635b0734c9c94fbd20f8c3d5d453ad21.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

Biomedical Informatics Standards for interoperable EHR Narrowing the Research-Practice Divide in Evidence. Based Medicine with the Adoption of EHRs NIDA Christopher G Chute MD Dr. PH Professor, Biomedical Informatics Mayo Clinic College of Medicine July 13, 2009

Biomedical Informatics Health Care Is An Information Intensive Industry • Control of Health Care Costs. . . • Improved Quality of Care. . . • Improved Health Outcomes. . . • Appropriate Use of Health Technology. . . • Compassionate Resource Management. . . F. . . depend upon information F… Ultimately Patient Data © 2009 Mayo Clinic 2

Biomedical Informatics Information Beyond Practice Secondary Re-use as Primary A • Data Collected Interest Care Forms for Clinical the Basis for Patient Experience Repositories • The Importance of a Well Characterized, High Quality Patient Experience Repository May Exceed the Value of the Primary Information Many Fold © 2009 Mayo Clinic 3

Biomedical Informatics Repositories of Patient Information • Disease Natural History • Treatment Response (non-RCT) • Basis for Guidelines, Clinical Paths, Best Practice • “Just in Time” Source for Decision Support • Have we seen a patient just like this… • Efficient and Effective Care Delivery © 2009 Mayo Clinic 4

Biomedical Informatics Medical Concepts Events, Observations, Interventions • How should we represent it? Language: • • Nuance, detail, unfettered combination Timely, current, never obsolete Natural, friendly, established [Ambiguous, imprecise, unpredictable] • • Concise, precise Structured, consistent, well formed Analyzable, manipulable [Rigid, tedious, high maintenance] • Codes: © 2009 Mayo Clinic 5
Biomedical Informatics Mayo: A Century-Long Tradition of Studying Patient Outcomes Demographics Diagnoses Procedures Narratives Laboratories Pathology… High-Volume Data Storage © 2009 Mayo Clinic 6

Biomedical Informatics Semantic Organizati on © 2009 Mayo Clinic 7

Biomedical Informatics From Practice-based Evidence to Evidence-based Practice Data Patient Encounters Clinical Databases Registries et al. Shared Semantics Standards Inference Medical Knowledge Vocabularies & Terminologies Decision Expert support Systems © 2009 Mayo Clinical Knowledge Guidelines Managemen 8

Biomedical Informatics Value Proposition “Those with more detailed, reliable and comparable data for cost and outcome studies, identification of best practices, guidelines development, and management will be more successful in the marketplace. ” SP Cohn; Kaiser Permanente © 2009 Mayo Clinic 9

Biomedical Informatics Standards as the Basis for Scientific Data Representation and Interchange Without Standards. . . • Health Data is non-comparable • Health Systems cannot Interchange Data • Secondary Uses (Research, Efficiency) are not possible • Linkage to Decision Support Resources not Possible • Translational research is hobbled © 2009 Mayo Clinic 10

Biomedical Informatics US Health Standards Initiatives • 1986 Laboratory transport message – ASTM • 1987 HL 7 founded • 1991 Coalition for HISPP within ANSI • Health Information Standards Planning Panel • 1992 HISPP formed • 1995 HISB formed (Board) • 1996 HIPAA passed; NCVHS rechartered • 1998 ISO TC 215 formed • 2005 Office of the National Coordinator © 2009 Mayo Clinic 11

Biomedical Informatics 2009– ARRA Requirements and Tiger EHR Centric IS Teams • Capitalize on existing HITSP Process specifications • Organize according to EHR Information Exchanges • Establish Capability Concept Security, Privacy, and Infrastructure • Define Infrastructure Service Collaborations • Integrate Security and Privacy functions Quality IS [adopted from HITSP Panel] • Ability to interoperably specify Measure • Ability to extract patientspecific data from EHR and other sources for a measure
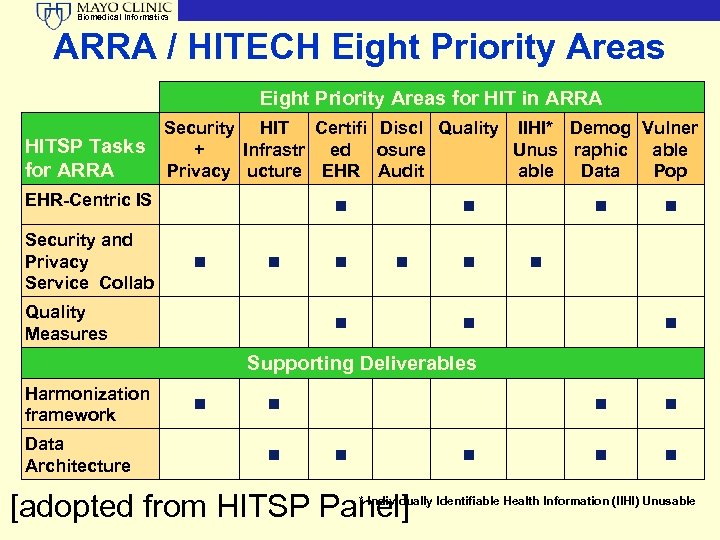
Biomedical Informatics ARRA / HITECH Eight Priority Areas for HIT in ARRA HITSP Tasks for ARRA Security HIT Certifi Discl Quality IIHI* Demog Vulner + Infrastr ed osure Unus raphic able Privacy ucture EHR Audit able Data Pop EHR-Centric IS Security and Privacy Service Collab n n n Quality Measures n n n n n Supporting Deliverables Harmonization framework Data Architecture n n n [adopted from HITSP Panel] n n n * Individually Identifiable Health Information (IIHI) Unusable
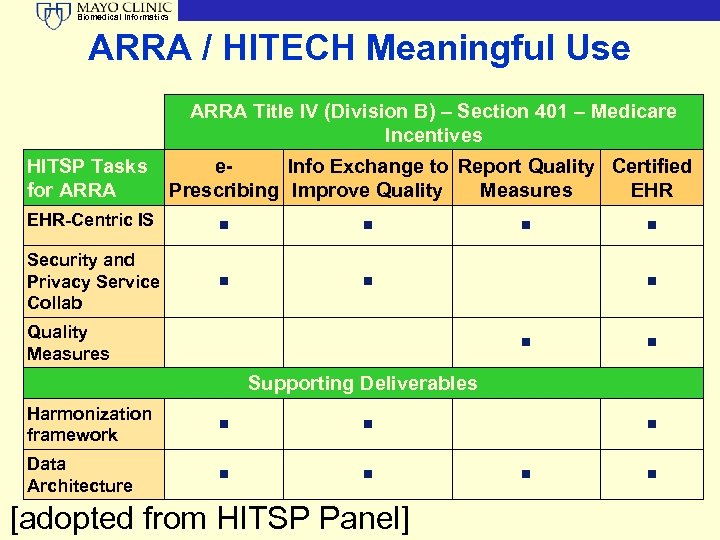
Biomedical Informatics ARRA / HITECH Meaningful Use ARRA Title IV (Division B) – Section 401 – Medicare Incentives HITSP Tasks for ARRA e. Info Exchange to Report Quality Certified Prescribing Improve Quality Measures EHR-Centric IS n n Security and Privacy Service Collab n n Quality Measures n n n Supporting Deliverables Harmonization framework n n Data Architecture n n [adopted from HITSP Panel] n n n

Biomedical Informatics Clinical Research in EHRs • Proposed presentation to AHIC – early 2007 • Discussed at CTSA/ca. BIG meeting w/ ONC • AHIC approves as “alternative path” June 2008 • Funding to coordinate from research community • ANSI convenes EHR Clinical Research Value Case Workgroup – fall 2008 • CCHIT adds Clinical Research to © 2009 Mayo Clinic 15

Biomedical Informatics HL 7 Reality • ANSI accredited standards organization • Peer international organization with ISO and CEN • Roughly 5000 person members • Working Group meetings three times per year • Roughly 500 attendees for one week • De facto think tank and forum for state of the art issues in Health care record, messages, and content © 2009 Mayo Clinic 16

Biomedical Informatics So we are all using HL 7, what is the problem? Equivalence OBX|1|CE|ABO^ABO GROUP| not obvious |O^Type O| to computer OBX|1|CE|BLDTYP^ABO GROUP| |TYPEO^Type O| OBX|1|CE|ABOTYPE^ABO GROUP| |OPOS^Type O| ¯OBX|1|CE|883 -9^ABO GROUP |F-D 1250^Group O| © 2009 Mayo Clinic 17
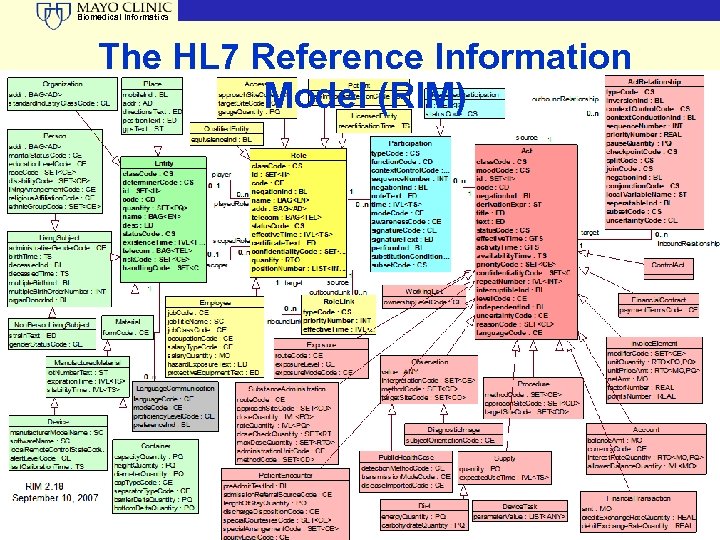
Biomedical Informatics The HL 7 Reference Information Model (RIM) © 2009 Mayo Clinic 18
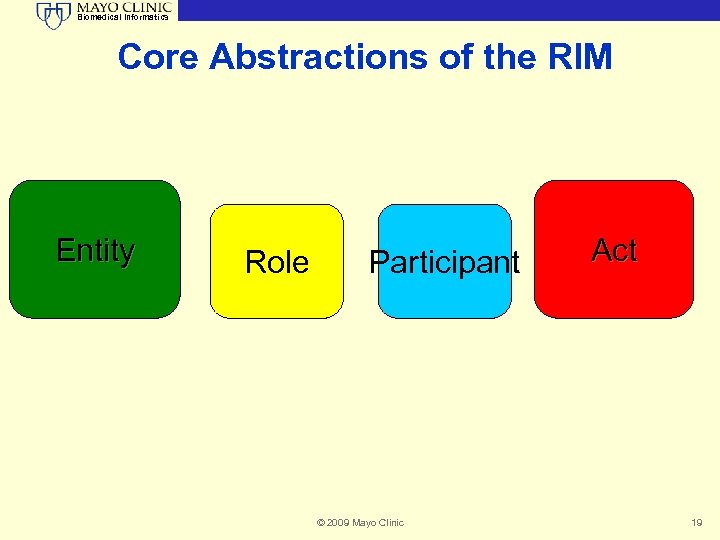
Biomedical Informatics Core Abstractions of the RIM Entity Role Participant © 2009 Mayo Clinic Act 19

Biomedical Informatics Is that all? • The RIM adheres to a high-level abstract model • Most of the “detail” exists within the vocabulary extensions of the RIM • The Model goes much deeper than the boxes • The surface boxes are the veneer © 2009 Mayo Clinic 20
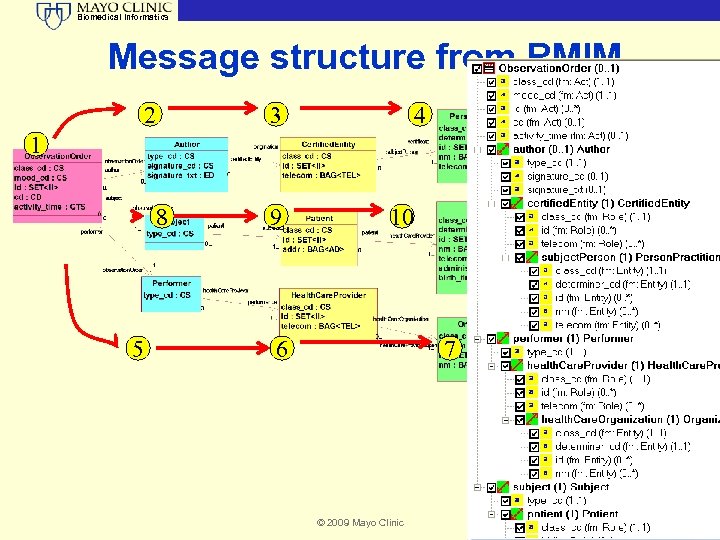
Biomedical Informatics Message structure from RMIM 2 3 4 1 8 5 9 10 6 7 © 2009 Mayo Clinic 21
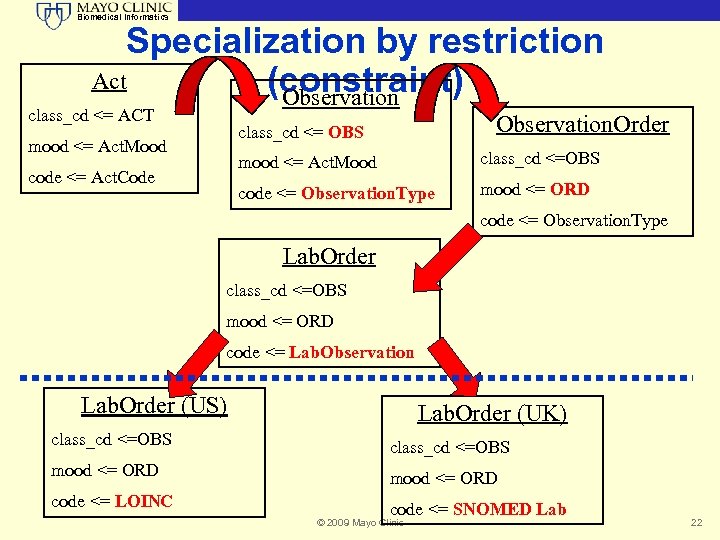
Biomedical Informatics Specialization by restriction Act (constraint) Observation class_cd <= ACT Observation. Order class_cd <= OBS mood <= Act. Mood code <= Observation. Type code <= Act. Code class_cd <=OBS mood <= ORD code <= Observation. Type Lab. Order class_cd <=OBS mood <= ORD code <= Lab. Observation Lab. Order (US) Lab. Order (UK) class_cd <=OBS mood <= ORD code <= LOINC code <= SNOMED Lab © 2009 Mayo Clinic 22
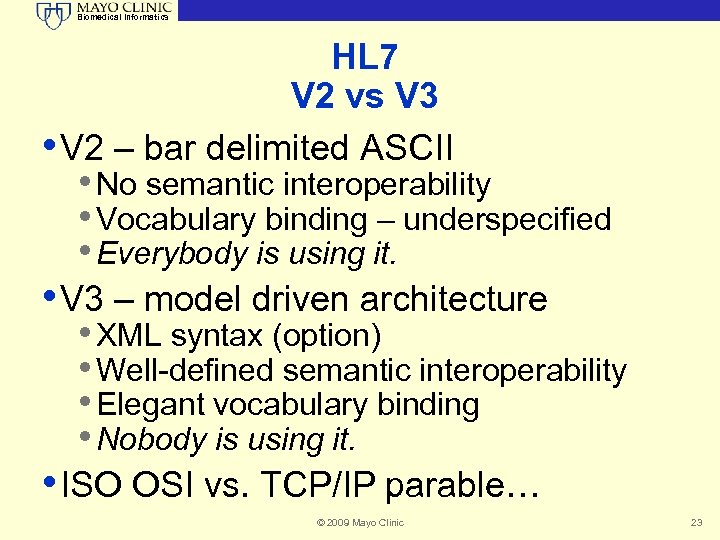
Biomedical Informatics HL 7 V 2 vs V 3 • V 2 – bar delimited ASCII • No semantic interoperability • Vocabulary binding – underspecified • Everybody is using it. • V 3 – model driven architecture • XML syntax (option) • Well-defined semantic interoperability • Elegant vocabulary binding • Nobody is using it. • ISO OSI vs. TCP/IP parable… © 2009 Mayo Clinic 23

Biomedical Informatics • Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium – a global, open non-profit standards development organization (SDO) • Standards openly available (www. cdisc. org) • Initiated as volunteer group 1997; incorporated 2000 • now > 230 organizational members • biopharmaceutical companies, technology providers, contract research organizations © 2009 Mayo Clinic 24 24

Biomedical Informatics Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium – CDISC (2) • CDISC has established global standards for collection, exchange, regulatory submission and archive of medical research data. • Charter Agreement with HL 7 since 2002; commitment to harmonize standards • Liaison A status to ISO TC 215 (Healthcare) © 2009 Mayo Clinic 25
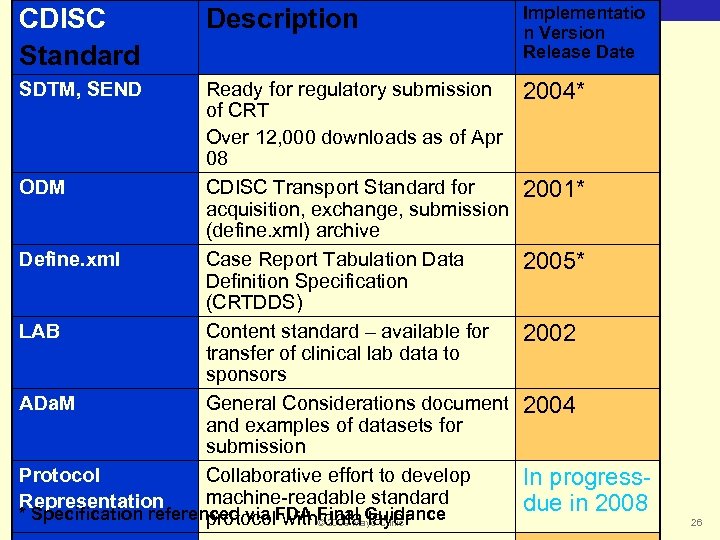
CDISC Standard Biomedical Informatics SDTM, SEND Description Ready for regulatory submission of CRT Over 12, 000 downloads as of Apr 08 ODM CDISC Transport Standard for acquisition, exchange, submission (define. xml) archive Define. xml Case Report Tabulation Data Definition Specification (CRTDDS) LAB Content standard – available for transfer of clinical lab data to sponsors ADa. M General Considerations document and examples of datasets for submission Protocol Collaborative effort to develop machine-readable standard Representation * Specification referenced via FDA ©data Guidance protocol with. Final layer 2009 Mayo Clinic Implementatio n Version Release Date 2004* 2001* 2005* 2002 2004 In progressdue in 2008 26

Biomedical Informatics The BRIDG Model* A clinical research domain analysis model (UML) initiated by CDISC, BRIDGing • Organizations (CDISC, HL 7, FDA, NCI) • Standards - all CDISC standards harmonized into BRIDG • Research and Healthcare Towards semantic interoperability; a Portal to Healthcare Represents clinical research in the context of the HL 7 RIM Open source ; Collaborative Project • See BRIDG Model on CDISC website or www. bridgmodel. org *Biomedical Research Integrated Domain Group (BRIDG) Model © 2009 Mayo Clinic 27 27
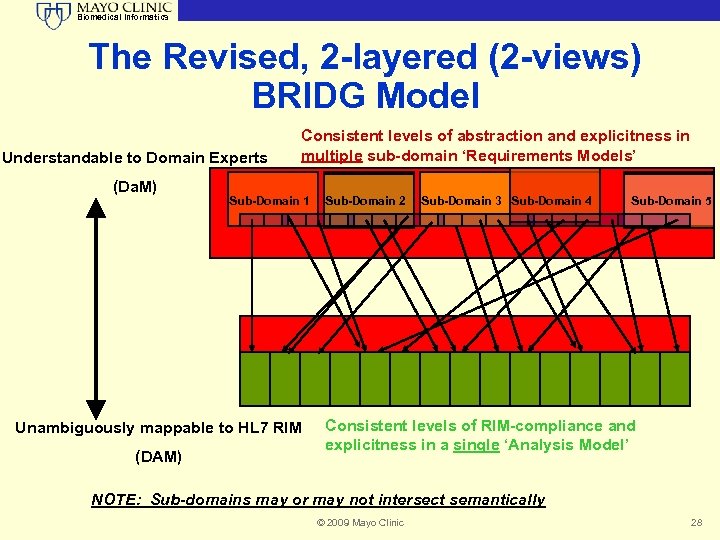
Biomedical Informatics The Revised, 2 -layered (2 -views) BRIDG Model Understandable to Domain Experts (Da. M) Consistent levels of abstraction and explicitness in multiple sub-domain ‘Requirements Models’ Sub-Domain 1 Unambiguously mappable to HL 7 RIM (DAM) Sub-Domain 2 Sub-Domain 3 Sub-Domain 4 Sub-Domain 5 Consistent levels of RIM-compliance and explicitness in a single ‘Analysis Model’ NOTE: Sub-domains may or may not intersect semantically © 2009 Mayo Clinic 28

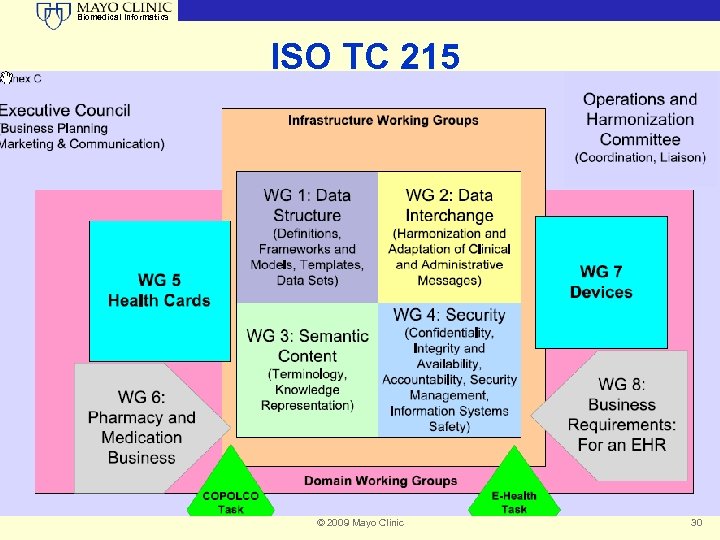
Biomedical Informatics ISO TC 215 Health Informatics • Created in 1998 • Heritage of national standards organizations • Many countries REQUIRE use of ISO standards if they exist (not USA) • Organized by Core Infrastructure and Use Cases • Coordinates with other standards development organizations through Joint Initiative Council © 2009 Mayo Clinic 29
Biomedical Informatics ISO TC 215 © 2009 Mayo Clinic 30
![Biomedical Informatics [IOM testimony] Urgent Need for US Health Terminology Authority • Model after Biomedical Informatics [IOM testimony] Urgent Need for US Health Terminology Authority • Model after](https://present5.com/presentation/635b0734c9c94fbd20f8c3d5d453ad21/image-31.jpg)
Biomedical Informatics [IOM testimony] Urgent Need for US Health Terminology Authority • Model after HL 7 “US Realm” notion • Forum for adjudicating “value set” contents • Prototyped within HITSP Foundations Committee • Must also identify National Terminology Service • Distribution point for USHTA Content • Download whole code systems, values sets • Synchronizing master for “local” © 2009 Mayo Clinic 31

Biomedical Informatics HL 7 Codes and Values – this week… • 364 Concept Domains • Kinds of things, Dx, Px, Appt, drug, … • 251 code systems • 155 internally maintained • 96 managed by reference (ICD, CPT, SNOMED…) • 1579 Value sets (hierarchical) • Lists of things used in messages or applications • Drawn from coding systems • Used to represent Concept Domains © 2009 Mayo Clinic 32

Biomedical Informatics Proliferation of Content “Have it your way” Vocabulary Models • Major ontologies • SNOMED CT; Gene Ontology; LOINC; NDF-RT • UMLS Metathesaurus; NCI Thesaurus • HL 7 RIM and Vocabulary; DICOM Rad. Lex • CDC bioterrorism PHIN standards • ca. BIG DSR / CDEs (Common Data Elements) • All created with differing formats and models © 2009 Mayo Clinic 33

Biomedical Informatics Mayo Lex. Grid Project Ontology Services • HL 7 ANSI Standard • ISO Standard • Open specification • Provide consistency and standardization required to support large-scale vocabulary adoption and use • Common model, tools, formats, and interfaces • Standard terminology model (Excel to OWL) © 2009 Mayo Clinic 34
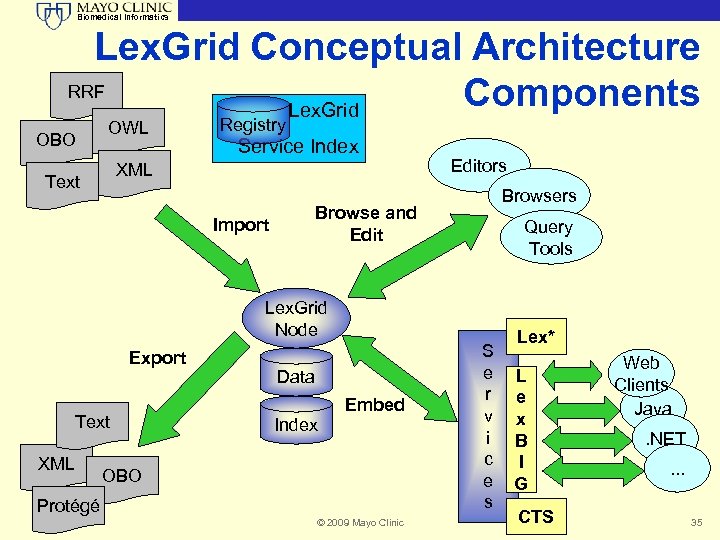
Biomedical Informatics Lex. Grid Conceptual Architecture RRF Components Lex. Grid OBO OWL Registry Service Index XML Text Editors Browse and Edit Import Query Tools Lex. Grid Node Export Text XML Data Index Embed OBO Protégé © 2009 Mayo Clinic S e r v i c e s Lex* L e x B I G CTS Web Clients Java. NET. . . 35
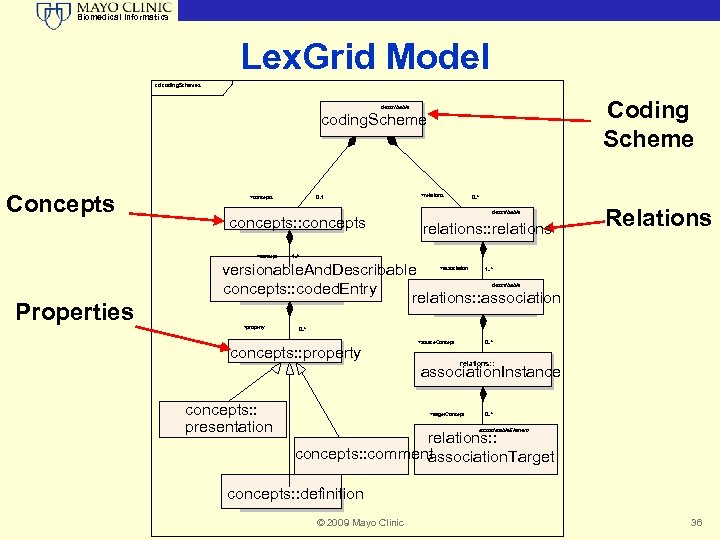
Biomedical Informatics Lex. Grid Model cd coding. Schemes Coding Scheme describable coding. Scheme Concepts +concepts 0. . 1 concepts: : concepts +concept +relations 0. . * describable relations: : relations Relations 1. . * versionable. And. Describable concepts: : coded. Entry relations: : association +association 1. . * describable Properties +property 0. . * concepts: : property +source. Concept 0. . * relations: : association. Instance concepts: : presentation +target. Concept 0. . * associatable. Element relations: : concepts: : comment association. Target concepts: : definition © 2009 Mayo Clinic 36

Biomedical Informatics Examples and Proof of Concept • HL 7 Vocabulary Model • Common Terminology Services • NIH Road. Map: Nat. Center Biomedical Ontologies • Mayo Lex. Grid project • Clinical and basic science (Gene Ontology) communities • NCI ca. BIG – Bioinformatics Grid • Lex. EVS (Enterprise Vocabulary Services) • NIH CTSA – Translational science © 2009 Mayo Clinic 37
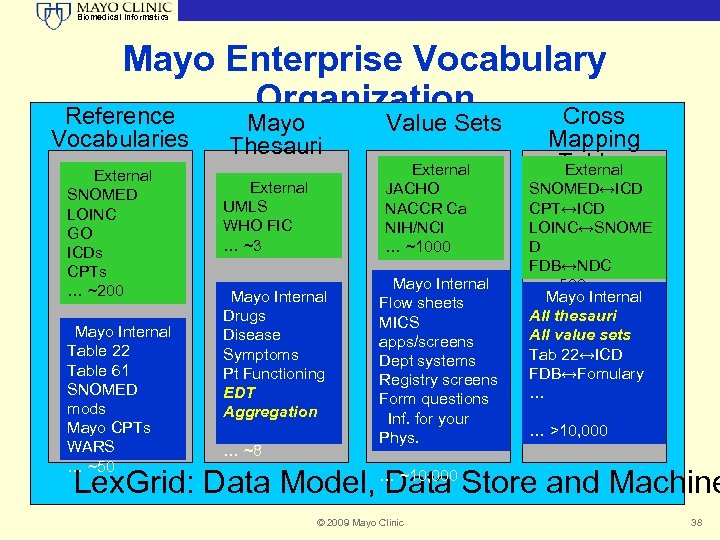
Biomedical Informatics Mayo Enterprise Vocabulary Organization Reference Cross Vocabularies External SNOMED LOINC GO ICDs CPTs … ~200 Mayo Internal Table 22 Table 61 SNOMED mods Mayo CPTs WARS … ~50 Mayo Thesauri External JACHO NACCR Ca NIH/NCI … ~1000 External UMLS WHO FIC … ~3 Mayo Internal Drugs Disease Symptoms Pt Functioning EDT Aggregation … ~8 Value Sets Mayo Internal Flow sheets MICS apps/screens Dept systems Registry screens Form questions Inf. for your Phys. Mapping Tables External SNOMED↔ICD CPT↔ICD LOINC↔SNOME D FDB↔NDC … ~500 Mayo Internal All thesauri All value sets Tab 22↔ICD FDB↔Fomulary … … >10, 000 Lex. Grid: Data Model, … ~10, 000 Store and Machine Data © 2009 Mayo Clinic 38

Biomedical Informatics NCBO – A Bridge Across the Chasm © 2009 Mayo Clinic 39
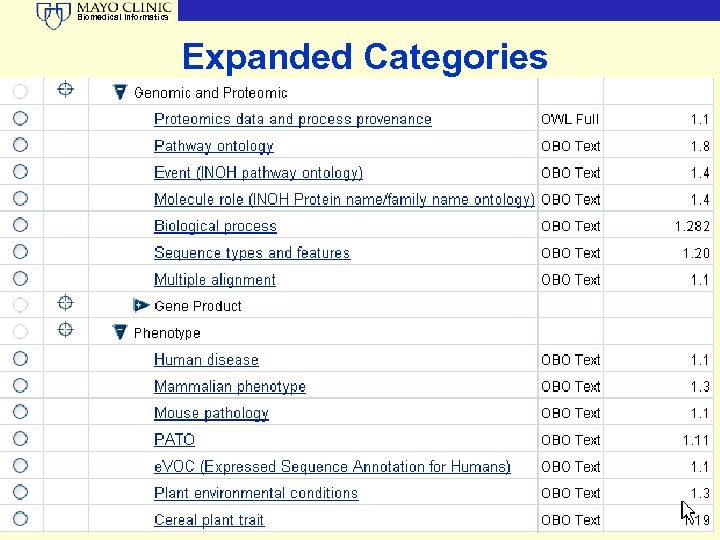
Biomedical Informatics Expanded Categories © 2009 Mayo Clinic 40
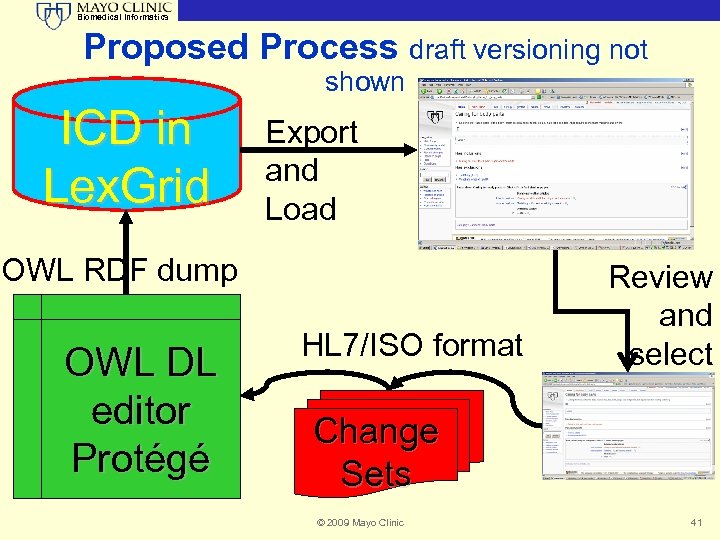
Biomedical Informatics Proposed Process draft versioning not shown ICD in Lex. Grid Export and Load OWL RDF dump OWL DL editor Protégé HL 7/ISO format Review and select Change Sets © 2009 Mayo Clinic 41
Biomedical Informatics ICD-11 Joint Alternate Future ICD-IHTSDO Effort SNOMED © 2009 Mayo Clinic 42

Biomedical Informatics Where is This Going? • Standards and interopreabilty are emerging as a first-rank US health priority • The boundary between “clinical” and “research” standards in biology and medicine is eroding • Information models and vocabulary exist along a continuum, that must integrate. • Information standards, especially vocabularies, are the foundation for © 2009 Mayo Clinic 43
635b0734c9c94fbd20f8c3d5d453ad21.ppt