70827c04e18865bd04348022a486d044.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

Biology prefixes, root words, and suffixes Mrs. Harris 2015

pneumonoultramic roscopicsilicovolcan oconiosis?
pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolc anoconiosis?

What Makes Biology So Hard? Vocabulary – If you knew the prefixes and suffixes, you can tackle the tough words!!! Have you ever heard of pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolc anoconiosis?

Yes, this is an actual word. What does it mean? It is an obscure term ostensibly referring to a lung disease caused by silica dust, sometimes cited as one of the longest words in the English language.

What do these terms mean? Ursus maritimus Odocoileus virginianus nocturnal enuresis borborygmi. gustatory rhinitis horripilation. crepitus

Biology can be filled with words that sometime seem incomprehensible. By "dissecting" these words into discrete units, even the most complex terms can be understood. The following pages are designed to give you the tools needed to understand the most common prefixes and suffixes in biology. By using these prefixes and suffixes, even the most difficult words like the one above can be easily understood.

Means - A or An – Not or without Examples – asexual, abiotic

Anti Means – Against or opposite Example - Antibiotic

Aqua - water
-ase meaning – enzymes Example - Lactase

Auto – meaning: self Examples - autotroph
Bacter – bacteria Examples: Bacteria
Bi Means – two, twice, double Example - biceps

Bio Means – life Example - biotechnology
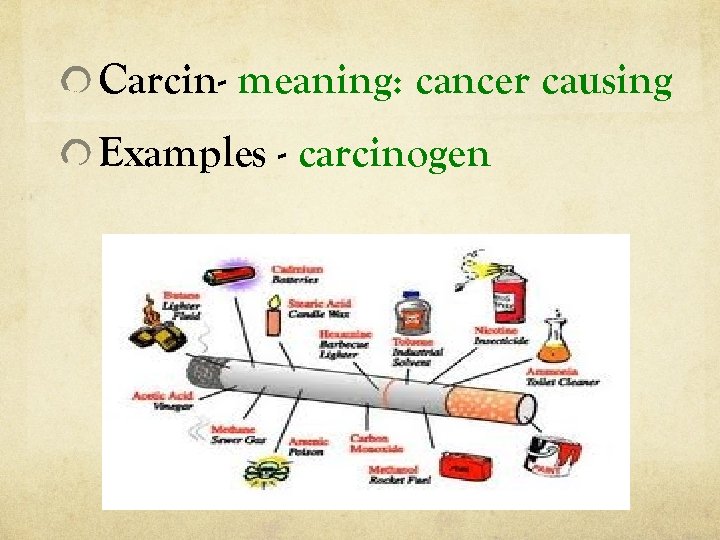
Carcin- meaning: cancer causing Examples - carcinogen

Carn Means – meat or flesh Example - Carnivore

Cholor. Means - green Example - chlorophyll

- cid(e) Means - kill Example – suicide, pesticide

Cilia Means – hair like Example - ciliates

Co Means – together or with Example - coevolution
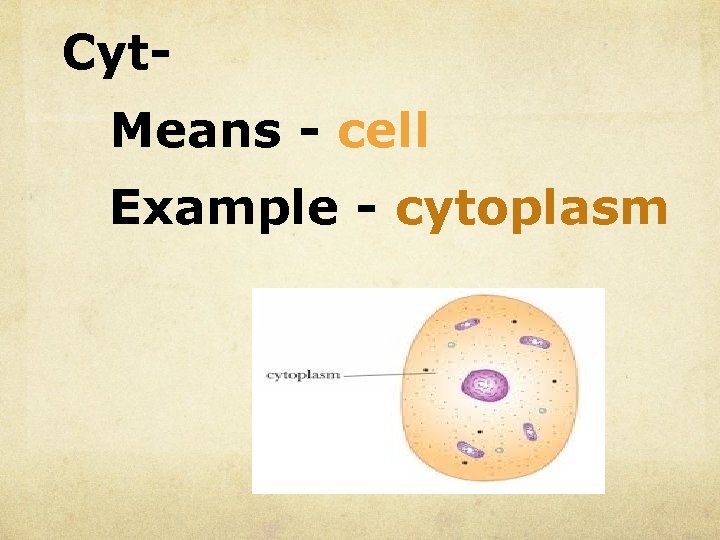
Cyt. Means - cell Example - cytoplasm

Di Means –two Example – diurnal & dichotomous

Eco Means – house Example – ecosystem

Endo Means – inner Example - endoderm
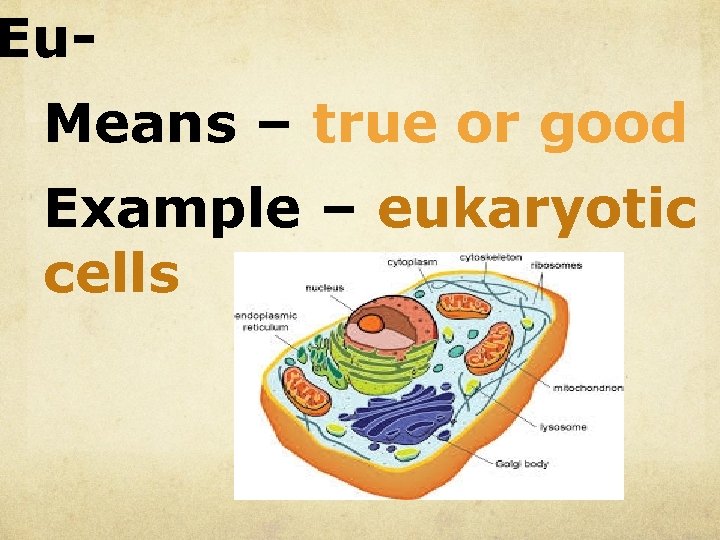
Eu. Means – true or good Example – eukaryotic cells
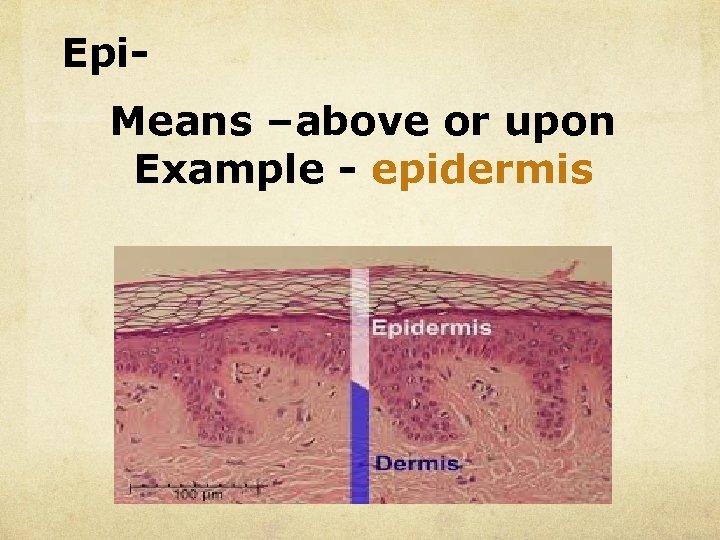
Epi. Means –above or upon Example - epidermis
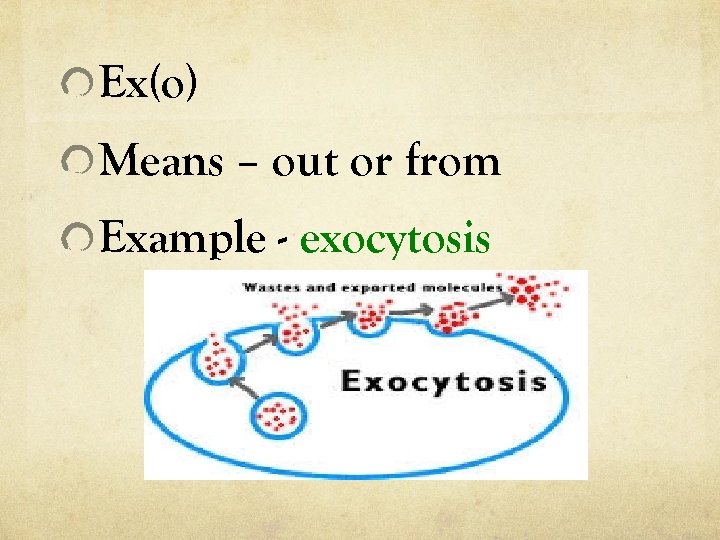
Ex(o) Means – out or from Example - exocytosis

gene Means – origin or birth Example - biogenesis
Glyco() Means – sugar Example - glycogen
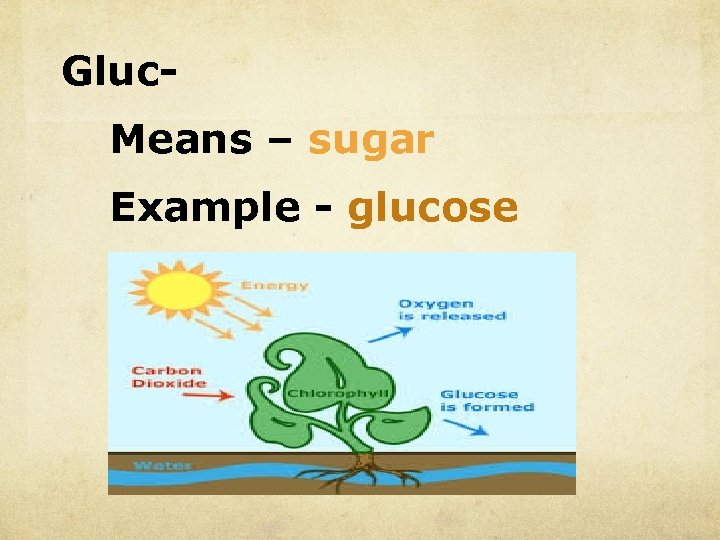
Gluc. Means – sugar Example - glucose

Herb Means – plant Example - herbivore

Hetero Means – other or different Example - heterosexual Mr. & Mrs. Forman July 2004

Hibern – Means – Sleep Example - Hibernate

Homo or Homeo Means – same Example - homocercal
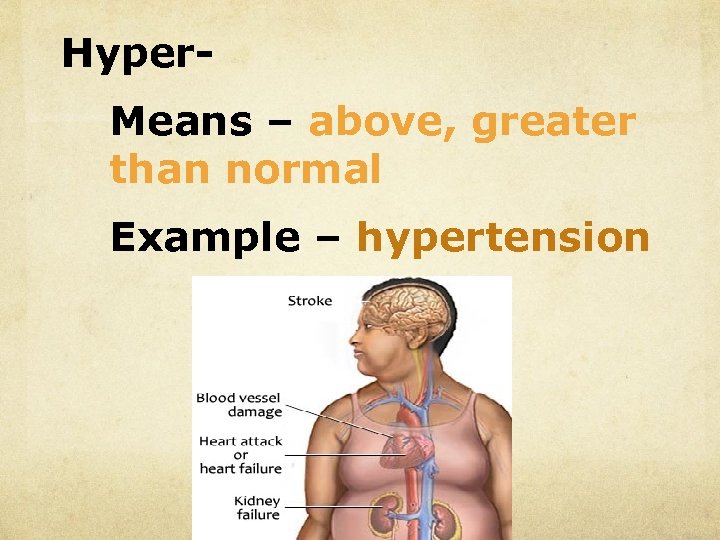
Hyper. Means – above, greater than normal Example – hypertension

Hydr Means – water Example - hydrology
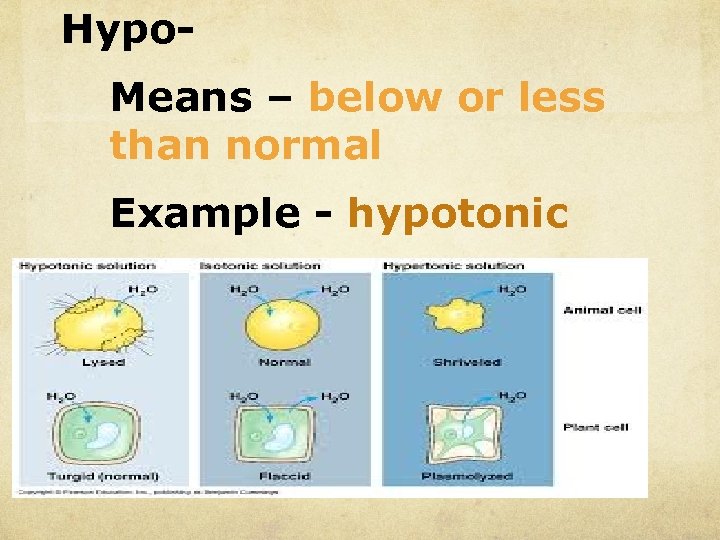
Hypo. Means – below or less than normal Example - hypotonic

-ist Means – person who studies Example - cytologist
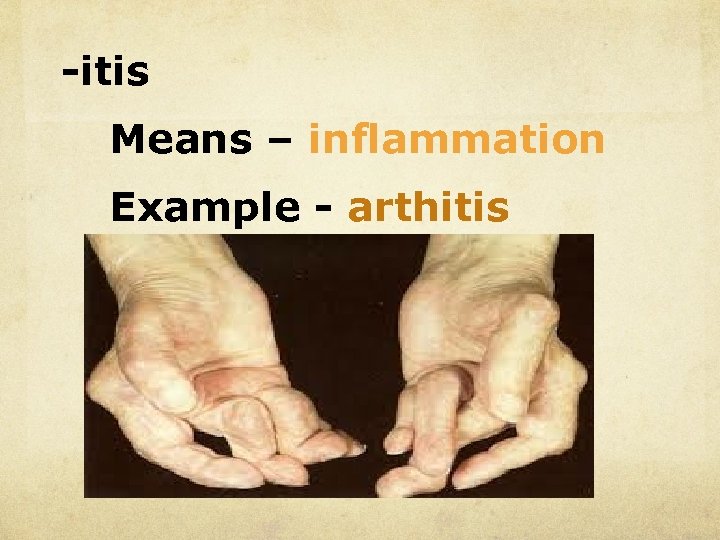
-itis Means – inflammation Example - arthitis
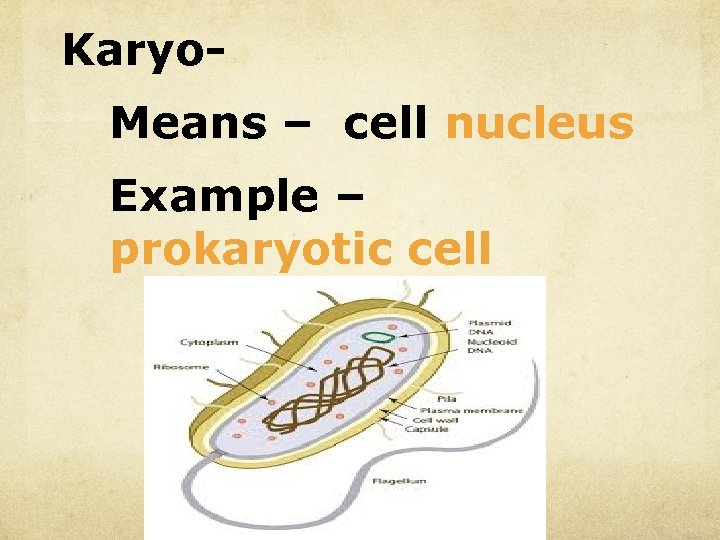
Karyo. Means – cell nucleus Example – prokaryotic cell
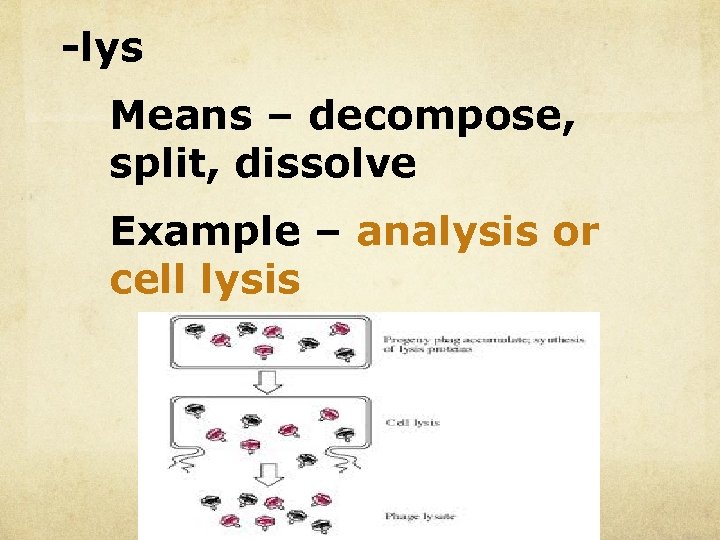
-lys Means – decompose, split, dissolve Example – analysis or cell lysis

Macr(o)Means – large Example Macromolecule

Micro. Means – small Example – microscope
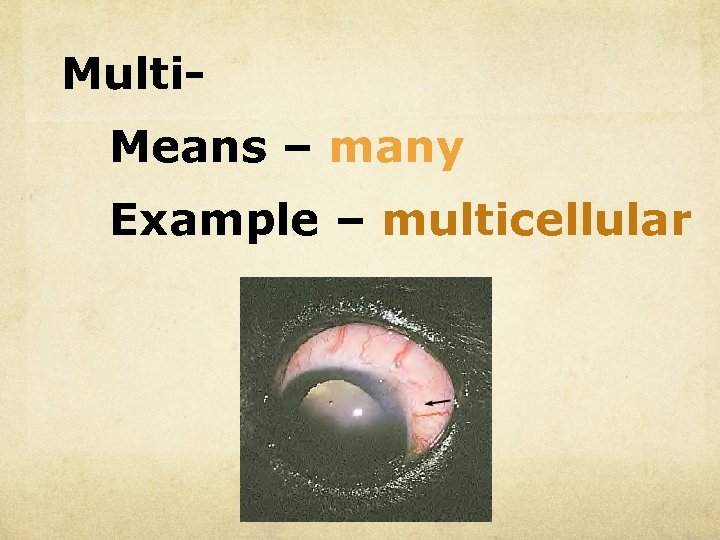
Multi. Means – many Example – multicellular

ology Means – study of Example – paleontology

-phil Means – love Example – hydophilia or hemophilia

phob Means – fear Example – arachnophobia

photo Means – light Example – photosynthesis or phototropism
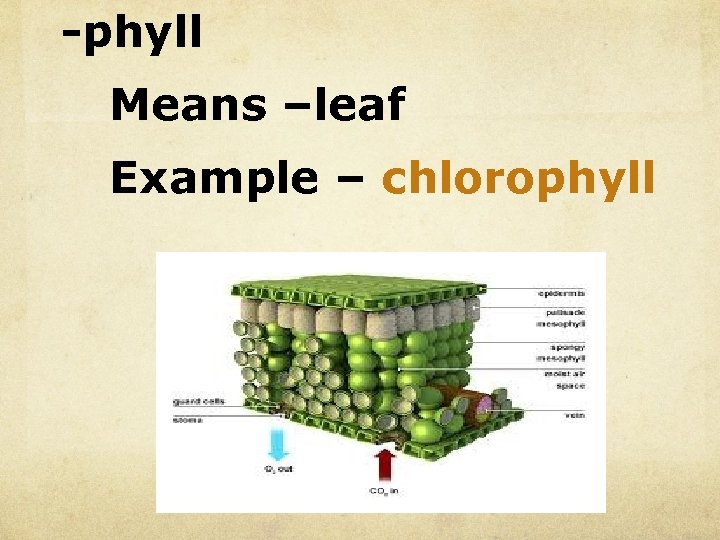
-phyll Means –leaf Example – chlorophyll
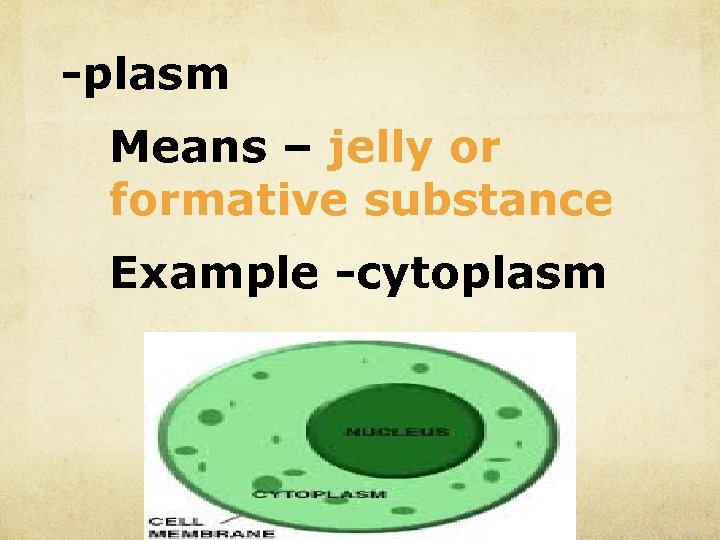
-plasm Means – jelly or formative substance Example -cytoplasm

-pod Means – foot Example - arthopod
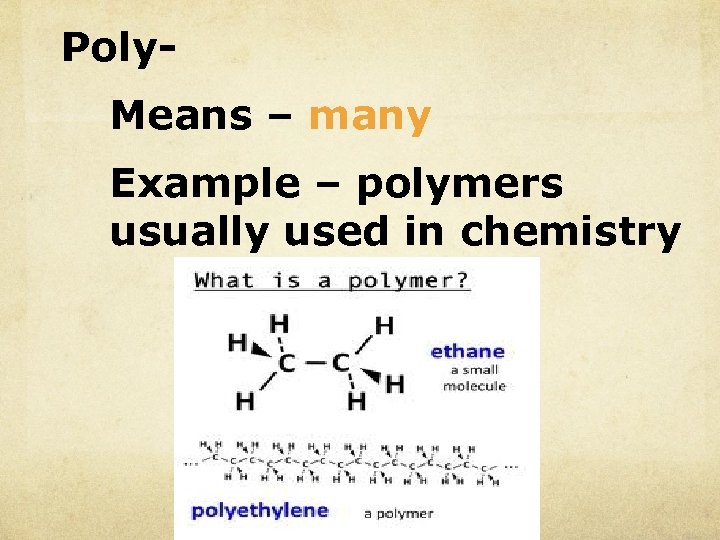
Poly. Means – many Example – polymers usually used in chemistry
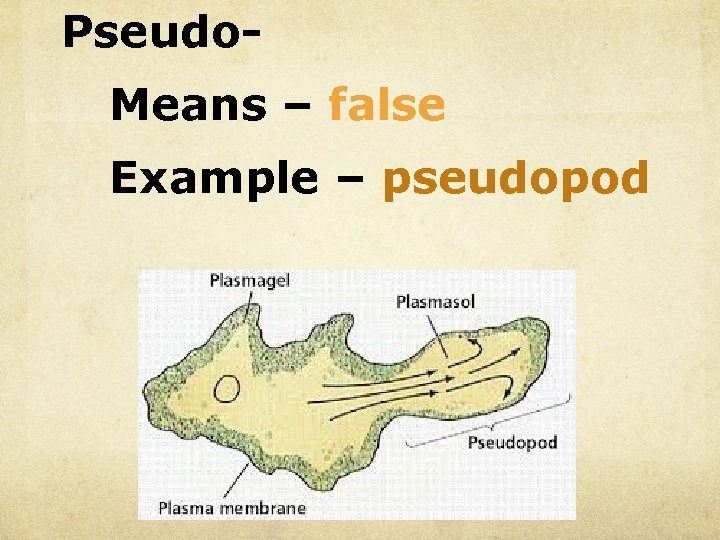
Pseudo. Means – false Example – pseudopod
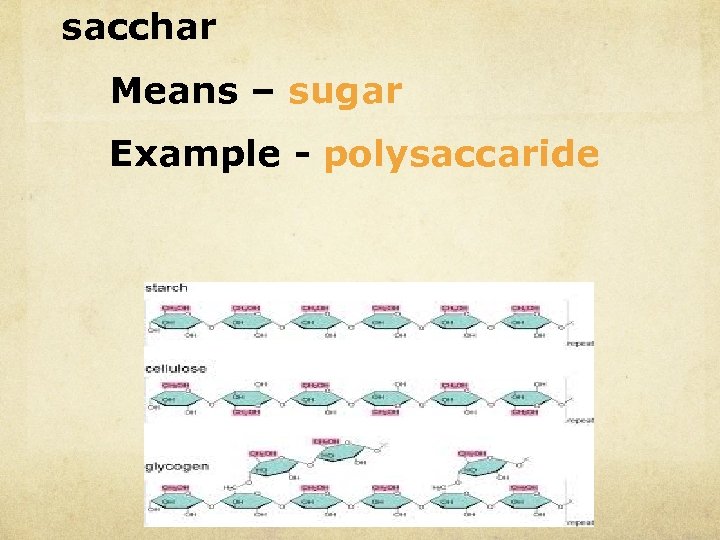
sacchar Means – sugar Example - polysaccaride
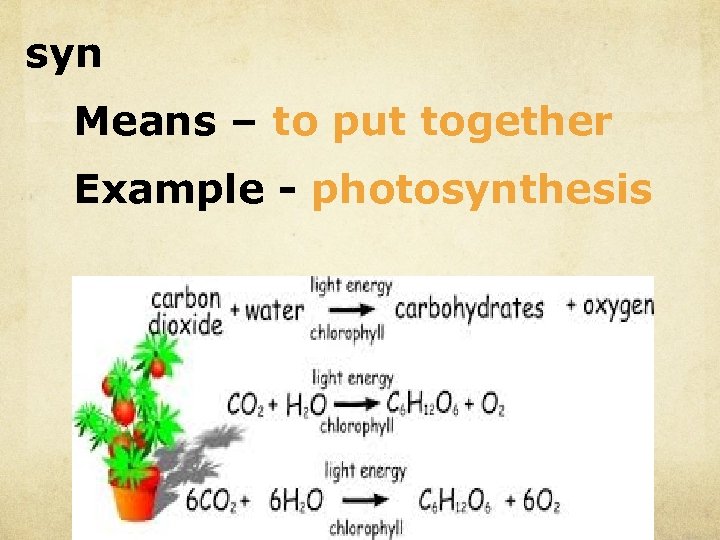
syn Means – to put together Example - photosynthesis

Troph Means – nourishment or one who feeds Example - Autotroph

-therm Means – heat Example – endothermic or exothermic
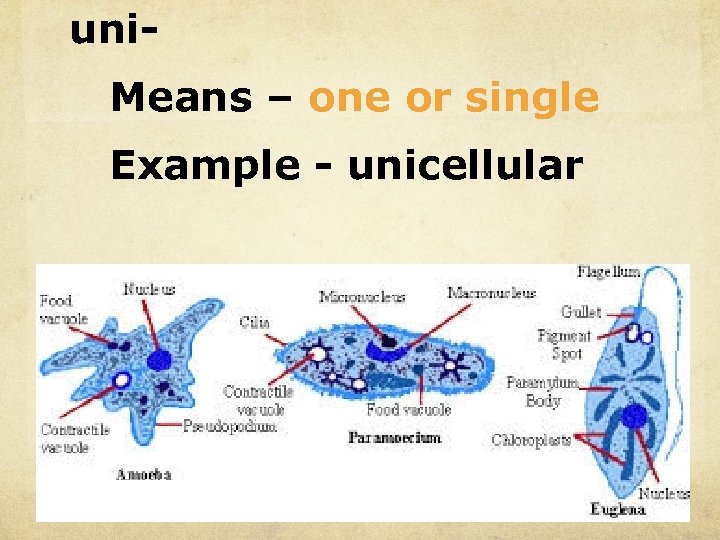
uni. Means – one or single Example - unicellular

-vor- means- devour or eat Examples - carnivore

Zo/zoa Means – animal Example – protozoa – protist that are animal like - consumer
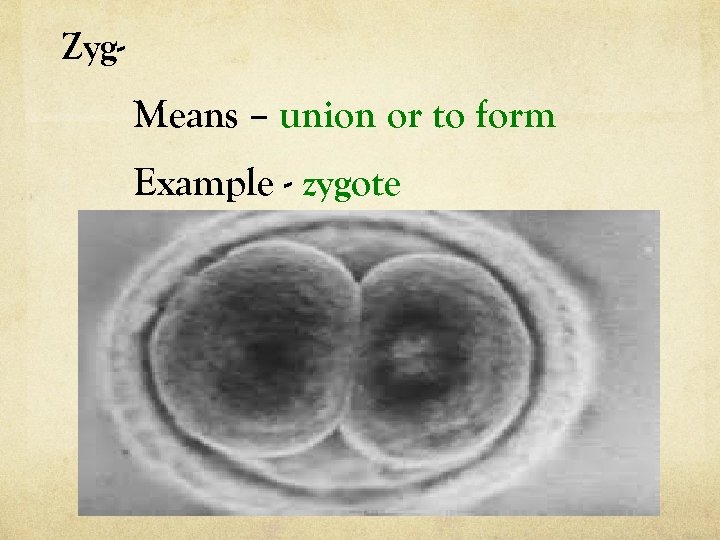
Zyg- Means – union or to form Example - zygote

Homework Monday 8/18 There will be a matching quiz on these words. Create at least 20 flash cards to study – due day of quiz Practice!
70827c04e18865bd04348022a486d044.ppt