973324914c19d93d549e7dfc3b869e61.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Biotechnology

What Is Biotechnology? n n Using scientific methods with organisms to produce new products or new forms of organisms Any technique that uses living organisms or substances from those organisms to make or modify a product, to improve plants or animals, or to develop microorganisms for specific uses

What Are the Stages of Biotechnology Development n n n Ancient biotechnology- early history as related to food and shelter; Includes domestication Classical biotechnology- built on ancient biotechnology; Fermentation promoted food production, and medicine Modern biotechnology- manipulates genetic information in organism; Genetic engineering

Biotechnology – using living organisms, or the products of living organisms, for human benefit to make a product or solve a problem n Historical Examples n Fermentation n Selective breeding n Use of antibiotics n n Modern Examples Gene cloning n Genetic engineering n Recombinant DNA technology n Human Genome Project n

Biotechnology: involvement of organisms in food or industrial processing Fermentation
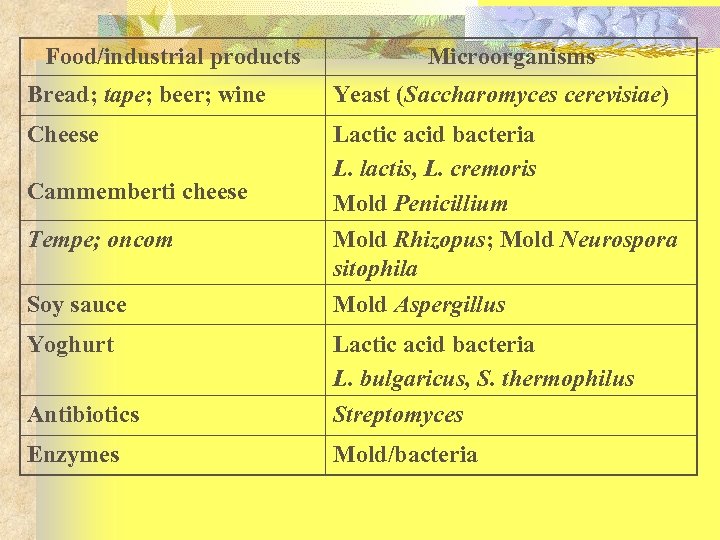
Food/industrial products Microorganisms Bread; tape; beer; wine Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Cheese Lactic acid bacteria L. lactis, L. cremoris Mold Penicillium Cammemberti cheese Tempe; oncom Soy sauce Yoghurt Mold Rhizopus; Mold Neurospora sitophila Mold Aspergillus Antibiotics Lactic acid bacteria L. bulgaricus, S. thermophilus Streptomyces Enzymes Mold/bacteria

What Is Biotechnology? n n GMO- genetically modified organisms. GEO- genetically enhanced organisms. With both, the natural genetic material of the organism has been altered. Roots in bread making, wine brewing, cheese and yogurt fermentation, and classical plant and animal breeding
What Is Biotechnology? n n Manipulation of genes is called genetic engineering or recombinant DNA technology Genetic engineering involves taking one or more genes from a location in one organism and either n n Transferring them to another organism Putting them back into the original organism in different combinations
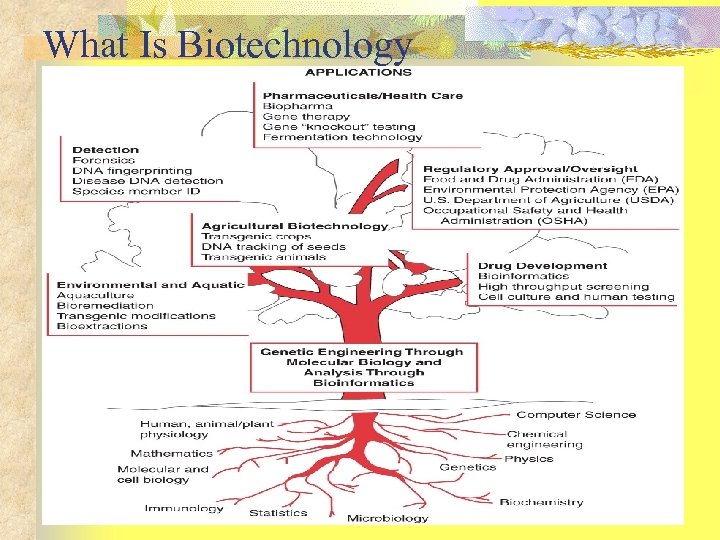
What Is Biotechnology
What Are the Areas of Biotechnology? n n Organismic biotechnology- uses intact organisms; Does not alter genetic material Molecular biotechnology- alters genetic makeup to achieve specific goals n Transgenic organism- an organism with artificially altered genetic material
What Are the Benefits of Biotechnology? n Medicine n n n n Human Veterinary Biopharming Environment Agriculture Food products Industry and manufacturing
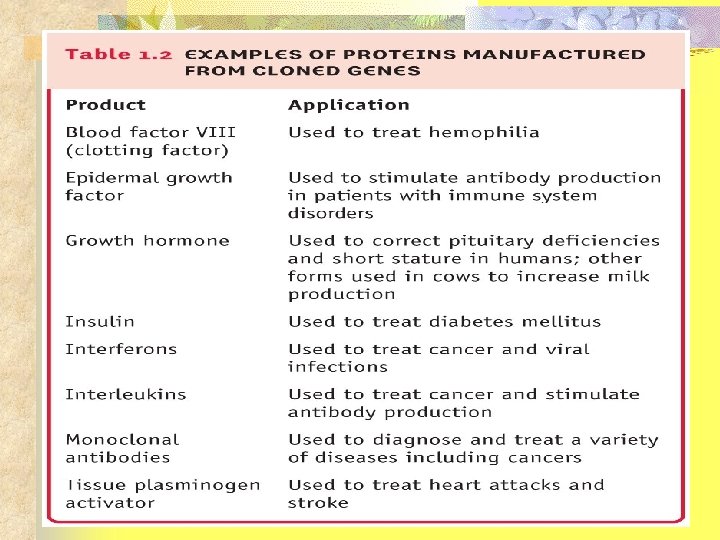
What Is Molecular Biology? n n Molecular biology- study of molecules in cells Metabolism- processes by which organisms use nutrients Anabolism- building tissues from smaller materials Catabolism- breaking down materials into smaller components
What Are Genetic Engineering Organisms? n n Genetic engineering- artificially changing the genetic information in the cells of organisms Transgenic- an organism that has been genetically modified GMO- a genetically modified organism GEO- a genetically enhanced organism

Types of Biotechnology n n n n Microbial Biotechnology Agricultural Biotechnology Animal Biotechnology Forensic Biotechnology Bioremediation Aquatic Biotechnology Medical Biotechnology Regulatory Biotechnology

n Microbial Biotechnology – manipulation of microorganisms such as yeast and bacteria n n Agricultural Biotechnology n n Create better enzymes More efficient decontamination processes for industrial waste product removal Used to clone and produce large amounts of important proteins used in human medicine Genetically engineered, pest-resistant plants Foods with higher protein or vitamin content Drugs developed and grown as plant products Estimated to be a $7 billion market in 2008
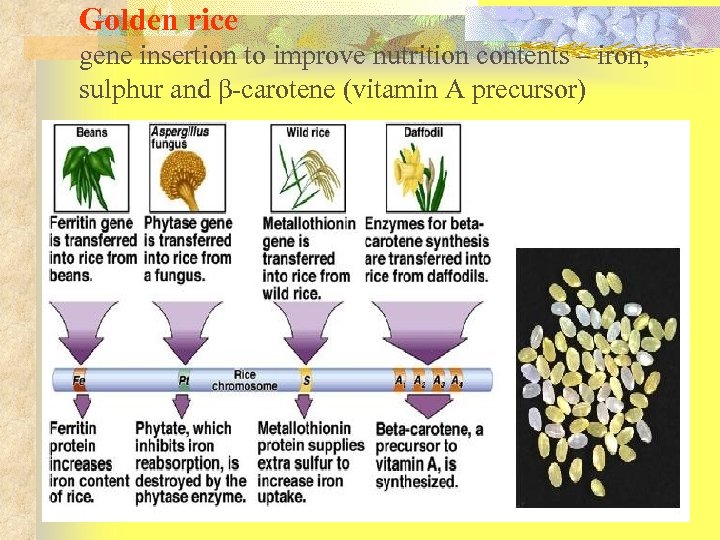
Golden rice gene insertion to improve nutrition contents – iron, sulphur and β-carotene (vitamin A precursor)
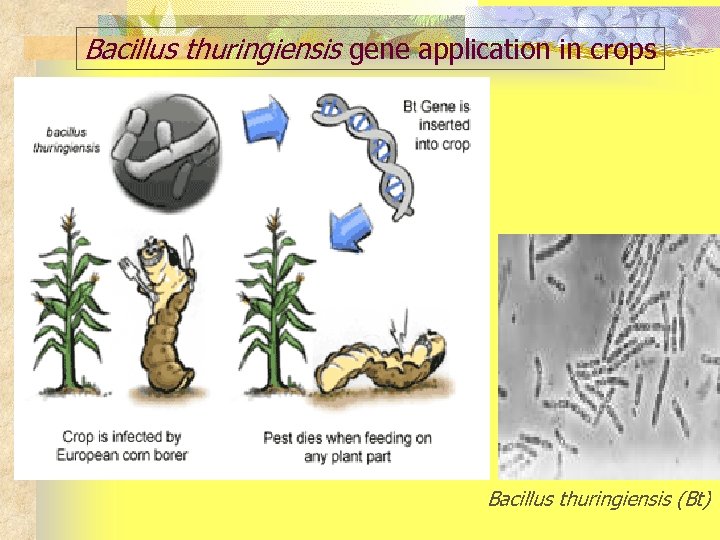
Bacillus thuringiensis gene application in crops Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)
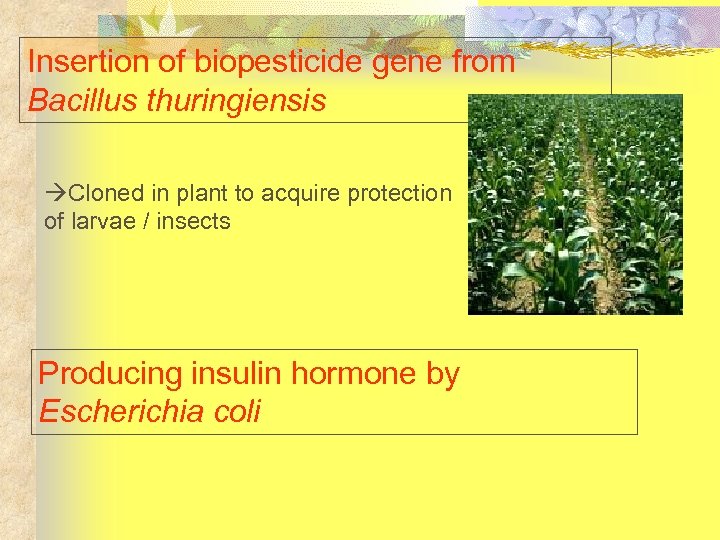
Insertion of biopesticide gene from Bacillus thuringiensis Cloned in plant to acquire protection of larvae / insects Producing insulin hormone by Escherichia coli
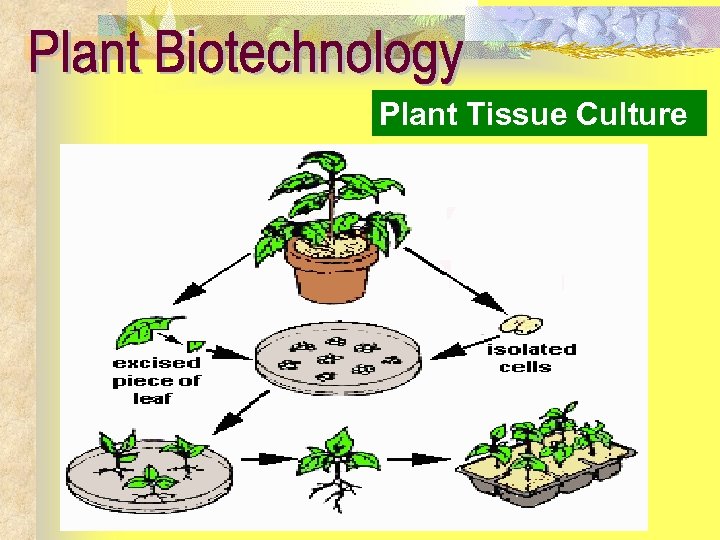
Plant Tissue Culture
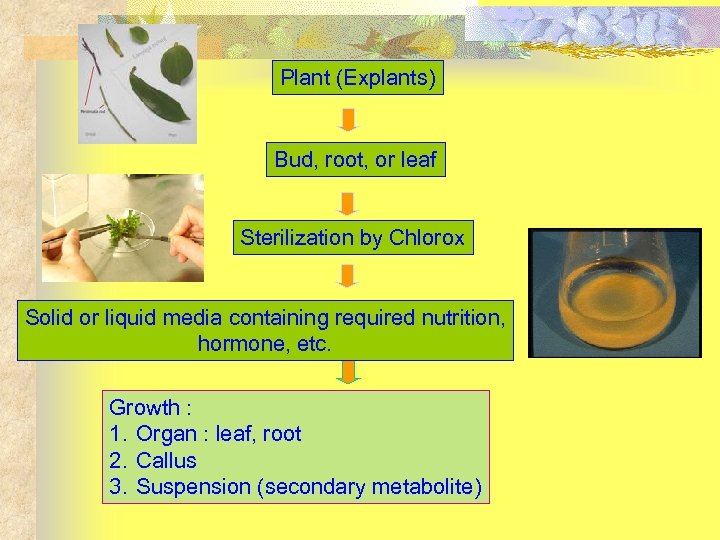
Plant (Explants) Bud, root, or leaf Sterilization by Chlorox Solid or liquid media containing required nutrition, hormone, etc. Growth : 1. Organ : leaf, root 2. Callus 3. Suspension (secondary metabolite)

Callus Plantlet
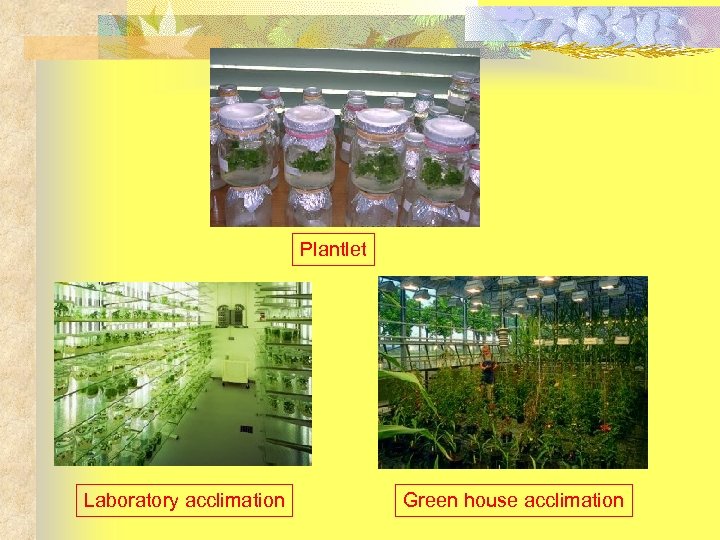

Plantlet Laboratory acclimation Green house acclimation

n Animal Biotechnology n Animals as a source of medically valuable proteins n Antibodies n Animals as important models in basic research n Gene “knockout” experiments n Design and testing of drugs and genetic therapies n Animal cloning n Source n of transplant organs Forensic Biotechnology n DNA fingerprinting n Inclusion or exclusion of a person from suspicion n Paternity cases n Identification of human remains n Endangered species

n Bioremediation n The use of biotechnology to process and degrade a variety of natural and manmade substances n Particularly n those that contribute to pollution For example, bacteria that degrade components in crude oil n 1989 Exxon Valdez oil spill in Alaska n 2010 Gulf oil spill

n Aquatic Biotechnology n Aquaculture – raising finfish or shellfish in controlled conditions for use as food sources n 30% n of all fish consumed by humans worldwide Genetic engineering n Disease-resistant strains of oysters n Vaccines against viruses that infect salmon and other finfish n Rich and valuable sources of new genes, proteins and metabolic processes with important applications for human benefits n Marine plankton and snails found to be rich sources of antitumor and anticancer molecules

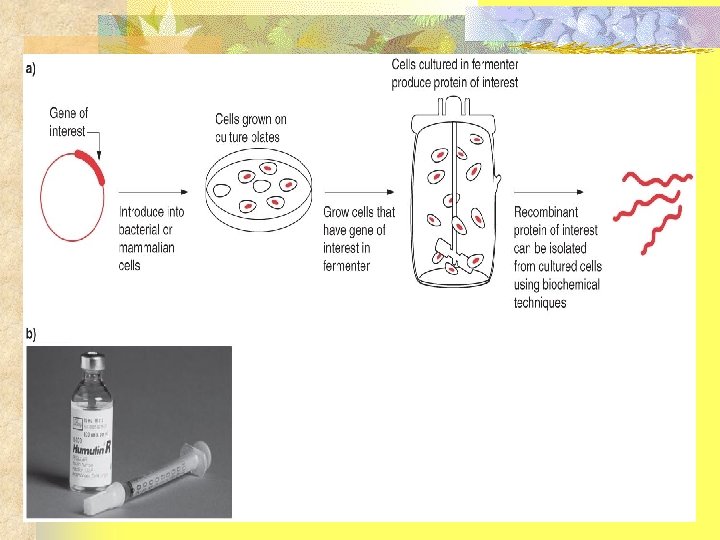
n Medical Biotechnology n Involved with the whole spectrum of human medicine n Preventive medicine n Diagnosis of health and illness n Treatment of human diseases n New information from Human Genome Project n Gene n therapy Stem cell technologies
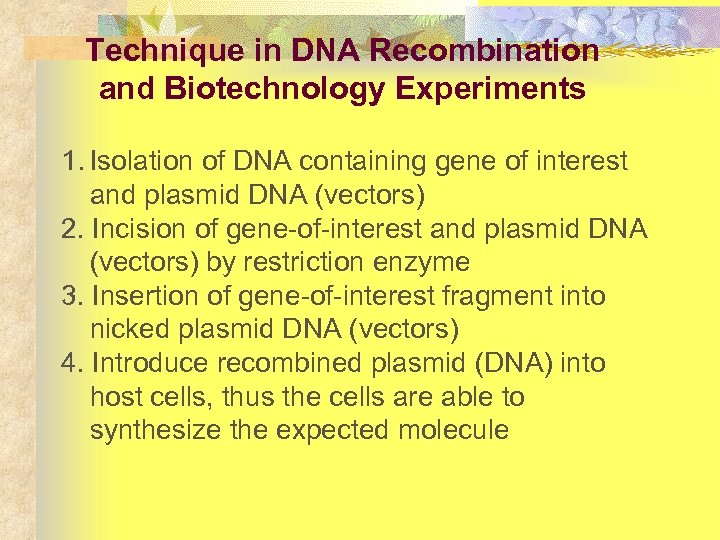
Technique in DNA Recombination and Biotechnology Experiments 1. Isolation of DNA containing gene of interest and plasmid DNA (vectors) 2. Incision of gene-of-interest and plasmid DNA (vectors) by restriction enzyme 3. Insertion of gene-of-interest fragment into nicked plasmid DNA (vectors) 4. Introduce recombined plasmid (DNA) into host cells, thus the cells are able to synthesize the expected molecule
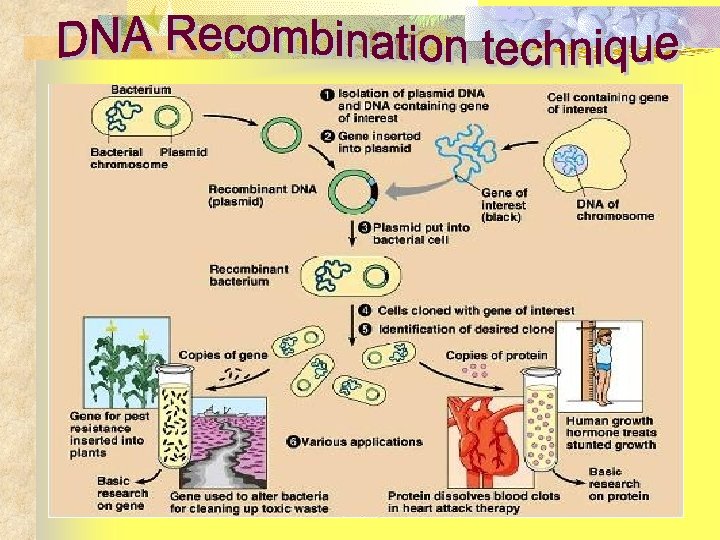
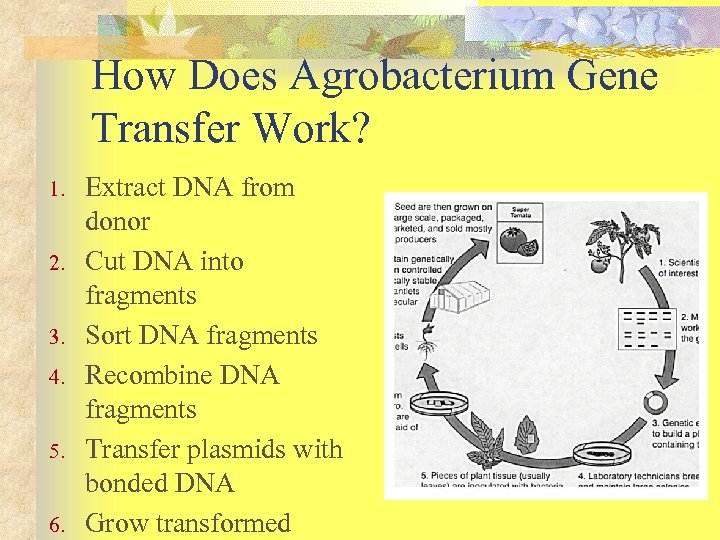
How Does Agrobacterium Gene Transfer Work? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Extract DNA from donor Cut DNA into fragments Sort DNA fragments Recombine DNA fragments Transfer plasmids with bonded DNA Grow transformed

What Are Methods of Classical Biotechnology? n Plant breeding methods; n n Line breeding- breeding successive generations of plants among themselves Crossbreeding- breeding plants of different varieties or species Hybridization- breeding individuals from two distinctly different varieties Selection

Why Are Plants Genetically Engineered? n n n Resist pests Resist herbicides Improved product quality Pharmaceuticals Industrial products

What Is a Test Tube Baby? n In vitro fertilization- fertilization of collected ova outside the reproductive tract; Usually in a test tube n n n Semen is collected from males of desired quality Ova are removed from females Sperm and ova are placed in a petri dish or test tube

What Is Gender Preselection? n Gender preselection- choosing the sex of offspring n n Sperm sorted before conception Sperm sorted on basis of chromosome differences X chromosomes produce female offspring Y chromosomes produce male offspring

What Is Embryo Transfer? n Embryo transfer- removing fertilized ova (embryos) from donor and implanting in a recipient n n Surgical and nonsurgical methods are used to remove and implant A quality donor female can produce more offspring

What Is Multiple Ovulation? n Multiple ovulation- promoting increased release of ova during estrus n n Hormone injections administered prior to estrus Used with embryo transfer AI may be used to fertilize ova After fertilization, embryos are removed and placed in recipients

What Is Cloning? n n n Clone- new organism that has been produced asexually from a single parent Genotype is identical to parent Cells or tissues are cultured
What Is Bioremediation? n n n Bioremediation- using biological processes to solve environmental problems Biodegradation- natural processes of microbes in breaking down hydrocarbon materials Biodegradable- capable of being decomposed by microbes

How Can Bioremediation Be Used? n n Oil spills Wastewater treatment Heavy metal removal Chemical degradation

What Is Phytoremediation? n Phytoremediation- process of plants being used to solve pollution problems n n Plants absorb and break down pollutants Used with heavy metals, pesticides, explosives, and leachate

What Is Composting? n n n Composting- a process that promotes biological decomposition of organic matter Compost bin- a facility that contains materials for composting In-vessel composting- using enclosed containers for composting
973324914c19d93d549e7dfc3b869e61.ppt