9f6345b3fbaebe0822dd8d2180cbc135.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

BIOE 301 Lecture Four

Special Guest n Dr. Bob Parkerson, Baylor College of Medicine n n n Co-director of the International Health Track for MD students Established WHO Collaborating Center for Family & Community Medicine Shoulder to Shoulder

BIOE in the News n Ethics – Lancet Study Faked! n n n Single pill for HIV n n http: //www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/entrez/query. fcg i? cmd=Retrieve&db=Pub. Med&list_uids=1622 6613&dopt=Abstract http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php ? story. Id=5165566 http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php ? story. Id=5163844 Packaging Malaria Drugs n http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php ? story. Id=5164602

Summary of Lecture 3 n Developing World 1. 2. 3. 4. n HIV/AIDS Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular diseases Tuberculosis Developed World 1. 2. 3. 4. Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular diseases Cancer Self-inflicted injuries

Overview of Lecture 4 n What are the major health problems worldwide? n Leading causes of mortality for ages 45 -59 n n n Developed world Developing world Global health challenges

Leading Causes of Mortality Ages 45 -60 n Developing World 1. 2. 3. 4. n Cardiovascular diseases, Cancer (malignant neoplasms), Unintentional injuries, and HIV/AIDS Developed World 1. 2. 3. 4. Cardiovascular diseases, Cancer (malignant neoplasms), Unintentional injuries, and Digestive Diseases
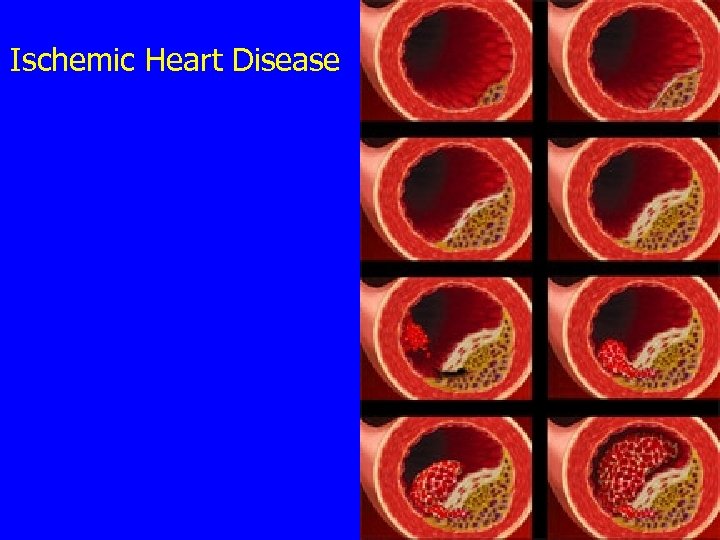
Ischemic Heart Disease
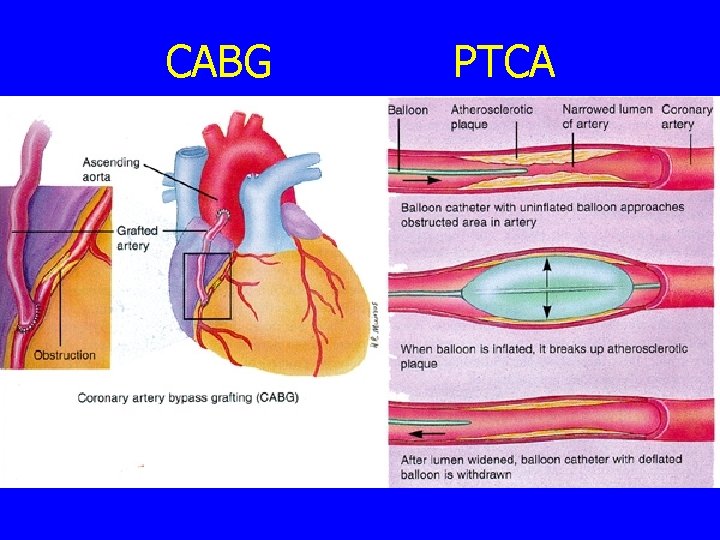
CABG PTCA

Cerebrovascular Disease: Stroke n Abrupt onset with focal neurologic deficit n Usually mini-event or warning signs n n Reversible ischemia n n 5 -20% transient ischemic attacks Some lasting 24 -72 hours Completed stroke Maximal deficit within hours n Often patient awakens with completed stroke n Usually preceded by TIA Progressive stroke n Ischemia worsens min. to min. or hour to hour n
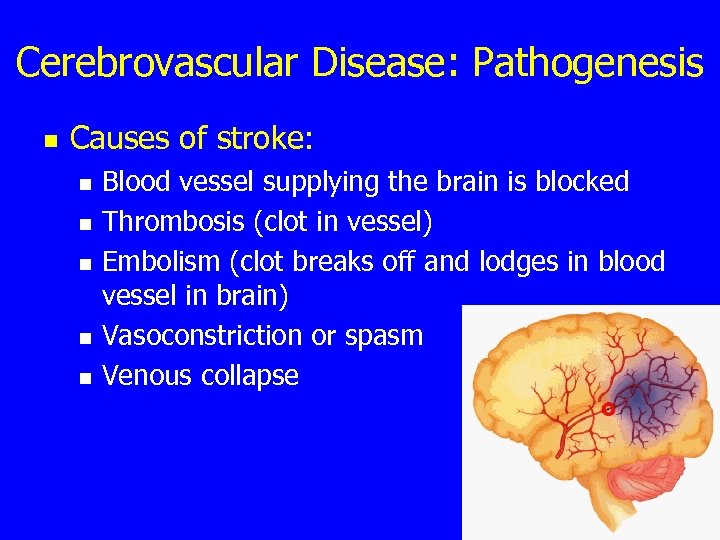
Cerebrovascular Disease: Pathogenesis n Causes of stroke: n n n Blood vessel supplying the brain is blocked Thrombosis (clot in vessel) Embolism (clot breaks off and lodges in blood vessel in brain) Vasoconstriction or spasm Venous collapse

Cerebrovascular Disease: Diagnosis n n n History Exam Imaging n n n CT Scan MRI CT/MR Angiography
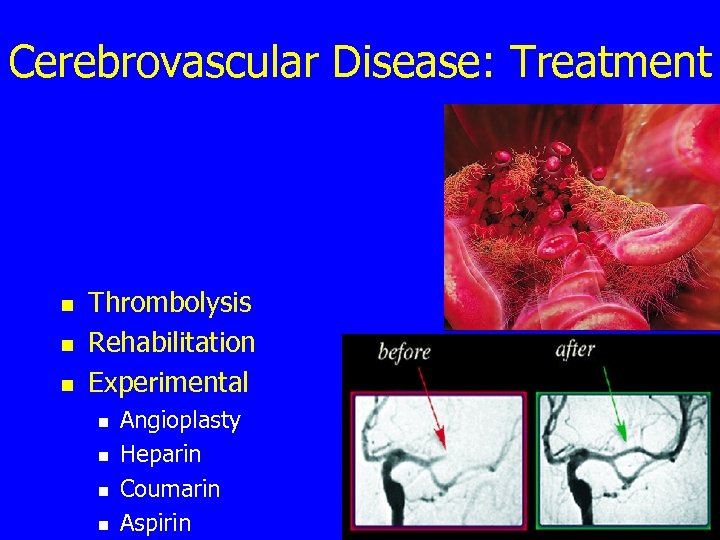
Cerebrovascular Disease: Treatment n n n Thrombolysis Rehabilitation Experimental n n Angioplasty Heparin Coumarin Aspirin

Cancer, Ages 45 -59 n n Cancer kills 1. 5 million people aged 45 -59 each year throughout the world each year Lung cancer n n Stomach cancer n n 185, 000 deaths/year Liver cancer n n 263, 000/year deaths in this age group 179, 000 deaths/year Breast cancer n 148, 000 deaths/year

Cancer n Tumor n n Types of Tumors: n n n Abnormal mass of tissue Growth exceeds that of normal tissue Purposeless and preys on host Benign Malignant Only malignant tumors can spread (Metastasize)
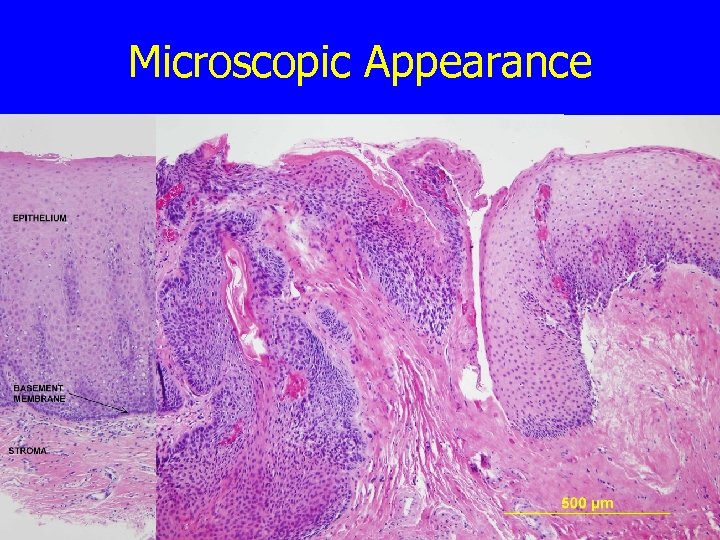
Microscopic Appearance
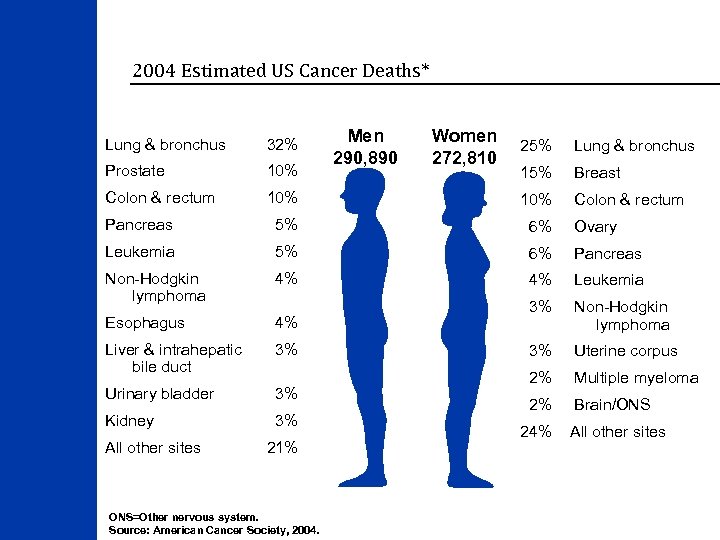
2004 Estimated US Cancer Deaths* Lung & bronchus 32% Prostate 10% Colon & rectum Men 290, 890 Women 272, 810 25% Lung & bronchus 15% Breast 10% Colon & rectum Pancreas 5% 6% Ovary Leukemia 5% 6% Pancreas Non-Hodgkin lymphoma 4% 4% Leukemia Esophagus 4% 3% Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Liver & intrahepatic bile duct 3% 3% Uterine corpus Urinary bladder 3% 2% Multiple myeloma Kidney 3% 2% Brain/ONS All other sites 21% ONS=Other nervous system. Source: American Cancer Society, 2004. 24% All other sites
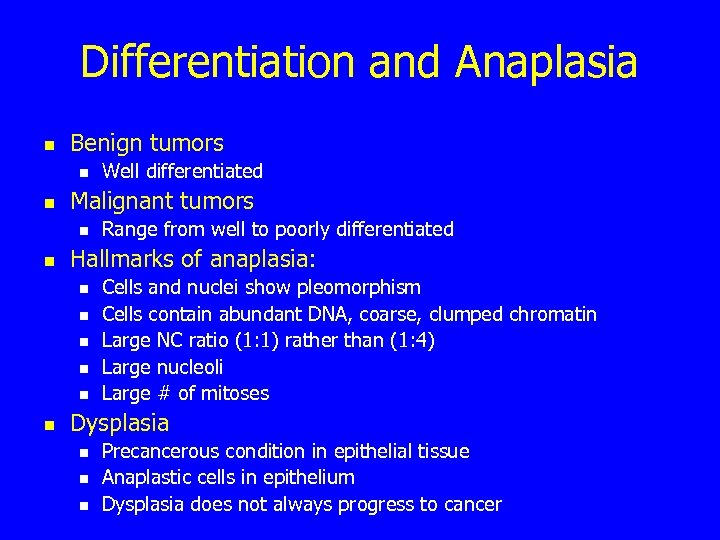
Differentiation and Anaplasia n Benign tumors n n Malignant tumors n n Range from well to poorly differentiated Hallmarks of anaplasia: n n n Well differentiated Cells and nuclei show pleomorphism Cells contain abundant DNA, coarse, clumped chromatin Large NC ratio (1: 1) rather than (1: 4) Large nucleoli Large # of mitoses Dysplasia n n n Precancerous condition in epithelial tissue Anaplastic cells in epithelium Dysplasia does not always progress to cancer

Carcinogensis n Carcinogenesis: n n Result of non-lethal genetic damage Tumor masses result from the clonal expansion of a single progenitor cell that has incurred genetic damage

Biology of Tumor Growth n Natural hx of most cancers has 4 phases: n n Malignant transformation in target cell Growth of transformed cells Local invasion Distant metastases
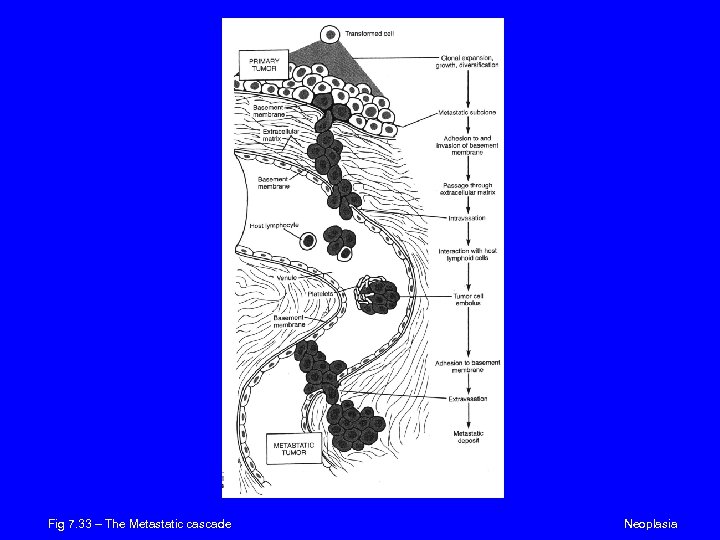
Fig 7. 33 – The Metastatic cascade Neoplasia

Tissue Invasion n n Metastasis causes 90% of cancer death How do tumors invade: n n n Detach from primary tumor Degrade surrounding matrix Migrate
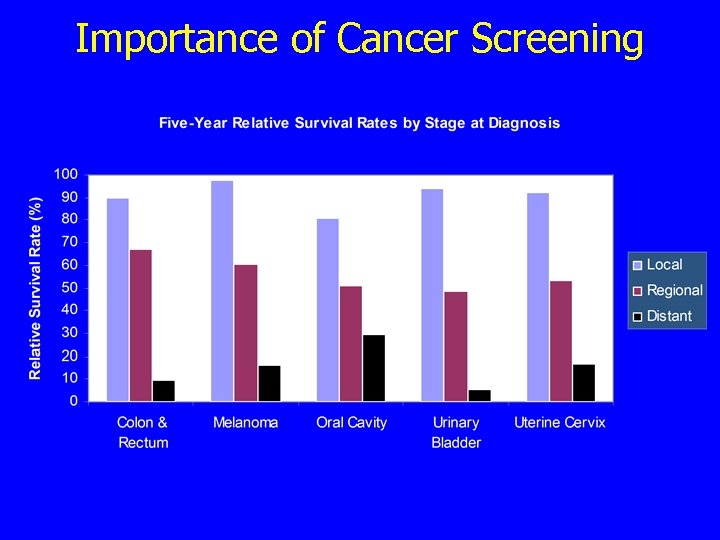
Importance of Cancer Screening

Lung Cancer: Epidemiology n United States n n n 99, 000 males die per year 78, 000 females die per year Five year survival: 14% Only 15% of patients are diagnosed with localized disease Risk factors n Smoking Actively: increases relative risk 13 X n Passively: increases relative risk 1. 5 X n

Lung Cancer: Clinical Manifestations n Signs and symptoms n n Coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, recurrent pneumonia Diagnosis: n Screening: n n Trials of CXR, sputum cytology, NOT SUCCESSFUL Diagnostic: CXR n CT directed biopsy n Bronchoscopically directed biopsy n n Staging: concept of localized vs. distant disease

Lung Cancer: Treatment n Localized n n n Small: Possibly surgery Large: Chemo or XRT + surgery Metastatic: n Chemo + XRT

Digestive Diseases n n Worldwide, 456, 000 people aged 45 -59 die each year from digestive diseases Cirrhosis of the liver n Kills 250, 000 people each year between the ages of 45 and 59
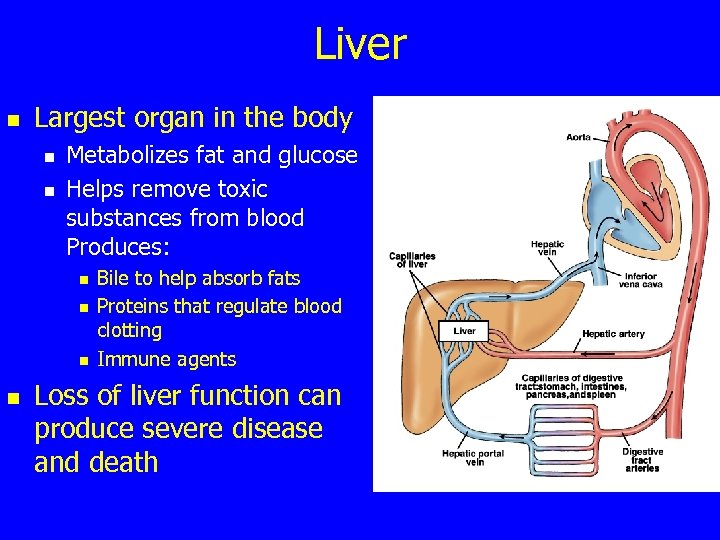
Liver n Largest organ in the body n n Metabolizes fat and glucose Helps remove toxic substances from blood Produces: n n Bile to help absorb fats Proteins that regulate blood clotting Immune agents Loss of liver function can produce severe disease and death
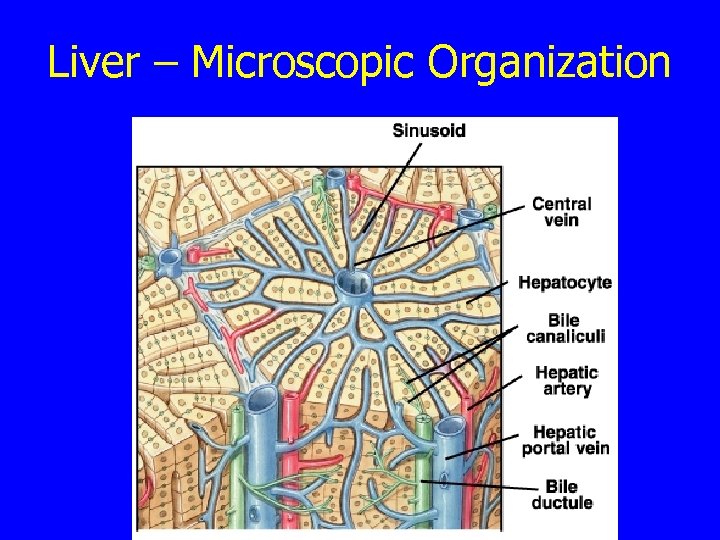
Liver – Microscopic Organization
Cirrhosis n n Normal liver is replaced with scar tissue as a result of chronic injury, interfering with liver function Causes of cirrhosis: n n n Chronic alcoholism Viral hepatitis infection Symptoms of cirrhosis: n n Exhaustion, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting blood, weakness, weight loss, and abdominal pain. Patients bruise and bleed easily and become highly sensitive to medicines with increasing loss of liver functions.
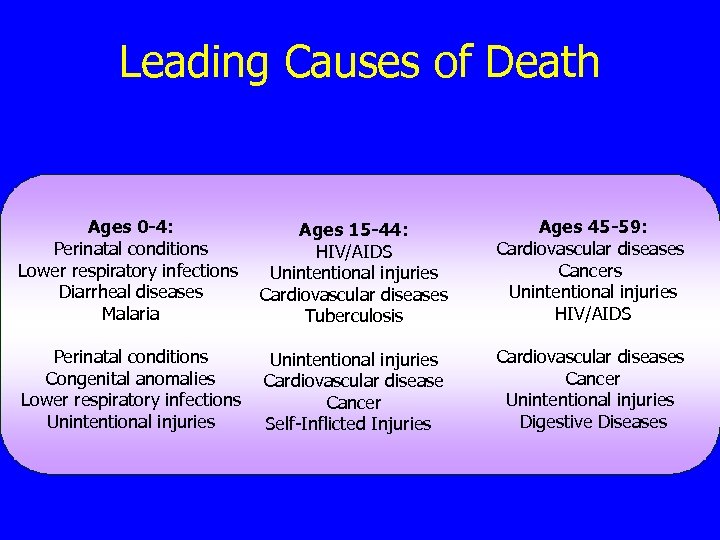
Leading Causes of Death Ages 0 -4: Ages 15 -44: Perinatal conditions HIV/AIDS Lower respiratory infections Unintentional injuries Diarrheal diseases Cardiovascular diseases Malaria Tuberculosis Ages 45 -59: Cardiovascular diseases Cancers Unintentional injuries HIV/AIDS Perinatal conditions Congenital anomalies Lower respiratory infections Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular diseases Cancer Unintentional injuries Digestive Diseases Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular disease Cancer Self-Inflicted Injuries
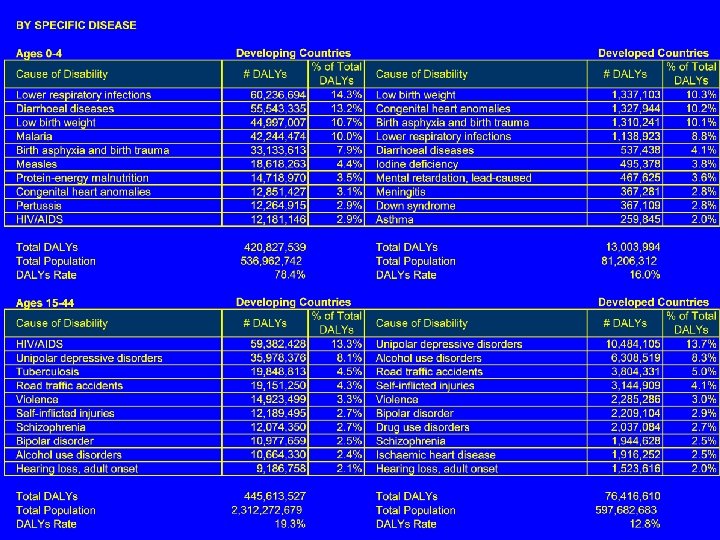
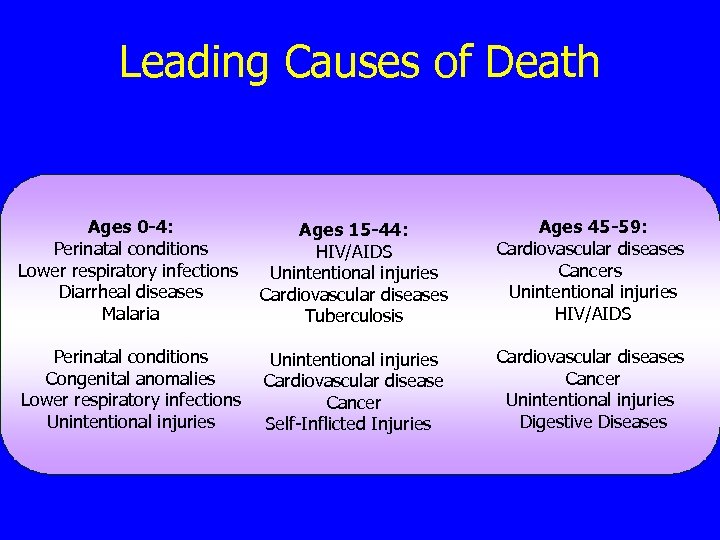
Leading Causes of Death Ages 0 -4: Ages 15 -44: Perinatal conditions HIV/AIDS Lower respiratory infections Unintentional injuries Diarrheal diseases Cardiovascular diseases Malaria Tuberculosis Ages 45 -59: Cardiovascular diseases Cancers Unintentional injuries HIV/AIDS Perinatal conditions Congenital anomalies Lower respiratory infections Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular diseases Cancer Unintentional injuries Digestive Diseases Unintentional injuries Cardiovascular disease Cancer Self-Inflicted Injuries
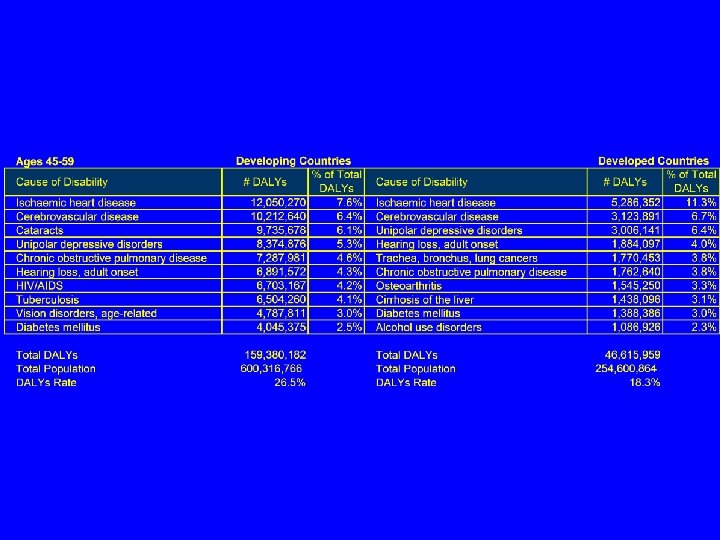
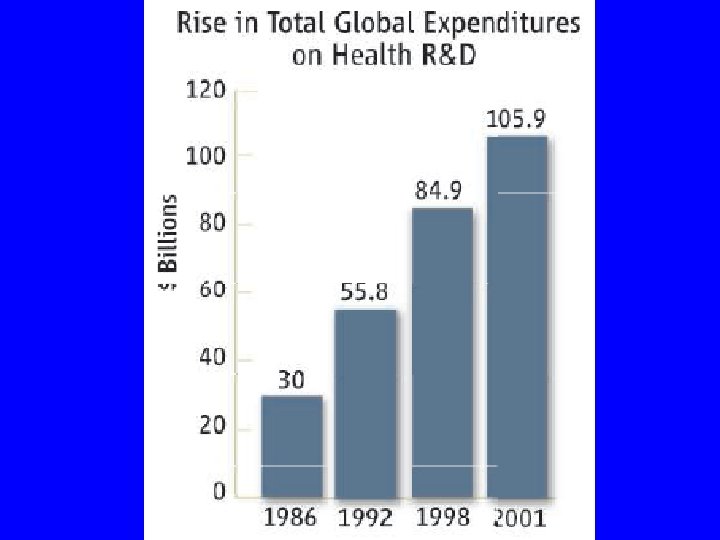

New World of Global Health n Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation n Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria n n Pledged $6 billion since 1999 to global health issues Roughly the same as the WHO budget during the same time $8. 6 billion to 128 countries launched in 2002 President’s Emergency Plan for HIV/AIDS Relief, 2004 n $15 billion

Challenges Faced n n Countries struggle with procurement policies, hard to convert $$ to drugs Shortages of trained health care workers n n n http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php ? story. Id=4987628 Corruption Lack of coherent approach

What is a grand challenge? n Scientific or technical innovation that: n n n Removes a critical barrier to solving an important health problem in developing world High likelihood of global impact and feasibility Different than: n Simple statement of a “big problem” in global health n n HIV/AIDS, malnutrition, lack of access to medical care, lack of resources Meant to: n Direct investigators to specific breakthrough that provides solution to a significant health problem(s)

Global Health Challenges n $200 million medical research initiative n n n Grand challenges in global health Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation Encourage scientific and technological solutions to diseases that disproportionately affect the developing world Announced in January 2003 http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php ? story. Id=939533

Call for Grand Challenges n Call For Ideas I (May 2003) n n 1048 submissions from scientists and institutions in 75 countries Scientific Board heard proposals (August 2003) n n Problem Roadblock (obstacle to progress) Challenge List of potential benefits

Goals and Grand Challenges n n n Seven Long Range Goals 14 Grand Challenges Heavily oriented toward infectious disease n n Infectious diseases account for the most profound discrepancies between advanced and developing economies Causes of infectious diseases are well-known Can more easily formulate technical and scientific obstacles to progress Results reported in Science (Oct 17, 2003)

Goals and Grand Challenges n Improve childhood vaccines n n GC 1 -Create effective, single dose vaccines that can be used soon after birth GC 2 -Prepare vaccines that do not require refrigeration GC 3 -Develop needle-free delivery systems for vaccines Create new vaccines n n n GC 4 -Devise reliable tests in model systems to evaluate live attenuated vaccines GC 5 -Solve how to design antigens for effective protective immunity GC 6 -Learn which immunological responses provide protective immunity

Goals and Grand Challenges n Control insects that transmit infectious disease n n n Improve nutrition to promote health n n GC 7 -Develop a genetic strategy to deplete or incapacitate a disease-transmitting insect population GC 8 -Develop a chemical strategy to deplete or incapacitate a disease-transmitting insect population GC 9 -Create a full range of optimal bioavailable nutrients in a single staple plant species Improve drug treatment of infectious disease n GC 10 -Discover drugs and delivery systems that minimize the likelihood of drug-resistant organisms

Goals and Grand Challenges n Cure latent and chronic infections n n n GC 11 -Create therapies that can cure latent infections GC 12 -Create immunologic methods that can cure chronic infections Measure disease and health status accurately in economically in poor countries n n GC 13 -Develop technologies that permit quantitative assessment of population health status GC 14 -Develop technologies that allow assessment of individuals for multiple conditions or pathogens at point-of-care

Grand Challenge Proposals n NIH issued request for proposals to address challenges n n Grants of up to $20 M over five years or less http: //www. grandchallengesgh. org/

Summary of Lecture Four n Developing World 1. 2. 3. 4. n Cardiovascular diseases, Cancer (malignant neoplasms), Unintentional injuries, and HIV/AIDS Developed World 1. 2. 3. 4. Cardiovascular diseases, Cancer (malignant neoplasms), Unintentional injuries, and Digestive Diseases

Assignments Due Next Time n HW 4
9f6345b3fbaebe0822dd8d2180cbc135.ppt