f1146b3f7cd3bbb9323fb935beb57f90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Bio. Med. CEP shaping for NBIS Call V 0. 91 Includes comments from (see http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=316&p=1325#p 1321 ff) - Dimitris Iakovidis 27 Dec 2011 - Andrew Hunter 3 Jan 2012 - Dimitris 4. Jan - Bernard de Bono 5. Jan - Dimitris 6. Jan - Bernard de Bono 6 Jan, 9 Jan - Wolfgang Maass 13 Jan - Rv. A 18 Jan --Rv. A 5 Feb Sot. A and What is Beyond materials

Objective ICT-2011. 9. 11 NBIS • learn more about the relationship between structure, dynamics and function in neuronal circuits and assemblies, and how information is represented or “coded” in a brain. • develop deeper and more comprehensive theories of neural processing, possibly building on results obtained in the domains of dynamic and complex systems. • close the gap between neuroscience and engineering by motivating interdisciplinary work that ties data with theories, novel computing paradigms, models and implementations. Target outcome • Developing and applying radically new neural recording, imaging or interfacing concepts and designs for a deeper understanding of neural information processing. • New multi-scale dynamical theories of neural representation for the development of neuro-bio-ICT systems that can perform high-level tasks (e. g. robust object recognition, or classification), going beyond purely sensory-driven information processing. Exocortex systems • Development and prototyping of modular brain-like computing architectures that combine neural processing primitives to give a better understanding of brain function and facilitate the design of more complex processing systems for real-time and optimized performance. • World-class global research cooperation and alliances in this area, and links with similar actions outside Europe, in particular with participants from USA and Japan. Expected impact 3 Target outcome in the case of IP: • New computing paradigms leading to advanced bio-inspired sensing and processing systems, which are naturally able to learn and adapt • New concepts leading to new brain-computer interface technologies • Target outcome in the case of CSA: New EU and global collaborations between researchers in multiple disciplines spanning engineering, physical and life science domains

Essence of the NBIS Call: The objectives of NBIS are more IT- than Health-related. If the IT objectives are met it would be a “plus” to have an impact on health, although it is not a requirement of the call. Main idea of NBIS is: “Study, analyze, model brain function(s), not necessarily of a human brain, and use this/these models to build artificial processing/sensing system(s) more efficient/effective than the state of the art ones, exploitable in the framework of novel brain-computer interface technologies. ”
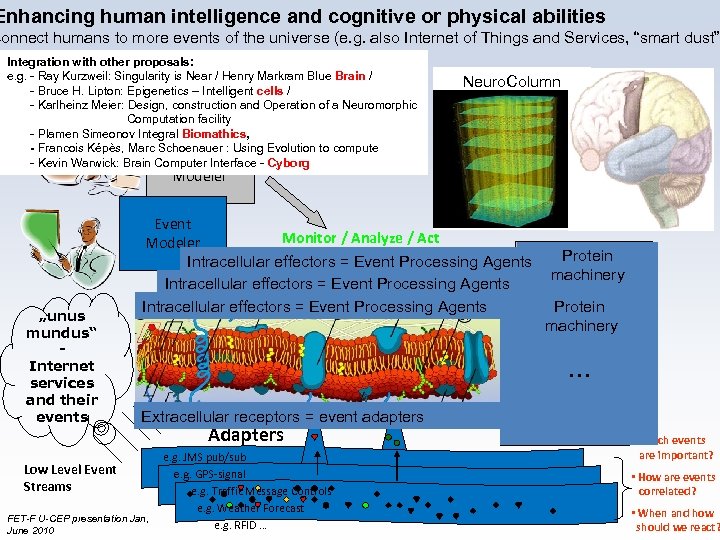
Enhancing human intelligence and cognitive or physical abilities connect humans to more events of the universe (e. g. also Internet of Things and Services, “smart dust”) Integration with other proposals: e. g. - Ray Kurzweil: Singularity is Near / Henry Markram Blue Brain / - Bruce H. Lipton: Epigenetics – Intelligent cells / - Karlheinz Meier: Design, construction and Operation of a Neuromorphic Computation facility - Plamen Simeonov Integral Biomathics, - Francois Képès, Marc Schoenauer : Using Evolution to compute Process - Kevin Warwick: Brain Computer Interface - Cyborg Neuro. Column Modeler „unus mundus“ Internet services and their events Event Monitor / Analyze / Act Modeler Process Engine Process Protein Intracellular effectors = Event Processing Agents Process Execution tbd: Models machinery Intracellular effectors = Event Processing Agents Language Event Processing Intracellular effectors = Event Processing Agents CEP Engine Protein analyse Model machinery tbd: Event Processing history… Language for U-CEP Event Middleware IF … Store Normalized events, … build higher level events Event Type Extracellular receptors = event adapters Low Level Event Streams FET-F U-CEP presentation Jan, June 2010 Adapters e. g. JMS pub/sub e. g. GPS-signal e. g. Traffic Message Controls e. g. Weather Forecast e. g. RFID … AND … FOLLOWED BY… WITHIN… ACTION • Which events are important? • How are events correlated? • When and how should we react?
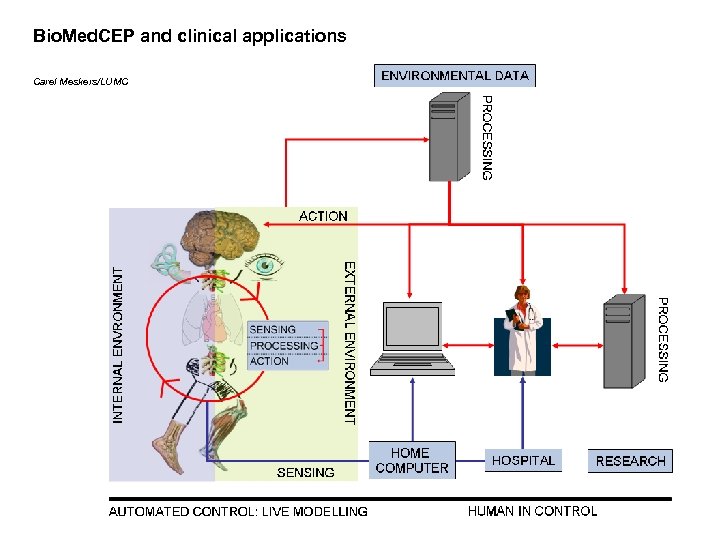
Bio. Med. CEP and clinical applications Carel Meskers/LUMC
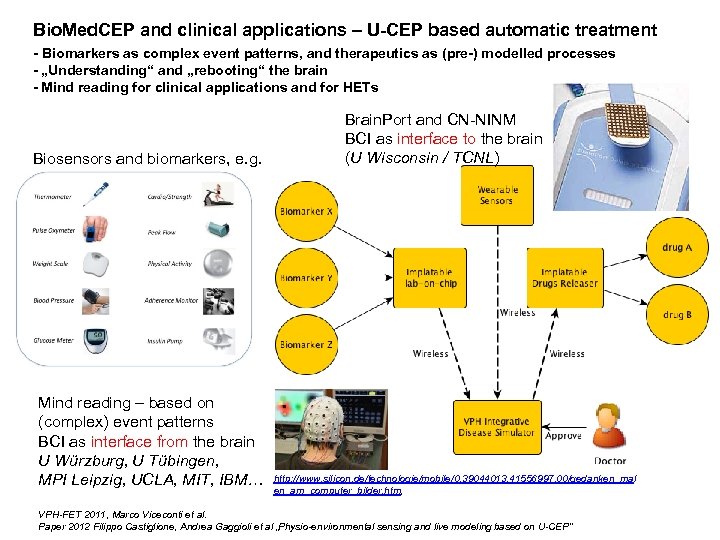
Bio. Med. CEP and clinical applications – U-CEP based automatic treatment - Biomarkers as complex event patterns, and therapeutics as (pre-) modelled processes - „Understanding“ and „rebooting“ the brain - Mind reading for clinical applications and for HETs Biosensors and biomarkers, e. g. Mind reading – based on (complex) event patterns BCI as interface from the brain U Würzburg, U Tübingen, MPI Leipzig, UCLA, MIT, IBM… Brain. Port and CN-NINM BCI as interface to the brain (U Wisconsin / TCNL) http: //www. silicon. de/technologie/mobile/0, 39044013, 41556997, 00/gedanken_mal en_am_computer_bilder. htm, VPH-FET 2011, Marco Viceconti et al. Paper 2012 Filippo Castiglione, Andrea Gaggioli et al „Physio-environmental sensing and live modeling based on U-CEP“

Bio. Med. CEP abstract -tbd – - http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=316&p=1332#p 1330 - http: //www. citt-online. com/downloads/Bio. Med. CEP-preprop_en. doc

Bio. Med. CEP EPSS para. 1. 1 ff “State of the Art / What is Beyond” 1 Scientific and Technical Quality, Relevant to the Topics addressed by the Call 1. 1 Concept and Objectives 1. 2 Progress beyond the State-of-the-art -Tbd, this extended abstract/paper has to adapted or enhanced according to the Call/Objective – http: //www. citt-online. de/downloads/3 -Danilov-Tyler-Ammon-Etzion. pdf + e. g. enhancement of Erwin Vlugt about clinical applications and Ageing/Mobility of elder people, etc. -Tbd, overview comparison Brain projects and Bio. Med. CEP positioning -http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=257&p=1364#p 1364
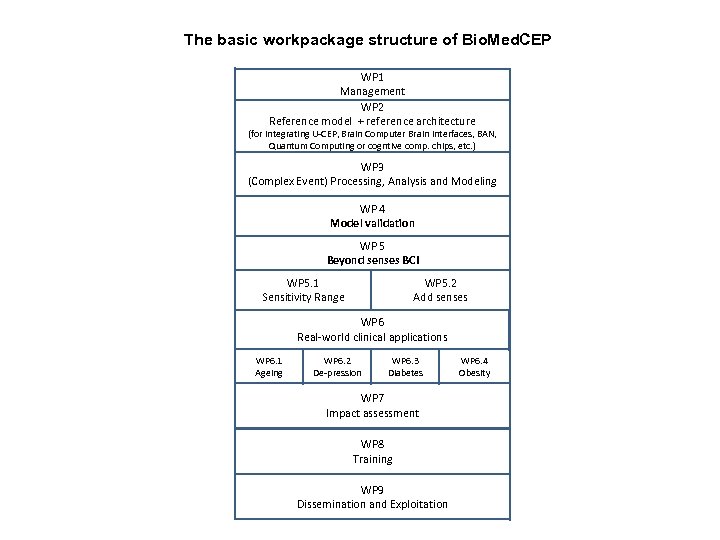
The basic workpackage structure of Bio. Med. CEP WP 1 Management WP 2 Reference model + reference architecture (for integrating U-CEP, Brain Computer Brain Interfaces, BAN, Quantum Computing or cogntive comp. chips, etc. ) WP 3 (Complex Event) Processing, Analysis and Modeling WP 4 Model validation WP 5 Beyond senses BCI WP 5. 1 Sensitivity Range WP 5. 2 Add senses WP 6 Real-world clinical applications WP 6. 1 Ageing WP 6. 2 De-pression WP 6. 3 Diabetes WP 7 Impact assessment WP 8 Training WP 9 Dissemination and Exploitation WP 6. 4 Obesity

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 2 (Reference Model and Reference Architecture for the Bio. Med. CEP approach): RM and RA integrate U-CEP, Event adapters, Brain Computer Brain Interfaces, BAN, Quantum Computing or Cognitive Comp. Chips, etc as a combined technology for WP 5. 1 „Enhancing sensitivity range“ and WP 5. 2 „Add new senses“ via an Exocortex. The term “reference model” could also mean the selection of the biological model which we would like to get inspired from. If this is what it means then we should provide 2 -3 justified alternatives. So far, Bio. Med. CEP uses the 6 -layered neuro-columns and the model that “old” or originally born event patterns are stored on the lower levels, the acquired or “historical” event patterns are stored in the middle layers and current, “inflying” events are processed on the top-level layer. Although the human brain can only process 120. 000 events per second unconsciously, and around 7 event patterns logically or consciously, but the performance comes from the combination of the event patterns of several layers and the fact that event patterns are not processed every time again. (more in our papers and references) However, in the case of a “fault” in event processing (or trauma situations, etc. ), this is the reason for diseases which could be treated or healed with the proposed U-CEP based approach, what should be covered by WP 6. Andrew Hunter (Ulincoln): …the focus that now really makes sense for us is on sensor/signal interpretation, real-time, using specialized parallel hardware (FPGA) and neurally-inspired architectures. In the BRAINS project, funded by the UK's Trade and Strategy Board, we have built a neurally-inspired architecture that has a number of modular computational capabilities, including collision detection, pattern recognition, anomaly detection and operates at high-speed, low current-consumption and therefore suitable for portable and/or wearable devices, and because FPGA-based has low reconfiguration/redesign costs. On the back of this we have built the world's first fully functional video-based security surveillance system programmed solely on FPGA, incorporation the full pipeline of video decoding, filtering, feature extraction, tracking, pattern recognition, anomaly detection of signal output. We would therefore like to contribute to WP 2 in the development of FPGA-based cognitive computing chips, the key concepts being: Design a neurally-inspired architecture with an architecture sufficiently well-aligned with natural neuronal structure to allow a "sympathetic" mapping, while respecting the architectural differences of the hardware platform (a key realisation for us is that you need to "respect the architecture" to make a really functional FPGA-based neural analogue); Ensure the resulting specialized hardware-based architecture can be integrated directly with sensors on a wearable system, is lowcost, low energy consumption and capable of massive computational demands on real-time scale, exploiting the FPGA inherently parallel architecture; Build neurally-inspired algorithms for signal translation/interpretation for this architecture.

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 3(Complex Event) Processing, Analysis and Modeling): Signal and complex event processing/analysis from multisource data in order to get a deeper understand neural information processing and build a novel dynamic model that would serve the simulation of complex dynamic systems. This model should be able to solve more efficiently real-world problems. Modelling approaches of (class) diagrams for thoughts or bio-markers will be some of the most challenging tasks in the Bio. Med. CEP project. "Mind reading„ and If we model a class diagram of "Thought" as software engineers, we would probably model it similarly to a "Notification Event Architecture of <domain>" like NEAR for the Retail domain - as a reference model of "Thought", not of "Thinking", because a class diagram does not model dynamics. The class diagram might become very complex, starting from a superclass of "Thought" with a lot of subclasses of special thoughts or components (Gen/Spec) and their attributes and operations or methods and a lot of associations, compositions, aggregations and so on. . . When we have this, we can define patterns and look for them in the brain and map them to machines or robots and manage or control them via "just thinking". Or vice versa and enhance the human by HET or by an exocortex as we have sketched it in our papers and references. Mind reading and what a human is thinking - based on a catalogue of thoughts or thinking patterns correlated with realtime f. MRI brain activity patterns. The most challenging part is probably the modelling of the class diagram We shall cooperate with other accordant projects from John Dylan-Haynes, Max-Planck-Institute für Kognitions- und Neurowissenschaften in Leipzig , UCLA's Laboratory of Integrative Neuroimaging Technology, etc. See also the Comparison of neuro-science or brain projects http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=257&p=1312#p 1301 The problem of modeling the context: What "context" or “world knowledge" means and why it is important as a precondition to model and trigger the accordant (re-) actions based on complex event patterns… When do we have to start on which level with modeling the context? Is there a hierarchy of contexts or a relationship between contexts? How do we model context? By UML and its class-, state- or activity diagrams? Or directly as SQL-like or another EPL code without any abstraction level? We have to check what the "studios" of all the CEP- or ed(B)PM platforms can offer or must be enhanced. There was also already an initiative of the OMG (Jim Odell) to standardize a notation, but is not started yet. We should such standardizing make a task in Bio. Med. CEP. http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=252&start=20#p 1317

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 4 (Model Validation): This WP validates theoretically based results of WP 3 and brings together the international key players of relevant technologies as named in WP 3. …

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 5 (Beyond Senses BCI) We focus on enhancing the sensitivity range of a sense and adding new senses – through brain-computer interfaces (BCI) exploiting the model developed in WP 3. This WP will develop and exploit an U-CEP based Exocortex and will experiment with an approach to map such enhanced sensitivity ranges and additional senses to the limited event processing capabilities of a human brain. Examples might be to smell pollution or radioactivity via new body area networks, bio-sensors, event adapters, etc. , as sketched http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=299 plus to (re-) act accordingly via (pre-) modeled processes. Another example might be to add a magnetic sense and to experiment with human behaviour and adapting brain functioning (according to first hints from belt technology, see U Osnabrück). More applications and examples for enhanced sensivity ranges and additional senses will be elaborated.

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 6 (Real-World Clinical Applications): All clinical applications are organized in WP 6 where we work on understanding the human brain and healing diseases by changing the event processing of a human brain or to “reboot” a brain (see Brain. Port, …) or to delete “false event patterns” in the memory (see http: //forum. complexevents. com/viewtopic. php? f=13&t=257&start=10#p 1316). This is seen as a “fault” in event processing (as a consequence of trauma situations, accidents, etc. ), what is the reason for diseases (balance, depression, …) which could be treated or healed with the proposed U-CEP based approach. To find accordant “treatments” will also help to learn more about the brain and to find more functions and applications of neuro-biologically inspired systems. Typical, main health problems and diseases of the today’s society (like ageing, depression, diabetes, obesity) are addressed. Each problem or disease represents a discriminant challenge of the Bio. Med. CEP approach. …

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 7 (Impact Assessment): …. Insert your suggestions

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 8 (Training): …. Insert your suggestions

Comments wrt the Workpackages: WP 9 (Dissemination and Exploitation) …. Insert your suggestions … isn’t exploitation already covered by WP 5 and WP 6? ? ? So we should only focus on Dissemination with WP 9? ? ? Dimitris: “Exploitation” usually refers to a formal viability study/exploitation plan that refers to the way the project’s results will and can be exploited after the end of project e. g. commercial products, possible chain reaction of future research that could be triggered etc.
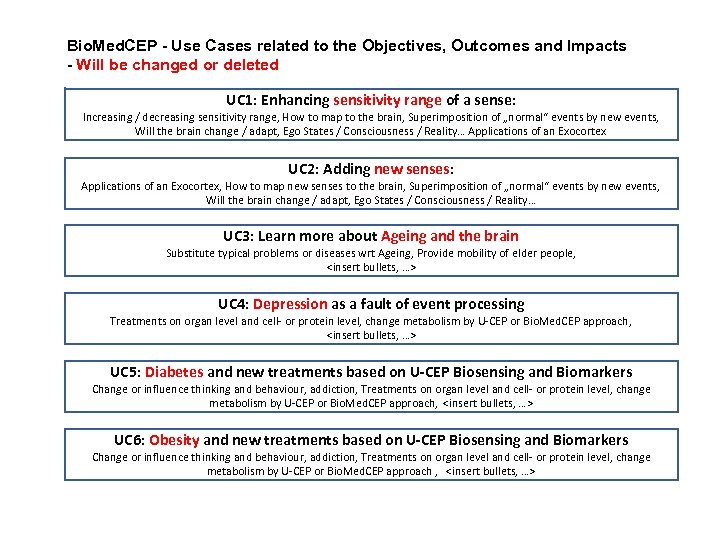
Bio. Med. CEP - Use Cases related to the Objectives, Outcomes and Impacts - Will be changed or deleted UC 1: Enhancing sensitivity range of a sense: Increasing / decreasing sensitivity range, How to map to the brain, Superimposition of „normal“ events by new events, Will the brain change / adapt, Ego States / Consciousness / Reality… Applications of an Exocortex UC 2: Adding new senses: Applications of an Exocortex, How to map new senses to the brain, Superimposition of „normal“ events by new events, Will the brain change / adapt, Ego States / Consciousness / Reality… UC 3: Learn more about Ageing and the brain Substitute typical problems or diseases wrt Ageing, Provide mobility of elder people, <insert bullets, …> UC 4: Depression as a fault of event processing Treatments on organ level and cell- or protein level, change metabolism by U-CEP or Bio. Med. CEP approach, <insert bullets, …> UC 5: Diabetes and new treatments based on U-CEP Biosensing and Biomarkers Change or influence thinking and behaviour, addiction, Treatments on organ level and cell- or protein level, change metabolism by U-CEP or Bio. Med. CEP approach, <insert bullets, …> UC 6: Obesity and new treatments based on U-CEP Biosensing and Biomarkers Change or influence thinking and behaviour, addiction, Treatments on organ level and cell- or protein level, change metabolism by U-CEP or Bio. Med. CEP approach , <insert bullets, …>
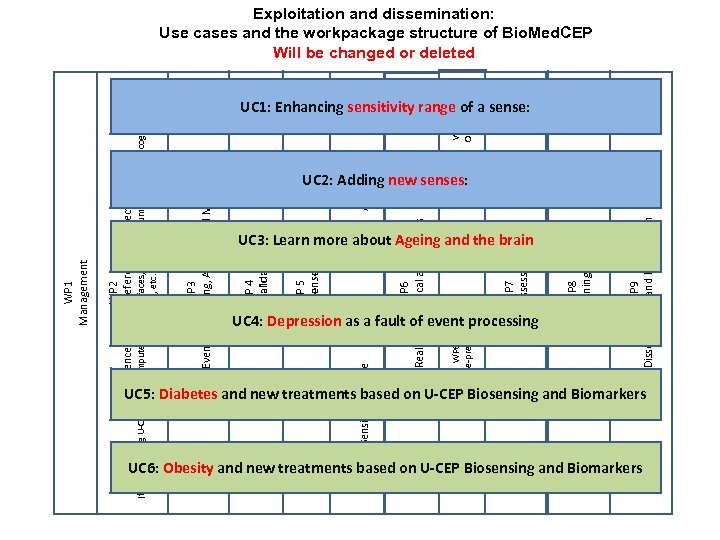
WP 2 Reference model + reference architecture WP 1 Management UC 5: Diabetes and new treatments based on U-CEP Biosensing and Biomarkers UC 6: Obesity and new treatments based on U-CEP Biosensing and Biomarkers WP 6. 1 Ageing UC 4: Depression as a fault of event processing WP 5 Beyond senses BCI WP 4 Model validation UC 3: Learn more about Ageing and the brain WP 6. 3 Diabetes WP 9 Dissemination and Exploitation WP 8 Training WP 7 Impact assessment WP 6. 2 De-pression WP 6 Real-world clinical applications WP 5. 1 Sensitivity Range WP 5. 2 Add senses WP 3 (Complex Event) Processing, Analysis and Modeling WP 6. 4 Obesity (for integrating U-CEP, Brain Computer Brain Interfaces, BAN, Quantum Computing or cogntive comp. chips, etc. ) Exploitation and dissemination: Use cases and the workpackage structure of Bio. Med. CEP Will be changed or deleted UC 1: Enhancing sensitivity range of a sense: UC 2: Adding new senses:
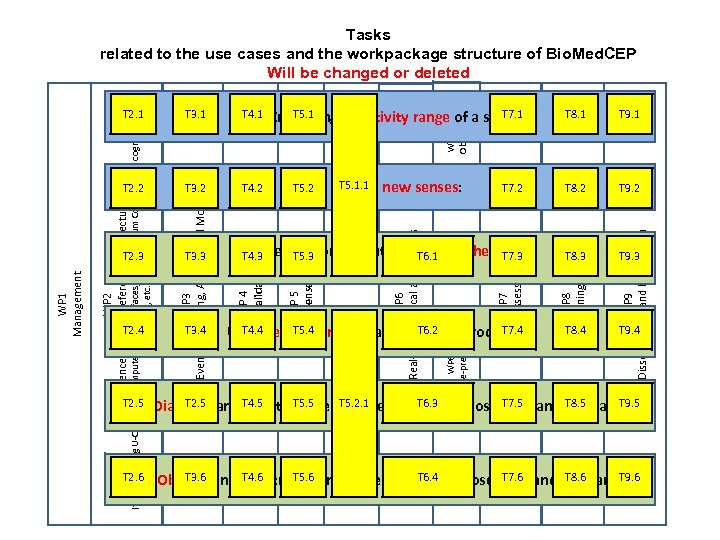
T 2. 2 T 8. 1 T 9. 1 T 8. 2 T 9. 2 T 3. 4 T 4. 4 T 5. 4 T 7. 4 UC 4: Depression as a fault of. T 6. 2 processing event WP 5. 1 Sensitivity Range WP 7 Impact assessment UC 3: Learn more about Ageing and the brain T 4. 3 T 5. 3 T 6. 1 T 7. 3 WP 6. 2 De-pression T 3. 3 T 8. 3 T 9. 3 T 8. 4 WP 9 Dissemination and Exploitation T 7. 2 WP 8 Training new senses: WP 6. 3 Diabetes T 5. 2 Adding UC 2: T 5. 1. 1 WP 6 Real-world clinical applications WP 5. 2 Add senses T 4. 2 WP 5 Beyond senses BCI T 2. 4 T 3. 2 WP 4 Model validation T 9. 4 T 2. 5 T 7. 5 T 9. 5 T 5. 2. 1 UC 5: Diabetes and T 4. 5 treatments based on T 6. 3 Biosensing and T 8. 5 new T 5. 5 U-CEP Biomarkers WP 6. 1 Ageing WP 1 Management T 2. 3 T 4. 1 T 5. 1 T 7. 1 UC 1: Enhancing sensitivity range of a sense: WP 6. 4 Obesity T 3. 1 WP 2 Reference model + reference architecture T 2. 1 WP 3 (Complex Event) Processing, Analysis and Modeling (for integrating U-CEP, Brain Computer Brain Interfaces, BAN, Quantum Computing or cogntive comp. chips, etc. ) Tasks related to the use cases and the workpackage structure of Bio. Med. CEP Will be changed or deleted T 6. 4 T 2. 6 T 3. 6 T 4. 6 T 5. 6 T 7. 6 T 8. 6 T 9. 6 UC 6: Obesity and new treatments based on U-CEP Biosensing and Biomarkers
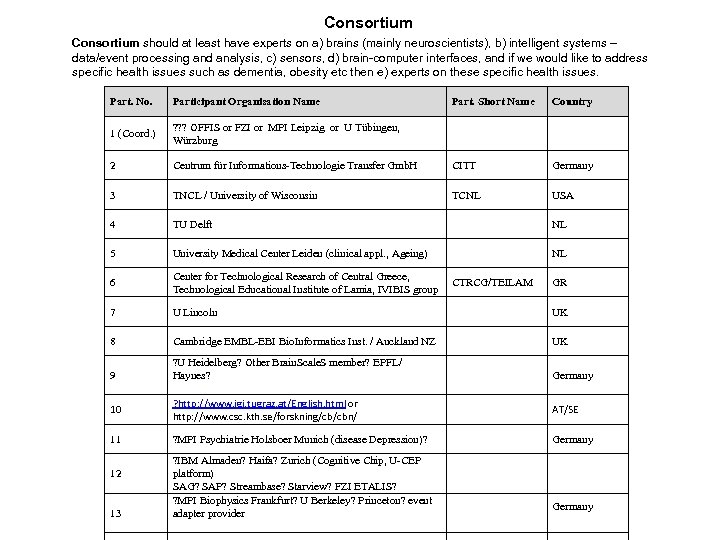
Consortium should at least have experts on a) brains (mainly neuroscientists), b) intelligent systems – data/event processing and analysis, c) sensors, d) brain-computer interfaces, and if we would like to address specific health issues such as dementia, obesity etc then e) experts on these specific health issues. Part. No. Participant Organisation Name Part. Short Name Country 1 (Coord. ) ? ? ? OFFIS or FZI or MPI Leipzig or U Tübingen, Würzburg 2 Centrum für Informations-Technologie Transfer Gmb. H CITT Germany 3 TNCL / University of Wisconsin TCNL USA 4 TU Delft NL 5 University Medical Center Leiden (clinical appl. , Ageing) NL 6 Center for Technological Research of Central Greece, Technological Educational Institute of Lamia, IVIBIS group 7 U Lincoln UK 8 Cambridge EMBL-EBI Bio. Informatics Inst. / Auckland NZ UK 9 ? U Heidelberg? Other Brain. Scale. S member? EPFL/ Haynes? Germany CTRCG/TEILAM GR 10 ? http: //www. igi. tugraz. at/English. html or http: //www. csc. kth. se/forskning/cb/cbn/ AT/SE 11 ? MPI Psychiatrie Holsboer Munich (disease Depression)? Germany 12 13 ? IBM Almaden? Haifa? Zurich (Cognitive Chip, U-CEP platform) SAG? SAP? Streambase? Starview? FZI ETALIS? ? MPI Biophysics Frankfurt? U Berkeley? Princeton? event adapter provider Germany
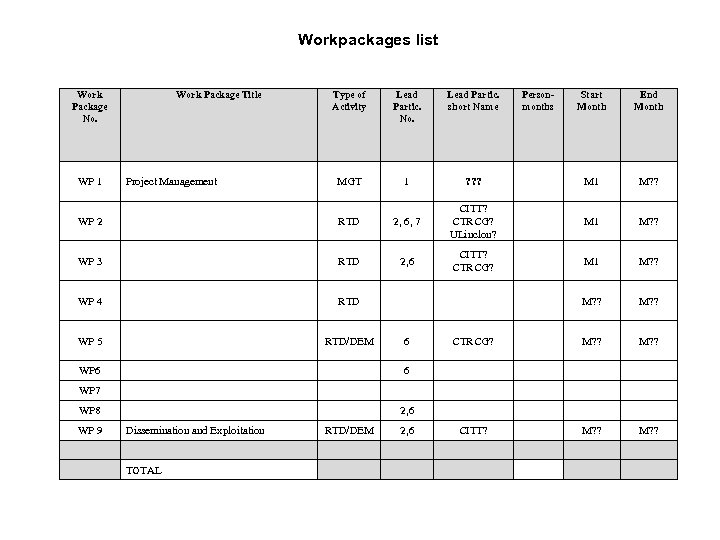
Workpackages list Work Package No. WP 1 Work Package Title Project Management Type of Activity Lead Partic. No. Lead Partic. short Name MGT 1 Start Month End Month ? ? ? M 1 M? ? M? ? CTRCG? M? ? CITT? M? ? WP 2 RTD 2, 6, 7 CITT? CTRCG? ULinclon? WP 3 RTD 2, 6 CITT? CTRCG? WP 4 RTD WP 5 RTD/DEM WP 6 6 Personmonths 6 WP 7 WP 8 WP 9 2, 6 Dissemination and Exploitation TOTAL RTD/DEM 2, 6
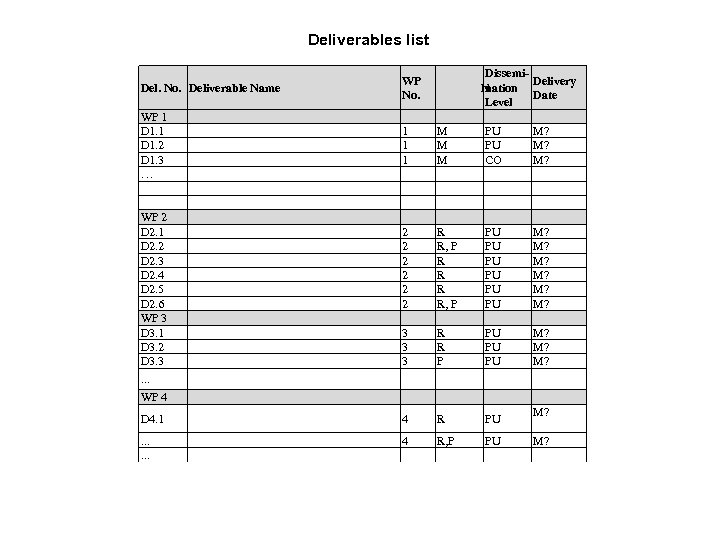
Deliverables list Dissemi. Delivery N nation Date Level Del. No. Deliverable Name WP No. WP 1 D 1. 2 D 1. 3 … 1 1 1 M M M PU PU CO M? M? M? 2 2 2 R R, P PU PU PU M? M? M? 3 3 3 R R P PU PU PU M? M? M? D 4. 1 4 R PU . . . 4 R, P PU WP 2 D 2. 1 D 2. 2 D 2. 3 D 2. 4 D 2. 5 D 2. 6 WP 3 D 3. 1 D 3. 2 D 3. 3. . . WP 4 M? M?
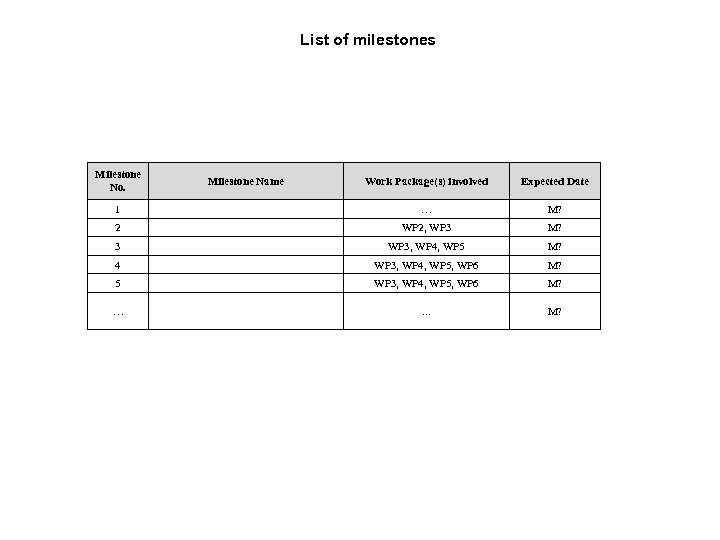
List of milestones Milestone No. Milestone Name Work Package(s) involved Expected Date 1 … M? 2 WP 2, WP 3 M? 3 WP 3, WP 4, WP 5 M? 4 WP 3, WP 4, WP 5, WP 6 M? 5 WP 3, WP 4, WP 5, WP 6 M? … . . . M?
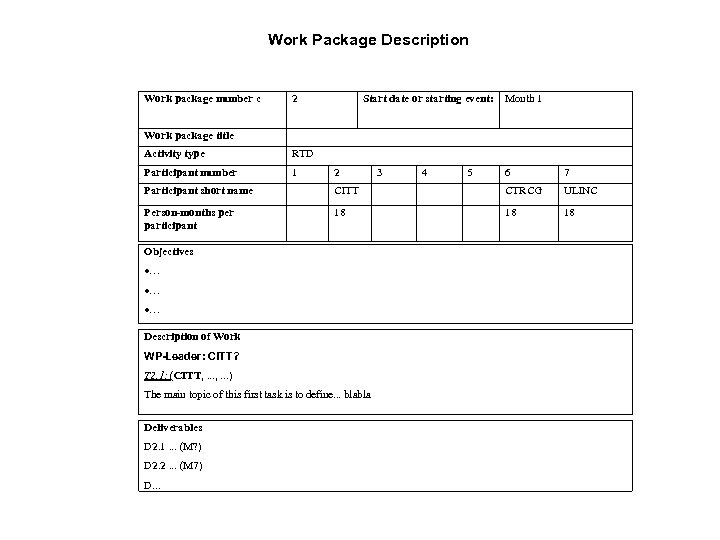
Work Package Description Work package number c 2 Start date or starting event: Month 1 Work package title Activity type RTD Participant number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Participant short name CITT CTRCG ULINC Person-months per participant 18 18 18 Objectives … … … Description of Work WP-Leader: CITT? T 2. 1: (CITT, . . . ) The main topic of this first task is to define. . . blabla Deliverables D 2. 1. . . (M? ) D 2. 2. . . (M 7) D. . .
f1146b3f7cd3bbb9323fb935beb57f90.ppt