840d523bb440d33ef4078a0ef17fd328.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Big Business & Labor How do the “Robber Barons” make their fortunes?

The Robber Barons • Businessmen and bankers who amassed huge personal fortunes, by using unfair business practices 1) A. Carnegie - Steel 4) L. Stanford railroad 2) JP Morgan. Banking 5) C. Vanderbilt – Ships, railroad 3) J. Rockefeller Oil 6) J. Gould banking

Andrew Carnegie • Immigrates from Scotland in 1848 at age 12 • Clerk for the Superintendent the Pennsylvania Railroad by age 18. • Does great job, boss offers him stock in company • Become Superintendent of RR at age 24, starts investing money in other companies (oil, metal, cables) • Forms a steel company in 1870 s, most successful co in US • Sells steel company to US Steel in 1901 for a HUGE profit

Carnegie’s Business Strategy 1. Vertical Integration: Buy out suppliers of needed products and services so you control production top to bottom 2. Horizontal Integration: buy out competing producers so you are only co that offers that business 3. Pay workers low wages

John Rockefeller & Standard Oil Trust • Rockefeller makes Standard Oil one of the biggest and most profitable American cos • Rockefeller tactics: • Paid very low wages, lowered prices to force competition to sell • Formed trusts, trusts bought out companies (avoids monopoly laws)

Government Reaction to “robber barons” -Govt wants to protect free market, but feared big business is hurting competition -Sherman Anti-trust Act, 1890: tried to stop monopolies, making it illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade/competition - difficult to enforce

Problems in the workplace 1) Terms of employment: 6 -7 day weeks, 12+ hour days, no vacation, no sick leave 2) Poor physical conditions: polluted and often dangerous 3) Low Wages: so bad that millions of women/children forced to work -Eugene V. Debs forms American Railway Union - Samuel Gompers forms AFL for skilled workers -1905: radical unionists and socialists formed the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) - Goal: organize unskilled labor and semi-skilled workers

Great RR Strike of 1877 -80, 000 railroad workers strike -Shut down most railroad traffic for week -Joined by many other workers, property damage begins -President Hayes authorizes use of federal troops to stop the violence, end the strike

Haymarket Riot, 1886 - Chicago Police kill a striker. 3, 000 gather to protest the police killing of striker, Chicago Mayor sends in Police to breakup the protest -someone throws bomb into police line, 7 police killed -Public opinion begins to turn against unions and strikes, connecting them to violence
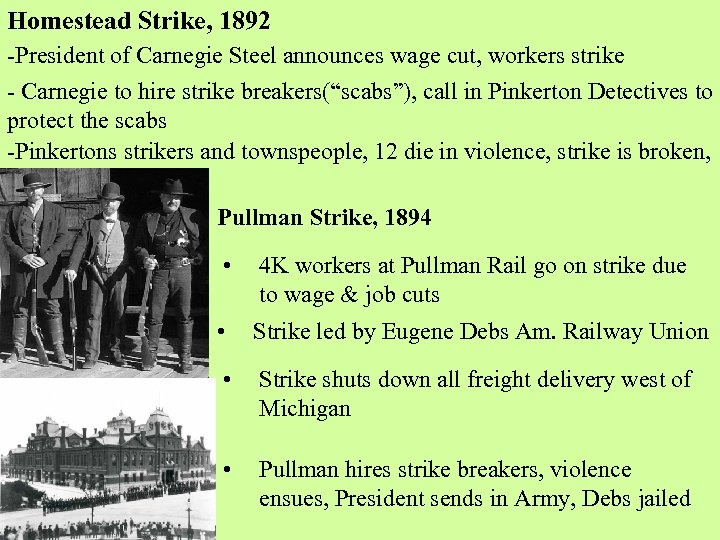
Homestead Strike, 1892 -President of Carnegie Steel announces wage cut, workers strike - Carnegie to hire strike breakers(“scabs”), call in Pinkerton Detectives to protect the scabs -Pinkertons strikers and townspeople, 12 die in violence, strike is broken, Pullman Strike, 1894 • 4 K workers at Pullman Rail go on strike due to wage & job cuts • Strike led by Eugene Debs Am. Railway Union • Strike shuts down all freight delivery west of Michigan • Pullman hires strike breakers, violence ensues, President sends in Army, Debs jailed
840d523bb440d33ef4078a0ef17fd328.ppt