
* Bezruckova Olga 10 “Б”

* 1. Introduction 2. Genetics • What is genetics? • About our organism (cells, DNA, RNA, chromosomes, protein) • Genes • Heredity 3. Genetics as a science • Cloning 4. Conclusion
* Genetics is a discipline of biology, the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms.
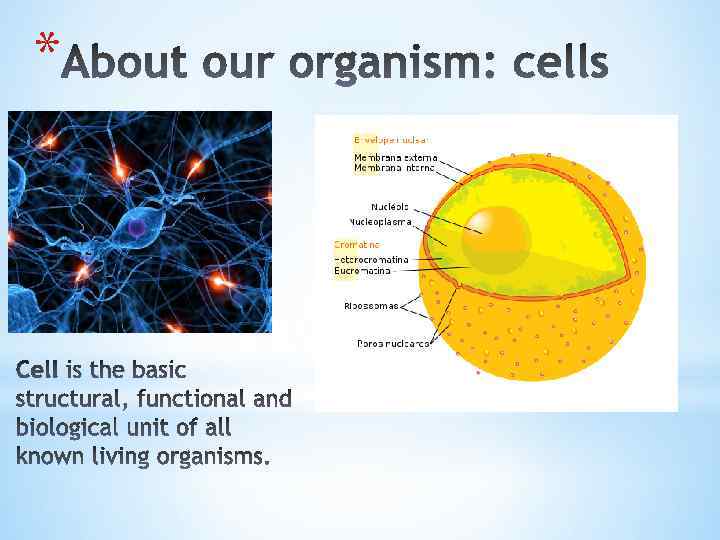
*
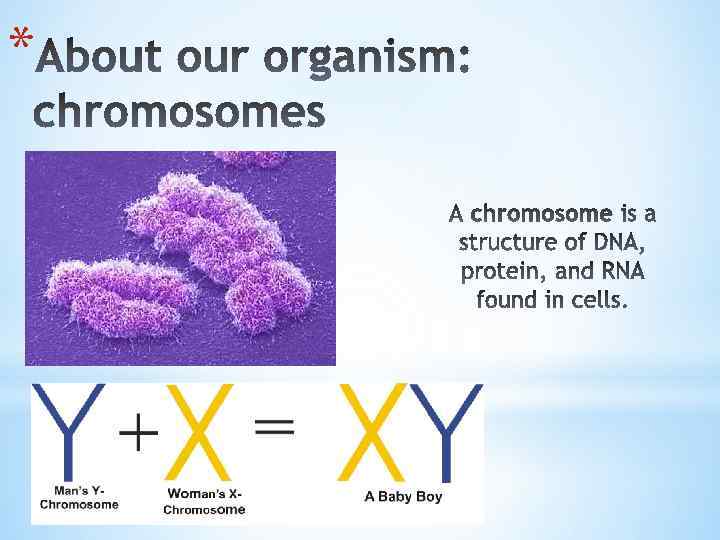
*
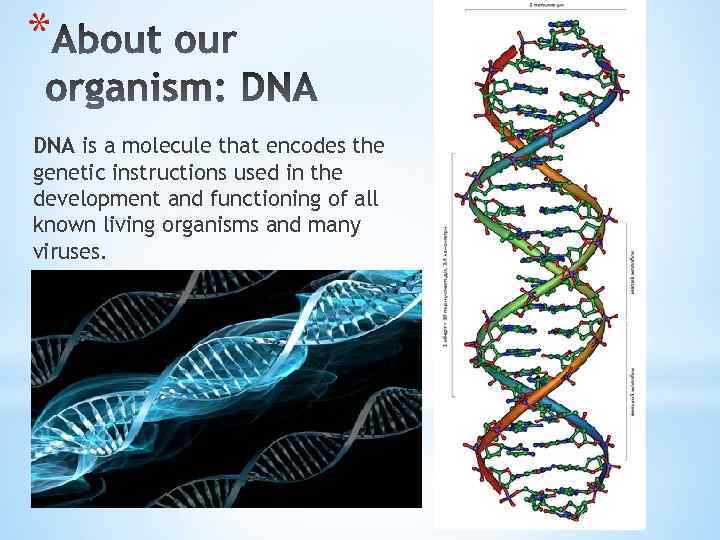
* DNA is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
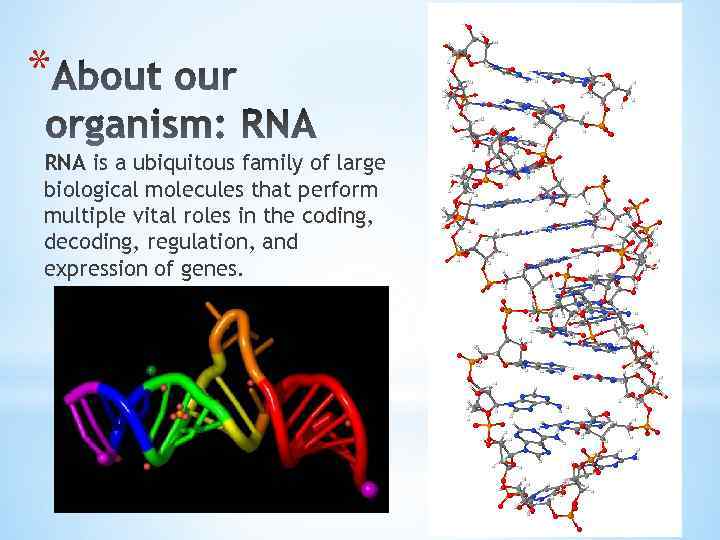
* RNA is a ubiquitous family of large biological molecules that perform multiple vital roles in the coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
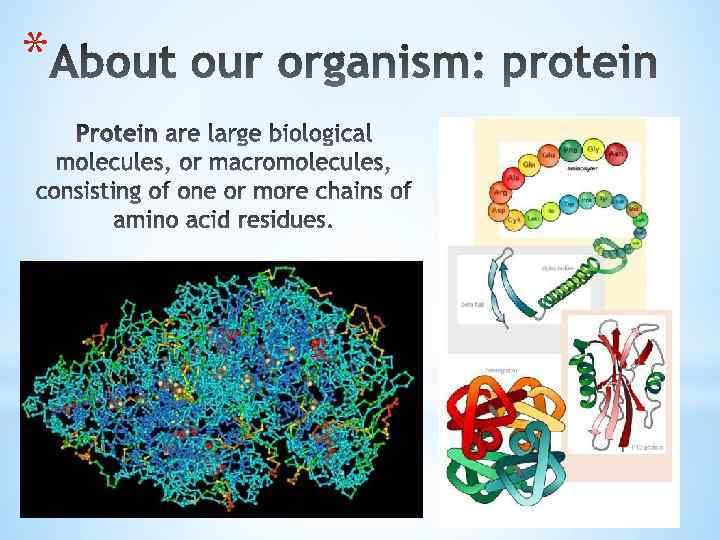
*
* A gen is the molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is used extensively by the scientific community as a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA.
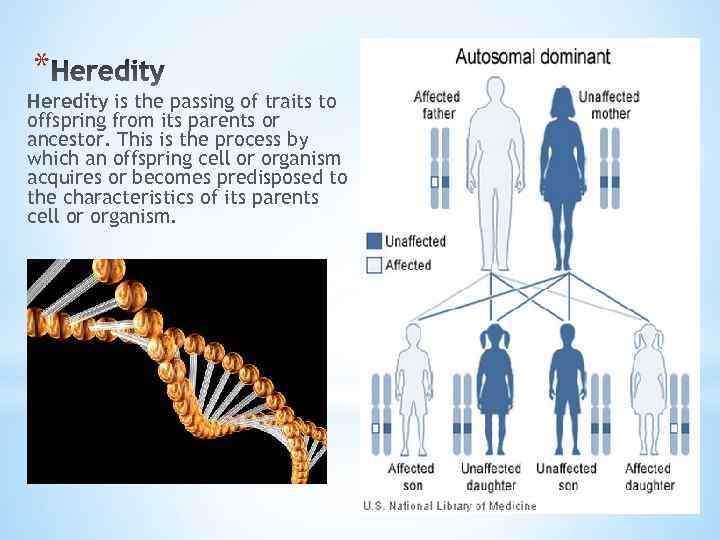
* Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring from its parents or ancestor. This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parents cell or organism.
* Initially genetics studied General laws of heredity and variability on the basis of phenotypic data.
* The understanding of the mechanisms of heredity, which are the roles of genes as elementary carriers of hereditary information, the chromosome theory of heredity, etc. became possible with application to the problem of heredity methods of Cytology, molecular biology and other related disciplines.
* At an institute of pharmaceutical engineering Virginia, USA, scientists injected pigs with a human gene that produces a protein called Factor VIII. The fourth generation of these pigs will possibly produce enough Factor VIII in their milk to supply the world’s demand.
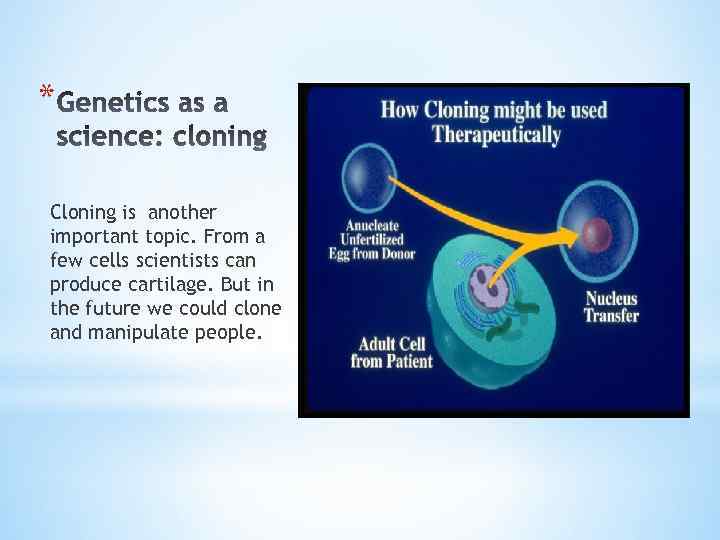
* Cloning is another important topic. From a few cells scientists can produce cartilage. But in the future we could clone and manipulate people.
