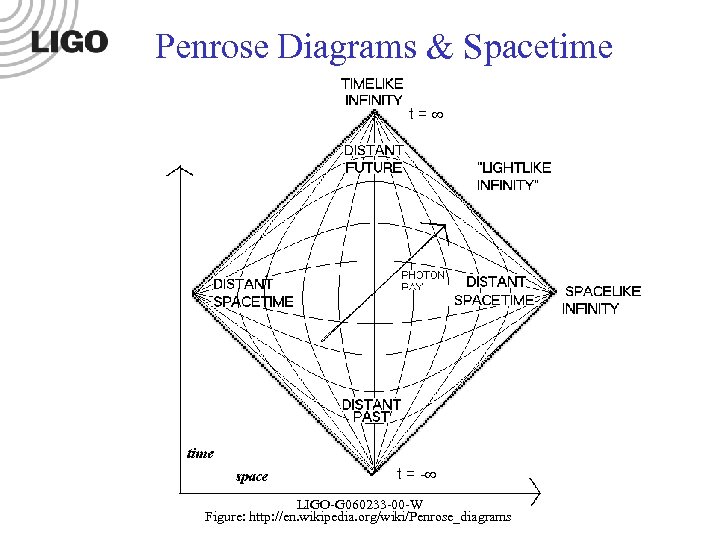
Penrose Diagrams & Spacetime t= t = - LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Figure: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Penrose_diagrams

Popular: Further Reading Example LIGO Scientific Collaboration Papers: LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Textbooks:
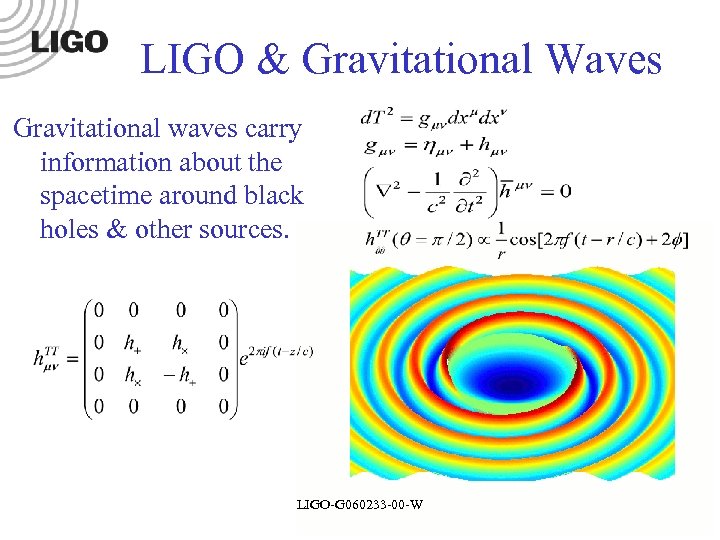
LIGO & Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves carry information about the spacetime around black holes & other sources. LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
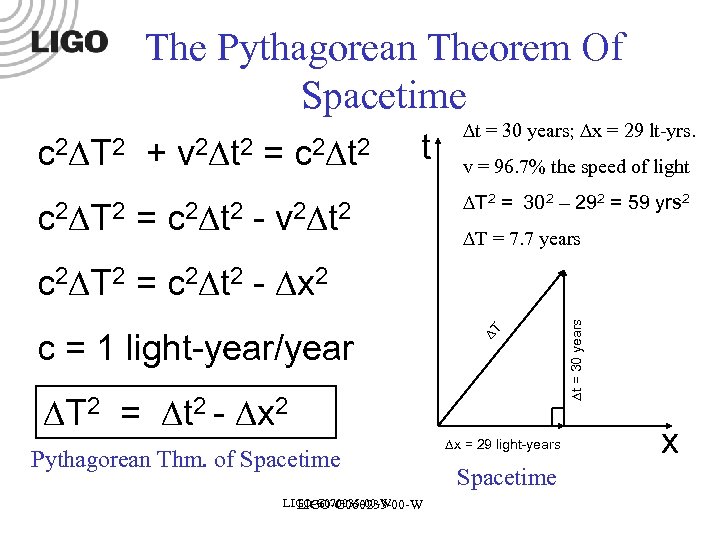
The Pythagorean Theorem Of Spacetime c 2 T 2 + v 2 t 2 = c 2 t c 2 T 2 = c 2 t 2 - v 2 t 2 t = 30 years; x = 29 lt-yrs. v = 96. 7% the speed of light T 2 = 302 – 292 = 59 yrs 2 T = 7. 7 years T 2 = t 2 - x 2 Pythagorean Thm. of Spacetime LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W x = 29 light-years Spacetime t = 30 years c = 1 light-year/year T c 2 T 2 = c 2 t 2 - x 2 x
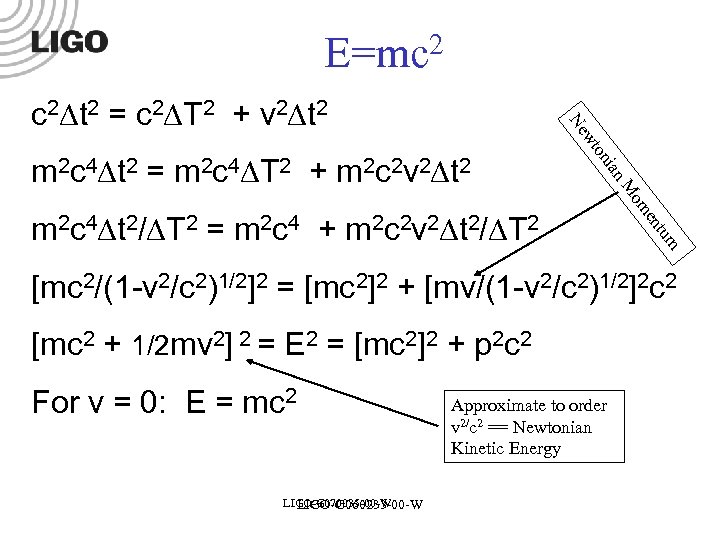
E=mc 2 tum en m 2 c 4 t 2/ T 2 = m 2 c 4 + m 2 c 2 v 2 t 2/ T 2 om M m 2 c 4 t 2 = m 2 c 4 T 2 + m 2 c 2 v 2 t 2 ian on wt Ne c 2 t 2 = c 2 T 2 + v 2 t 2 [mc 2/(1 -v 2/c 2)1/2]2 = [mc 2]2 + [mv/(1 -v 2/c 2)1/2]2 c 2 [mc 2 + 1/2 mv 2] 2 = E 2 = [mc 2]2 + p 2 c 2 For v = 0: E = mc 2 LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W Approximate to order v 2/c 2 == Newtonian Kinetic Energy
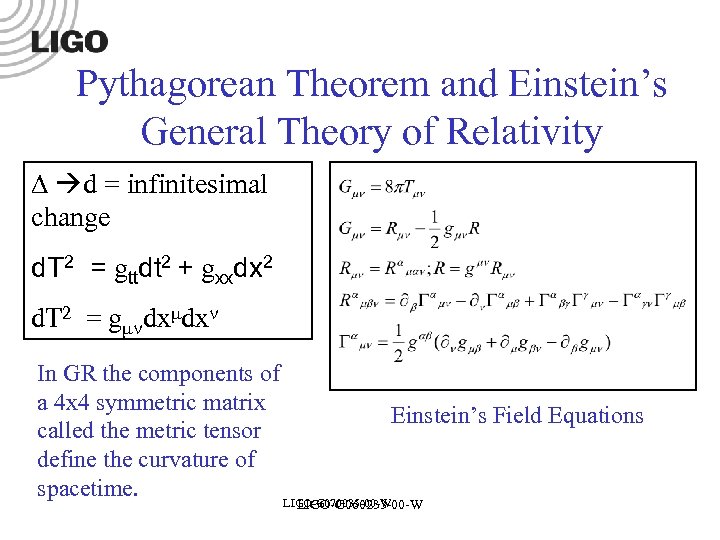
Pythagorean Theorem and Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity d = infinitesimal change d. T 2 = gttdt 2 + gxxdx 2 d. T 2 = g dx dx In GR the components of a 4 x 4 symmetric matrix Einstein’s Field Equations called the metric tensor define the curvature of spacetime. LIGO-G 070035 -00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Black Hole Formation: Supernovae Photo: Supernova 1987 A http: //www. aao. gov. au/images/captions/aat 050. html Anglo-Australian Observatory, photo by David Malin. LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Black Holes & Accretion Disks image by Dana Berry/NASA; NASA News Release posted July 2, 2003 on Spaceflight Now. http: //researchnews. osu. edu/archive/fuzzballpic. htm (Illustration: CXC/M. Weiss) LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W

Black Hole Detection LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W
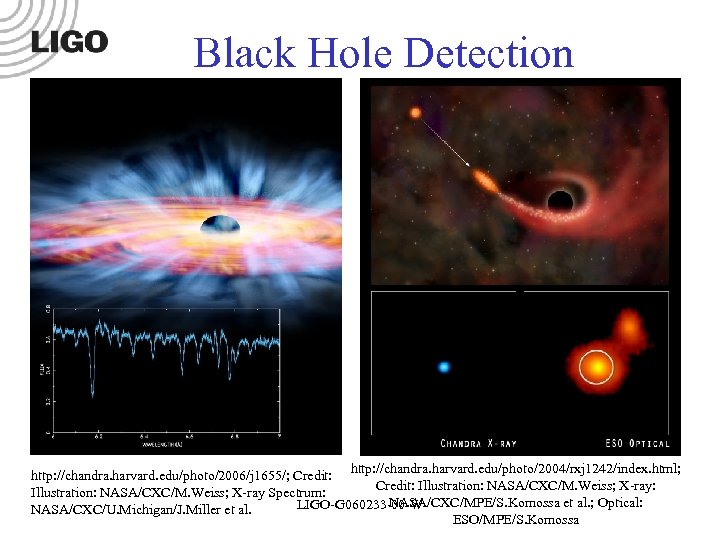
Black Hole Detection http: //chandra. harvard. edu/photo/2004/rxj 1242/index. html; http: //chandra. harvard. edu/photo/2006/j 1655/; Credit: Illustration: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss; X-ray: Illustration: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss; X-ray Spectrum: NASA/CXC/MPE/S. Komossa et al. ; Optical: LIGO-Gnnnnnn-00 -W LIGO-G 060233 -00 -W NASA/CXC/U. Michigan/J. Miller et al. ESO/MPE/S. Komossa
46ba47c52a0344380897663e575a6ace.ppt