
Biology lesson

Tissue • Tissue is a group of cells that perform same function and has same size and shape.
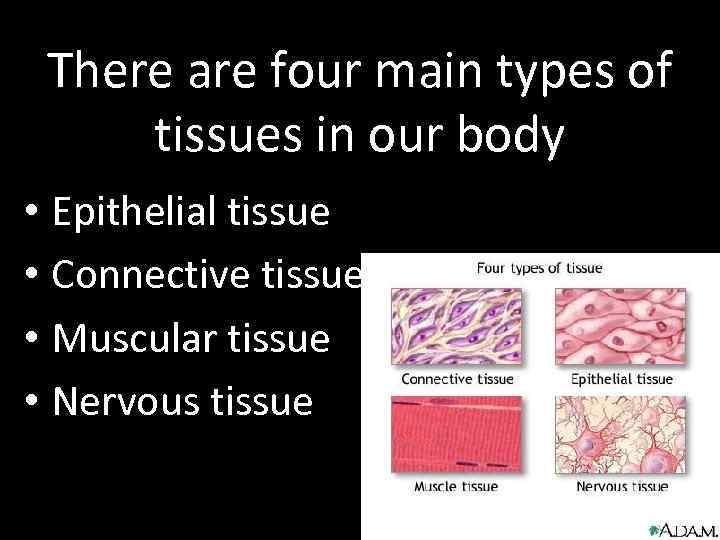
There are four main types of tissues in our body • Epithelial tissue • Connective tissue • Muscular tissue • Nervous tissue
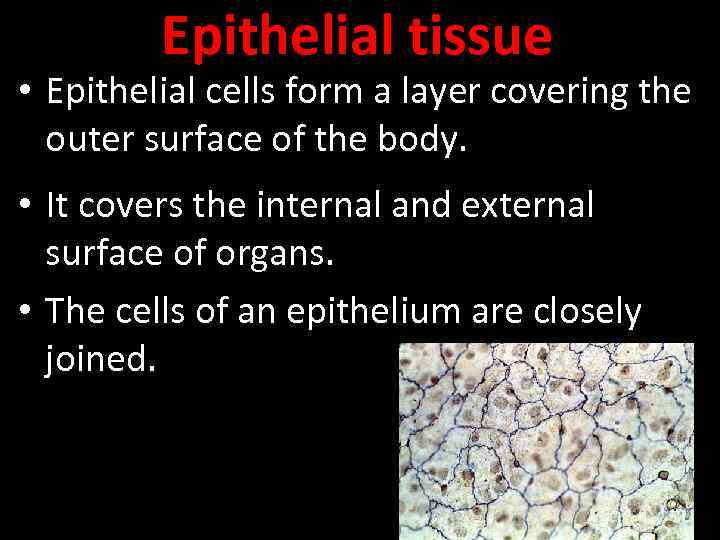
Epithelial tissue • Epithelial cells form a layer covering the outer surface of the body. • It covers the internal and external surface of organs. • The cells of an epithelium are closely joined.

Functions: • Protection of the body and its internal organs. • Absorption of nutrients from the intestines. • Sensory reception found in the skin, eyes, ears, nose and on the tongue.

Connective tissue • Connective tissue binds together, supports, and connects body parts; it is the most abundant tissue in the body.

Connective tissues are found in: • ligaments (binding bone to bone), • tendons (binding muscle to bone) • cartilage, blood and bone. • organs that must stretch, like the lungs.

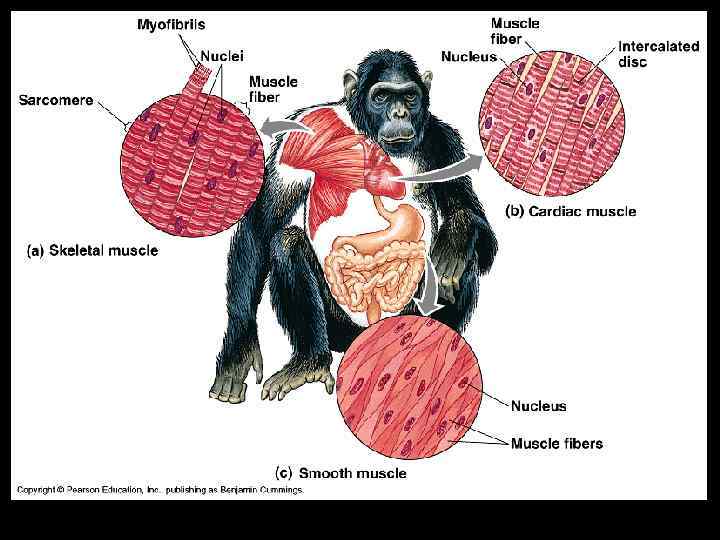
Muscle Tissue: Movement • Muscle tissue contracts in response to stimulation, then passively lengthens; movement is a highly coordinated action. • There are three types of muscle: – Skeletal muscle tissue attaches to bones for voluntary movement.

– Smooth muscle tissue contains cells that function in involuntary movement; it lines the gut, blood vessels, and glands. – Cardiac muscle is only found in the wall of the heart.
Nervous Tissue: Communication • Nervous tissue consist of cells, including neurons (nerve cells) and support cells; nervous tissue forms the body’s communication network. • Neurons carry messages.
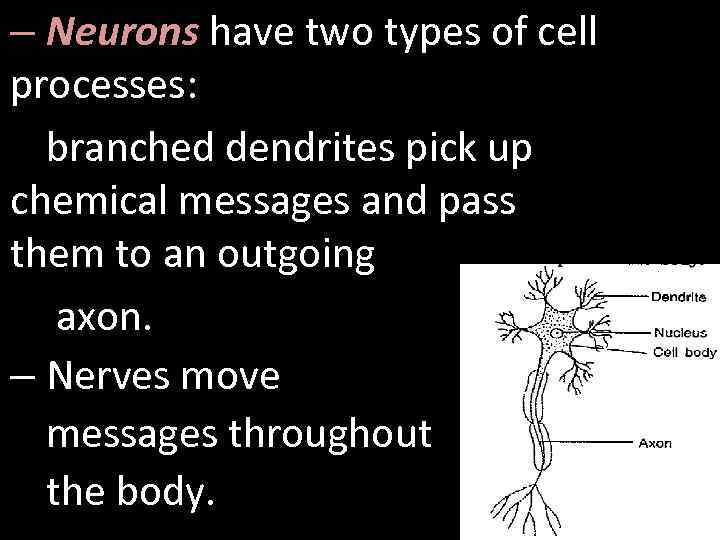
– Neurons have two types of cell processes: branched dendrites pick up chemical messages and pass them to an outgoing axon. – Nerves move messages throughout the body.