718b09b18e330ec0ebed6c3412c89da5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

BIOLOGY 12 Protein Synthesis

WHAT DO YOU KNOW ABOUT RNA? § single stranded § uracil instead of thymine § 3 types – m. RNA, r. RNA, t. RNA § can go through nucleus into cytoplasm

WHAT DO YOU KNOW ABOUT PROTEINS? § polypeptides, long chains of amino acids § amino group, carboxyl group, peptide bonds § made in ribosomes § used for structure – hair, muscles, nails, feathers, wool, hormones

GENE § a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that provides the instructions to build a particular polypeptide § note: one gene codes for one polypeptide

CODONS § sequence of three bases in DNA or m. RNA that code for a particular amino acid § triplet of nucleotides § more than one codon can code for a single amino acid examples: CAA or GCU
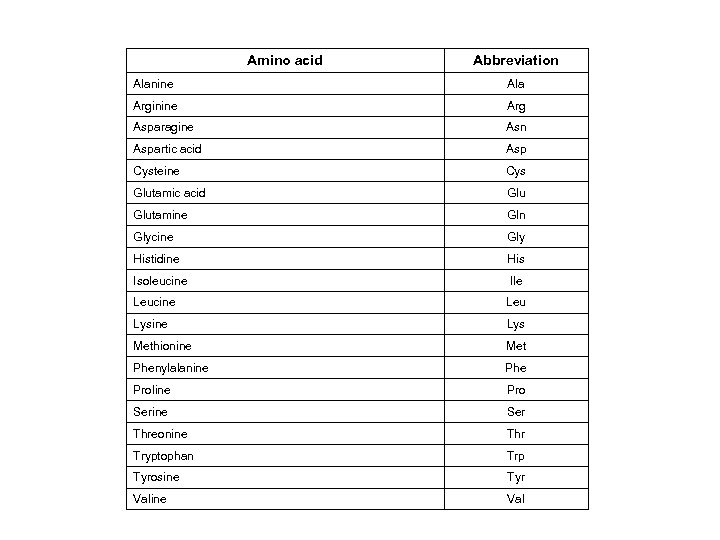
Amino acid Abbreviation Alanine Ala Arginine Arg Asparagine Asn Aspartic acid Asp Cysteine Cys Glutamic acid Glutamine Gln Glycine Gly Histidine His Isoleucine Ile Leucine Leu Lysine Lys Methionine Met Phenylalanine Phe Proline Pro Serine Ser Threonine Thr Tryptophan Trp Tyrosine Tyr Valine Val
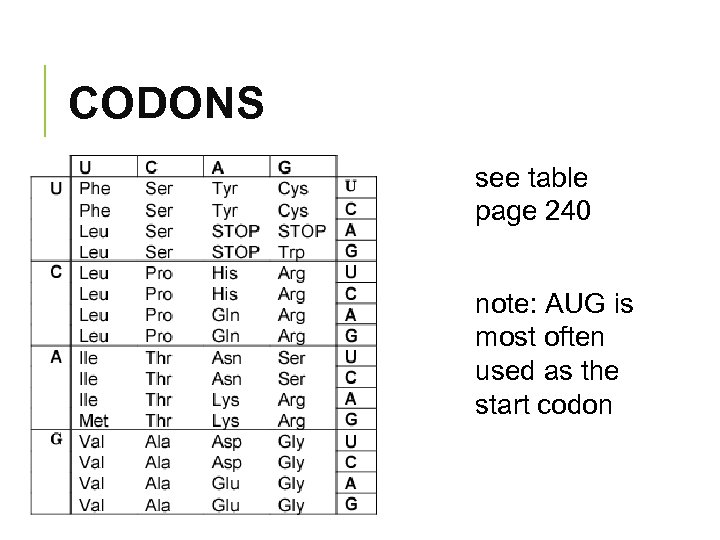
CODONS see table page 240 note: AUG is most often used as the start codon

RNA § * remember: DNA never leaves the nucleus § RNA is used as a messenger and a transporter
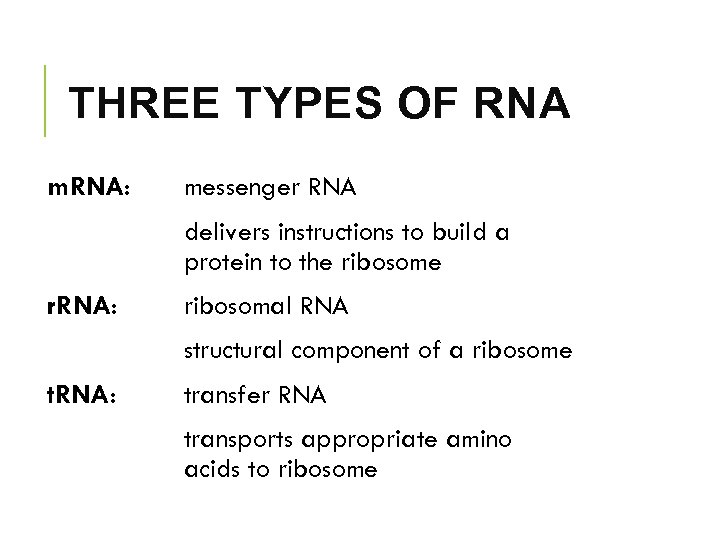
THREE TYPES OF RNA m. RNA: messenger RNA delivers instructions to build a protein to the ribosome r. RNA: ribosomal RNA structural component of a ribosome t. RNA: transfer RNA transports appropriate amino acids to ribosome
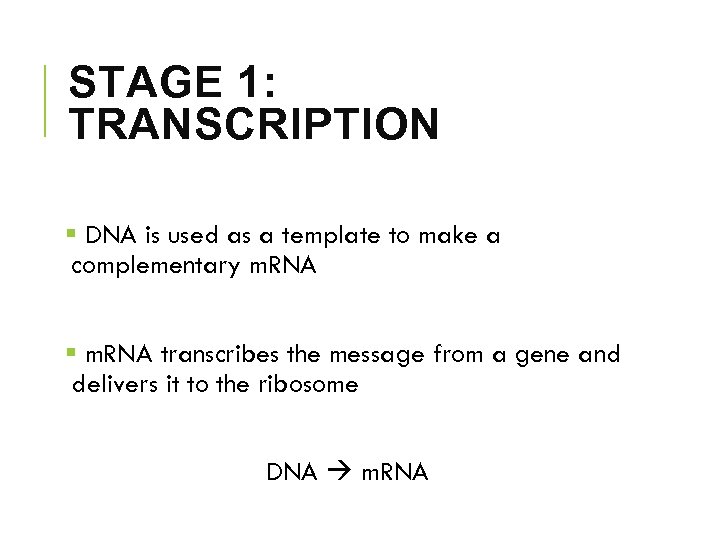
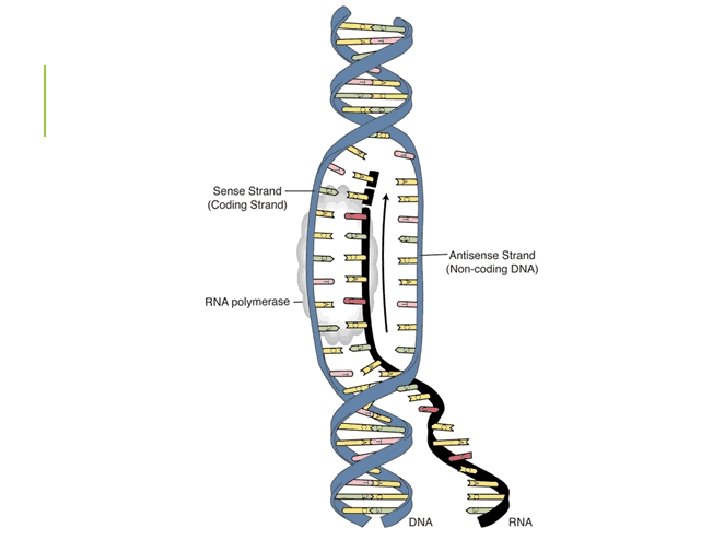
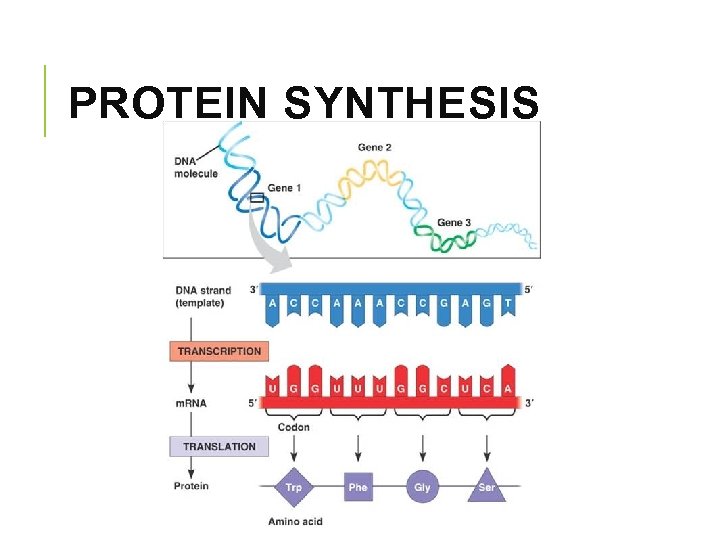
STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION § DNA is used as a template to make a complementary m. RNA § m. RNA transcribes the message from a gene and delivers it to the ribosome DNA m. RNA
STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION Initiation § DNA uncoils at the site of a gene § one strand will act as a template
STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION Elongation § RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA § RNA nucleotides match up to the DNA template forming m. RNA § base pair rules: A-U and C-G

STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION Termination § m. RNA is released
STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION Posttranscriptional Modification § 5’ cap added to start of m. RNA, for protection from digestion § poly-A tail is a string of adenine bases at the end of m. RNA § then m. RNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pores
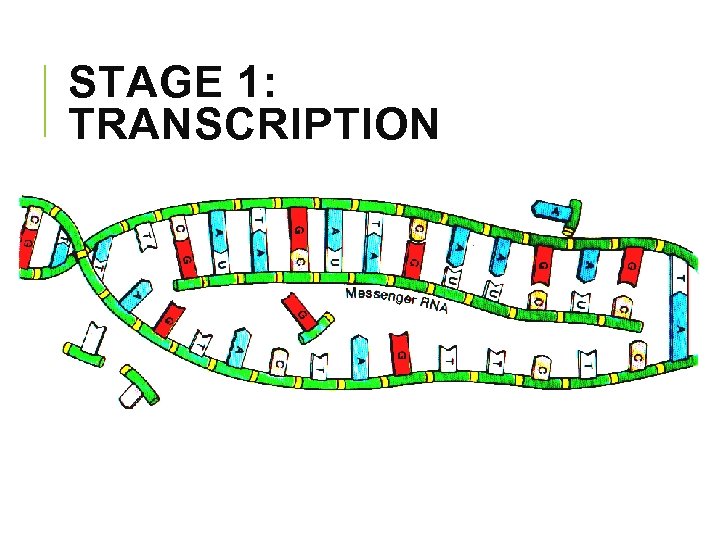
STAGE 1: TRANSCRIPTION

STAGE 2: TRANSLATION § a ribosome assembles amino acids in a specific sequence § m. RNA is transcribed into a polypeptide m. RNA protein

STAGE 2: TRANSLATION § two subunits of a ribosome bind to the m. RNA § the ribosome moves along the m. RNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction, three nucleotides at a time § this is the reading frame

STAGE 2: TRANSLATION § the ribosome recognizes the start codon (AUG) § new amino acids are added each time the ribosome reads a new codon

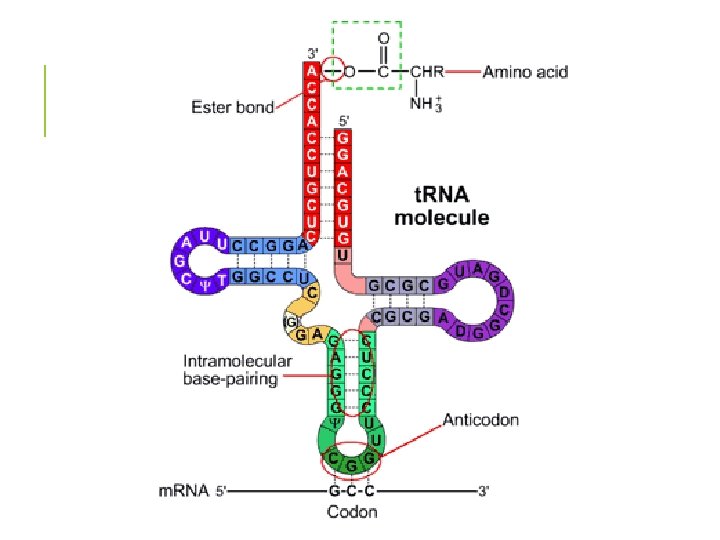
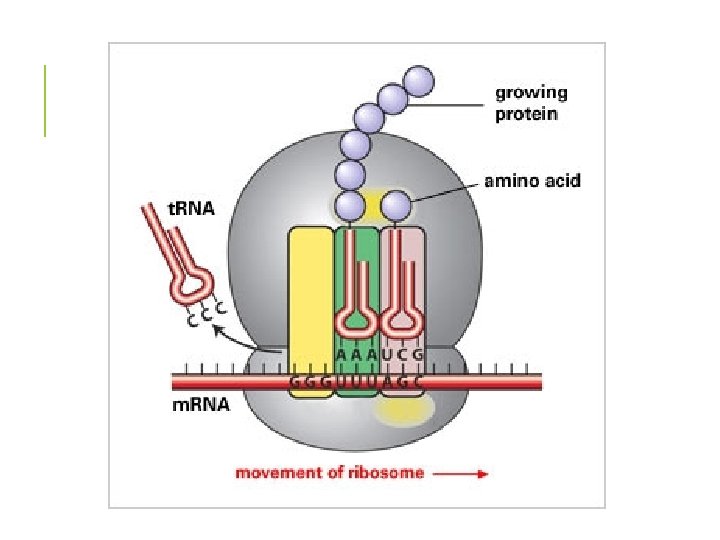
STAGE 2: TRANSLATION § t. RNA delivers the amino acids § it’s anti-codon recognizes the codons in the m. RNA § each t. RNA arrives at the A site (acceptor) § the next t. RNA arrives at the A site and the t. RNA prior to that shifts to the P site (peptide) § this is where peptide bonds are formed between adjoining amino acids

STAGE 2: TRANSLATION § the ribosome then shifts (translocates) to the next codon § the process will continue until the ribosome reaches a stop codon
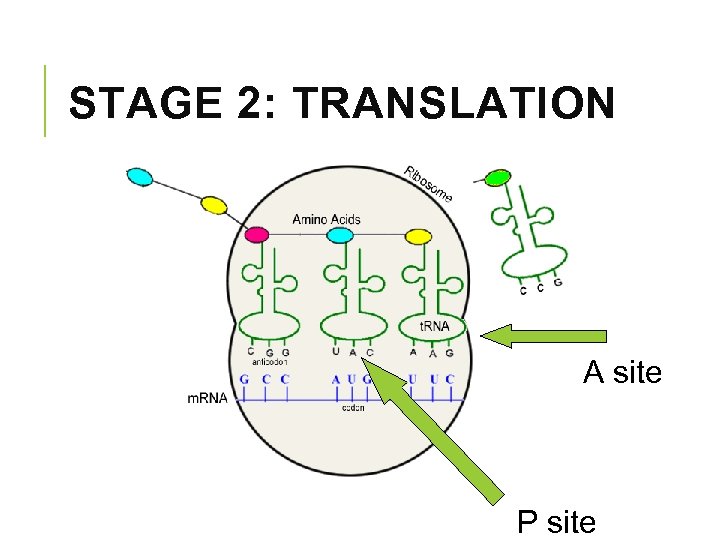
STAGE 2: TRANSLATION A site P site
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Transcribe and Translate http: //learn. genetics. utah. edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/

TEXTBOOK REVIEW protein synthesis Read: pages 237 -244 pages 250 -253 Questions: page 241 # 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 page 254 # 3, 9
718b09b18e330ec0ebed6c3412c89da5.ppt