6c9c87ca91bcf4c21b04528ddf4122c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Biomarkers for early disease detection Stuart Dashper Melbourne Dental School & Bio 21 University of Melbourne
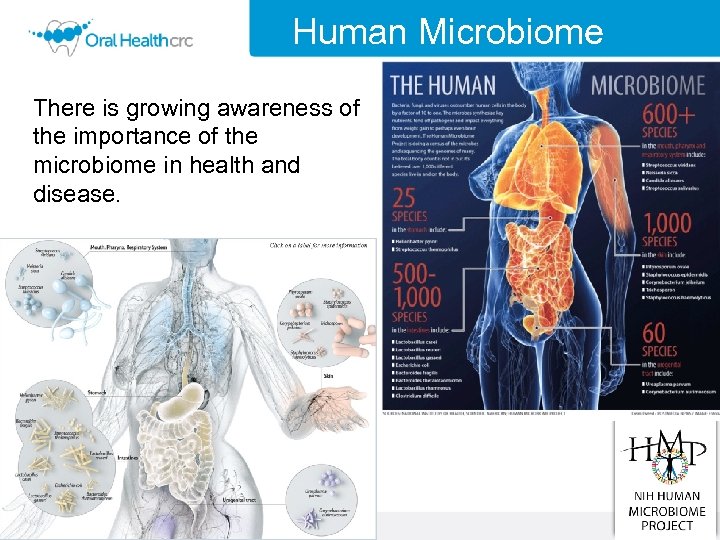
Human Microbiome There is growing awareness of the importance of the microbiome in health and disease.
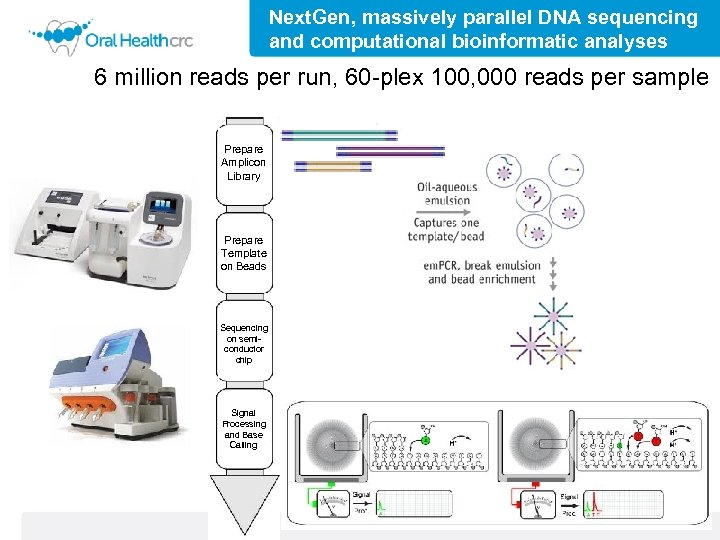
Next. Gen, massively parallel DNA sequencing and computational bioinformatic analyses 6 million reads per run, 60 -plex 100, 000 reads per sample Prepare Amplicon Library Prepare Template on Beads Sequencing on semiconductor chip Signal Processing and Base Calling
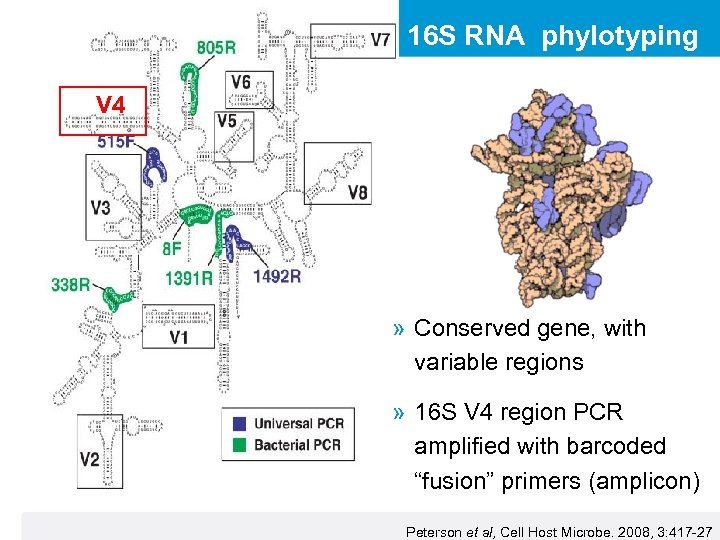
16 S RNA phylotyping V 4 » Conserved gene, with variable regions » 16 S V 4 region PCR amplified with barcoded “fusion” primers (amplicon) Peterson et al, Cell Host Microbe. 2008, 3: 417 -27

The Oral Microbiome • Each individual human oral microbiome is composed of well over 700 species of bacteria. • The human oral cavity is continuously bathed in saliva. • Regular dietary intake. • Bacterial are accreted to the hard nonshedding surfaces of the teeth as complex polymicrobial biofilms. • Numerous microhabitats within the oral cavity.
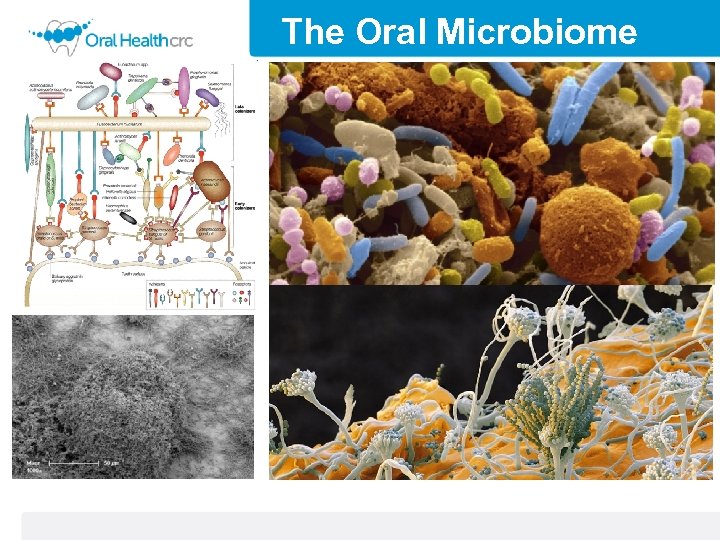
The Oral Microbiome
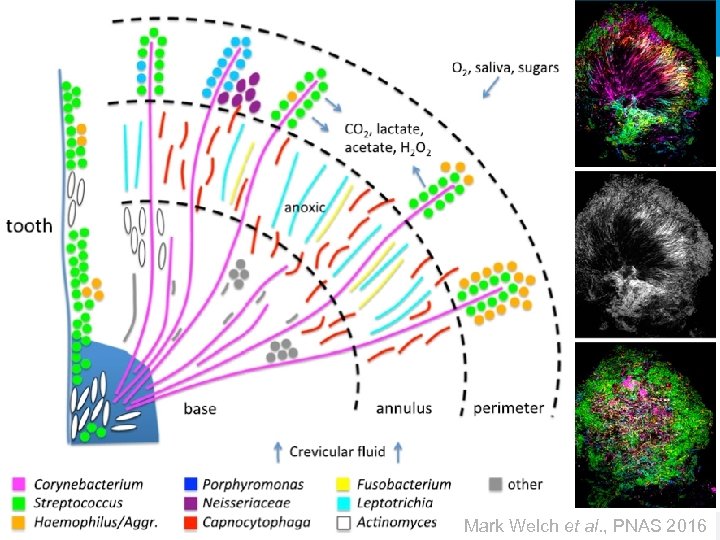
Mark Welch et al. , PNAS 2016

Biomarkers of Disease Biomarkers are objectively measured and evaluated indicators of normal biologic processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to therapeutic intervention. Biomarkers exist in a variety of different forms, including antibodies, microbes, DNA, RNA, lipids, metabolites, and proteins. Alterations in their concentration, structure, function, or action can be associated with the onset, progression, or even regression of a particular disorder or result from how the body responds to it. Thus, biomarkers serve as a valuable and attractive tool in the detection, risk assessment, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of disease.

Biomarkers O Prognostic biomarker - provides information on the likely course of disease in an untreated individual O Diagnostic biomarker – informs the clinician of the existence of a disease O Predictive biomarkers - give an indication of the probable effect of a treatment on patient • Prognosis from the Greek "fore-knowing, foreseeing"
Saliva Testing • Non-invasive, easy to collect • Development of small, portable, and rapid processing technologies for saliva samples holds promise for faster identification of health issues and earlier access to treatment (NIH, USA) • Oral and systemic diseases www. skb. ucla. edu/wonglab/index. html
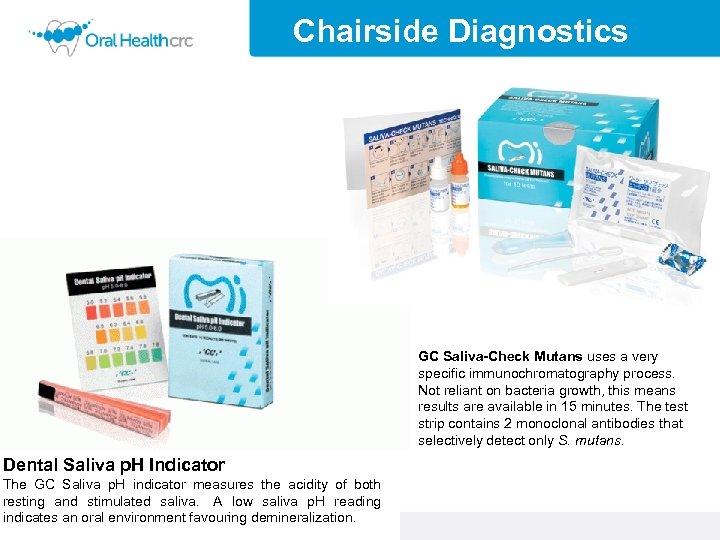
Chairside Diagnostics GC Saliva-Check Mutans uses a very specific immunochromatography process. Not reliant on bacteria growth, this means results are available in 15 minutes. The test strip contains 2 monoclonal antibodies that selectively detect only S. mutans. Dental Saliva p. H Indicator The GC Saliva p. H indicator measures the acidity of both resting and stimulated saliva. A low saliva p. H reading indicates an oral environment favouring demineralization.
Laboratory Diagnostics 1 2 3 4

Early Childhood Caries • The disease of early childhood caries (ECC) is defined as the presence of one or more decayed (non-cavitated or cavitated lesions), missing (due to caries), or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth in a child under the age of six years. • If left untreated, tooth destruction can be so extensive that extraction of teeth is necessary

Early Childhood Caries • ECC continues to be one of the most prevalent childhood diseases globally. • By six years of age approximately 47% of Australian children have experience of dental decay, of which 60% is untreated. (Armfield, 2008) • The most severely affected 10% of children with ECC have five times the national average caries experience with almost 10 teeth affected (The 2007 Child Dental Health Survey) • In Victoria, 7. 1% of children aged <12 years have had a general anaesthetic for dental treatment • Systemic infections can result from severe dental caries

Dental Caries Polymicrobial chronic disease: - Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus casei, Streptococcus sobrinus, Bifidobacterium spp. , Scardovia spp. Dynamic process that takes place in the dental plaque on the surface of the tooth. There is a dysbiosis in the plaque leading to an increase in abundance of cariogenic species and a decrease in commensal or beneficial species. These species produce and tolerate acid which results in a loss of the equilibrium between the enamel of the tooth and the surrounding plaque fluid so that over time there is a net loss of calcium and phosphate from the tooth eventually leading to irreversible cavitation. Approximately half of the oral microbiota of over 700 species remains uncultivated

Vic. Gen - Birth Cohort Study • Prospective Cohort Study (2008) • 232 mother-infant dyads followed for 5 years after birth (466 enrolled followed for first section of study) • Assessed at 7 times: - 2, 8, 13, 19, 38, 48, 60 months of age NH&MRC Primary Health Care Project Grant
Vic. Gen - Birth Cohort Study • Questionnaire » - socio-economic, behavioural and dietary information • Clinical assessment (ICDAS II) • Biological sampling (saliva) de Silva-Sanigorski A, Calache H, Gussy M, Dashper S, Gibson J, Waters E. The Vic. Generation study - A birth cohort to examine the environmental, behavioural and biological predictors of early childhood caries: Background, aims and methods. BMC Public Health 10: 97 (2010).
Project Goals • Prognostic Biomarkers of ECC » How does the saliva microbiome develop in infants? » Is ECC incidence and severity associated with changes in the saliva microbiome? » Are there particular species or consortia of oral bacteria in saliva that can be used as biomarkers to predict disease?
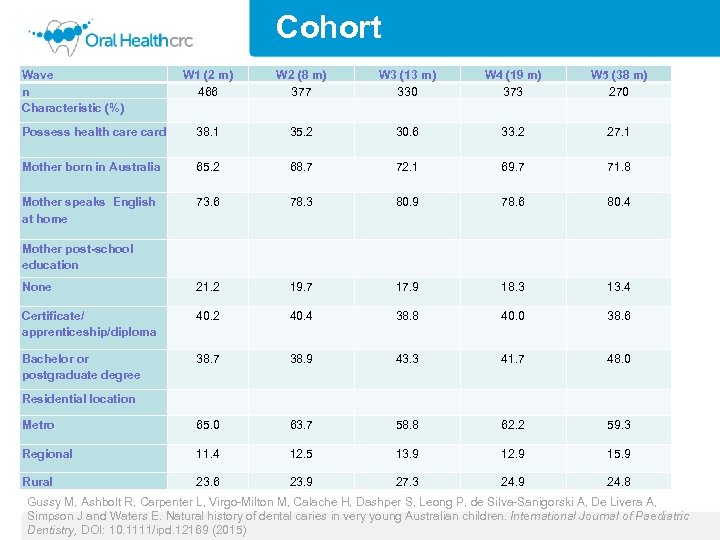
Cohort Wave n Characteristic (%) W 1 (2 m) 466 W 2 (8 m) 377 W 3 (13 m) 330 W 4 (19 m) 373 W 5 (38 m) 270 Possess health care card 38. 1 35. 2 30. 6 33. 2 27. 1 Mother born in Australia 65. 2 68. 7 72. 1 69. 7 71. 8 Mother speaks English at home 73. 6 78. 3 80. 9 78. 6 80. 4 None 21. 2 19. 7 17. 9 18. 3 13. 4 Certificate/ apprenticeship/diploma 40. 2 40. 4 38. 8 40. 0 38. 6 Bachelor or postgraduate degree 38. 7 38. 9 43. 3 41. 7 48. 0 Residential location Metro 65. 0 63. 7 58. 8 62. 2 59. 3 Regional 11. 4 12. 5 13. 9 12. 9 15. 9 Rural 23. 6 23. 9 27. 3 24. 9 24. 8 Mother post-school education Gussy M, Ashbolt R, Carpenter L, Virgo-Milton M, Calache H, Dashper S, Leong P, de Silva-Sanigorski A, De Livera A, Simpson J and Waters E. Natural history of dental caries in very young Australian children. International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry, DOI: 10. 1111/ipd. 12169 (2015)

Johnson S, Carpenter L, Amezdroz E, Dashper S, Gussy M, Calache M, De Silva A, Waters E. Cohort profile: The Vic. Generation study – an Australian oral health birth cohort. International J. Epidemiology doi: 10. 1093/ije/dyw 024 (2016).
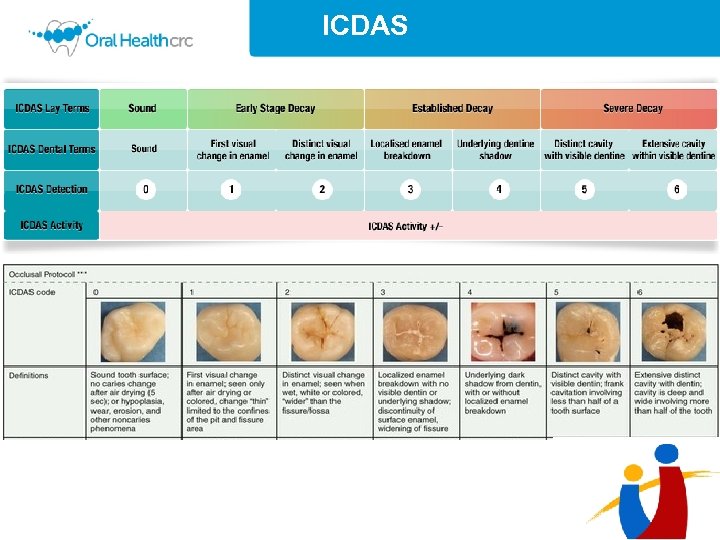
ICDAS

Inclusion/ Exclusion criteria: • Clinical assessment required for four time points » (4 th -7 th visit; 19 -60 months of age). • All tooth surfaces scored at all time points. • No regression from an ICDAS-II score ≥ 3. • Infants who had teeth exfoliate at the seventh visit were included, so long as the exfoliated tooth did not have an ICDAS -II score >0 at the sixth visit. • A total of 57 infants were excluded on these criteria. » 24 infants missed a clinical assessment at one or more time points. » 9 infants did not have all tooth surfaces scored. » 7 infants had recorded regression of ICDAS-II scores ≥ 3 from the sixth visit. » A total of 11 primary incisors from 6 infants had exfoliated by the 7 th visit

Classification of disease • Only a few instances of more than one surface per tooth with a carious lesion. • Data analysed at a tooth level rather than tooth surface level. • If a tooth did have more than one ICDAS-II score, the highest score was chosen to represent that tooth. • Restorations given an ICDAS-II score of 5. • Extractions given an ICDAS-II score of 6. • <20 ICDAS-II scores per infant.
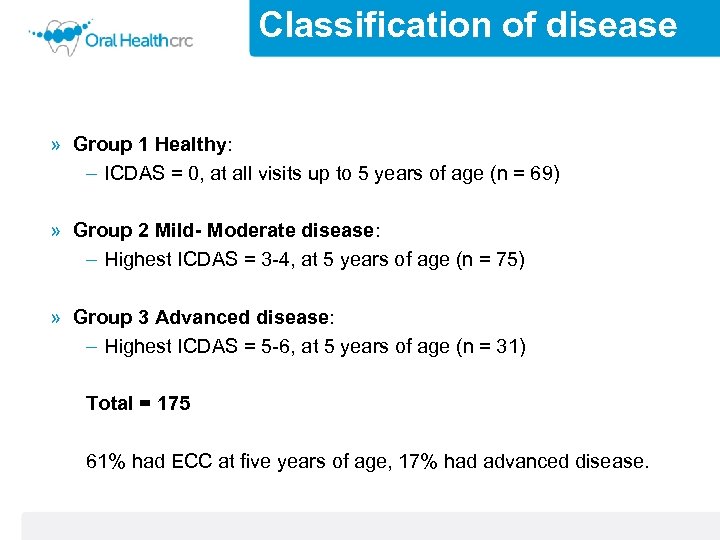
Classification of disease » Group 1 Healthy: – ICDAS = 0, at all visits up to 5 years of age (n = 69) » Group 2 Mild- Moderate disease: – Highest ICDAS = 3 -4, at 5 years of age (n = 75) » Group 3 Advanced disease: – Highest ICDAS = 5 -6, at 5 years of age (n = 31) Total = 175 61% had ECC at five years of age, 17% had advanced disease.
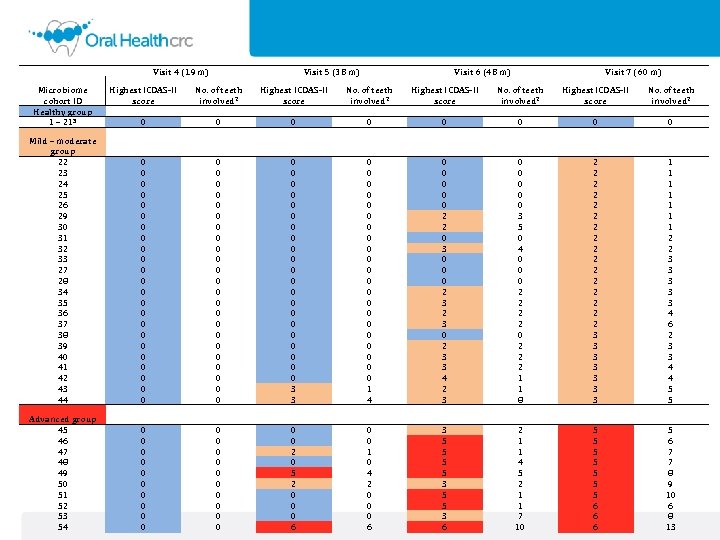
Visit 4 (19 m) Visit 5 (38 m) Visit 6 (48 m) Microbiome cohort ID Healthy group 1 – 213 Highest ICDAS-II score 0 No. of teeth involved 2 0 Mild – moderate group 22 23 24 25 26 29 30 31 32 33 27 28 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 4 Advanced group 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 5 2 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 0 4 2 0 0 0 6 Visit 7 (60 m) Highest ICDAS-II score 0 No. of teeth involved 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 3 0 0 0 2 3 3 4 2 3 0 0 0 3 5 0 4 0 0 0 2 2 2 1 1 8 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 6 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 3 6 2 1 1 4 5 2 1 1 7 10 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 5 6 7 7 8 9 10 6 8 13
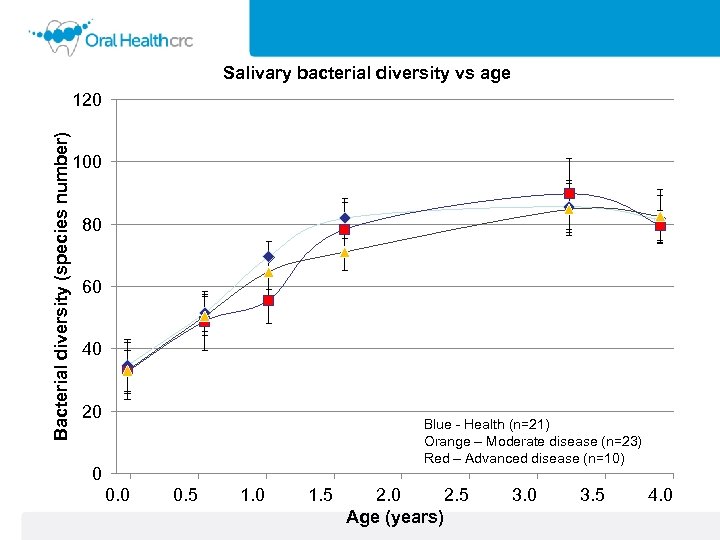
Salivary bacterial diversity vs age Bacterial diversity (species number) 120 100 80 60 40 20 Blue - Health (n=21) Orange – Moderate disease (n=23) Red – Advanced disease (n=10) 0 0. 5 1. 0 1. 5 2. 0 2. 5 Age (years) 3. 0 3. 5 4. 0
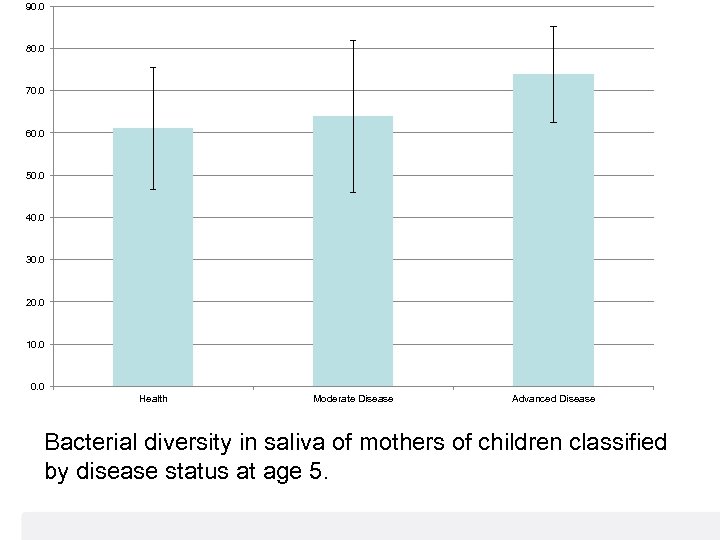
90. 0 80. 0 70. 0 60. 0 50. 0 40. 0 30. 0 20. 0 10. 0 Health Moderate Disease Advanced Disease Bacterial diversity in saliva of mothers of children classified by disease status at age 5.
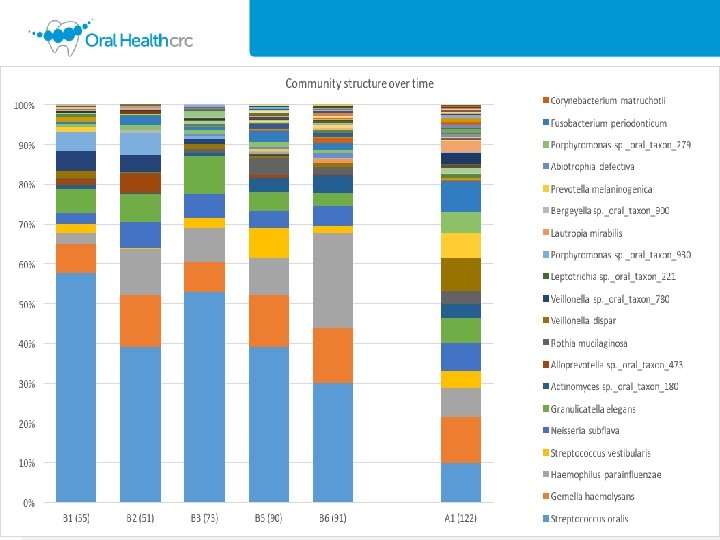
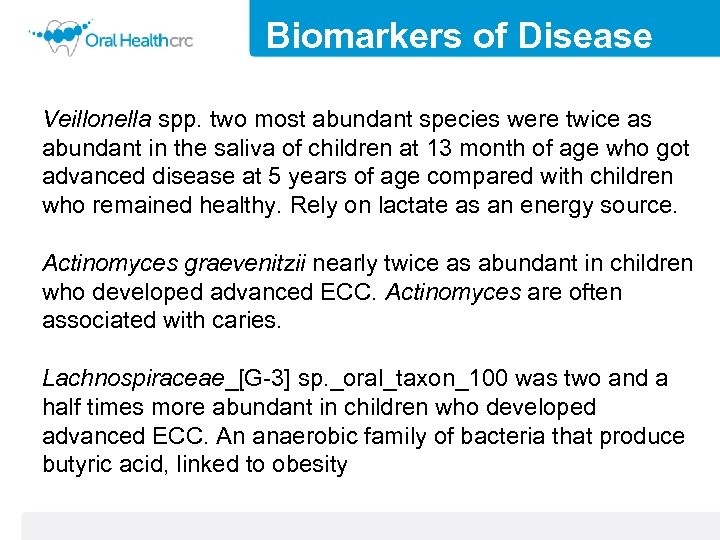
Biomarkers of Disease Veillonella spp. two most abundant species were twice as abundant in the saliva of children at 13 month of age who got advanced disease at 5 years of age compared with children who remained healthy. Rely on lactate as an energy source. Actinomyces graevenitzii nearly twice as abundant in children who developed advanced ECC. Actinomyces are often associated with caries. Lachnospiraceae_[G-3] sp. _oral_taxon_100 was two and a half times more abundant in children who developed advanced ECC. An anaerobic family of bacteria that produce butyric acid, linked to obesity
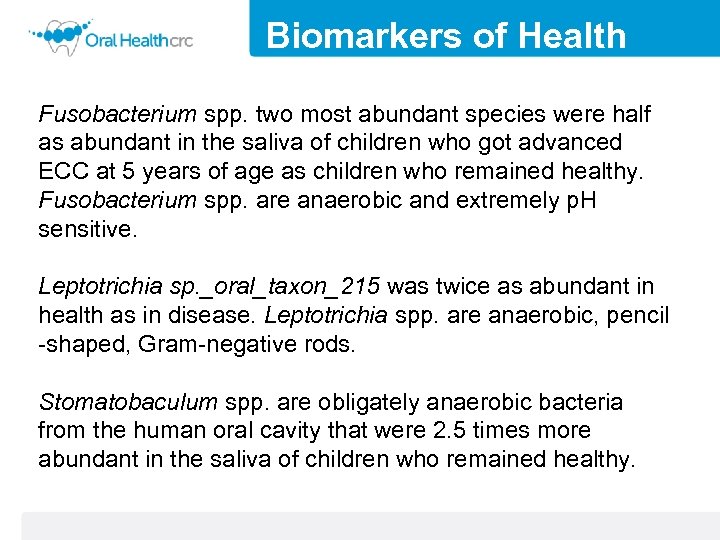
Biomarkers of Health Fusobacterium spp. two most abundant species were half as abundant in the saliva of children who got advanced ECC at 5 years of age as children who remained healthy. Fusobacterium spp. are anaerobic and extremely p. H sensitive. Leptotrichia sp. _oral_taxon_215 was twice as abundant in health as in disease. Leptotrichia spp. are anaerobic, pencil -shaped, Gram-negative rods. Stomatobaculum spp. are obligately anaerobic bacteria from the human oral cavity that were 2. 5 times more abundant in the saliva of children who remained healthy.

Conclusions In an observed cohort over 60% of children developed caries in their deciduous teeth by 5 years of age. The salivary microbiome increased from 2 months of age to 3. 5 years of age in healthy children. Those children who had advanced disease at five years of age had a less diverse saliva microbiome at 13 months of age. The abundance of specific bacterial species in saliva offers promise as biomarkers of disease. Development of a multivalent probalistic predictive model of caries development in infants.

Opportunities Development of a prognostic biomarker screening test for early childhood caries based on bacterial diversity and the abundance of specific biomarker species in saliva. Administered by Maternal and Child Health Nurse Service (consultations at 8, 12, 18, 24 & 44 months of age) Development of an integrated care delivery system for children who are predicted to develop advanced caries.

Acknowledgements Project Reference Group • • The late Professor Elizabeth Waters (The Melbourne School of Population and Global Health) Professor Stuart Dashper (Oral Health CRC, Melbourne Dental School) Professor Hanny Calache, Dr Andrea de Silva (Dental Health Services Victoria) A/Professor Mark Gussy (La. Trobe University) Funding: • • • National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Dental Health Services Victoria (DHSV) Foundation for Children Department of Education and Early Childhood Development Jack Brockhoff Child Health and Wellbeing Program

Acknowledgements The Melbourne Dental School of Population School Life Sciences Computation Centre and Global Health • Elizabeth Waters • Helen Mitchell • Simon Gladman • Udit Bhatnagar • Dieter Bulach • David Manton • Torsten Seemann • Eric Reynolds • Deanne Catmull • Dayana Andrenacci • Brigitte Hoffmann • Linh Ngo • Samantha Byrne • Sarah Johns • Geoff Adams • Shae Johnson • Lauren Carpenter • Lisa Gibbs • Emily Amezdroz • Hannah Morrice
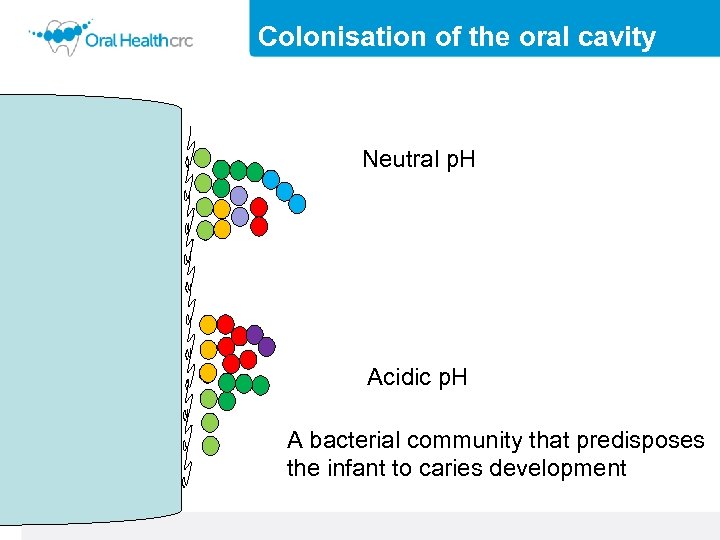
Colonisation of the oral cavity Neutral p. H Acidic p. H A bacterial community that predisposes the infant to caries development
6c9c87ca91bcf4c21b04528ddf4122c6.ppt