b63c2e2e9dcd0b808c15bc0f22233999.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 122

Biofeedback for Hypnotists • Part 2

Robert Grove, Ph. D • HMI Graduate – 1981 • Ph. D Minnesota – – Psychology & Medical Pharmacology • Past President & Current Board Member – Biofeedback Society of California

From Part I • • Is biofeedback like hypnosis? Who benefits? How do you motivate? How many sessions? Who coaches? What is your role? When do you end? – Hint: I did not emphasize this last point.

Ok, how does coaching work? • A coach shapes performance by raising shapes the criteria for good performance. • How would you shape performance? • [You talk now!]

Thresholds in physiology. . • A Coach always sets a threshold for good performance. • In biofeedback, you shape performance by adjusting the threshold / the criteria – dividing good from bad • If good is to go high, Above Threshold is on • – a tone sounds when above • If good is to go low, the Below Threshold is on • - a tone sounds when below • It is the job of the coach to know when it is too easy and when it is too difficult.
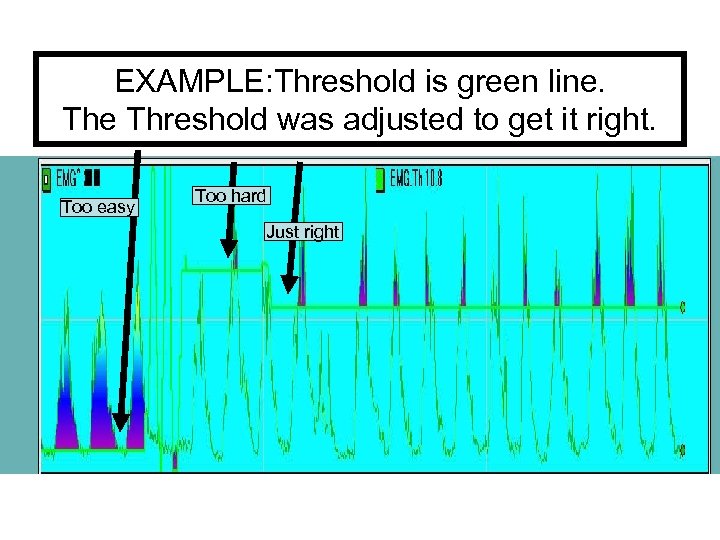
EXAMPLE: Threshold is green line. The Threshold was adjusted to get it right. Too easy Too hard Just right

WHY IS THRESHOLD CONTROL IMPORTANT FOR FEEDBACK? • Thresholds cut off signals above or below a selected value. • Reduces information to : • Yes/No • Tone/No Tone

SUMMARY You are the coach. Your job is to: • 1. Vary the threshold and vary the difficulty of the task, and • 2. Shape threshold and refine the task.

Some Neurofeedback Protocols

Does it make any difference: Tone vs Display? • Tone feedback: – EEG alpha BF is generally blocked through visual cues. SO VISION CUES BLOCK ALPHA – Tone is best for increasing alpha/theta activity. – • Visual feedback is best for Beta/SMR training [coming later]
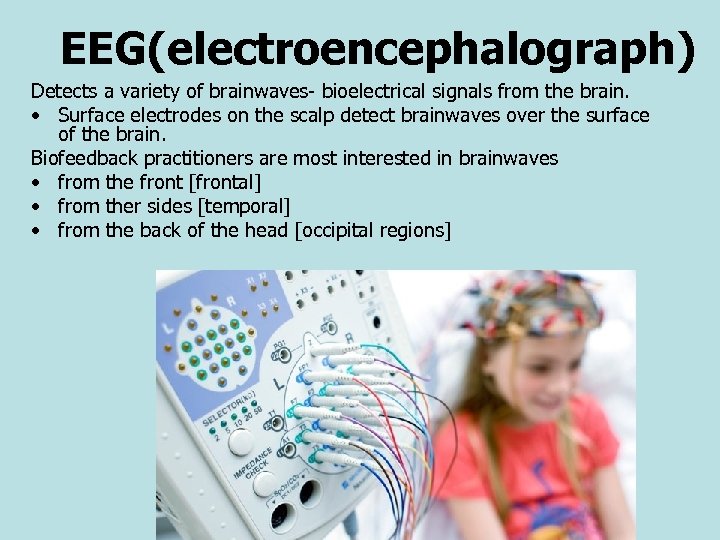
EEG(electroencephalograph) Detects a variety of brainwaves- bioelectrical signals from the brain. • Surface electrodes on the scalp detect brainwaves over the surface of the brain. Biofeedback practitioners are most interested in brainwaves • from the front [frontal] • from ther sides [temporal] • from the back of the head [occipital regions]

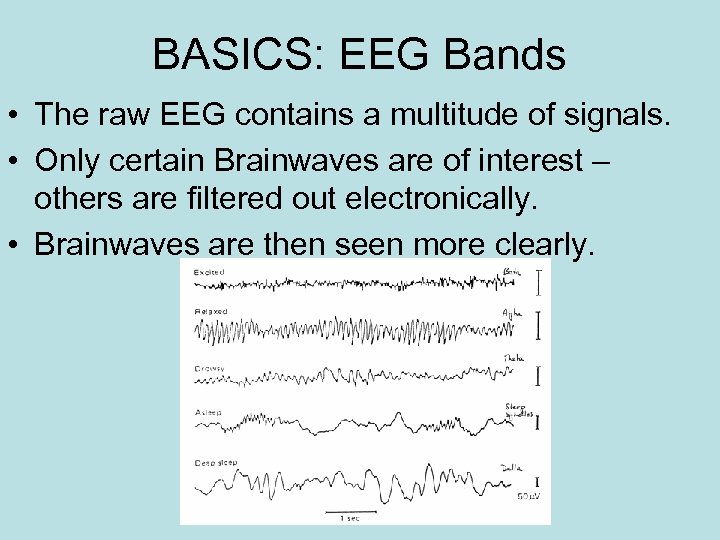
BASICS: EEG Bands • The raw EEG contains a multitude of signals. • Only certain Brainwaves are of interest – others are filtered out electronically. • Brainwaves are then seen more clearly.
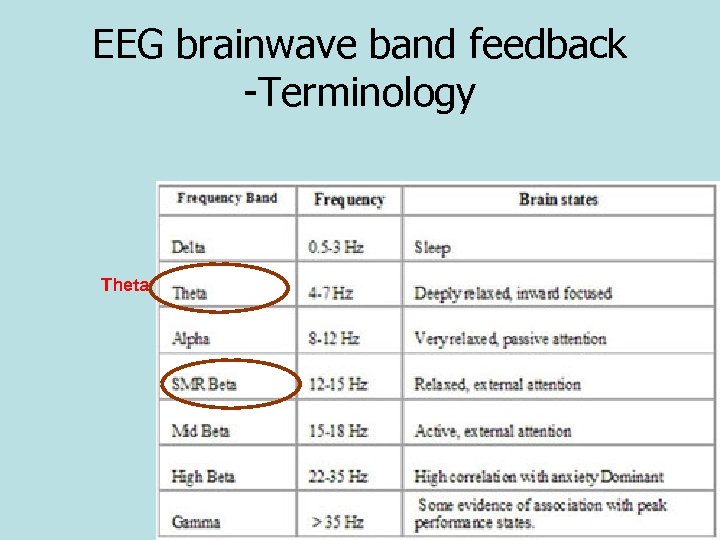
EEG brainwave band feedback -Terminology Theta

Good Theta and Bad Theta • We all go into Theta when we ‘chunk’ [save] information – this is Good Theta. • In many disorders. Theta never varies- and they space out: Bad Theta.

‘SMR’ –the band you never heard of. • • SMRSensory Motor Rhythm A True Muscle Relaxation Response [in the Beta range]

Neurotherapy: Shaping Brainwaves with Threshold Control Example: Rehearsal Neurofeedback aka Neurotherapy

Alpha-Theta Neurofeedback First- Goal: To shape a sustained Low-Arousal State. • First, set up a ‘cue hierarchy’ with the client.

• Second, shape Brainwaves using Thresholds. – Just focus on ‘feedback – Make sure they can maintain a low-arousal state.

Part III • Third, use Brainwaves with Cue Heirarchies. – makes sure client stays in a low-arousal state during imaginal cue exposure – Cues are suggested during a low-arousal state. • This is Circle Therapy

TOOLS • Need a hierarchy • Need a Q-EEG

Alpha-Theta Neurotherapy • There are lots of uses: – Positive Performance / Peak Performance – Sex Addiction / Sex Victims – Process Addictions – Athletic Performance – Mental Rehearsal – Fears and Phobias

Alpha-Theta Neurotherapy • Neurotherapy for substance abuse • One of the most difficult!

What’s this from?

The Reality So what’s wrong with this picture?

NEUROSCIENCE : Addiction Cues Trigger Arousal • Not the same as being Stressed • Stress now triggers cravings • Totally unconscious until … – Cravings overpower good intentions • A typical response in a drug-free client: • “It’s such a rush. It’s hard to impossible to think about anything else. So what if it’s bad. At that point, I just don’t care. ”

A Little Thought Experiment • Put Your emails/texts aside. Relax. Clear your mind. Ready?

Imagine a bright juicy lemon.
Humm …

Like this. . .

WHAT DID YOU EXPERIENCE?

WHAT DID YOU EXPERIENCE? • Immediate Salivation • • Immediate change in focus Other thoughts pushed into background Physiological Arousal heightened Yet you know there is no lemon here!

“But there is no lemon!’ • This happens all the time • Right now, you may be struggling to get this idea • You are simultaneously using memory and arousal systems to learn this. • To anchor this in memory, you need to wake up – arousal yourself and distract for a moment, disengage • The arousal component is key to Neuro. Behavioral Learning.

Neurotherapy relies on the lemon effect, but for … • • Drug triggers in addictions Fear triggers in public speaking Doubt triggers about performance. Etc

How do you manage triggers? • Triggers are normal & involve arousal. • Triggers become abnormal when. . – Drugs hijack the emotional system. – We become obsessed with something. • Triggers are pre-conscious, non-rational • You need to treat them in a non-arousal state. • We call this a low-arousal state.

Low Arousal Alpha-Theta Training • By simulateously raising alpha and theta, a person enters a low-arousal state. • Eugene Penniston discovered this in 1989. Other names: • Neurotherapy • Rehearsal Neurofeedback.

Alpha-Theta Training : for Drug & Alcohol Abuse • Penniston trained alcoholics to increase alpha/theta and suppress beta activity - 1989 – combined EEG sessions, temperature biofeedback and counseling • Phenomenal success– 80% abstinent – sharp decrease in self-assessed depression, compared to control group. • 13 month follow-up showed sustained effect

Rehearsal Neurofeedback Follows the Model for Hypnotherapy • Neurotherapy with Imagery & Desensitization

Always Train in Safety Imagery First • Triggers produce physiological arousal. • The surprise of triggers amplifies the arousal. • Your task is to bring arousal under control. So …. . • Always give them a safe place to retreat to first. • Discuss what cues or triggers are easiest to cope with, and which are hardest. • Discuss how to cope and feel good about it
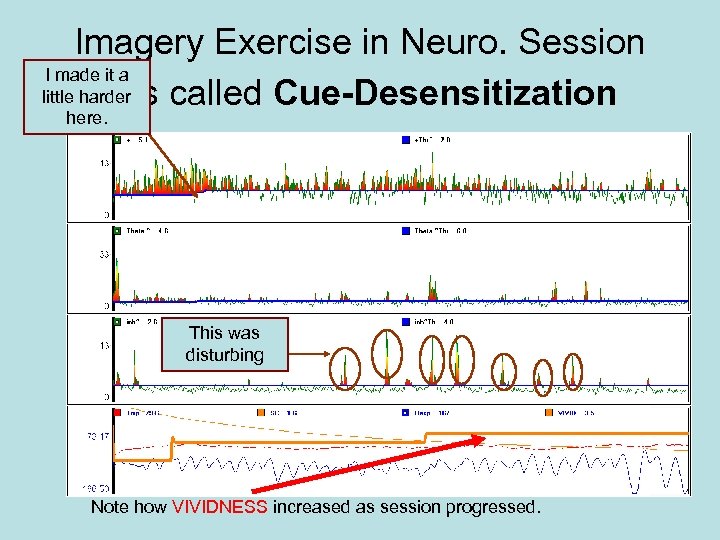
Imagery Exercise in Neuro. Session I made it a little harder It is called Cue-Desensitization here. This was disturbing Note how VIVIDNESS increased as session progressed.

Basics: Add Mental Rehearsal of Coping Successfully with Relapse Situations • Always go over their Rehearsed Cues BEFORE going into an altered state. – Rather than add a new situation every day, the idea is to repeat the same images until mastery occurs. – This is the reason for many sessions. • Examples – Drive by pusher's corner or house. – Your friend is hot and pops open a cold beer. – I'm tired of feeling so crappy. A hit is all I need.
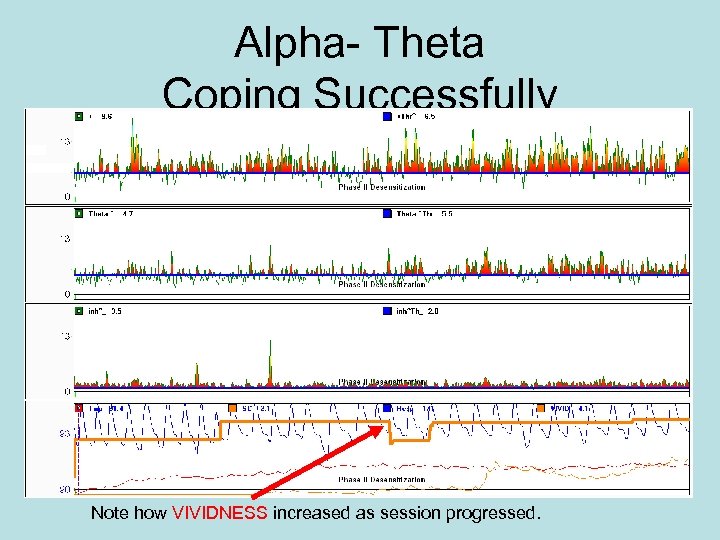
Alpha- Theta Coping Successfully Note how VIVIDNESS increased as session progressed.

Conclusion 1. Triggers change the brain, sometimes permanently. 2. Most Therapies work well under low-arousal conditions. 1. Hypnotherapy 2. Neurotherapy 3. Some ‘Guided Imagery’ [ not reliable] 3. Triggers elicit kindling, a preternatural [unexpected] state. 4. Surprise increases arousal even more- use desensitization.
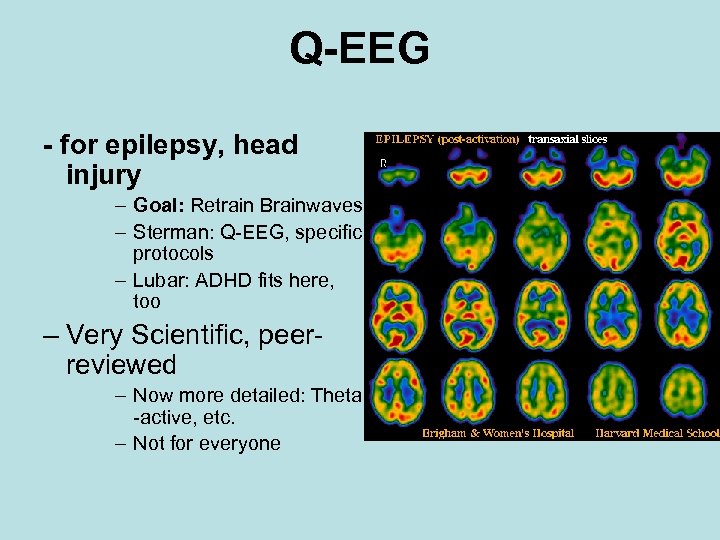
Q-EEG - for epilepsy, head injury – Goal: Retrain Brainwaves – Sterman: Q-EEG, specific protocols – Lubar: ADHD fits here, too – Very Scientific, peerreviewed – Now more detailed: Theta -active, etc. – Not for everyone

Stimulant Drugs and ADHD • Stimulant drugs loose effectiveness over time : • http: //www. nytimes. com/2012/01/29/opinio n/sunday/childrens-add-drugs-dont-worklong-term. html? _r=2&pagewanted=all& • Stimulant drugs work for four to eight weeks, then their effectiveness wears off over weeks or months.

Ritalin Gone Wrong By L. ALAN SROUFE Published: January 28, 2012 THREE million children in this country take drugs for problems in focusing. Toward the end of last year, many of their parents were deeply alarmed because there was a shortage of drugs like Ritalin and Adderall that they considered absolutely essential to their children’s functioning. … Stimulants generally have the same effects for all children and adults. They enhance the ability to concentrate, especially on tasks that are not inherently interesting or when one is fatigued or bored, but they don’t improve broader learning abilities. … If drugs, which studies show work for four to eight weeks, are not the answer, what is? Many of these children have anxiety or depression; others are showing family stresses. We need to treat them as individuals. As for shortages, they will continue to wax and wane. Because these drugs are habit forming, Congress decides how much can be produced. The number approved doesn’t keep pace with the tidal wave of prescriptions. By the end of this year, there will in all likelihood be another shortage, as we continue to rely on drugs that are not doing what so many well-meaning parents, therapists and teachers believe they are doing. L. Alan Sroufe is a professor emeritus of psychology at the University of Minnesota’s Institute of Child Development.

NFB for Attention Goal is three-fold: 1. to increase SMR activity (12 -15 Hz) especially with hyperactive subjects – this decreases hyperactivity 2. increase beta activity (16 -20 Hz). this increases attention 1. At the same time you supress theta (4 -8 Hz) – decreases fuzziness. 2. Movement and EMG are also surpressed.

Attention is a Skill • Type 2 Skill: often train the ratio of beta to alpha or beta to theta – client must be very alert, but also relaxed and quiet – best is Bidirectional Training. • Type 3: Eventually they practice doing this while performing a demanding task requiring concentration (a game or typing)

Results • large percentage of subjects were rated as very much improved, or much improved. • greatest improvements in homework, fidgeting, frustration, and crying.

IQ & Performance • IQ: increase of 10 WISC-R full scale points and a significant decrease in inattentiveness vs. no change in the waiting group controls (Linden) • PERFORMANCE: improvements in TOVA scores of >10 points in verbal and performance IQ.
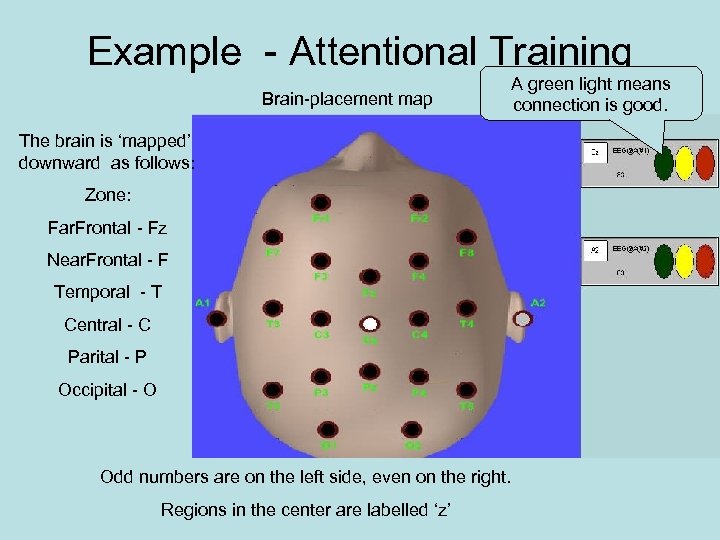
Example - Attentional Training Brain-placement map A green light means connection is good. The brain is ‘mapped’ downward as follows: Zone: Far. Frontal - Fz Near. Frontal - F Temporal - T Central - C Parital - P Occipital - O Odd numbers are on the left side, even on the right. Regions in the center are labelled ‘z’
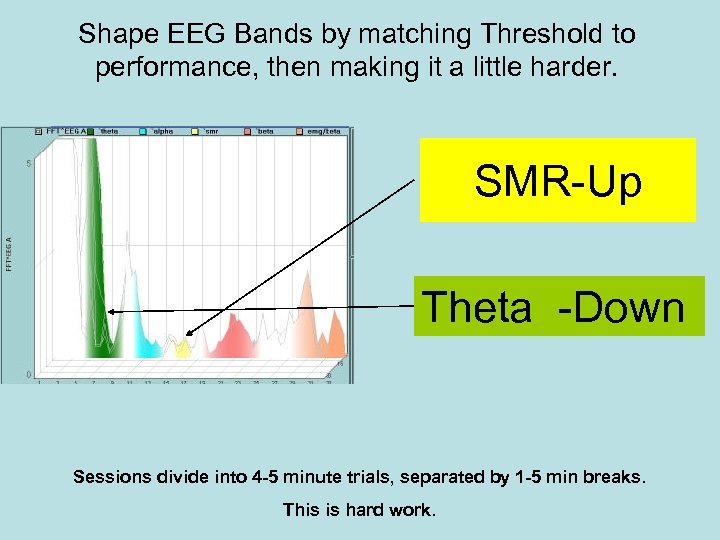
Shape EEG Bands by matching Threshold to performance, then making it a little harder. SMR-Up Theta -Down Sessions divide into 4 -5 minute trials, separated by 1 -5 min breaks. This is hard work.
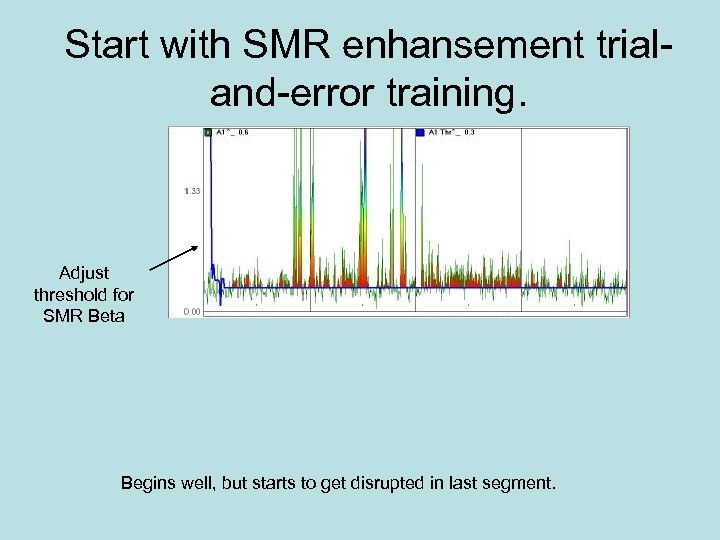
Start with SMR enhansement trialand-error training. Adjust threshold for SMR Beta Begins well, but starts to get disrupted in last segment.
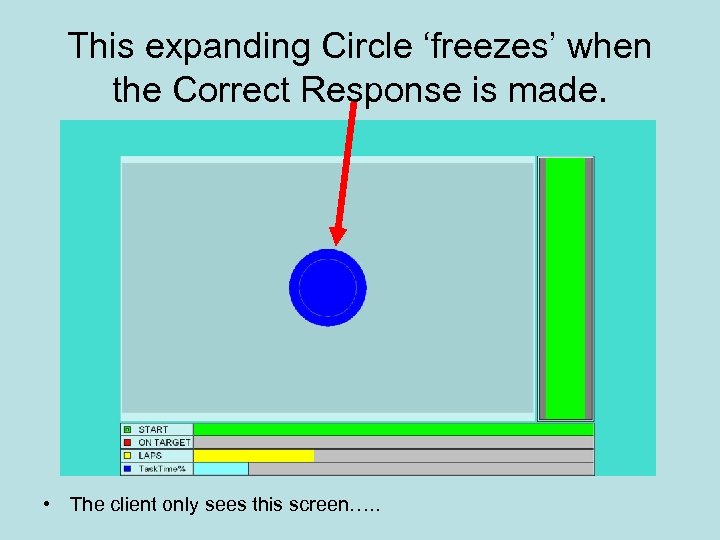
This expanding Circle ‘freezes’ when the Correct Response is made. • The client only sees this screen…. .
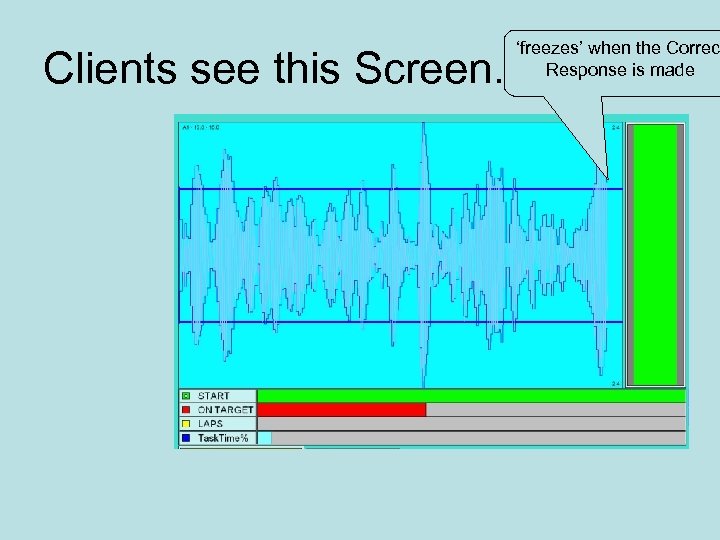
Clients see this Screen. ‘freezes’ when the Correc Response is made

What did you learn? • Bi-directional – Lots of repetition, few changes • Tones, Screens guide trial-and-error – Watch for fatigue. – No more than 4 -5 min per trial – 5 -6 trial per session • Test by monitoring without feedback
![[SIDEBAR] • So, how is biofeedback different from hypnosis for ADHD? • What about [SIDEBAR] • So, how is biofeedback different from hypnosis for ADHD? • What about](https://present5.com/presentation/b63c2e2e9dcd0b808c15bc0f22233999/image-58.jpg)
[SIDEBAR] • So, how is biofeedback different from hypnosis for ADHD? • What about problems with disruptions? • Do you need a diagnosis of ADHD or ADD? • Is neurofeedback different for ADD and ADHD? • At what age can you start training?

Treating Depression with NFB: Left Alpha > Right Alpha Two-Channel Neuofeedback: • • • Depressed people show brainwave asymmetry. In depression, one side of the brain is hypoactive. Left-side alpha was lower than right-side alpha. • In NFB, this is reversed: • Rosenfeld et al trained right (F 3 referenced to Cz) minus left (F 4 minus Cz) – alpha EEG (with ground lead to center of forehead). – Depressed subjects could significantly alter their EEG assymetry. – Signs of depression diminished.

So, How Many Ways Can You ‘Do’ Neurofeedback? • Who answers this question? – Confusing to the public. – Confusing to Insurance. – Confusing to Patients. • We need to be more mindful of this, eh?

QUIZ

Tone feedback, rather than visual feedback, is preferred for Alpha Up Training. This is because: • Alpha waves are naturally blocked when you open your eyes. • Visual is more distracting. • Research discovered you can not relax with eyes-open. • Alpha waves increase with arousal.

Rosenthal et all found that one type of depression involved: . • Left-side alpha was greater than right-side alpha • Decreased EEG caused by Restricted Breathing • Frontal lobe alpha was greater than alpha in other areas • EEG patterns due to sleep abnormalities.

Alcohol and drug abuse • • Cravings occur long after addicts are detoxified Cravings are triggered by emotions Good intentions are cancelled by drug triggers All of the above

In EEG studies, ‘bipolar’ refers to: • A type of electrode placement. • Wide mood swings. • Detected 6. 4 Hz EEG fluctuations generated by Earth’s magnetic fields. • Any EGG placement that subtracts Left from Right.

Tone feedback, rather than visual feedback, is preferred for Alpha Up Training. This is because: • Alpha waves are naturally blocked when you open your eyes. • Visual is more distracting. • Research discovered you can not relax with eyes-open. • Alpha waves increase with arousal.

Rosenthal et all found that one type of depression involved: • Left-side alpha was greater than right-side alpha • Decreased EEG caused by Restricted Breathing • Frontal lobe alpha was greater than alpha in other areas • EEG patterns due to sleep abnormalities.

End of Section

EMG Biofeedback • Muscle Biofeedback – Neuromuscular Biofeedback – Myofeedback – s. EMG Training • “Relaxation Training” • “Trigger Point Training”
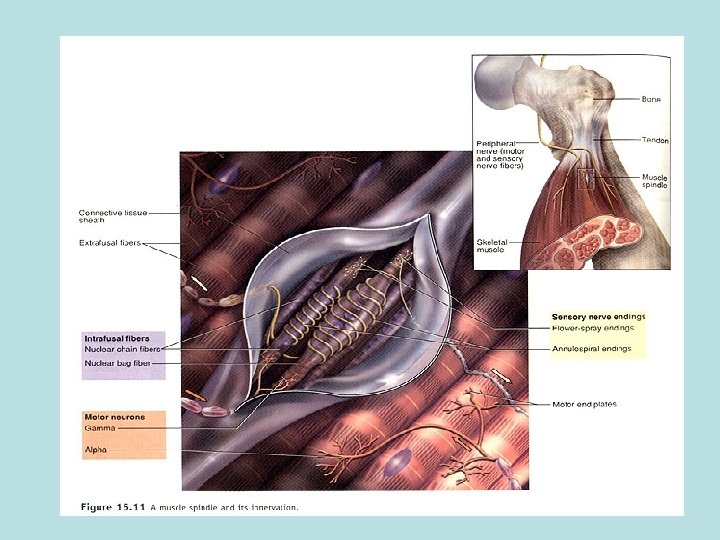
Surface Electromyography: • Surface EMG detects the summed electrical activity of muscle fibers. – motor units fire below the surface of the electrodes.
Dynamic SEMG & Neuromuscular Pain s. EMG takes many forms

BIG BUSINESS? • Muscle pain - a primary cause for more than 30% of all primary care visits. • 66% lifetime prevalence of neck pain among adults • at least 30% of people working at the computer reporting neck, back, hand, and arm pain. – (Peper et al. , 2010),
Basics MINDFULNESS TECHNIQUES • Trigger point considerations • Check for s. EMG muscle fatigue • Check for Micro. Breaks • Dysponesis – – excessive unnecessary tension

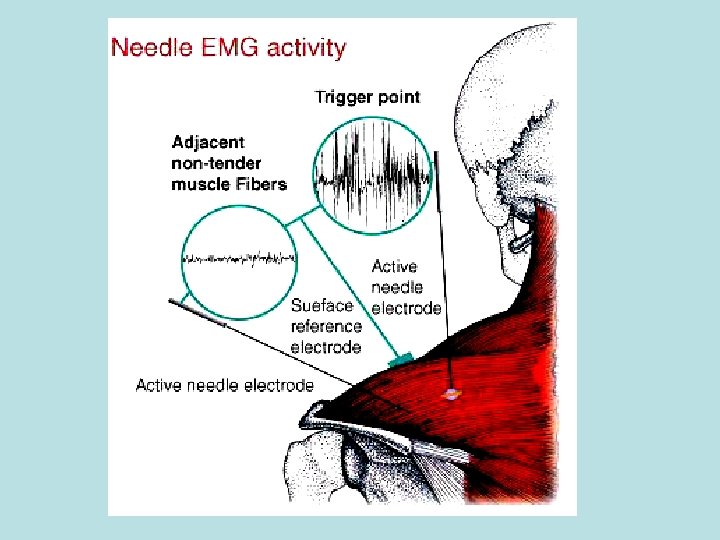
Trigger Points • Pain with Post-Movement Irritability? – May be due to the presence of a trigger point.
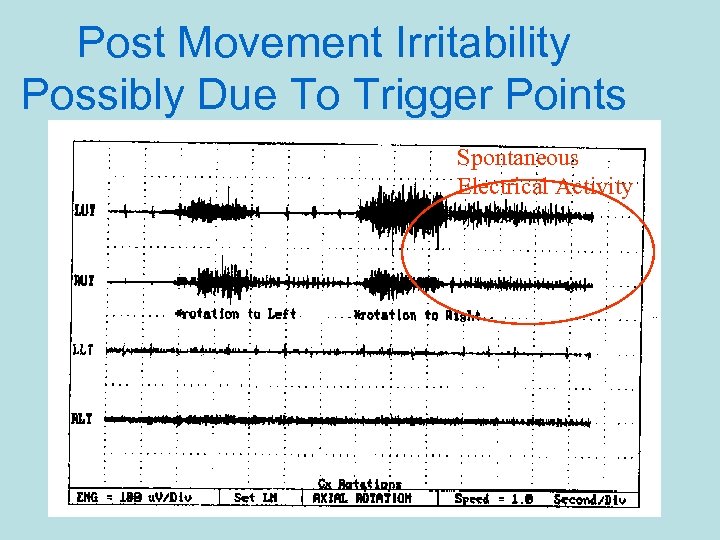
Post Movement Irritability Possibly Due To Trigger Points Spontaneous Electrical Activity
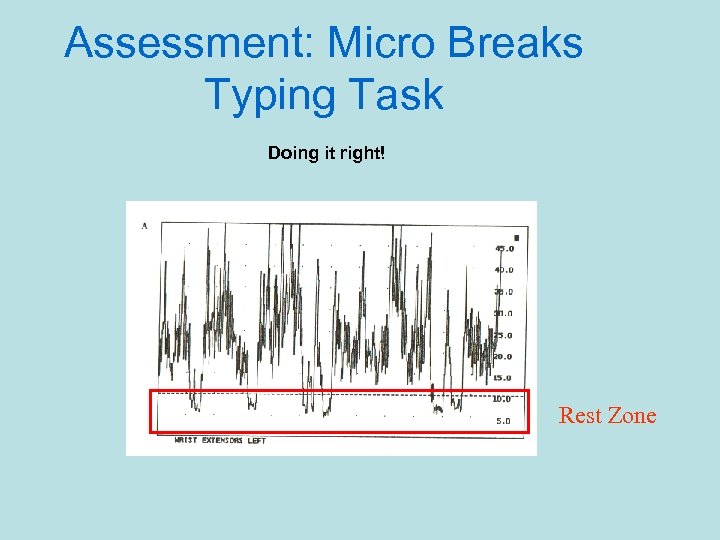
Assessment: Micro Breaks Typing Task Doing it right! Rest Zone
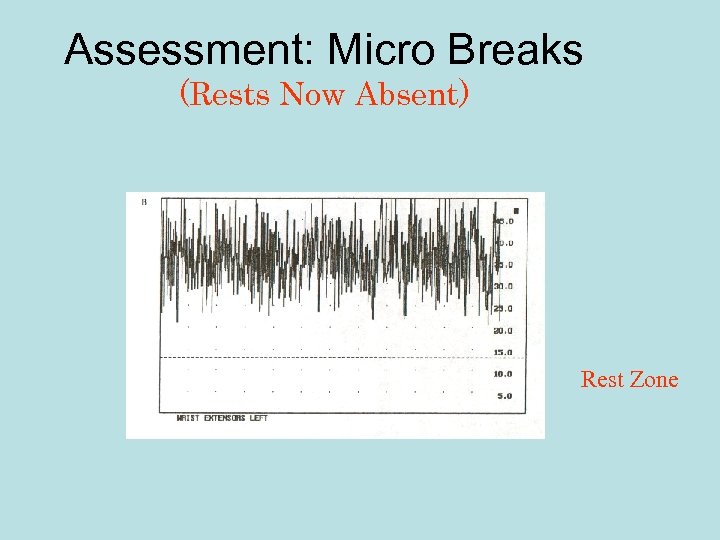
Assessment: Micro Breaks (Rests Now Absent) Rest Zone

DYSPONESIS • ‘misplaced effort’ • a reversible “physiopathologic state made up of errors in energy expenditure within the nervous system. ” – Whatmore and Kohli (1974).

Four types of misplaced effort : • misplaced effort while Performing – Excessive force in normal activities • misplaced effort with Bracing – Anticipatory tensing prior to action • misplaced effort while Recalling – Unneeded motor tension caused by remembering stressful events. • misplaced effort during intense Attention – Excessive motor tension while concentrating

Common Examples • • Clenched jaw Squinting eyes Furrowed brow Rigid, tense neck with head held forward Raised, tense shoulders Clenched fists Tense or “sucked in” abdomen.
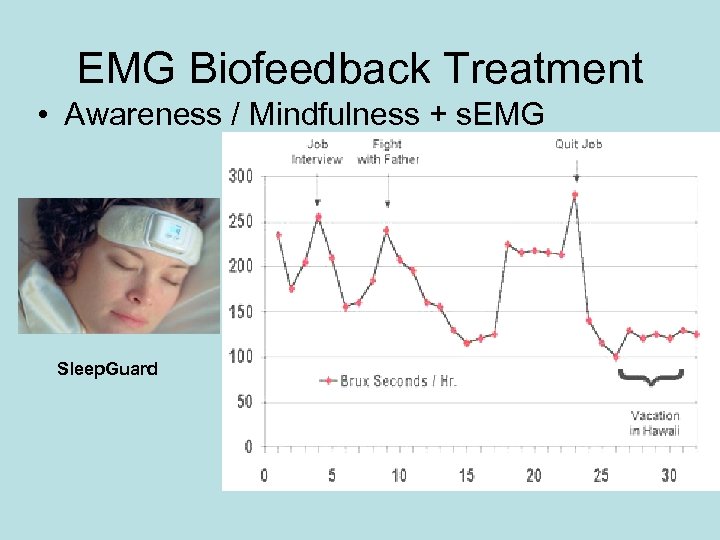
EMG Biofeedback Treatment • Awareness / Mindfulness + s. EMG Sleep. Guard

ADVANCED BIOFEEDBACK TECHNIQUES Impairments related to…. • Stress • Recovery • Joints
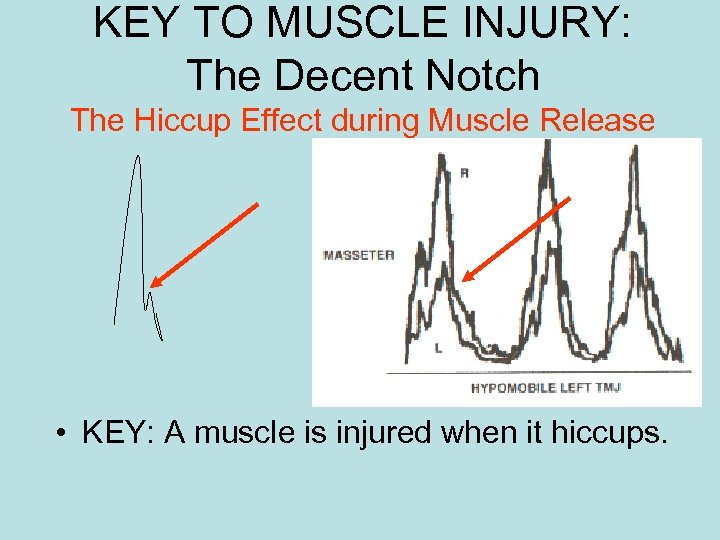
KEY TO MUSCLE INJURY: The Decent Notch The Hiccup Effect during Muscle Release • KEY: A muscle is injured when it hiccups.

Relaxation EMG Biofeedback • Goal is to increase awareness of muscle relaxation. • Two muscle groups are best: – Wrist-to-wrist EMG – includes ECG [HR] – Forehead EMG – minimizes ECG
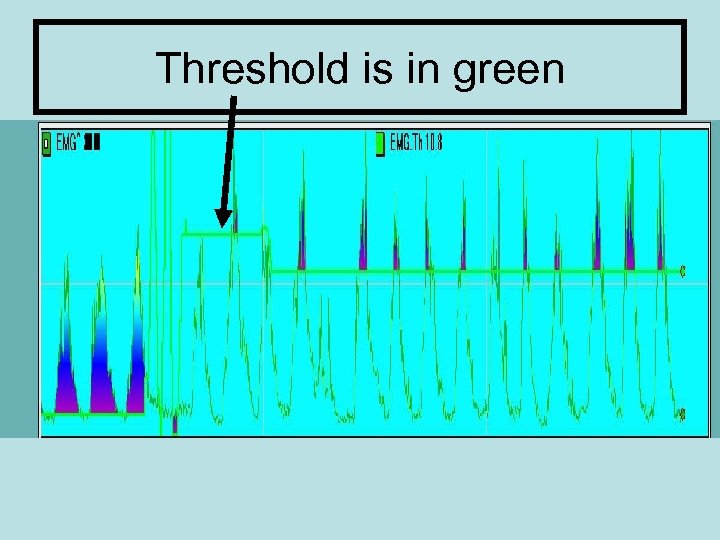
Threshold is in green
Relaxation EMG Biofeedback • A single channel is used • Goal is to increase awareness of muscle relaxation. • ‘Dynamic EMG’ – when EMG is measured both at rest and during movement.
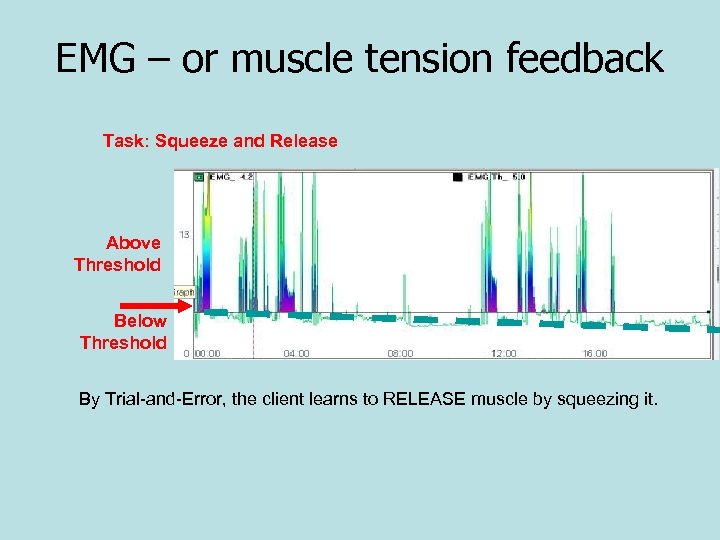
EMG – or muscle tension feedback Task: Squeeze and Release Above Threshold Below Threshold By Trial-and-Error, the client learns to RELEASE muscle by squeezing it.
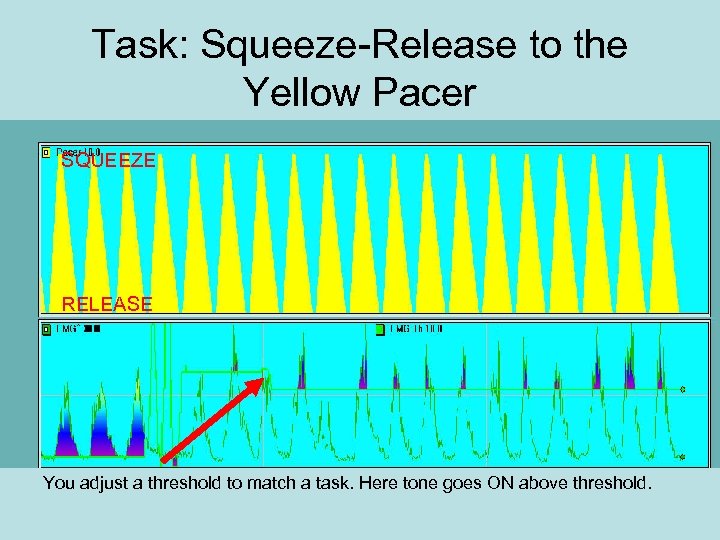
Task: Squeeze-Release to the Yellow Pacer SQUEEZE RELEASE You adjust a threshold to match a task. Here tone goes ON above threshold.

Here the picture is filled in as more Correct Responses are made.

End of Relaxation EMG
Humm!
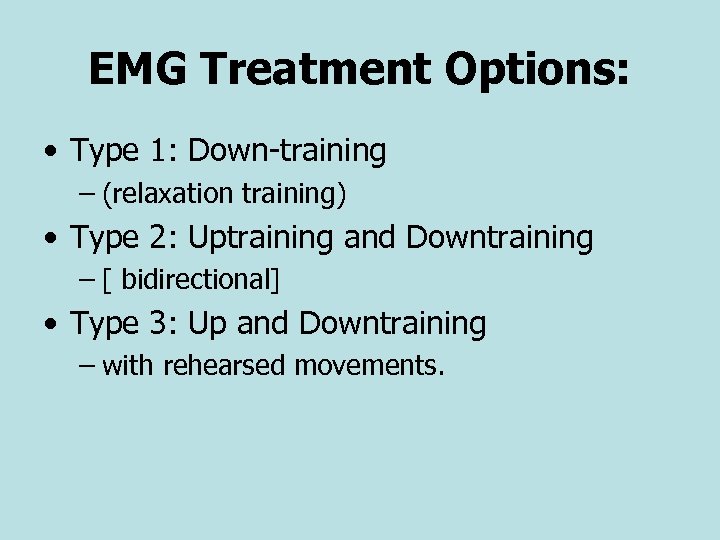
EMG Treatment Options: • Type 1: Down-training – (relaxation training) • Type 2: Uptraining and Downtraining – [ bidirectional] • Type 3: Up and Downtraining – with rehearsed movements.
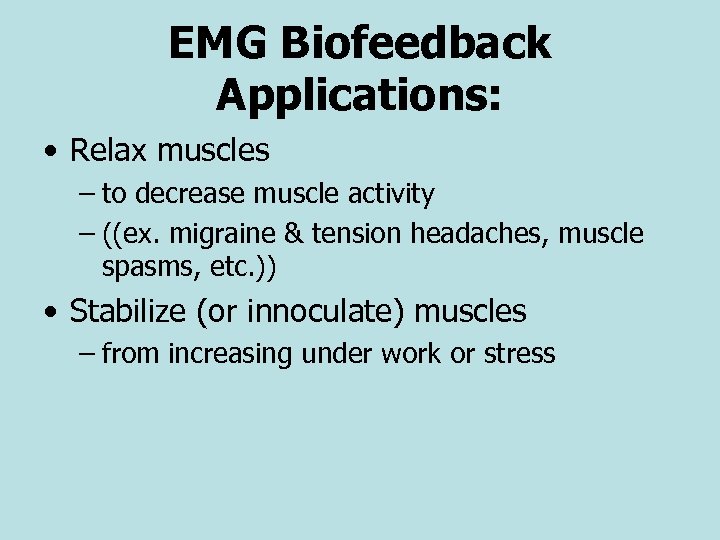
EMG Biofeedback Applications: • Relax muscles – to decrease muscle activity – ((ex. migraine & tension headaches, muscle spasms, etc. )) • Stabilize (or innoculate) muscles – from increasing under work or stress
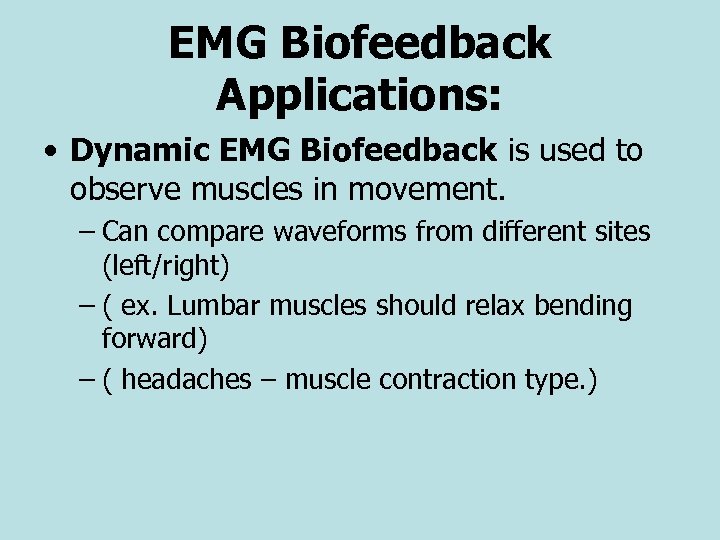
EMG Biofeedback Applications: • Dynamic EMG Biofeedback is used to observe muscles in movement. – Can compare waveforms from different sites (left/right) – ( ex. Lumbar muscles should relax bending forward) – ( headaches – muscle contraction type. )
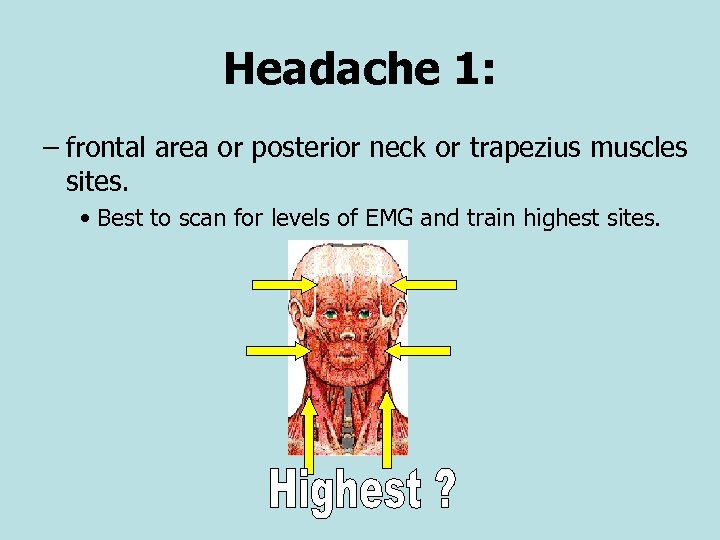
Headache 1: – frontal area or posterior neck or trapezius muscles sites. • Best to scan for levels of EMG and train highest sites.
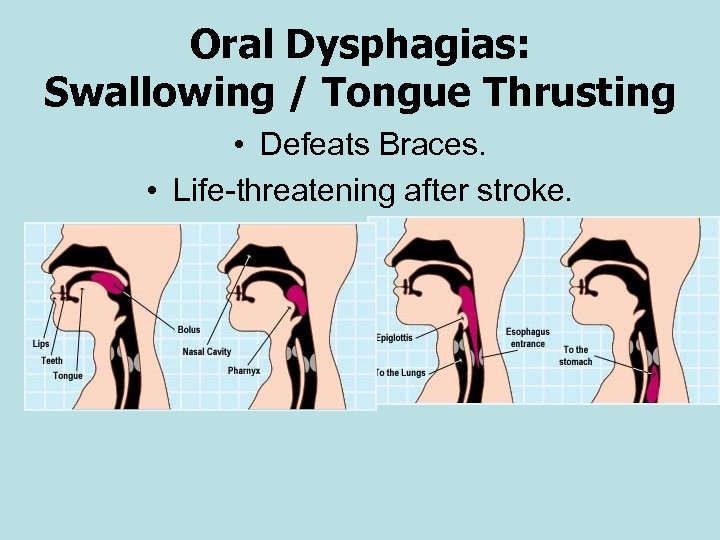
Oral Dysphagias: Swallowing / Tongue Thrusting • Defeats Braces. • Life-threatening after stroke.
![Tongue Thrust EXAMPLE [Loma Linda] Tongue Thrust EXAMPLE [Loma Linda]](https://present5.com/presentation/b63c2e2e9dcd0b808c15bc0f22233999/image-99.jpg)
Tongue Thrust EXAMPLE [Loma Linda]
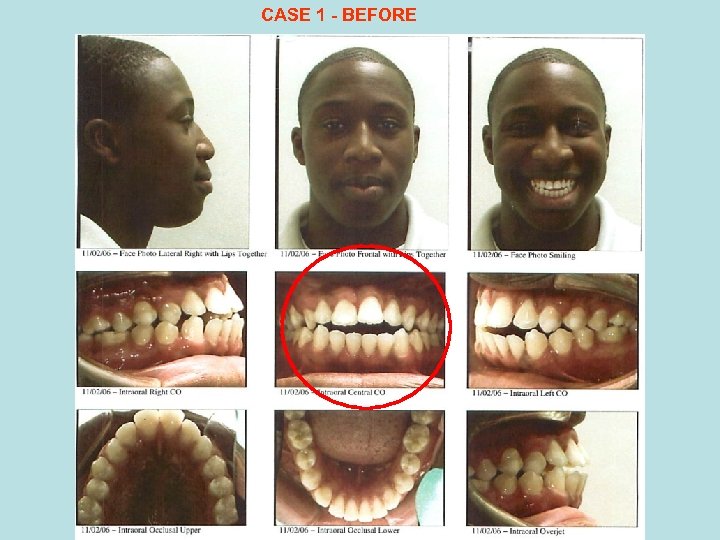
CASE 1 - BEFORE
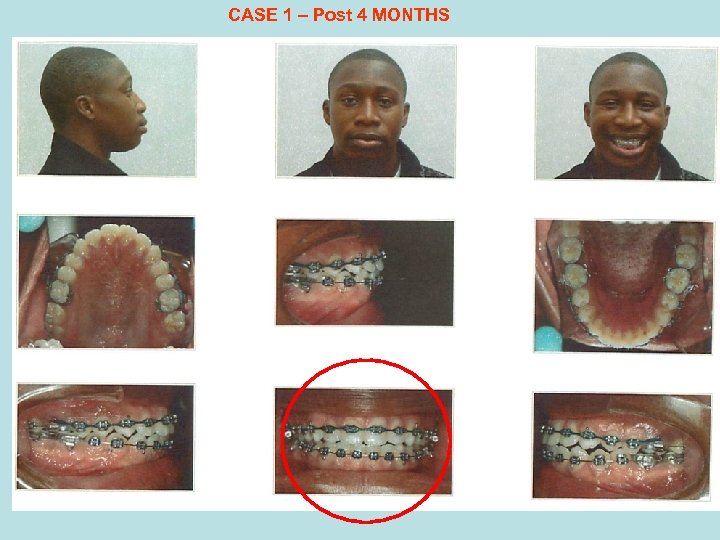
CASE 1 – Post 4 MONTHS

CASE I WAS VERY CO-OPERATIVE AND ATTENDED EVERY SESSION HOW DID CASE I’s RESPIRATION & ORAL HABITS PROFILE LOOK? Next Slide…
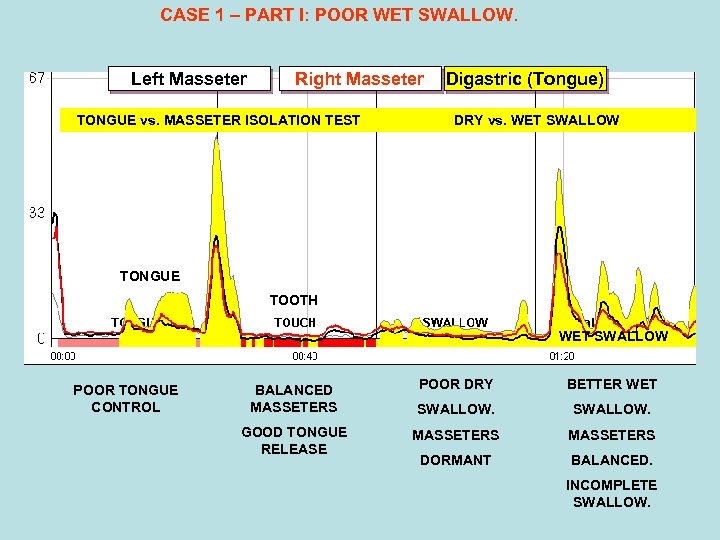
CASE 1 – PART I: POOR WET SWALLOW. Left Masseter Right Masseter TONGUE vs. MASSETER ISOLATION TEST Digastric (Tongue) DRY vs. WET SWALLOW TONGUE TOOTH WET SWALLOW POOR TONGUE CONTROL BALANCED MASSETERS GOOD TONGUE RELEASE POOR DRY BETTER WET SWALLOW. MASSETERS DORMANT BALANCED. INCOMPLETE SWALLOW.

Fecal and urinary Incontinence: • EMG Biofeedback training • This is a vaginal sensor

FIN • s. EMG Disorders have multiple Syndromes – Each Syndrome has a specific treatment. – Dysponesis can be corrected with biofeedback • Aspects of EMG are easy to learn: • The Decent Notch is diagnostic of muscle problems.
QUIZ: So what did you learn? • Select the answer that best completes the question. One answer per item, please:

EMG biofeedback requires a clean signal : • • a different setting equipment. different types of suggestion. a medical referral.

To obtain the narrowest s. EMG signal, place the electrodes: : • • Close together Far apart Over clothing None of the above.

A wrist-to-wrist EMG signal will have ‘spikes’ in at when: • • Heart Rate is detected Emotional topics are felt Breathing becomes more relaxed All of the above

To be certain that someone has learned EMG relaxation: • • Frustrate them Relax them. Hypnotize them. Send them your bill.

In most cases, to relax a target muscle, you must identify and relax a non-target muscle. This is called: . • • Distal Dysponesis Linking. Dissociation.

The biofeedback technique of gradually shaping muscle performance through repetition and successive approximation is called: • Motivating. • Shaping. • Reflecting. • Tightening.

When right-left pairs of s. EMGs are used during movements, this is called: : • • Dynamic s. EMG Assymmetry s. EMG Static s. EMG scanning

The Decent Notch refers to an involuntary pause while a relaxing muscle: • True • False

‘An EMG biofeedback procedure that trains a specific state in preparation of imagery, or movement’ is an example of procedures called: • Type 1 • Type 2 • Type 3 • Type 4

The correct term for relaxing a muscle is: • • Down-Training Up-Training. Specificity-Training. Muscle-Regulation Training.

s. EMG biofeedback training with rehearsed movements is an example of: • Type 3 EMG Training. . • A form of post-hypnotic suggestion disguised as EMG biofeedback. • Meridian-linked EMG biofeedback. • EMG Mindfulness Training.

Tension headaches that have muscle involvement are most frequently traced to : • • Frontal areas. Masseter. Neck areas. All of the above.

End of Section

The End of the Beginning. . • In traditional medicine, patients are treated as passive recipients. • The biofeedback process applies technology and awareness to promote self-mastery and independence. • Patients are more likely to approach hypnosis after gaining confidence with biofeedback. • Biofeedback builds your confidence when you do hypnosis.

End

b63c2e2e9dcd0b808c15bc0f22233999.ppt