69af03764b653d1a3c120df8794e175d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Beyond Virtual Libraries Dr. Laverna Saunders Duquesne University March 17, 2005 3/16/2018 Computers in Libraries

Managing Change n Goal: q q n To present broad environmental trends driving technological change for academic libraries To stimulate ideas for local action “Our world is about to change in a big, big way. ”—Daniel Greenstein, California Digital Library (NY Times, 12 -14 -04) Computers in Libraries

Trend Trackers & Innovators n n n n OCLC Gartner Research Educause CNI Pew Research Center Walt Crawford CIL (of course!) n n n MIT Media Lab MIT AI Lab OCLC R & D Ray Kurzweil Stanford University Carnegie Mellon Univ. Computers in Libraries

Negroponte’s Vision, 1992 “…the campus will be the first place where computing becomes like air…” Trends: n Vanishing desktop n Reversal of roles between wires and wireless transmission n Role of delegation vs. direct manipulation at the interface Computers in Libraries
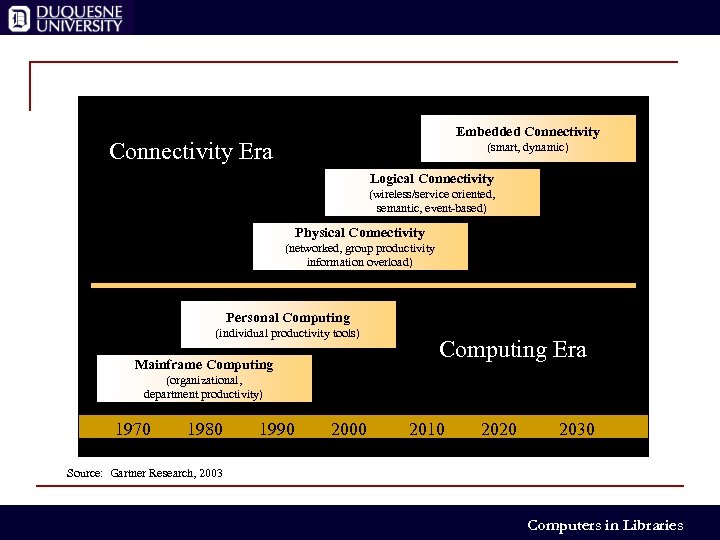
Embedded Connectivity Era (smart, dynamic) Logical Connectivity (wireless/service oriented, semantic, event-based) Physical Connectivity (networked, group productivity information overload) Personal Computing (individual productivity tools) Mainframe Computing Era (organizational, department productivity) 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030 Source: Gartner Research, 2003 Computers in Libraries
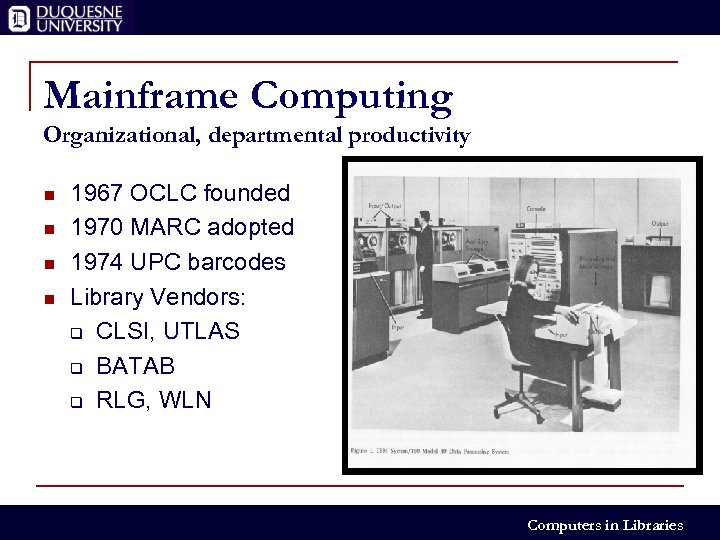
Mainframe Computing Organizational, departmental productivity n n 1967 OCLC founded 1970 MARC adopted 1974 UPC barcodes Library Vendors: q CLSI, UTLAS q BATAB q RLG, WLN Computers in Libraries
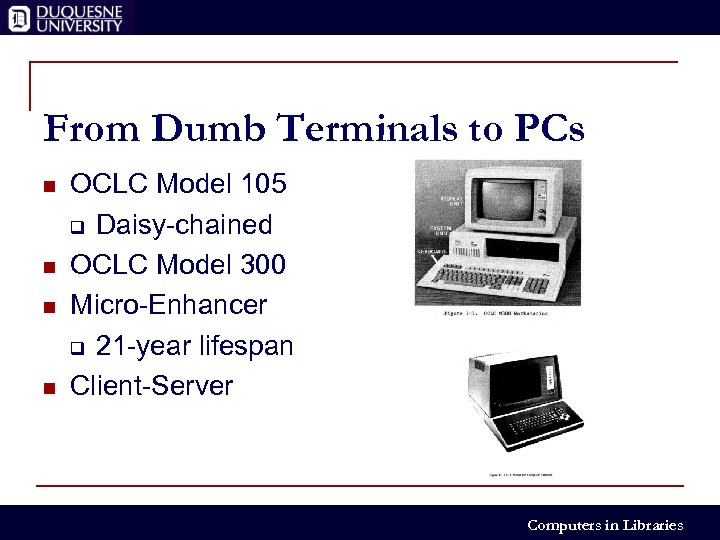
From Dumb Terminals to PCs n n OCLC Model 105 q Daisy-chained OCLC Model 300 Micro-Enhancer q 21 -year lifespan Client-Server Computers in Libraries

Personal Computing Individual Productivity Tools n n 1977 Apple II & Radio Shack TRS-80 1983 IBM PC rules 1983 Apple Macintosh 1984 CD-ROMs in PCs n n n 1985 Aldus Page. Maker 1986 32 -bit chip 1988 GUI 1993 Apple Newton 1996 Palm Pilot Computers in Libraries
Physical Connectivity Networked, Group Productivity n n n 1979 BITNET (Because It’s Time Network) 1985 NSF uses T 1 1987 CREN (Corporation for Research & Educational Computing) n n 1989 WWW created 1991 NREN (National Research & Education Network) 1993 Pres. Clinton promotes Information Superhighway 1993 Mosaic developed Computers in Libraries

Evolving Internet n 1996 Internet 2 http: //www. internet 2. edu q q 207 U. S. universities, working with industry and government to develop advanced network applications “accelerating the creation of tomorrow's Internet” Computers in Libraries

Where are we now? n n Marc Andreessen: I try to look at it in a longterm perspective. Any new technology tends to go through a 25 -year adoption cycle. With the Internet, we're really 10 years into what will ultimately look like a 25 -year cycle from invention to full implementation. (Wired News, Feb. 14, 2003) http: //www. wired. com/news/business/0, 1367, 57661, 00. html Computers in Libraries

Logical Connectivity Wireless/service-oriented n “Five years from now there will be 83 million homes with broadband connections -- nearly as many as the 88 million that now have cable and satellite hookups, according to Bernstein projections. The number of wireless subscriptions in the U. S. will grow 20%, to 243 million, in the same period. ” (Source: Business Week Online, March 7, 2005) http: //www. businessweek. com/magazine/content/05_10/b 3923120_mz 016. htm) Computers in Libraries

Embedded Connectivity Smart, dynamic n n n RFID q Human implants q Future student ID? Smarter library buildings & classrooms More--TBD Computers in Libraries

Demographics & Expectations n n n Builders, born 1901 -1945 Early Boomers, born 1946 -1955 Late Boomers, born 1956 -1964 Gen X, born 1965 -1976 Net Generation (a. k. a. N-Gen, Generation Y, Millennials), born 1977 -2003 Computers in Libraries

N-Gen: Born Digital … Live Digital n n n n IM E-mail Cell phones MP 3 s i. Pods High-speed, high bandwidth Multitasking http: //www. educause. edu/content. asp? page_id= 5989%26 bhcp=1 Computers in Libraries

Interactive & Collaborative Learning n n n 73% current students more likely to use Internet than go to library Learning is more like Nintendo (trial & error) than logic File-sharing, keyboarding, cut & paste Computers in Libraries

New Customer Services n Students Expect q q q q 24 x 7 Prompt responses Everything digital Fast connectivity Mobility Paperless Spaces for groups n Universities & Libraries q q q q Portals IM Virtual Reference Electronic Resources CMS + resource links E-portfolios Group study areas Computers in Libraries

n n Ubiquitous (like air) OCLC collaboration and Google Scholar Digitizing > 15 million books of research libraries @ cost of $10 (Harvard, Michigan, Stanford, NYPL, Oxford) Google as the #1 largest library by 2025 q “Stand on the shoulders of giants” Computers in Libraries

Publishing Trends n n n More E-books (selective) and E-Journals Aggregators vs. Publishers control Corporate control Fate of University Presses? SPARC & Create Change Open Access q q Public Library of Science Bio. Med Central Computers in Libraries

Digital Libraries & Repositories n n n Library of Congress Internet Archive California Digital Library e. Scholarship Repository DSpace Vendor products Computers in Libraries

Budget Impact n n n Budget reallocation from print to electronic and technology support Pressures toward cooperative collection development for print Shared remote storage facilities house older, littleused print collections Preservation for > formats Joint repositories Jurisdictional concerns Computers in Libraries

Copyright & Licensing Concerns n n Amazon/Google: teaser selections of copyrighted books; costs, pricing not known Contract law vs. copyright law & fair use Individual libraries lack clout of consortia Who owns the intellectual property rights? Computers in Libraries

Libraries and Learning n n n Extension of the classroom or lab Librarians teaching Active learning zones Support e-learning & CMS Outcomes assessment Accreditation standards Computers in Libraries
Learning Objects n n n Any digital resource that can be reused to support learning Examples: animation, simulation, interactive map, game, applet Usually developed by faculty http: // www. priweb. org/ed/earthtrips. html Computers in Libraries

Rich Media n n n May improve learning outcomes Improves student satisfaction and retention, increases time-on-task Opportunity to create a diverse, global network of learning object developers and repositories of high-quality, pedagogically sound materials DOD standard: SCORM (Shareable Content Object Reference Model) New opportunity for library involvement Computers in Libraries

Redefining Roles n New Opportunities: q q q q Virtual Reference Knowledge Managers Partnerships with faculty and campus IT Instructional design Teaching Technical skills Reinventing core functions Computers in Libraries

Beyond Virtual Libraries and … n n Toward convergence and integration of multiple technologies for learning and communication Toward the library as a repository of content in many formats, searchable and linked to learning systems Toward digital assets accessed by users Toward more change and lifelong learning Computers in Libraries

Toward Ubiquity Computers in Libraries
69af03764b653d1a3c120df8794e175d.ppt