09ef40793af132762f21e175c13e177a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81

Beyond Moore’s Law The best way to predict the future is to invent it. --Alan Kay Gordon Bell Bay Area Research Center Microsoft Corporation Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Beyond Moore’s Law Just FCB (faster, cheaper, better)… COTS will soon mean consumer off the shelf n Moore’s Law and technology progress likely to continue for another decade for: n processing, memory, storage, LANs, WANs System-on-a chip of interesting sizes will emerge to create 0 cost systems n Any displacement technology is unlikely … Carver Mead’s Law c 1980 A technology takes 11 years to get established n On the other hand, we are on Internet time! n No DNA, molecular, or quantum computers, or Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws new stores n

Beyond Moore’s Law Results n n n n Is the Internet aka www. everything? Moore’s Law to get cheaper, one chip systems that increase portability, ubiquity, etc. Paper-competitive Screens Disks of 1 TB Wireless for ubiquity; including GPS Bridges to television Bridges to PSTN for phones, PDAs, etc. Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Beyond Moore’s Law Results n n n The more uniform the system, the more attractive it is for developers to produce many varieties of low cost apps The more uniform the system, the more susceptible they are to viruses Change will be due to ubiquity of computing brought about by networking PLUS Interesting, new platforms that interface use/users When can we speak to these computers? – Sensors e. g. cameras of all types – GPS and direction (pointing) – MEMS & Biochips in particular – laws and Computing Laws forces, beyond Moore’s Law that determine IT n. Copyright Gordonmany other There are Bell & Jim Gray

Big event of 1999: massive infusion of venture capital n n n >$3 Billion/quarter (1/3 for Internet). …Esprit $3 B/3 yrs Capital is pulling people from research. Product development beats research if you have an idea what you’re looking for Little technology. Apps development. 1960 -2000: shift from central to distributed back to fully distributed computing Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
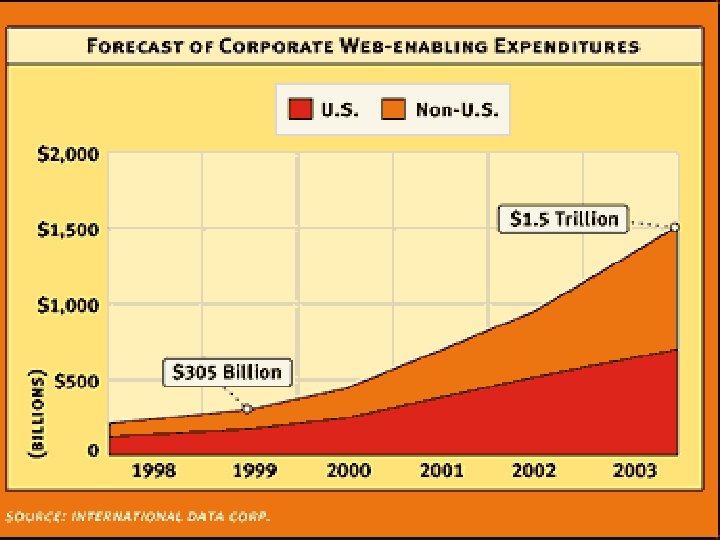
Forecast of corp web-enabled expenditures Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

In a decade we can/will have: n more powerful personal computers processing 10 -100 x – 4 x resolution (2 K x 2 K) displays to impact paper – Large, wall-sized and watch-sized displays – low cost, storage of one terabyte for personal use – n adequate networking? ? ubiquitous access = today’s fast LANs – Competitive wireless networking – One chip, networked platforms including light bulbs, cameras everywhere, etc. n Some well-defined platforms that compete with the PC for mind (time) and market share watch, pocket, body implant, home n Inevitable, continued cyberization… the challenge… interfacing platforms and people. n

What if could or when can we store everything we’ve: read/written, heard, and seen? Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Storing all we’ve read (written), heard (listened to), & seen (presented) Human data-types read text, few pictures /hr 200 K /day (/4 yr) 2 -10 M/G /lifetime 60 -300 G speech text @120 wpm speech @1 KBps 43 K 3. 6 M 0. 5 M/G 40 M/G 15 G 1. 2 T video-like 50 Kb/s POTS video 200 Kb/s VHS-lite 22 M 90 M . 25 G/T 1 G/T 25 T 100 T video 4. 3 Mb/s HDTV/DVD 1. 8 G 20 G/T 1 P Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

High Performance Computing Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
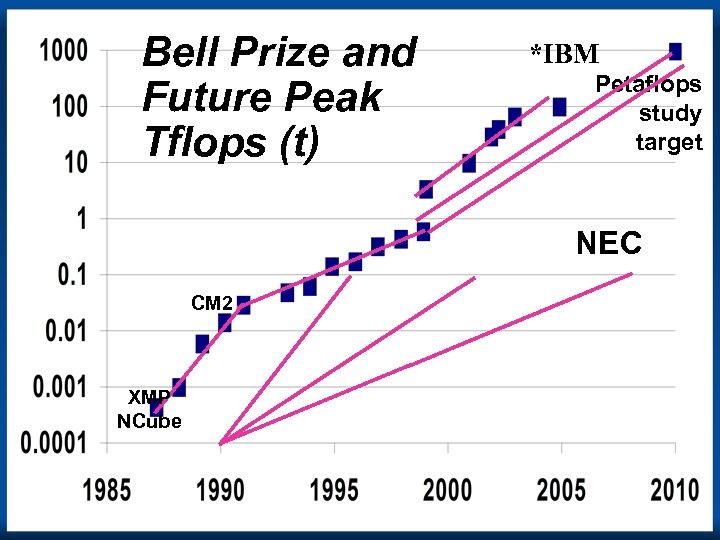
Bell Prize and Future Peak Tflops (t) *IBM Petaflops study target NEC CM 2 XMP NCube Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
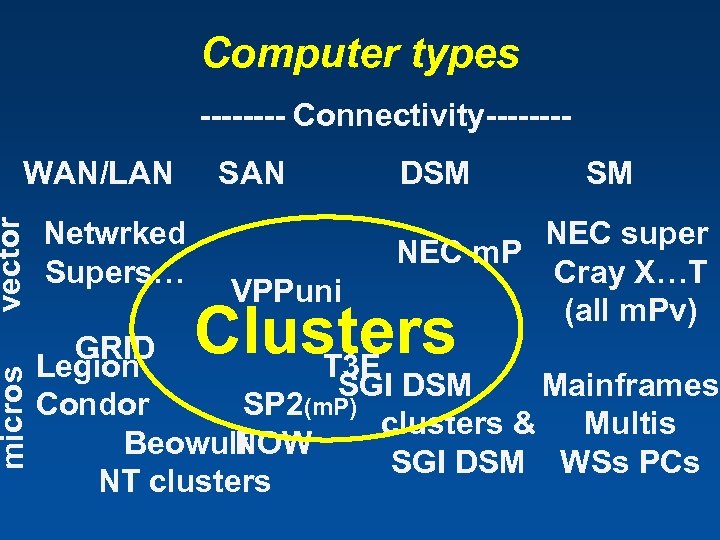
Computer types ---- Connectivity-------DSM SM vector SAN Netwrked Supers… micros WAN/LAN GRID Legion T 3 E SGI DSM Mainframes Condor SP 2(m. P) clusters & Multis Beowulf NOW SGI DSM WSs PCs NT clusters VPPuni NEC super NEC m. P Cray X…T (all m. Pv) Clusters

High Performance Computing n n n Supers we knew are Japanese; scalability & COTS in… but you have to roll your own else pay the Unix & proprietary taxes Beowulf is $14 K/TB ( 6 x 40 GB) IBM 4000 R 1 rack: 2 x 42 500 Mhz processors, 84 GB, 84 disks (3 TB @36 GB/disk) $420 K … still cheaper than the “big buys” $10 -20 K/node for special purpose vs $2 K for a MAC EMC, IBM at $1 million/TB; vs $14 K Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Everything cyberizable will be in Cyberspace and covered by a hierarchy of computers! Continent World Body Region/ Cars… phys. nets Intranet Home… Campus buildings Fractal Cyberspace: a network of … networks of … platforms
Cyberization: interface to all bits and process information Coupling to all information and information processors n Pure bits e. g. printed matter n Bit tokens e. g. money n State: places, things, and people n State: physical networks n Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Bell’s law of computer class formation to cover Cyberspace New computer platforms emerge based on chip density evolution n Computer classes require new platforms, networks, and cyberization n New apps and content develop around each new class n Each class becomes a vertically disintegrated industry based on hardware and software standards n Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
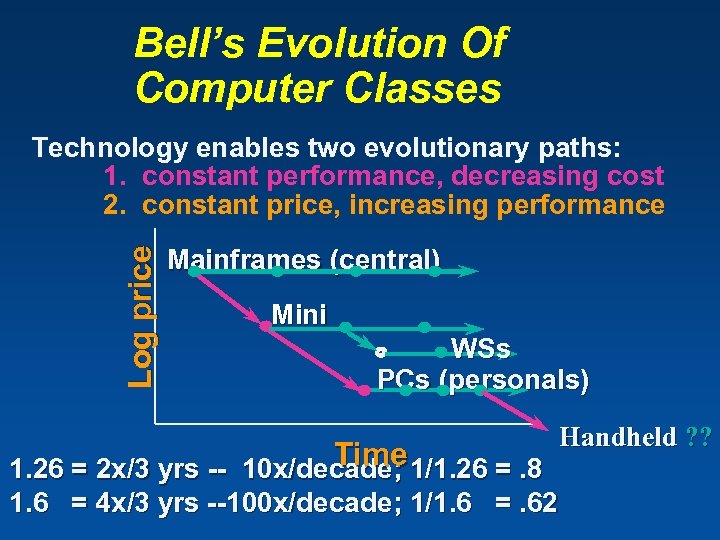
Bell’s Evolution Of Computer Classes Log price Technology enables two evolutionary paths: 1. constant performance, decreasing cost 2. constant price, increasing performance Mainframes (central) Mini WSs PCs (personals) Time 1. 26 = 2 x/3 yrs -- 10 x/decade; 1/1. 26 =. 8 1. 6 = 4 x/3 yrs --100 x/decade; 1/1. 6 =. 62 Handheld ? ?
Platform evolution: What do they do that’s useful? How do they communicate? Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Price, performance, and class of various goods & services Computer price = $10 x 10 class# Computer weight =. 05 x 10 class# Car price = $6 K x 1. 5 class # Transportation artifact prices = k x $10 type (shoes, . . . cars, . . . trains, . . . ICBMs) French Restaurants(t='95) = f(ambiance, location) x $25 x 1. 5 stars

Bell’s Ten+ Computer Price Tiers 1$: embeddables e. g. greeting card 10$: wrist watch & wallet computers 100$: pocket/ palm computers 1, 000$: portable computers 10, 000$: personal computers (desktop) • 100, 000$: departmental computers (closet) 1, 000$: site computers (glass house) 10, 000$: regional computers (glass castle) 100, 000$: national centers 1, 000, 000$: the grid Super server: costs more than $100, 000 “Mainframe”: costs more than $1 million an array of processors, disks, tapes, comm ports

On body and in body networks Third wearables conference Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Libretto, . 5 mm Not shown: ECG; PCS; Pilot GPS; Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Compass; altimeter Libretto PS, Ricoh Camera; Swiss Army Knife Computing Laws

22 years ago: 6 oz. Watch, manual size > watch size Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
Audio, pix, T, P, ECG, location, physiological parameters… 1 GB Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Steve Mann in Cyberspace Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
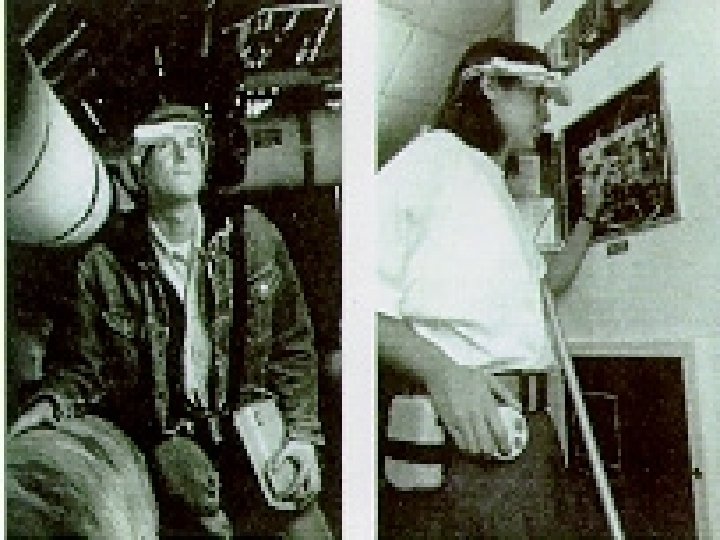
CMU wearable computers Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
M e d r o n I c Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Your husband just died, … here’s his black box Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

When will we have smart rooms? n n n Reasonable sized displays or panel for interaction Cameras that can recognize various people Mics and Speech based interface Speakers Coupled to all power, data, audio, and video/television networks Interval Research has a product to track individuals in stores!

Or be completely covered by a smart world Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

450 Old Oak Ct, Los Altos, CA

Webcams Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Webcam of Hospital in Sweden Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Economics-based laws determine the market n n n n As industries increase, they become horizontal Demand: doubles as price declines by 20% Learning curves: 10 -15% cost decline with 2 X units Nathan’s Laws of Software -- the virtuous circle Bill’s Law for the economics of PC software Linus’s Law for software… it is free plus support Sarnoff & Metcalf Laws for the “value of a network” Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
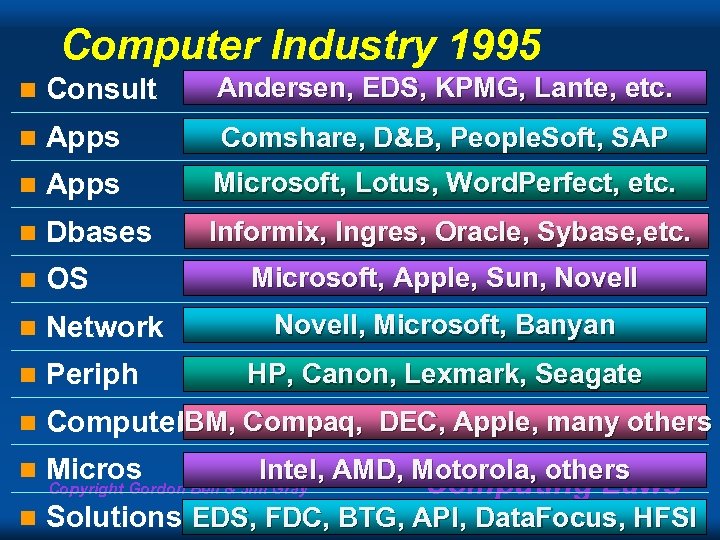
Computer Industry 1995 n Consult Andersen, EDS, KPMG, Lante, etc. n Apps Comshare, D&B, People. Soft, SAP n Apps Microsoft, Lotus, Word. Perfect, etc. n Dbases Informix, Ingres, Oracle, Sybase, etc. n OS n Network n Periph n IBM, Computers Compaq, DEC, Apple, many others n Intel, AMD, Motorola, others Micros Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws n Microsoft, Apple, Sun, Novell, Microsoft, Banyan HP, Canon, Lexmark, Seagate Solutions EDS, FDC, BTG, API, Data. Focus, HFSI
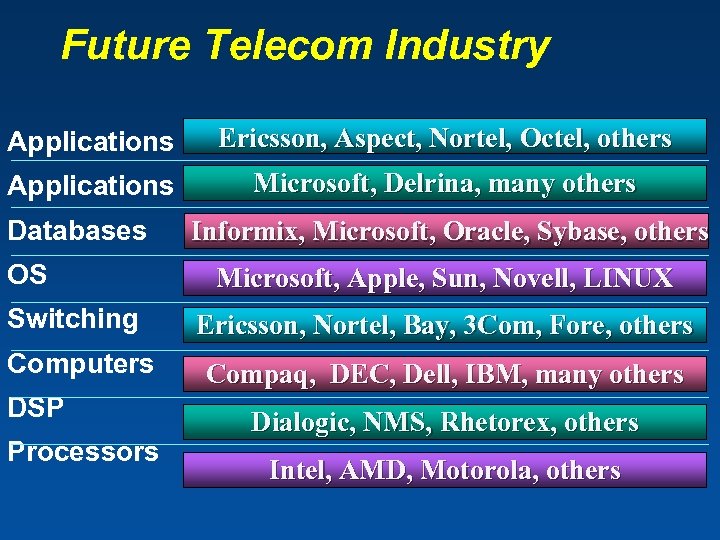
Future Telecom Industry Applications Ericsson, Aspect, Nortel, Octel, others Applications Microsoft, Delrina, many others Databases OS Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, others Microsoft, Apple, Sun, Novell, LINUX Switching Ericsson, Nortel, Bay, 3 Com, Fore, others Computers Compaq, DEC, Dell, IBM, many others DSP Processors Dialogic, NMS, Rhetorex, others Intel, AMD, Motorola, others
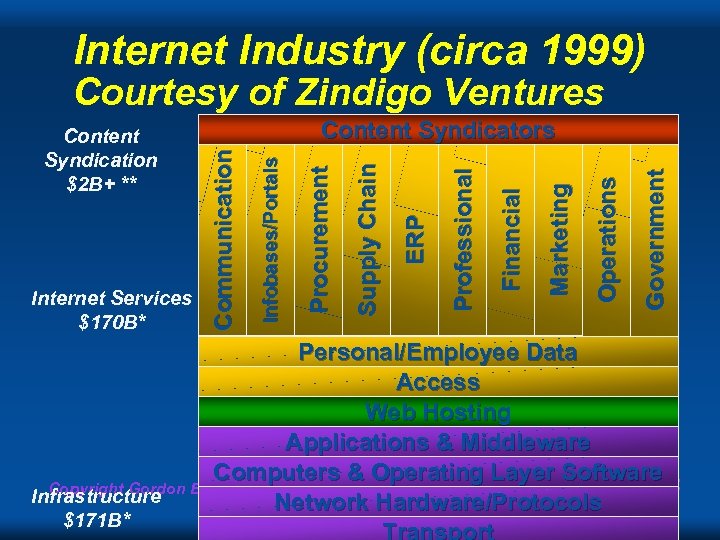
Internet Industry (circa 1999) Courtesy of Zindigo Ventures Government Operations Marketing Financial Professional ERP Supply Chain Procurement Infobases/Portals Internet Services $170 B* Content Syndicators Communication Content Syndication $2 B+ ** Personal/Employee Data Access Web Hosting Applications & Middleware Computers & Operating Layer Software Copyright Gordon Computing Laws Infrastructure Bell & Jim Gray Network Hardware/Protocols $171 B* Transport

Nathan’s Laws of software 1. Software is a gas. It expands to fill the container it is in 2. Software grows until it becomes limited by Moore’s Law 3. Software growth makes Moore’s Law possible 4. Software is only limited by human ambition and expectation …GB: and our ability to cyberize I. e. encode Computing Laws Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray

Software Economics: Bill’s Law Price = Fixed_cost Units + Marginal _cost Bill Joy’s law (Sun): don’t write software for <100, 000 platforms @$10 million engineering expense, $1, 000 price n Bill Gate’s law: don’t write software for <1, 000 platforms @$10 M engineering expense, $100 price n Examples: n –UNIX versus Windows NT: $3, 500 versus $500 –Oracle versus SQL-Server: $100, 000 versus $6, 000 –No spreadsheet or presentation pack on UNIX/VMS/. . . n Commoditization of base software and hardware
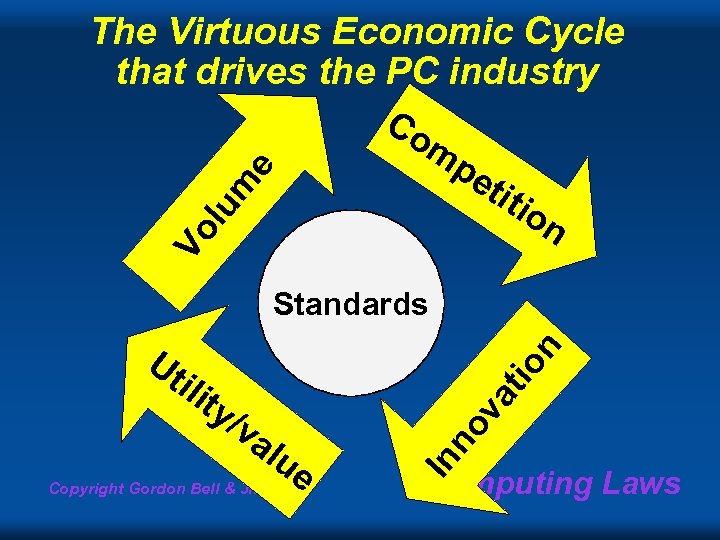
The Virtuous Economic Cycle that drives the PC industry Co mp Vo l um e eti tio n Standards at al u e Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray no v /v In ity io n Ut il Computing Laws

Linus’s Law: Linux everywhere n n n n Software is or should be free All source code is “open” Everyone is a tester Everything proceeds a lot faster when everyone works on one code Anyone can support and market the code for any price Zero cost software attracts users! All the developers write lots of code
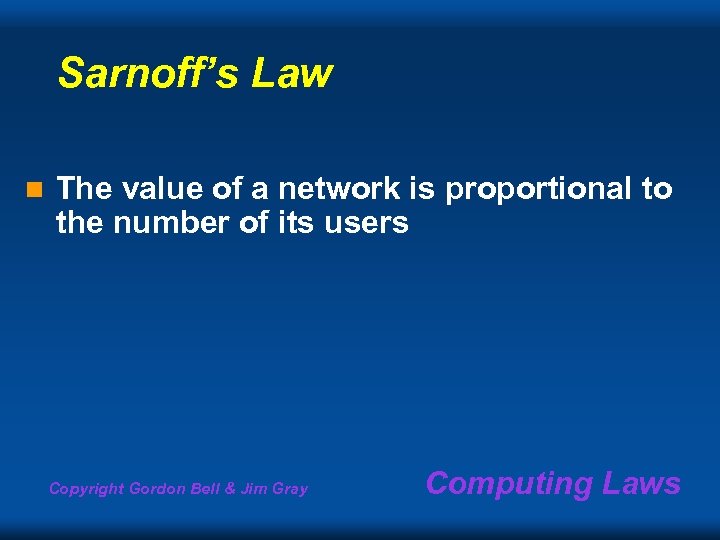
Sarnoff’s Law n The value of a network is proportional to the number of its users Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
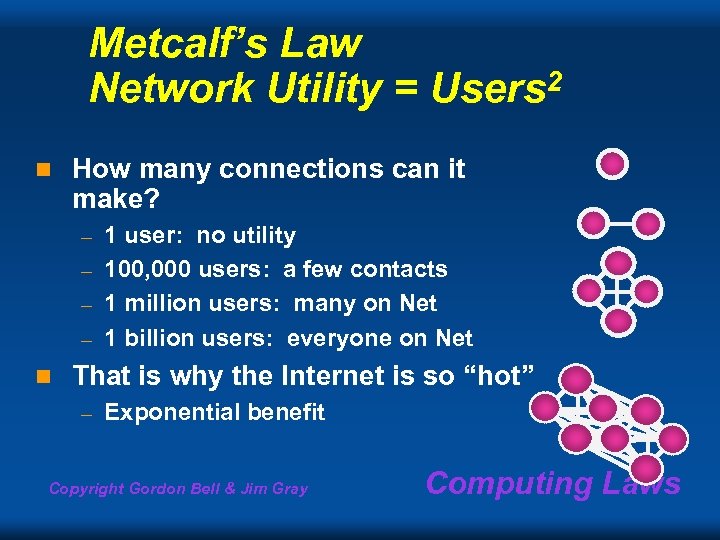
Metcalf’s Law Network Utility = Users 2 n How many connections can it make? 1 user: no utility – 100, 000 users: a few contacts – 1 million users: many on Net – 1 billion users: everyone on Net – n That is why the Internet is so “hot” – Exponential benefit Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
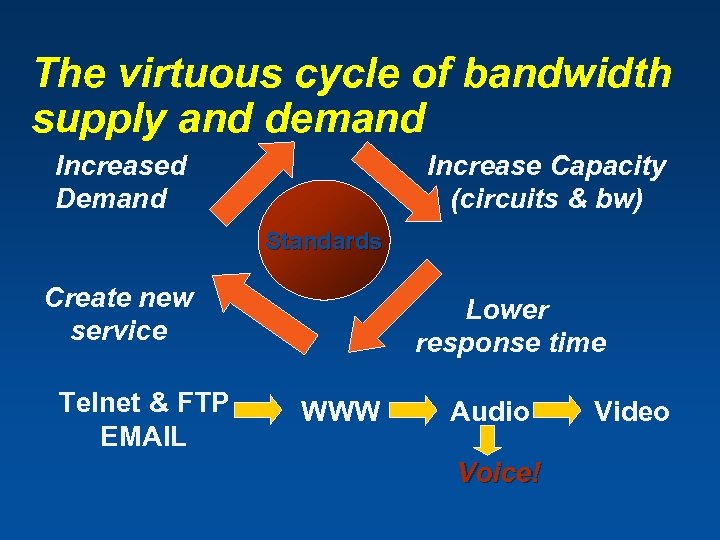
The virtuous cycle of bandwidth supply and demand Increased Demand Increase Capacity (circuits & bw) Standards Create new service Telnet & FTP EMAIL Lower response time WWW Audio Voice! Video
What is the value of combined network when television, telephone, and held web devices are added? How do you build a home network infrastructure, platforms, and interface to uses Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
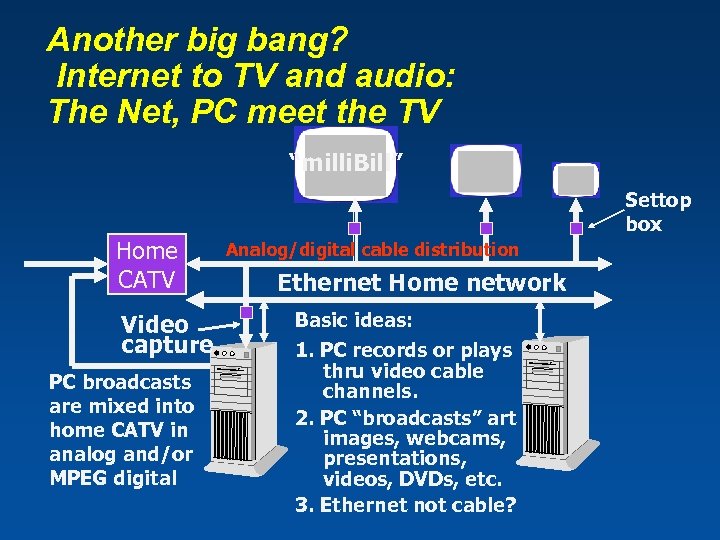
Another big bang? Internet to TV and audio: The Net, PC meet the TV “milli. Bill” Home CATV Video capture PC broadcasts are mixed into home CATV in analog and/or MPEG digital Settop box Analog/digital cable distribution Ethernet Home network Basic ideas: 1. PC records or plays thru video cable channels. 2. PC “broadcasts” art images, webcams, presentations, videos, DVDs, etc. 3. Ethernet not cable?

PCTV a. k. a. Milli. Billg Using PCs to drive large screens e. g. tv sets, Plasma Panels Gordon Bell Jim Gemmell Bay Area Research Center Microsoft Research Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws Copyright 1999 Microsoft Corporation

Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

The Next Convergence POTS connects to the Web a. k. a. Phone-Web Gateways Web Server PSTN Voice to WEB Bridge Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray The Web Data. Base Computing Laws

Web. On. Phone Mission: n. Enable voice and text access on phones, screen phones, PDAs and other devices to existing Internet infrastructure in an intelligent, customizable way. Web. On. Phone Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
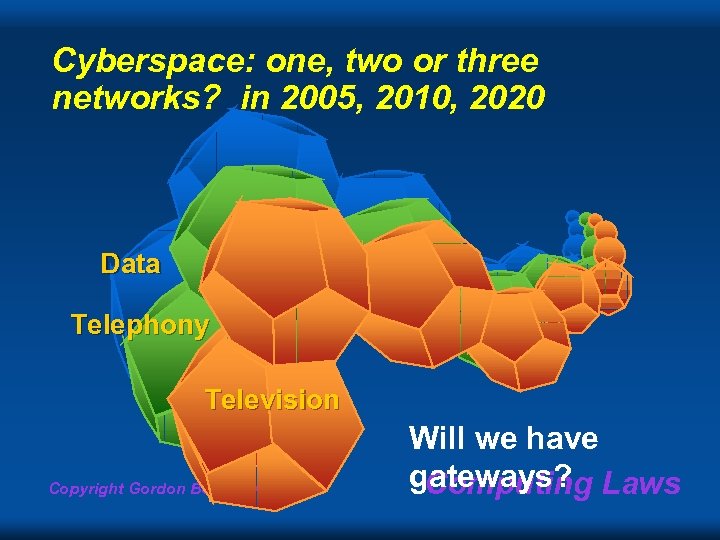
Cyberspace: one, two or three networks? in 2005, 2010, 2020 Data Telephony Television Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Will we have gateways? Laws Computing

Hardware technology: processing, memory, networking, and new interfaces enable the new computers Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
1. We get more Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
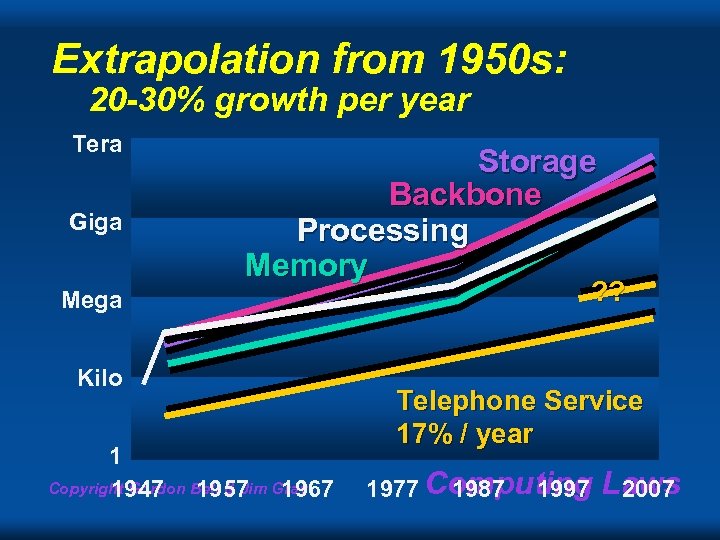
Extrapolation from 1950 s: 20 -30% growth per year Tera Giga Storage Backbone Processing Memory Mega Kilo 1 Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray 1947 1957 1967 ? ? Telephone Service 17% / year 1977 Computing 1987 1997 Laws 2007
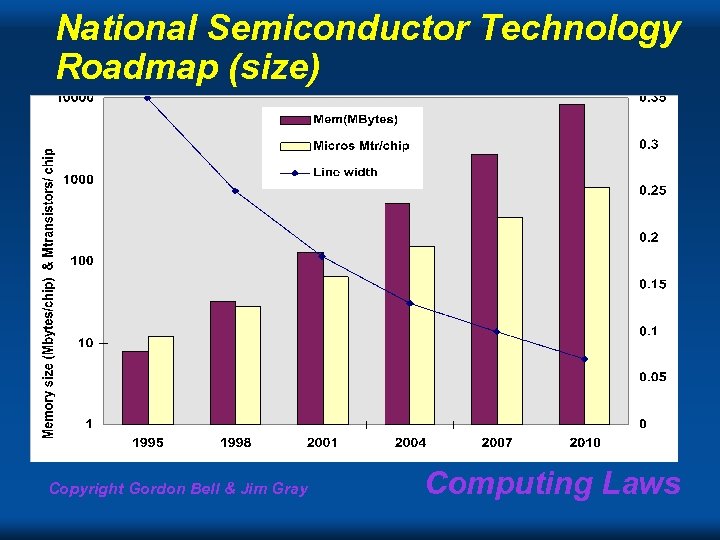
National Semiconductor Technology Roadmap (size) Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
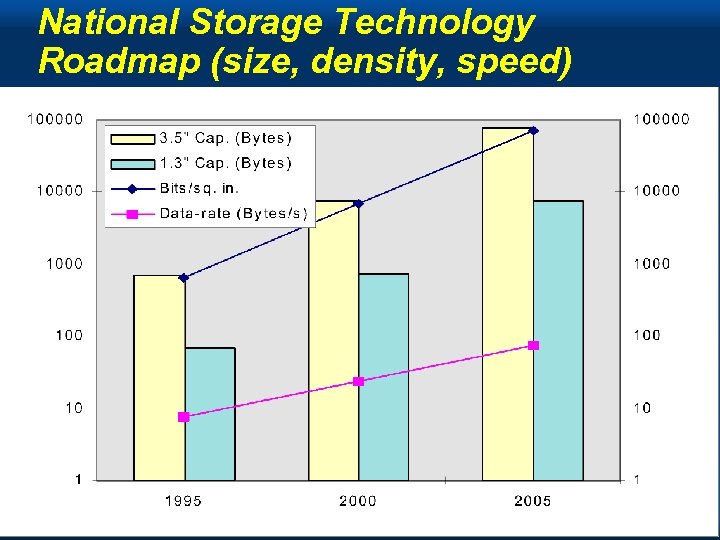
National Storage Technology Roadmap (size, density, speed) Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
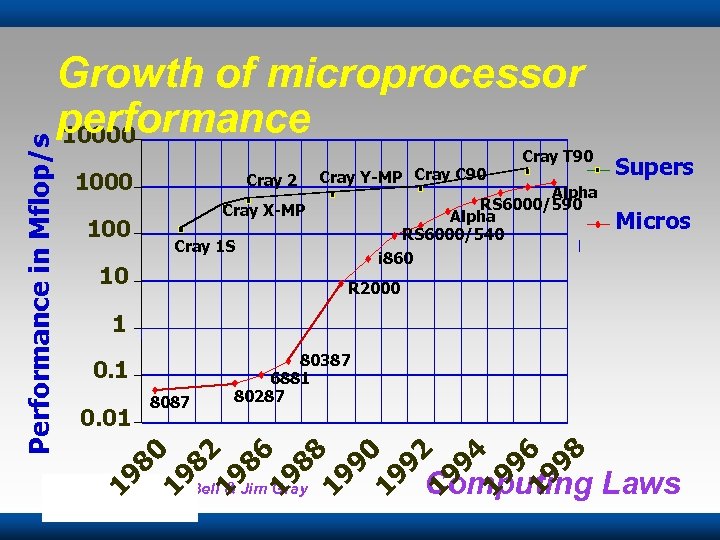
1000 Cray 2 Cray Y-MP Cray C 90 Cray 1 S 10 Cray T 90 Alpha RS 6000/540 i 860 Cray X-MP 100 Supers Micros R 2000 1 0. 1 80387 6881 80287 19 82 19 86 19 88 19 90 19 92 19 94 19 96 19 98 8087 80 0. 01 19 Performance in Mflop/s Growth of microprocessor performance 10000 Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
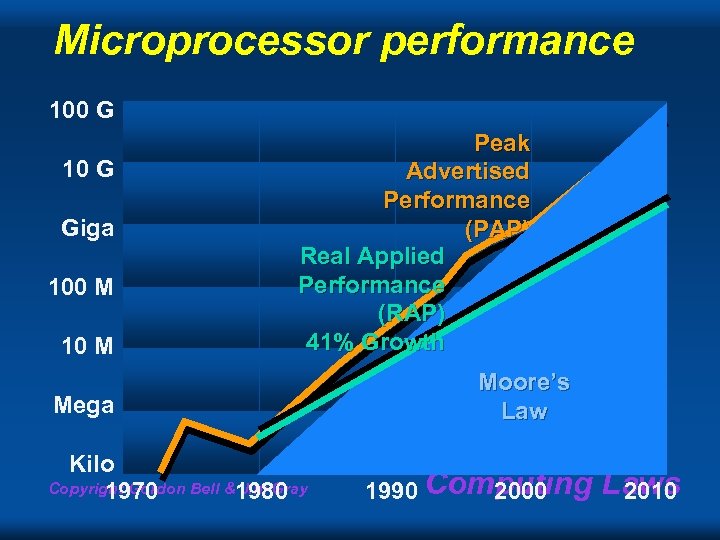
Microprocessor performance 100 G 10 G Giga 100 M 10 M Peak Advertised Performance (PAP) Real Applied Performance (RAP) 41% Growth Mega Kilo Copyright Gordon Bell &1980 Jim Gray 1970 Moore’s Law 1990 Computing 2000 Laws 2010

System-on-a-chip alternatives FPGA Sea of un-committed gate arrays Compile Unique processor for a system every app Systolic | Many pipelined or array parallel processors DSP | Special purpose VLIW processors Pc & Mp. Gen. Purpose cores. Specialized by I/O, etc. ASICS Universal Multiprocessor array, Micro programmable I/o Xylinx, Altera Tensillica TI Intel, Lucent, IBM Cradle

Cradle: Universal Microsystem trading Verilog & hardware for C/C++ UMS : VLSI n n n = microprocessor : special systems Software : Hardware Single part for all apps Programming @ run time via FPGA & ROM 5 quad m. Ps at 3 Gflops/quad = 15 Glops Single shared memory space, caches Programmable periphery including: 1 GB/s; 2. 5 Gips PCI, 100 base. T, firewire $4 per flops; 150 m. W/Gflops
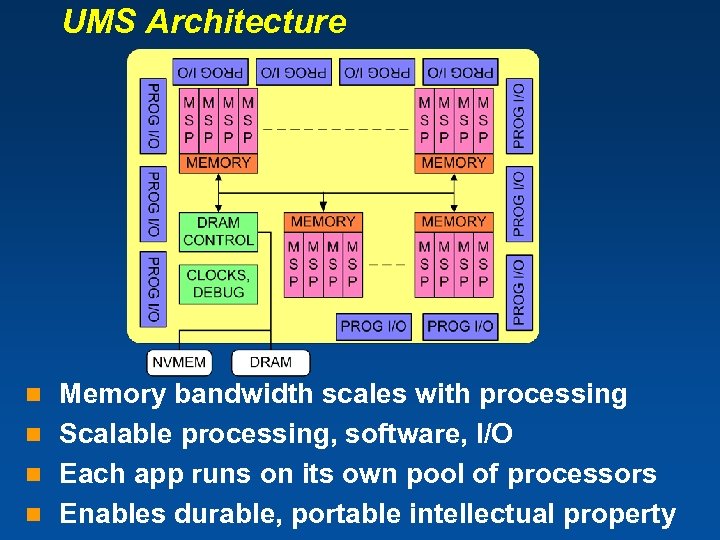
UMS Architecture Memory bandwidth scales with processing n Scalable processing, software, I/O n Each app runs on its own pool of processors n Enables durable, portable intellectual property n
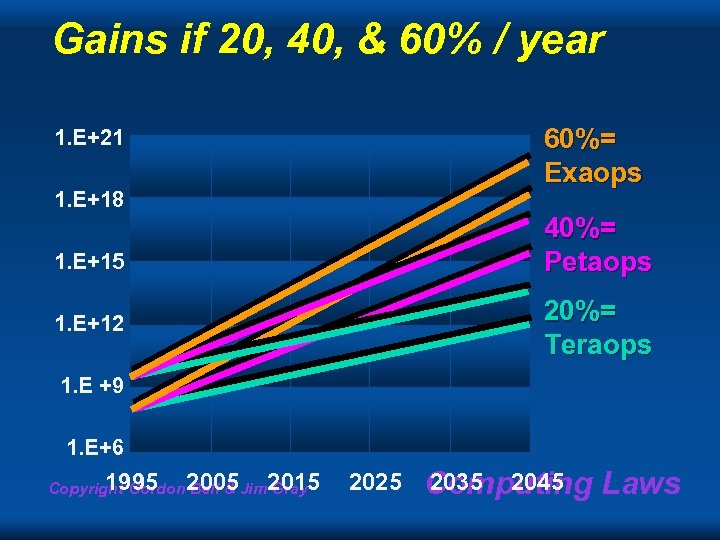
Gains if 20, 40, & 60% / year 60%= Exaops 1. E+21 1. E+18 40%= Petaops 1. E+15 20%= Teraops 1. E+12 1. E +9 1. E+6 1995 Bell & Copyright Gordon 2005 Jim 2015 Gray 2025 2035 2045 Computing Laws
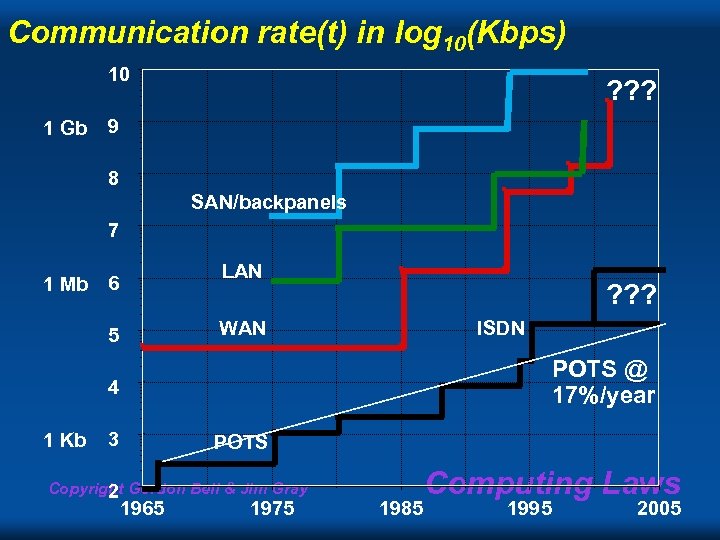
Communication rate(t) in log 10(Kbps) 10 1 Gb ? ? ? 9 8 SAN/backpanels 7 LAN 1 Mb 6 ? ? ? WAN 5 ISDN POTS @ 17%/year 4 1 Kb 3 POTS Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray 2 1965 1975 1985 Computing Laws 1995 2005

USA Today 1 Sept. 99 Video. . . Plus >>B/W Nomadicity Universality Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws

2. 0 0. 8 The evolution of wireless data standards 0. 4 0. 2 0. 1 0 UMTS 2 Mbps EDGE 384 kbps GPRS 115 kbps HSCSD Circuit data 57. 6 kbps <9. 6 kbps Computing Laws 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray
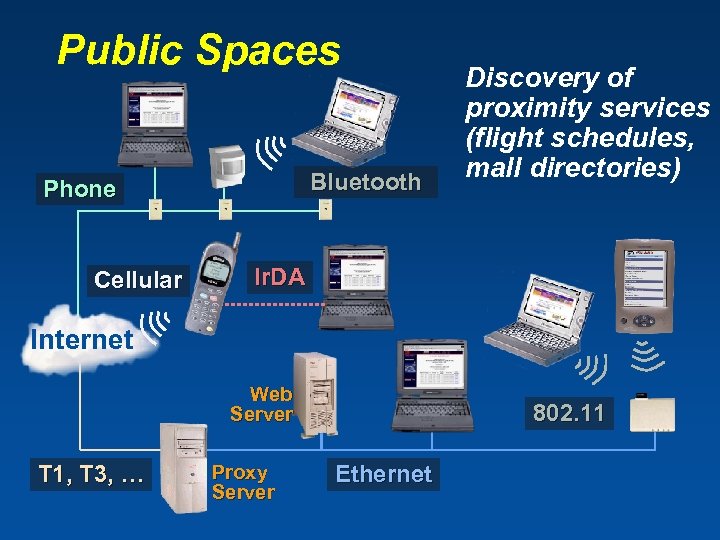
Public Spaces Bluetooth Phone Cellular Discovery of proximity services (flight schedules, mall directories) Ir. DA Internet Web Server T 1, T 3, … Proxy Server 802. 11 Ethernet
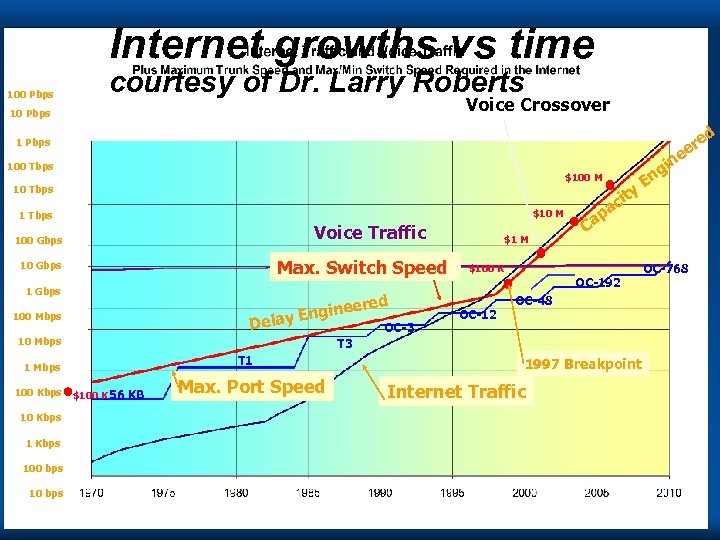
Internet growths vs time 100 Pbps courtesy of Dr. Larry Roberts Voice Crossover 10 Pbps d e er e 1 Pbps n 100 Tbps $100 M 10 Tbps $10 M 1 Tbps Voice Traffic 100 Gbps Max. Switch Speed 10 Gbps 1 Gbps red nginee E Delay OC-3 100 Mbps 10 Mbps E a p Ca $100 K OC-192 OC-768 OC-48 OC-12 T 3 T 1 1 Mbps 100 Kbps $1 M y cit i ng $100 K 56 KB Max. Port Speed 1997 Breakpoint Internet Traffic 10 Kbps 100 bps Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray 10 bps Computing Laws
Desktop-desktop @ 1 gbps http: //research. microsoft. com/ ~gray/papers/ Win 2 K_1 Gbps. doc Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
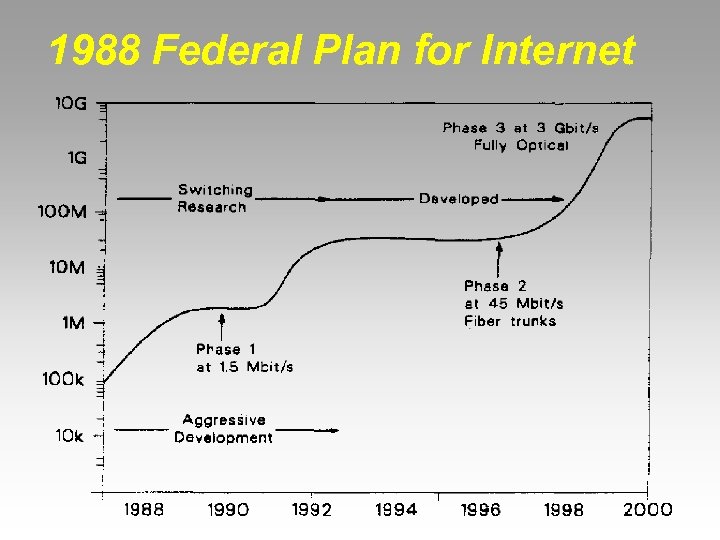
1988 Federal Plan for Internet

In a decade we can/will have: n more powerful personal computers processing 10 -100 x – 4 x resolution (2 K x 2 K) displays to impact paper – Large, wall-sized and watch-sized displays – low cost, storage of one terabyte for personal use – n adequate networking? ? ubiquitous access = today’s fast LANs – Competitive wireless networking – One chip, networked platforms including light bulbs, cameras everywhere, etc. n Some well-defined platforms that compete with the PC for mind (time) and market share watch, pocket, body implant, home n Inevitable, continued cyberization… the challenge… interfacing platforms and people. n

The End Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
Things get cheaper Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
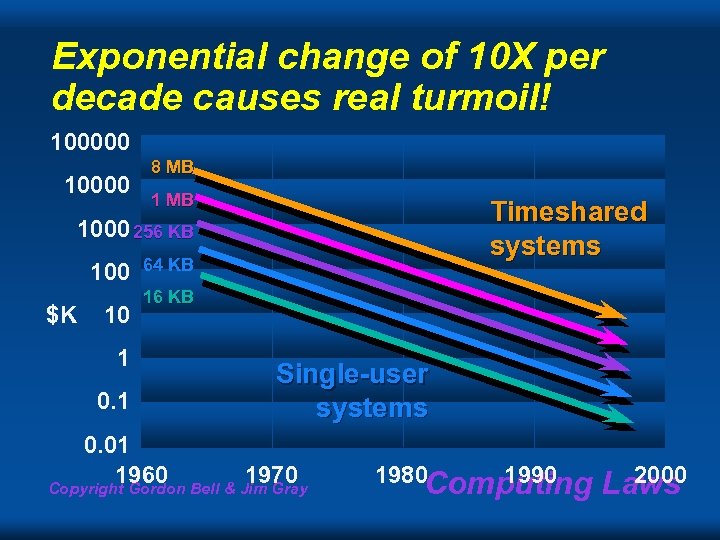
Exponential change of 10 X per decade causes real turmoil! 100000 10000 8 MB 1 MB Timeshared systems 1000 256 KB 100 $K 10 1 0. 1 64 KB 16 KB Single-user systems 0. 01 1960 1970 Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray 1980 Computing 1990 2000 Laws

VAX Planning Model 1975: I didn’t believe it n The model was very good – n 1978 timeshared $250 K VAXen cost about $8 K in 1997! Costs declined > 20% – users get more memory than predicted Single user systems didn’t come down as fast, unless you consider PDAs Copyright Gordon Bell out. Gray address bits! Computing Laws n VAX ran & Jim of n
Newer & cheaper always wins? … if it weren’t for the Law of Intertia Old New Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray New Computing Laws
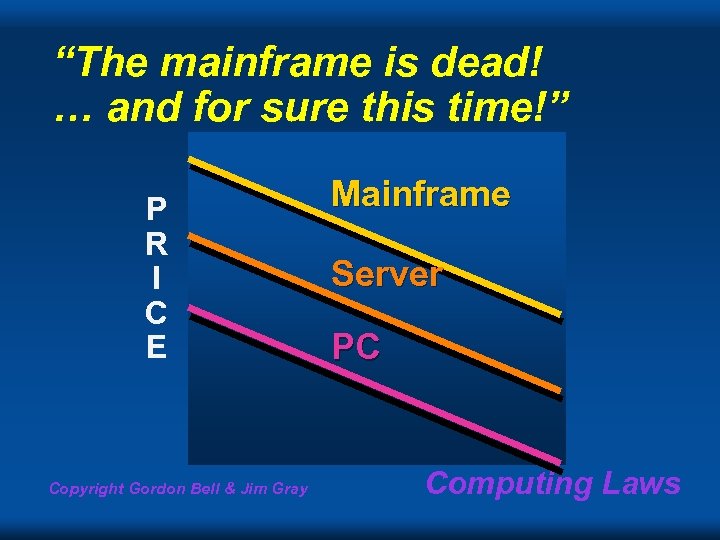
“The mainframe is dead! … and for sure this time!” P R I C E Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Mainframe Server PC Computing Laws

The law of data and program inertia sustains platforms! The investment in programs and processes to use them, and data exceed hardware costs n The cost to switch among platforms e. g. IBM mainframe, VMS, a Vendor. IX, or Windows/NT is determined by the data and programs n The goal of hardware suppliers is uniqueness to differentiate and lock-in n The goals of software/database suppliers are: to differentiate and lock-in and operate on as many platforms as possible in order to be not tied to a hardware vendor n Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
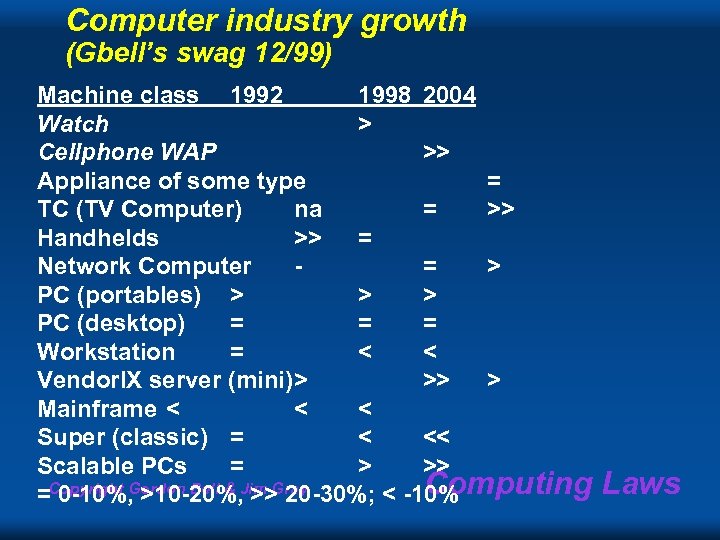
Computer industry growth (Gbell’s swag 12/99) Machine class 1992 1998 2004 Watch > Cellphone WAP >> Appliance of some type = TC (TV Computer) na = >> Handhelds >> = Network Computer = > PC (portables) > > > PC (desktop) = = = Workstation = < < Vendor. IX server (mini)> >> > Mainframe < < < Super (classic) = < << Scalable PCs = > >> Computing =Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray 0 -10%, >10 -20%, >> 20 -30%; < -10% Laws

The End Copyright Gordon Bell & Jim Gray Computing Laws
09ef40793af132762f21e175c13e177a.ppt