addd8ad3af4043c7a0a8e92170769a2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
Biomedicínský výzkum s podporou evropských zdrojů v nemocnicích (12. 4. 2012) Regression models in biomedical research RNDr. Karel Hrach, Ph. D.
Multiple regression („classical“)
Multiple regression (in Excel)
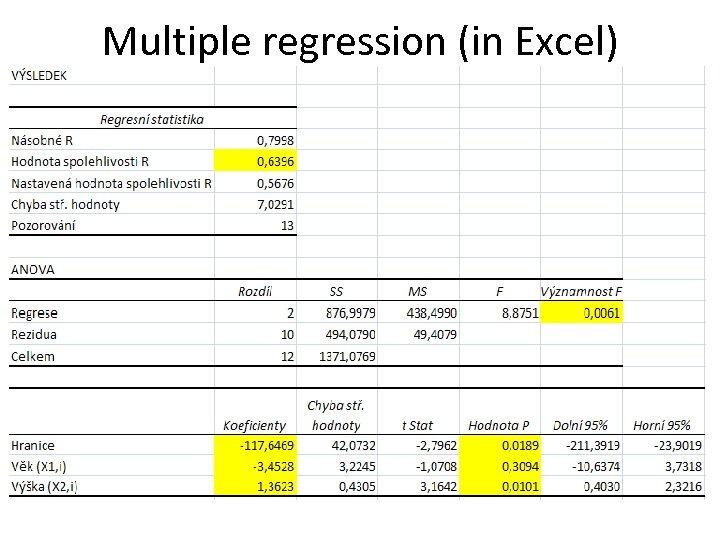
Multiple regression (in Excel)

Reduction of the model? Question: What if we omit the variable VĚK (Age)? Is the resulting model really BETTER than the previous one? There exists a model-building approach.

Stepwise regression (NOT in Excel) • type forward: adds the best candidating regressor so, that the new model is significantly better than the sub-model • type backward: removes the weekest regressor so, that the sub-model remains significant

Other types of regressors? • e. g. Y=blood pressure decrease (BPD) • X (X 1, …) might be nominal, e. g. „treatment“: X=1 … standard medication X=2 … experimantal medication X=3 … no medication (life-style change)

Other types of regressors? Y=α+βX+ε interpretation of β? • It should express the change of BPD, corresponding to the unit change of X (? ? ? )
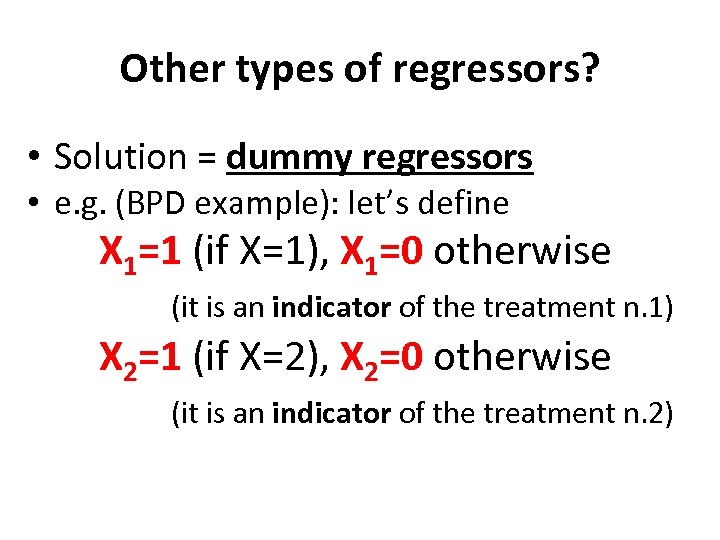
Other types of regressors? • Solution = dummy regressors • e. g. (BPD example): let’s define X 1=1 (if X=1), X 1=0 otherwise (it is an indicator of the treatment n. 1) X 2=1 (if X=2), X 2=0 otherwise (it is an indicator of the treatment n. 2)
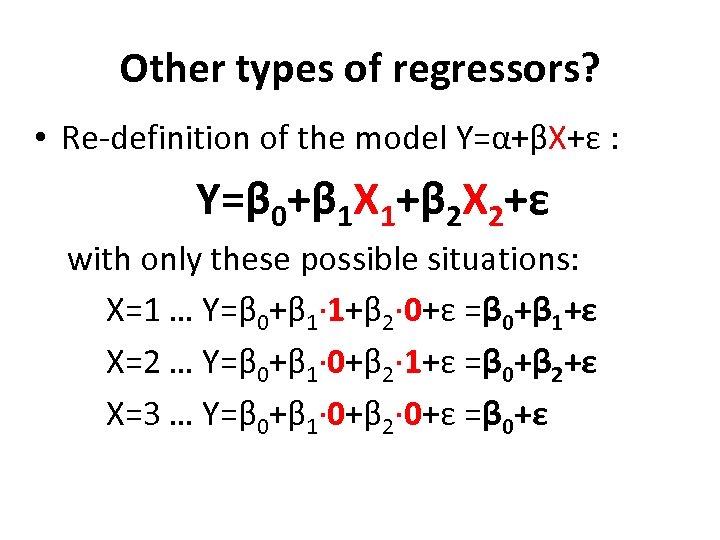
Other types of regressors? • Re-definition of the model Y=α+βX+ε : Y=β 0+β 1 X 1+β 2 X 2+ε with only these possible situations: X=1 … Y=β 0+β 1∙ 1+β 2∙ 0+ε =β 0+β 1+ε X=2 … Y=β 0+β 1∙ 0+β 2∙ 1+ε =β 0+β 2+ε X=3 … Y=β 0+β 1∙ 0+β 2∙ 0+ε =β 0+ε
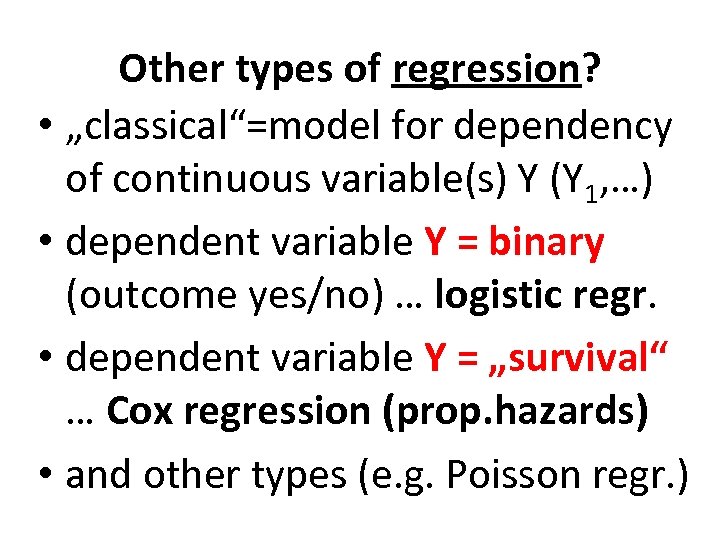
Other types of regression? • „classical“=model for dependency of continuous variable(s) Y (Y 1, …) • dependent variable Y = binary (outcome yes/no) … logistic regr. • dependent variable Y = „survival“ … Cox regression (prop. hazards) • and other types (e. g. Poisson regr. )
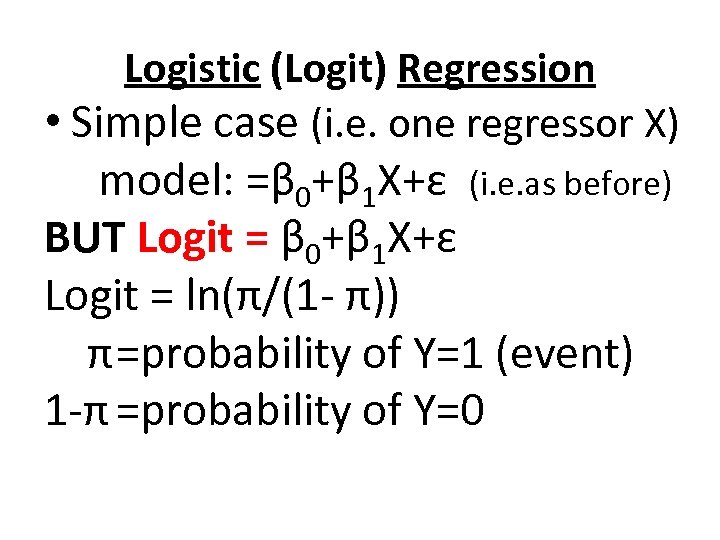
Logistic (Logit) Regression • Simple case (i. e. one regressor X) model: =β 0+β 1 X+ε (i. e. as before) BUT Logit = β 0+β 1 X+ε Logit = ln(π/(1 - π)) π=probability of Y=1 (event) 1 -π =probability of Y=0
Logistic Regression Application: Data from the project „The use of diffusion tensor imaging in preoperative planning and intraoperative neuronavigation“ (Masaryk Hospital, dpt. of neurosurgery)
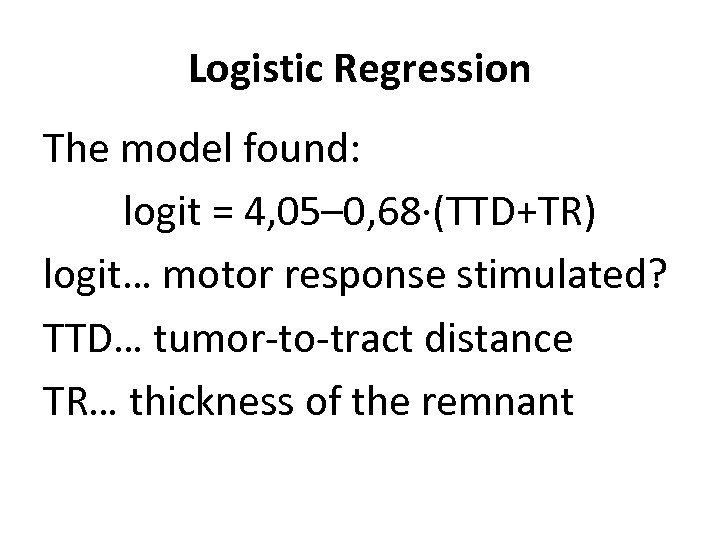
Logistic Regression The model found: logit = 4, 05– 0, 68∙(TTD+TR) logit… motor response stimulated? TTD… tumor-to-tract distance TR… thickness of the remnant
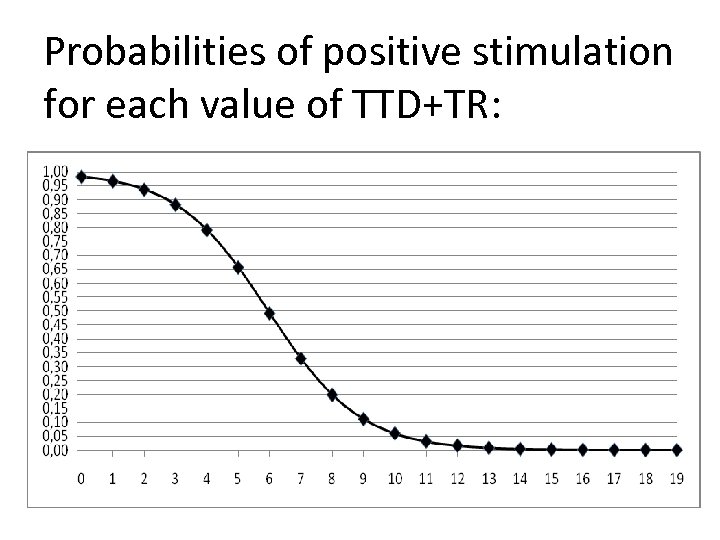
Probabilities of positive stimulation for each value of TTD+TR:
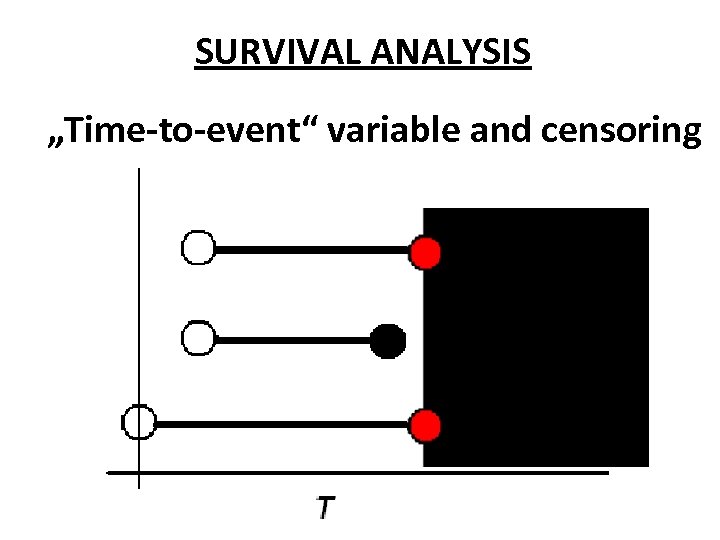
SURVIVAL ANALYSIS „Time-to-event“ variable and censoring

• SURVIVAL FUNCTION S: S (t ) = P (T ≥ t) • KAPLAN-MEIER ESTIMATE: SKM (t ) … cumulative relative frequency of surviving at the time t = time of event • LIFE-TABLE ESTIMATE : SLT (t ) … cumulative relative frequency of surviving inside given time-interval
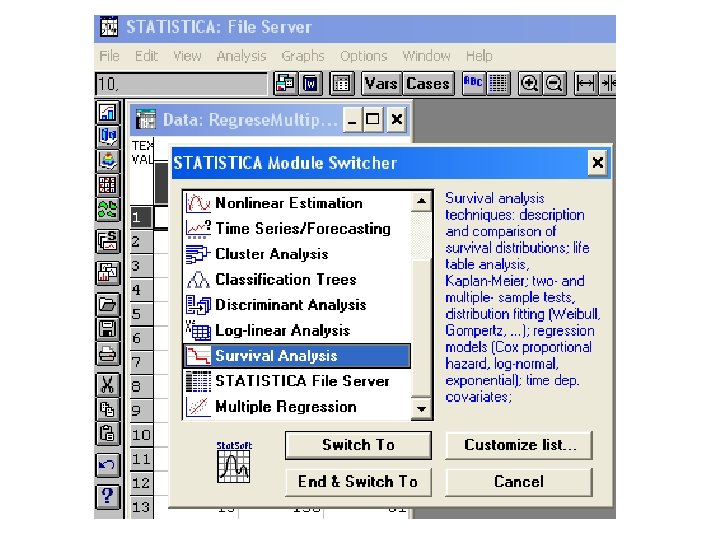
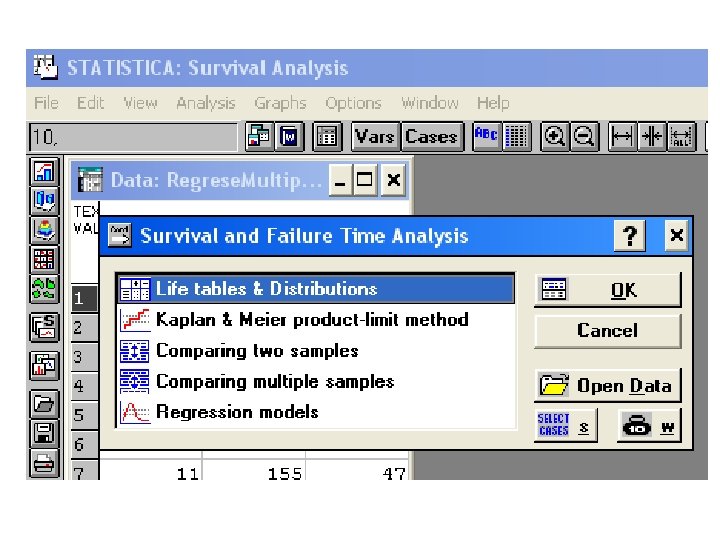
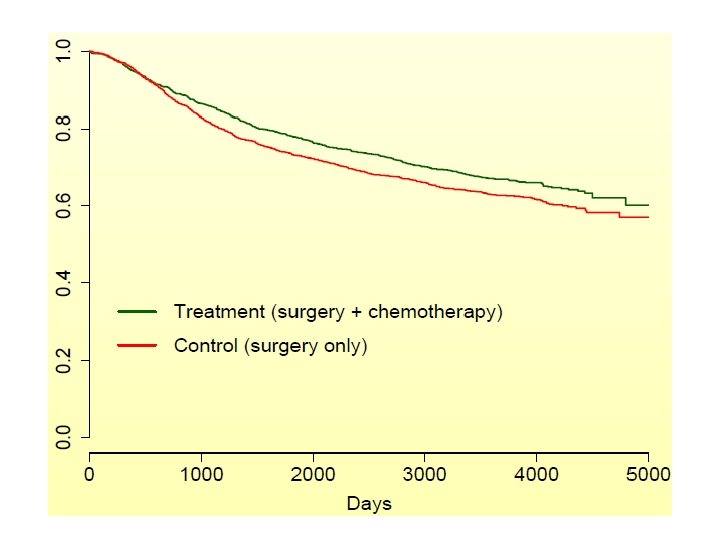
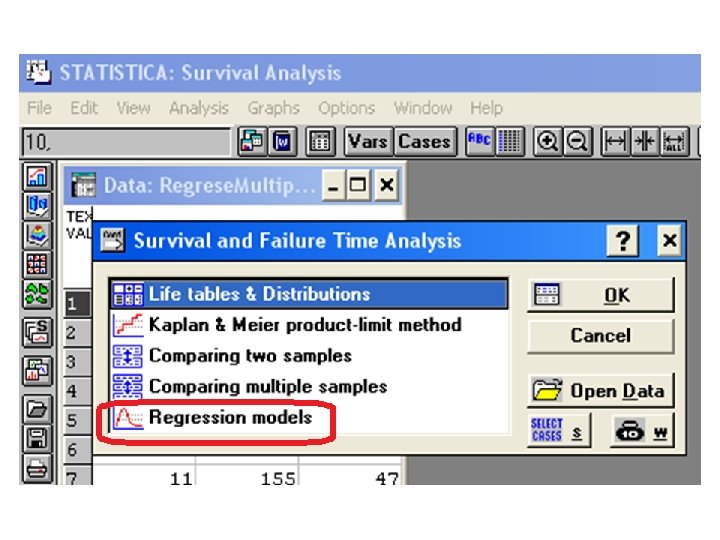
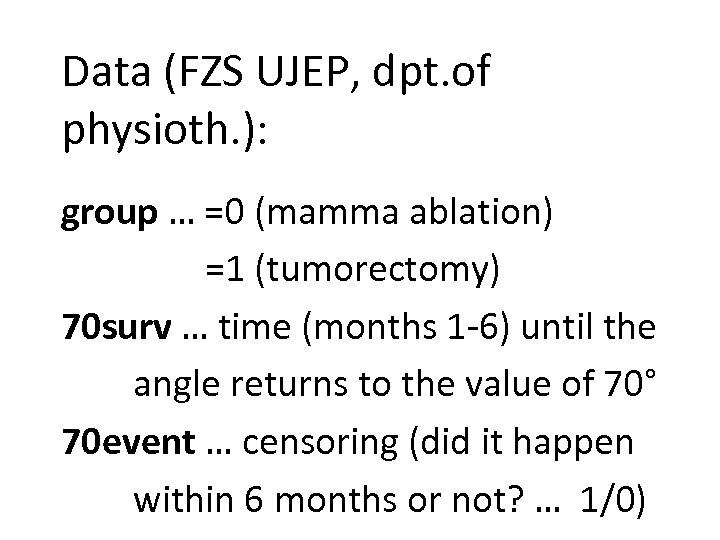
Data (FZS UJEP, dpt. of physioth. ): group … =0 (mamma ablation) =1 (tumorectomy) 70 surv … time (months 1 -6) until the angle returns to the value of 70° 70 event … censoring (did it happen within 6 months or not? … 1/0)
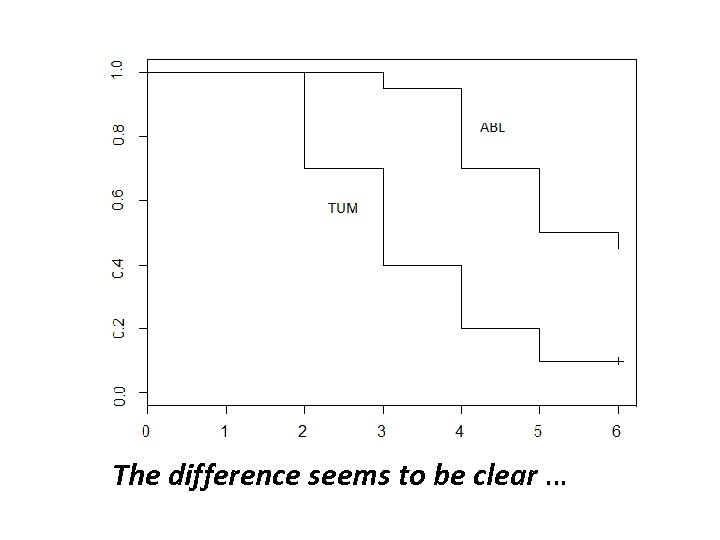
The difference seems to be clear …
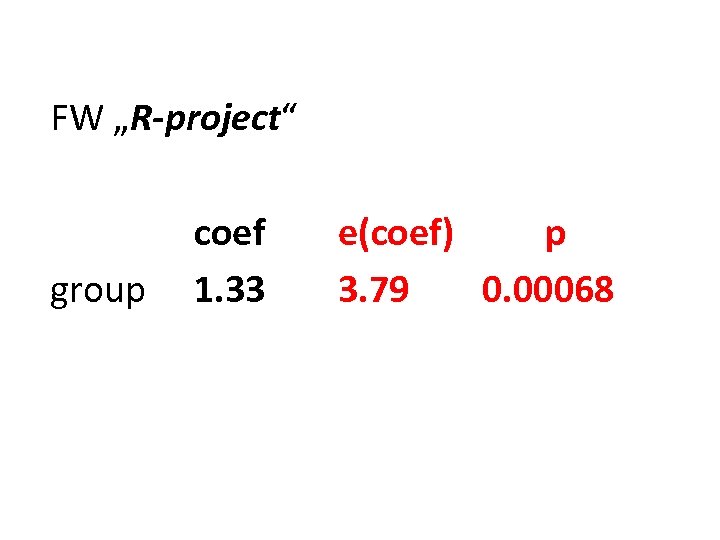
FW „R-project“ group coef 1. 33 e(coef) p 3. 79 0. 00068

The offer for co-operation with clinicians: Application of statistical methods (even „less-traditional“) SW available (Excel, R, STATISTICA)
addd8ad3af4043c7a0a8e92170769a2d.ppt