1cc70b29536a12cd74a208c599d67aa2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Biology & Personality
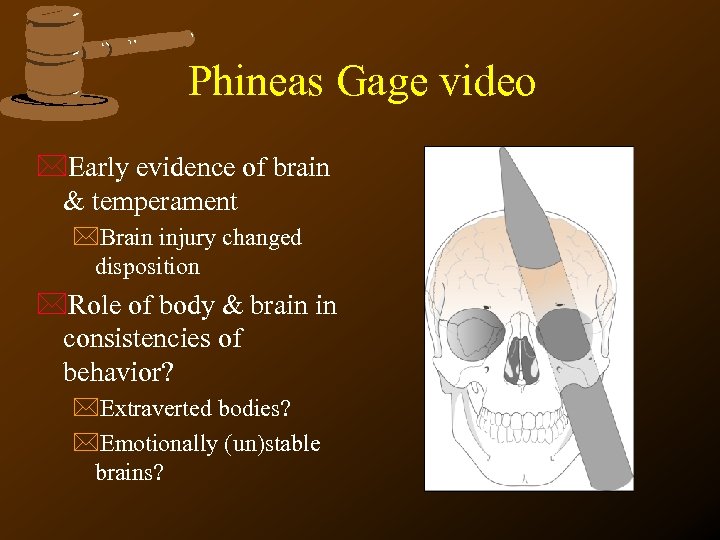
Phineas Gage video *Early evidence of brain & temperament *Brain injury changed disposition *Role of body & brain in consistencies of behavior? *Extraverted bodies? *Emotionally (un)stable brains?

Outline *Temperament *Evolution and personality *Behavioral genetics *Brain and temperament
Temperament *Individual differences in affective response *Inherited *Biologically based *Evidence from birth & stable throughout life *NOT traits but related *Traits not stable from birth & less pervasive influence

Temperament *Early views linked T w/ body features *Gall & phrenology *Kretschmer, Sheldon & body types *Inherited body determines T *Direction of effect problem *Recent work finds that endo NOT jolly

Temperament: Recent Research *New York Longitudinal Study (Thomas & Chess, 1977) *Kids followed from birth (1950) - adolescence *Parental reports revealed easy, difficult, & slow-towarm-up babies *Associated w/ later adjustment

Temperament: Recent Research *Kagan (1999): Inhibited v. uninhibited kids *Laboratory observations of 4 month olds revealed high & low reactivity *Stability of T at 4/8 years old *Change also due to parental influence

Temperament: Recent Research *In sum temperament construct supported *Link between biology & personality *Reciprocally causal *Temperaments linked w/ Big-5 (guide trait development) *Emotionality (~N) *Activity (~E) *Sociability (~E)

Jealousy *On a clean sheet of paper answer this Q: *What would bother you more: Your boy/girl friend (spouse) having sex with someone else or developing emotional feelings for someone else? *Sexual or emotional infidelity? *What is your gender?

Evolutionary Theory *Characteristics associated w/ survival selected *Ultimate causes of current behavior tendencies *Evolved psychological mechanisms (specific) *Nature of human nature (e. g. , social) *Individual differences *Directional v. stabilizing selection *Niches


Activity 9: Gender Differences *Provide a critical analysis of the research examining evolutionary predictions regarding gender differences in mate preferences & jealousy. *Does the evidence support these claims? *Can you think of any alternative explanations? *PLEASE TURN THIS IN AFTER CLASS!

Gender Differences *Problems w/ evidence for evolutionary account *1. Failures to replicate *Some studies find most men choose emotional infidelity *No gender differences in physiology *2. All forced choice methodology *No gender difference w other methods
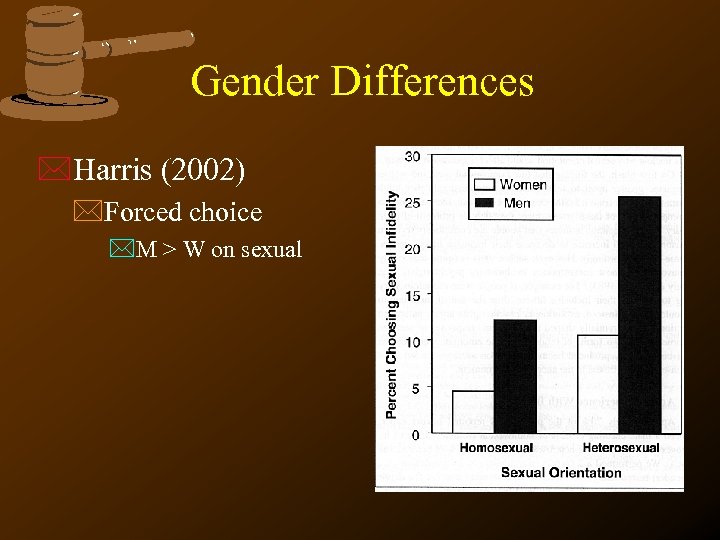
Gender Differences *Harris (2002) *Forced choice *M > W on sexual
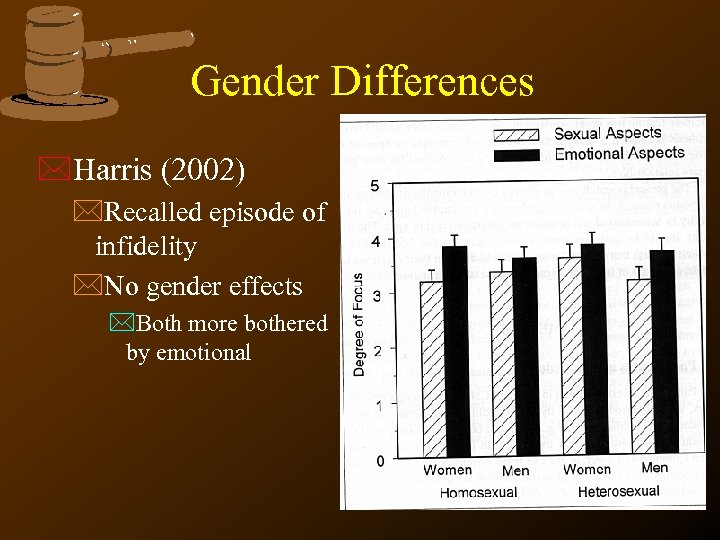
Gender Differences *Harris (2002) *Recalled episode of infidelity *No gender effects *Both more bothered by emotional

Gender Differences *3. Cultural/social theories: Similar predictions *Social Exchange Theory *Men control resources, women control sex *Women give sex to men in exchange for resources *Women most upset about losing resources (love = shifting loyalties) & choose resource-rich mate *Men most upset about losing sex & choose sexy mate

Day 2
Behavioral Genetics *Examine contribution of nature & nurture *Twin & adoption studies *Heritability coefficient (h 2) *Findings: h 2 s ~. 40 *Specific to population *Not fate *Not single genes “Bummer of a Birthmark Hal”

Shared & Non-Shared Environment *Variability in characteristics in population *40% genetic *40% environment (+ 20% error) *Shared (same family, house, etc. ): 5% *Non-shared (unique experiences, including perceived even w/in same family): 35%

Shared & Non-Shared Environment *Similar environments have little impact *Similar experiences do not -> personalities more alike *Genes make us similar *Non-shared environment makes us different

Reaction Paper 7: Rearing Influences *How much variability in personality is due to shared environmental influences? Does this suggest that rearing practices & parents are not important in personality development? Was Dan Quail wrong in saying single parent homes are bad for the children?

Neuroscience & Personality *Where in the brain is personality? *Specific areas & systems show individual differences
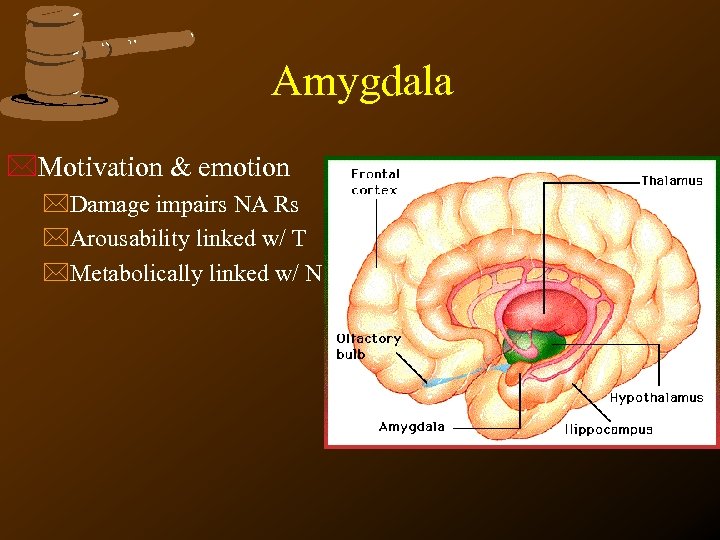
Amygdala *Motivation & emotion *Damage impairs NA Rs *Arousability linked w/ T *Metabolically linked w/ N
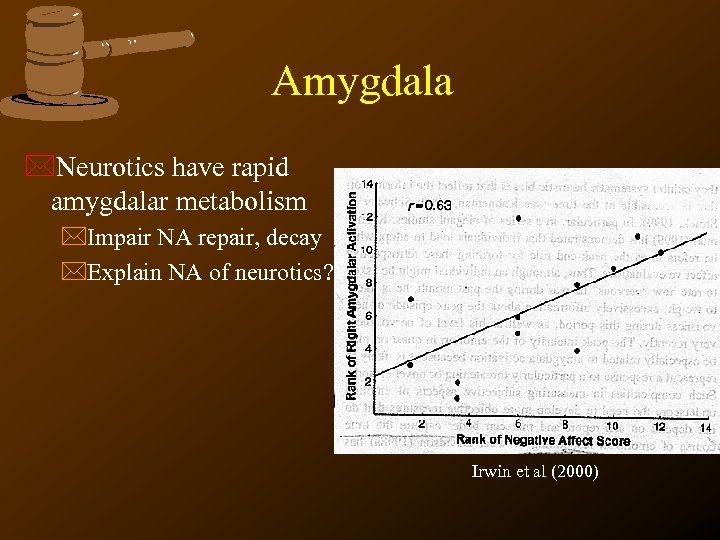
Amygdala *Neurotics have rapid amygdalar metabolism *Impair NA repair, decay *Explain NA of neurotics? Irwin et al (2000)
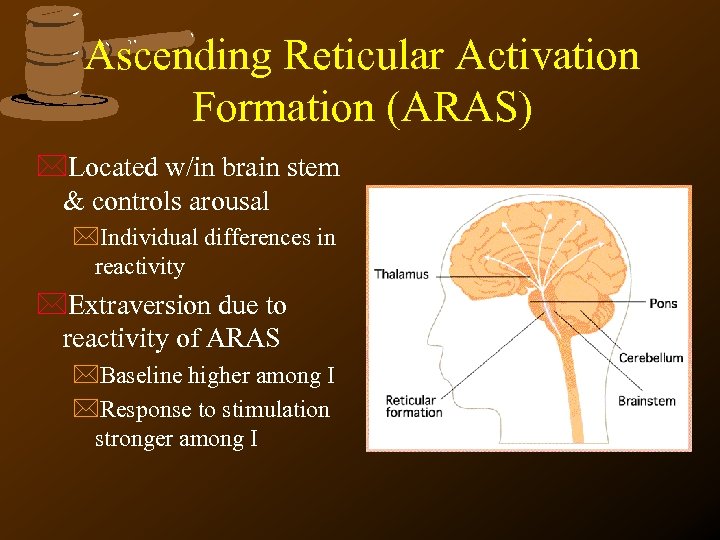
Ascending Reticular Activation Formation (ARAS) *Located w/in brain stem & controls arousal *Individual differences in reactivity *Extraversion due to reactivity of ARAS *Baseline higher among I *Response to stimulation stronger among I

Extraversion and ARAS arousal

Optimal Arousal *Comfortable functioning *Es under-aroused & should prefer high stimulation activities *Is over-aroused & should prefer low stimulation activities *Stimulus shy (I) or Stimulus hungry (E)

Evidence *Task choice *E choose higher stimulating behavior than I *Physiological arousal *I > E for given level of stimulation *Task performance *Is do better at monotonous jobs (air traffic) & moderate levels of stimulation *Es do better at fast paced jobs & higher levels of stimulation

Approach & Inhibition Systems *2 Brain system involved with: *Approach behaviors & positive emotions *Inhibit behaviors & negative emotions *Key are individual differences in the reactivity of these brain systems

Behavioral Approach System (BAS) *Structures in left Pre Frontal Cortex (PFC) *Cause approach behavior (GO!) during incentives *Controls positive emotions *Individual differences in reactivity (hi lo) *Associated w/ E & uninhibited T

Behavioral Inhibition System (BIS) *Structures in right Pre Frontal Cortex (PFC) *Cause avoidance/inhibitory behavior (Stop/Reverse!) *Activated during punishment/danger/threat *Controls negative emotions regarding punishment *Individual differences in reactivity (hi lo) *Associated w/ N & inhibited T

BAS/BIS Measurement *EEG activity *High baseline (left or right PFC) & strong response to positive or negative stimuli *Self-Report Measures *Reward or Punishment sensitivities, seek/avoid *When I get something I want I feel excited & energized *Criticism or scolding hurts me quite a bit *Correlated w/ PFC activity
BAS & BIS BAS *Independent dimensions *Individual differences on both *All combinations possible *These combos are key for understanding personality BIS

Neurotransmitters *BAS, PE associated w/ dopamine *Genes producing dopamine & dopamine reactivity linked to self-reported BAS *BIS, NE associated w/ serotonin *Genetic evidence mixed
1cc70b29536a12cd74a208c599d67aa2.ppt