6784b2e4e65e64feabb08b7b593a93b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

BGS Customer Relationship Management Chapter 1 Introduction to Customer Relationship Management Thomson Publishing 2007 All Rights Reserved

OLD VS. NEW MARKETING • OLD MARKETING – – – Transaction oriented Market share oriented All customers are equal Marketers sell 4 P marketing Mass marketing Sell to the customer Focus on new customers Offensive Broadcast oriented Transaction profit • NEW MARKETING – – – Relationship oriented Share of wallet oriented All customers are not equal Marketers manage demand Relationship marketing Individual marketing Manage customer experience Focus on existing customers Defensive Dialogue oriented Customer lifetime value

Five Different Orientations Toward CRM 1. CRM is software, system, technology. 2. CRM is data storage and analysis. 3. CRM is a change in corporate culture from a transaction focus to a customer centric one. 4. CRM is “managing demand. ” 5. CRM is a strategy cycle focusing on customers.

A CRM System Contains Four Components • Data warehouse • Analytical tools • Campaign management tools • Interfaces to maintain databases

CRM System Failure When CRM systems fail, it tends to be as a result of cultural as opposed to technological issues.

The Market Share Fallacy Increasing market share should not be a company’s goal. Rather, increasing share of the right kinds of customers should be the goal.

CRM is Founded on Four Tenets 1. 2. 3. 4. Customers should be managed as important assets. Not all customers are equally desirable. Customers vary in their needs, preferences, and buying behavior. By better understanding their customers, companies can tailor their offerings to maximize their overall value.
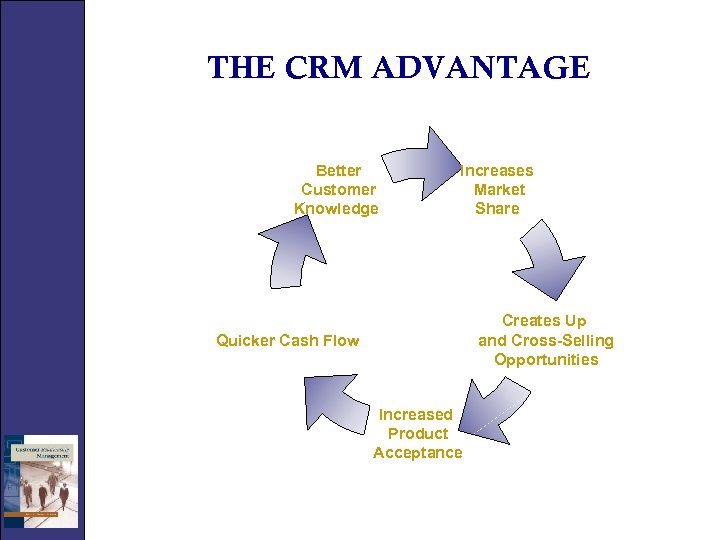
THE CRM ADVANTAGE Better Customer Knowledge Increases Market Share Creates Up and Cross-Selling Opportunities Quicker Cash Flow Increased Product Acceptance

Definition “Customer Relationship Management is the initiation, enhancement, and maintenance of mutually beneficial customer and partner long-term relationships through business intelligence-generated strategies based on the capture, storing, and analysis of information gathered from all customer and partner touch points and transaction processing systems. ” Baran, Galka, Strunk

Do You Want To Keep These Customers? • • • Do not buy frequently Buy your products only when they are on sale Frequently return your merchandise Complain a lot Recommend your company to others just like them

Offensive vs. Defensive Marketing • OM refers to increasing your customer base. • DM refers to activities aimed at existing customers. – Defensive marketing has become more profitable. “Mass and Blast” is being replaced by 1: 1.

Why CRM Systems are Being Used • • • Identifying prospects Acquiring customers Developing customers Cross-selling and up-selling Managing migration Servicing Retaining Increasing loyalty Winning back defectors

Four Basic Steps in CRM 1. ID your customers in detail. 2. Differentiate the most and least profitable. 3. Interact. 4. Customize your offerings to fit each customer’s needs.

CRM Systems • Allow companies to ID and focus on their high-profit customers while enabling companies to transform low -value customers into higher-value ones.

Retail Banks Have Realized the Following Benefits from CRM Benefits • Increase in average products sold per customer over one year from 4. 6 to 6. 2 • 3 -5 percent decrease in administrative costs • 200 percent return on technology investment through cost reduction over one year • 96 percent reduction in average time for a CCC agent to refer a customer to a branch loan office • 83 percent decrease in average customer info retrieval time • 15 percent increase in product revenue in one year

CRM Benefits • Benefits Realized in Retail Banking – Increase in average products sold per customer over one year from 4. 6 to 6. 2 – 3 -5 percent decrease in administrative costs – 200 percent return on technology investment through cost reduction over one year – 96 percent reduction in average time for a CCC agent to refer a customer to a branch loan office – 83 percent decrease in average customer info retrieval time – 15 percent increase in product revenue in one year

A Customer Focus Can Aid Retention • Annual Defection Rates – – – Newspaper subscriptions Residential tree and lawn care U. S. long distance telephone Clothing catalogues Internet service providers Griffen and Lowenstein 2001 66 percent 32 percent 30 percent 25 percent 22 percent

Customer Retention and Profits • Increase retention 5 percent and improve profitability in net present value from 20 -85 percent. • It costs five to ten times more to obtain a new customer than it does to keep an existing one.

The Objectives of CRM • ID potential customers • Understand needs • Differentiate dollars and cents • Decrease attrition • Increase usage • Increase cross usage • Increase usage of more prestigious items • Increase satisfaction • Integrate marketing and sales throughout channels • • Improve campaign management Increase referrals Win back lost customers Move customers up relationship hierarchy – – Strangers Acquaintances Friends Partners

Multichannel Marketing • Over half of all customers in certain industries (apparel and banking) are using multiple channels for shopping and purchasing: store, telephone, ATM/Kiosk, catalogue, online, etc. • Multiple channel users have two to four times more to spend. In retail banking they are 25 -50 percent more profitable.

Customers Transact Business through the Following Channels • • • Web application Free form e-mail Telephone with a live agent Internet VOIP through a live agent Text chat with a live agent Telephone through an interactive VRS Fax ATM/Kiosk Entering the store or branch

Which Companies Benefit Most from CRM? • Companies serving large numbers of customers through complex and frequent interactions: – Communications companies – Retail banks – Insurance companies – Healthcare organizations – Utilities • Companies with a steep skew • Companies in “lost for good” markets
Which Companies Benefit the Least from CRM Today? • Companies that engage in minimal interactions with each customer – Auto dealers – Government agencies • Companies with simple transactions Movie theaters Retail stores

Questions?
6784b2e4e65e64feabb08b7b593a93b2.ppt