dd9380721ea2fee59453790e8a0f0ce6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Biodiversity The Wonderful Variety of Critters on Earth!
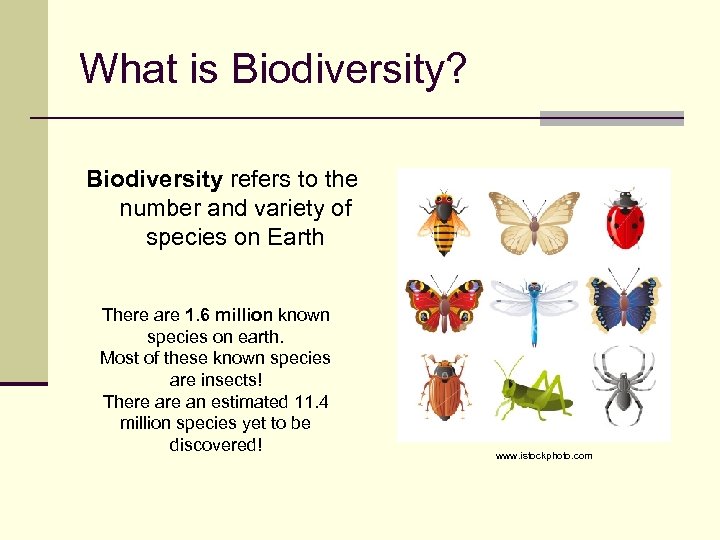
What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity refers to the number and variety of species on Earth There are 1. 6 million known species on earth. Most of these known species are insects! There an estimated 11. 4 million species yet to be discovered! www. istockphoto. com

Reasons for Present Day Extinctions … n Destruction of habitats n Illegal hunting n Introduction of non-native species All of these are caused by human activity!

Habitat Loss – n Habitat loss is the leading cause of extinctions. n 75% of all extinctions are due to the loss of an organism’s habitat. n If its habitat is destroyed, where will it live? What will it eat? tpeblog. wordpress. com

Habitat Loss – The Florida Panther n The Florida panther is one of the most endangered mammals in North America. n It requires a large territory which has been chopped up by roads, canals, and subdivisions. frretsinthesun. silvernexuse. com

Habitat Loss – The Whooping Crane n The whooping crane was almost driven to extinction due to the loss of its breeding grounds to homes and farms. n It was forced to migrate to Canada where many were shot by hunters and farmers. http: //www. learner. org/jnorth/images/graphics/c/crane. HY 04_007. jpg

Aransas National Wildlife Refuge n This refuge in Texas was set aside to give the whooping crane a place to breed. n The whooping crane is on its way to recovery! n Its numbers have increased from 15 to more than 350!

Habitat Degradation n Habitat degradation can also lead to the extinction of species. n Habitat degradation is damage to an ecosystem caused by pollution. n Pollution can affect the air, water, or land. www. uprct. nsw. gov. au www. activeset. org

Illegal Hunting (Poaching) Illegal hunting wiped out half of the African elephant population between 1979 and 1989. www. elephantcountryweb. com

Elephants were killed for their ivory tusks. www. awionline. org www. sciencemuseum. org. uk

Which are (or used to be) made into items like … Mrs. Koeval’s piano keys… …or a happy dancing Buddha!

Illegal Hunting (Poaching) n Currently, many species are still being killed illegally. n The mountain gorilla has recently suffered from attacks by poachers. n On August 9, 2007, a family of mountain gorillas was found shot dead in a Congolese national park. www. zsl. org

An exotic species is one that is not native to an area. n They can totally “take over” a habitat since they have no natural enemies. n Native species also have no defense against them. n Ex. Brown Tree Snake “invasion” of Guam has made 10 of the only 12 bird species extinct!!

The melaleuca tree is an exotic species. n The melaleuca tree was brought to Florida to dry up the Everglades so they could be developed. n It spreads at a rate of 50 acres a day! n It’s very hard to get rid of.

Exotic species take over! This is kudzu…

Keystone Species n A keystone species is one that is so vital to an ecosystem that without it, the ecosystem would not function properly. n The sea otter is a great example – it eats sea urchins – keeping their population under control so the urchins don’t eat all of the kelp. http: //www. icanteachmyself. com withquiz. org. uk www. teara. govt. nz

Endangered Species An endangered species is one whose numbers are so low that it is in danger of becoming extinct.

The Endangered Species Act n Lists threatened and n n endangered species Requires a Species Recovery Plan for T/E species Forbids catching, killing, selling T/E species Forbids federal projects that jeopardizes T/E species http: //www. fws. gov/endang ered/

The Tellico Dam Project The construction of this dam in Tennessee was halted when the snail darter – an endangered fish – was found there. § Proponents of the dam believed that hydroelectric power was needed. § Opponents did not want to harm the snail darter. § www. scionline. org

The Tellico Dam § A dam compromise was made. § The snail darter was moved and the dam was built!

World Wildlife Fund q Encourages sustainable use of natural resources through fund raising, education and adoptions. q www. wwf. org The "Tundra Buggy" Reports

The Nature Conservancy n Manages a system of nature sanctuaries in the United States and around the world q http: //www. nature. org/

Conservation International A mangrove conservation project in Banda Aceh which was devastated by the 2004 tsunami. q Develops ecosystem conservation projects with local people in countries that are rich in biodiversity. q http: //www. conservation. org/Pages/default. aspx

Greenpeace International q Stages dramatic protests to help stop the destruction of rain forests and the killing of endangered species. q http: //www. greenpeace. org/international/

Who are the IUCN? n The World Conservation Union is the world’s largest and most important conservation network. The Union brings together 83 States, 110 government agencies, more than 800 non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and some 10, 000 scientists and experts from 181 countries in a unique worldwide partnership. The Union’s mission is to influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve the integrity and diversity of nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable. The World Conservation Union is a multicultural, multilingual organization with 1100 staff located in 40 countries. Its headquarters are in Gland, Switzerland. n Examples of IUCN projects include the preservation of sea turtle habitat on S. American beaches and helping citizens of Uganda halt the poaching of endangered species. n (http: //www. iucn. org/en/about/) “These orphan chimpanzees were rescued from Ugandan poachers and live in the Ugandan Wildlife Education Centre. Poachers target adult chimpanzees for meat and their young for the pet trade. ” www. bbc. co. uk nscienceguy 288. wordpress. com

What is CITES? “CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) is an international agreement between governments. Its aim is to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival. ” n This treaty has been agreed to by 172 countries (as of 1/23/08) and is one of the largest of its kind. n It was developed in the 1960’s and entered in force in July 1975. n One of CITES victories includes the ban of ivory in 1989 which brought the African elephant from the brink of extinction. n http: //www. cites. org/ news. mongabay. com

Captive Breeding n Captive Breeding and Reintroduction programs breed and sometimes release organisms into an area where the species once lived. n Captive breeding is the breeding of animals under carefully managed conditions. n It is carried out primarily by zoos and its purpose is to increase the population of an endangered or threatened species.

An organism that is held by people is said to be in captivity. This could include plants or animals. n n n Zoos and aquariums provide a place for threatened and endangered species to live and possibly breed. They are also places for people to learn about and appreciate a variety of plants and animals. http: //www. nczoo. org/

Botanical Gardens nwww. mustseemiami. com n Botanical gardens house more than 90, 000 species of plants. n These gardens play a vital role in preserving the biodiversity of plant species. n Fairchild Tropical Garden in Miami, Fl is one such example. www. tripadvisor. com nwww. southbeach. com

Germ Plasm Banks… n Plant seeds and animal ncril. cimmyt. org sperm and egg cells can be stored in germ plasm banks for future breeding if necessary. n Germ plasm banks may be the only places to “retrieve” extinct species in the future. Maize seeds in a gene bank

A more effective way to preserve species… SAVE THEIR HABITAT! Conservationists suggest that at least 10 % of Earth’s land be set aside to protect biodiversity worldwide.
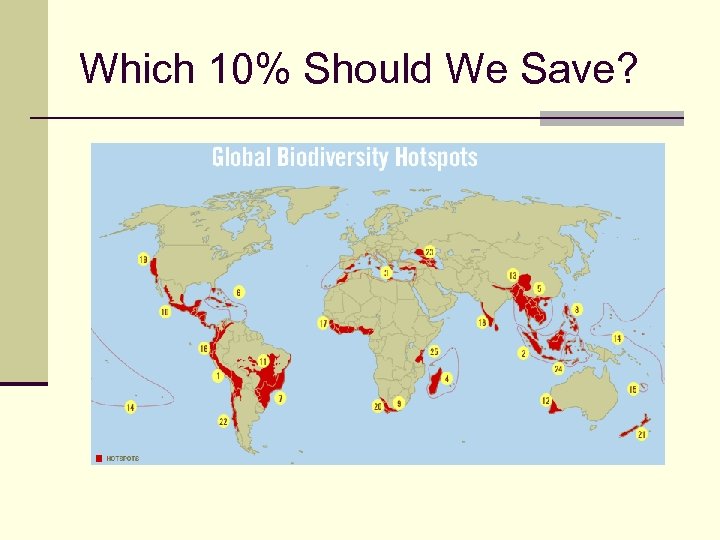
Which 10% Should We Save?

Hot Spots n Hot spots are regions that contain an unusually large number of species. n Examples of hot spots include: Northern Borneo, the Eastern Himalayas, and Southwestern Australia. n Hot spots contain species found no where else on Earth. Northern Borneo – The Sumatran Rhinoceros The Eastern Himalayas – The Lesser Red Panda Southwestern Australia – The Hairy-nosed Wombat
dd9380721ea2fee59453790e8a0f0ce6.ppt