8d699025ca3932c55a836eab6e841324.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
Biogeochemical Cycles : Carbon Conservation of Matter & Energy 1

u Law of Conservation of Matter : when a physical or chemical change occurs, no atoms are created or destroyed • Environmental consequence : there is no such thing as “throwing something away” or It will remain on Earth in a landfill BUT removed from the cycle This is a clear example of why we need: • Recycling!
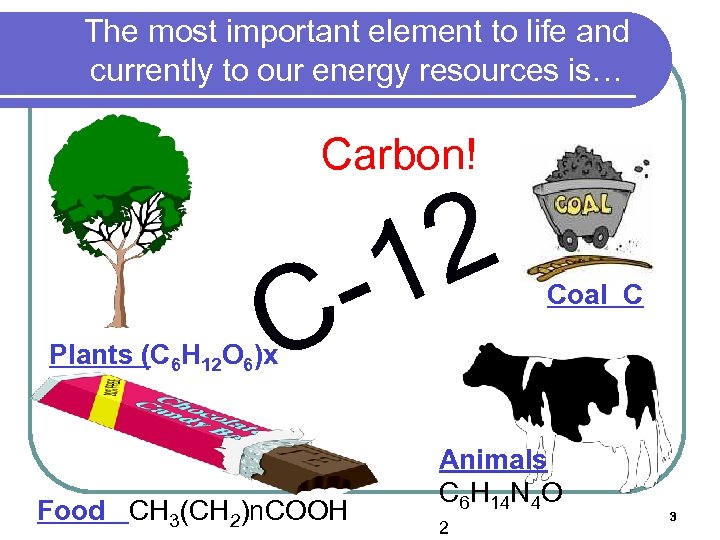
The most important element to life and currently to our energy resources is… Carbon! 2 1 - Carbon C Plants (C 6 H 12 O 6)x Food CH 3(CH 2)n. COOH Coal C Animals C 6 H 14 N 4 O 2 3
What Is Carbon? An element, one of the 118 basic building blocks of the universe. Carbon is main part of the chemistry of life on earth, It’s required to build new life in the form of macro molecules. Example: C 6 H 12 O 6 is glucose in your blood, every protein and even DNA contains carbon l Carbon is found in many carbonate rocks like limestone Ca. CO 3, dissolved in oceans, & atmosphere as carbon dioxide CO 2. 4

Carbon Cycle The same carbon atoms are used repeatedly on earth. They have to be since there is a limited amount! l Carbon cycles between the earth as a solid and the atmosphere as a gas. l It may seem weird but that means your carbon atoms have been used before, and will be used again! l Think of life as giant lego sets where the atomic pieces are always broken down and used again. l 5

Plants Use Carbon Dioxide l l l Plants remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it to make food & cellulose via: photosynthesis. CO 2 + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 **This plant carbon storage is called “carbon sequestration” It will reduce atmospheric CO 2 as long as it is… ALIVE. This is a reason why forests & algae are important. 6

Animals Eat Plants l When organisms (like us) eat plants (and animals), they take in the organic carbon it becomes part of their own bodies’ macromolecules. l All our cells and tissues are made of carbon compounds l “You are what you eat. ” True or false? l That is a “legit” statement from the atomic point of view 7
Plants and Animal Die, then… l When plants and animals die, most of their bodies are decomposed by: l aerobic bacteria. Releasing CO 2 carbon dioxide gas l If no oxygen: methane CH 4 is released. anaerobic decomposition (other stank sulfur compounds too) 8
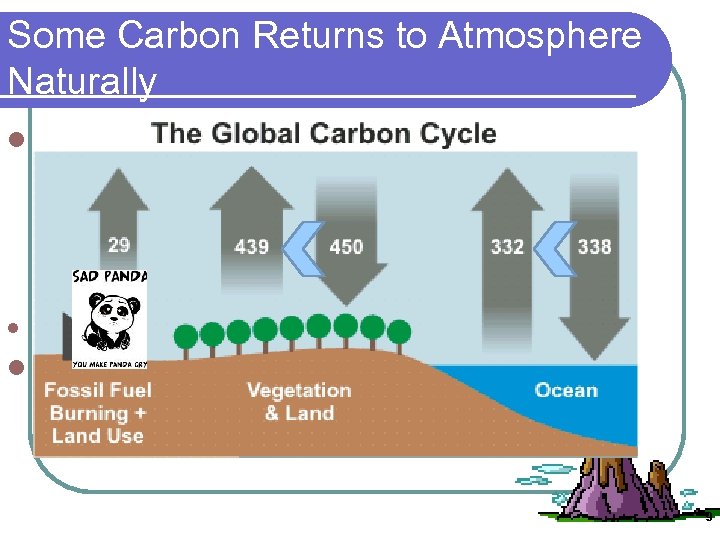
Some Carbon Returns to Atmosphere Naturally l Lithospheric plates containing organic matter or carbonate rock subduct, melt and Carbon can also be released rapidly in volcanic eruptions from CO 2 dissolved in magma l *largest natural addition to the cycle ~. 3 GT l Carbon cycle was in balance until US. 9

MORE Carbon in Oceans l l l (acid demo) MOST of earth’s carbon is stored in ocean as sediment composed of the mineral calcite, the rock limestone Many aquatic mollusks use dissolved Ca+ and this carbonate ion from water to make their: shells, Ex. clams, corals, urchins, snails Excess CO 2 reacts with ocean water forming H 2 CO 3 carbonic acid. This is called: Ocean acidification, which dissolves shells! Coral is a keystone species, recent coral loss of up to 1/3 of coral species (bleaching) destroying the habitat of millions of marine org 10
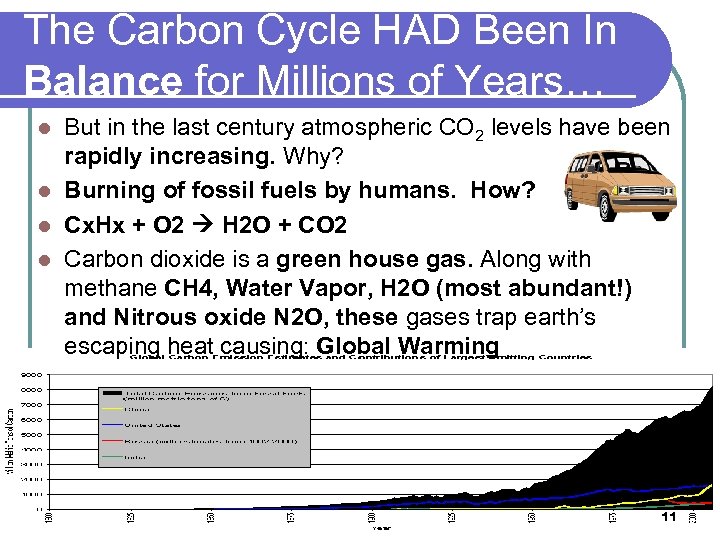
The Carbon Cycle HAD Been In Balance for Millions of Years… But in the last century atmospheric CO 2 levels have been rapidly increasing. Why? l Burning of fossil fuels by humans. How? l Cx. Hx + O 2 H 2 O + CO 2 l Carbon dioxide is a green house gas. Along with methane CH 4, Water Vapor, H 2 O (most abundant!) and Nitrous oxide N 2 O, these gases trap earth’s escaping heat causing: Global Warming l 11
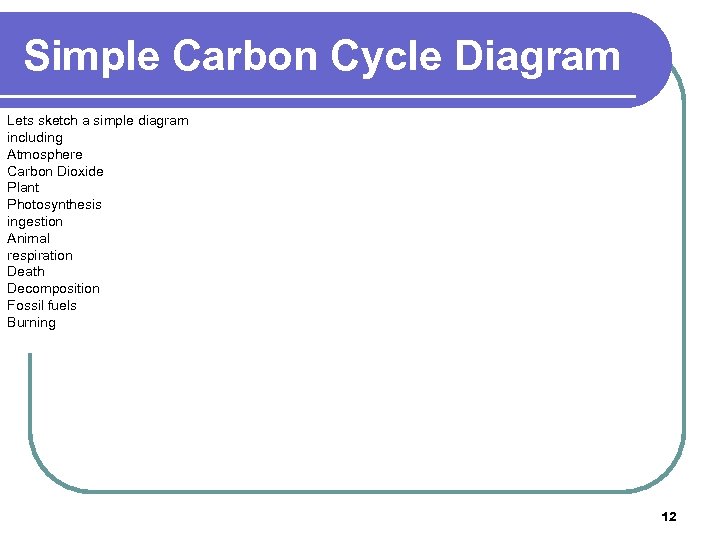
Simple Carbon Cycle Diagram Lets sketch a simple diagram including Atmosphere Carbon Dioxide Plant Photosynthesis ingestion Animal respiration Death Decomposition Fossil fuels Burning 12
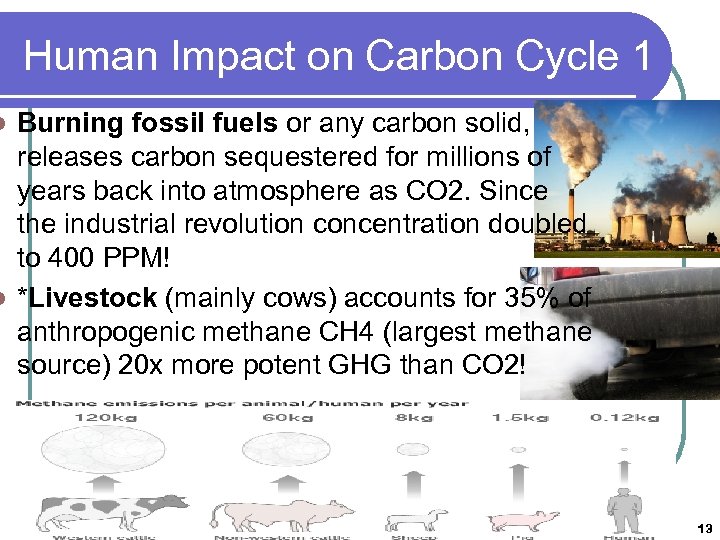
Human Impact on Carbon Cycle 1 Burning fossil fuels or any carbon solid, releases carbon sequestered for millions of years back into atmosphere as CO 2. Since the industrial revolution concentration doubled to 400 PPM! l *Livestock (mainly cows) accounts for 35% of anthropogenic methane CH 4 (largest methane source) 20 x more potent GHG than CO 2! l 13
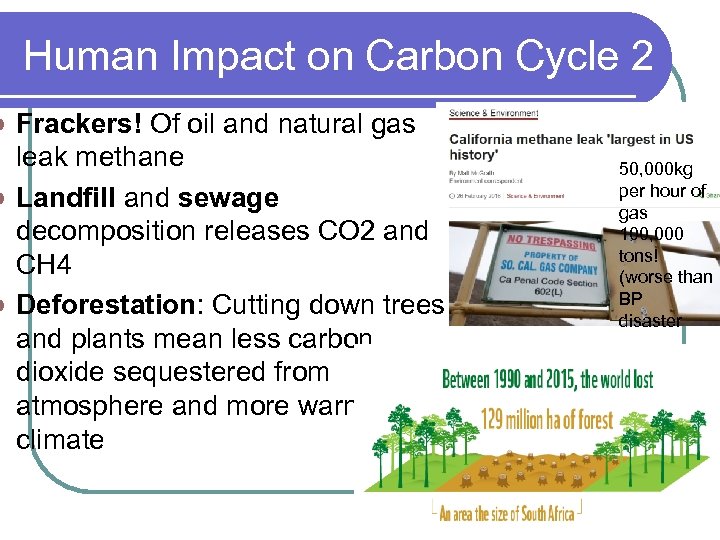
Human Impact on Carbon Cycle 2 Frackers! Of oil and natural gas leak methane l Landfill and sewage decomposition releases CO 2 and CH 4 l Deforestation: Cutting down trees and plants mean less carbon dioxide sequestered from atmosphere and more warming of climate l 50, 000 kg per hour of gas 100, 000 tons! (worse than BP disaster 14

l l l l Human Impact on Carbon Cycle: Feedback Loops We are trapped in a “positive” feedback loop with our alteration of the carbon cycle. 1. Melting white ice in glaciers/ice caps have dark Cirrus underneath absorbing more light… 2. Melting permafrost releases trapped CO 2 and methane which are green house gases… 3. Warmer oceans lead to more evaporation and water is a green house gas… Cumulus 4. Warmer temps lead to drier forests and more forest fires which release CO 2 + H 2 O… All of these increase warming and cause themselves to speed up, inc. occurrences… creating a positive feedback loop! Clouds role in this depends on the type. Cumulus clouds can be a negative feedback loop since they are white and reflective or Cirrus since they are more vapor they can behave as green house gases. 15

Reducing Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle: l l l l l #1 Burn less fossil fuels! How? Drive less or find new energy sources for cars (solar) Use electric/hybrid cars (power plants efficiency is better) Use less electricity or get it from other sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric power. Reduce landfill waste! Stop wasting food & compost Recycle paper Reforestation and conservation of all forests especially large rainforests by… Not using rainforest products Ex. Palm oil, coffee, mahogany, teak, soybeans, sodium laurel sulfate. This conserves the tree which stores carbon as cellulose. Plant…well. . plants!, especially forests with big trees that may persist for thousands of years keeping carbon sequestered… Prevent global warming which releases methane and CO 2 in frozen in permafrost soil and icecaps 16
8d699025ca3932c55a836eab6e841324.ppt