88026ed663cbb7501d42c17d6f65c14c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Beyond Best Practices: Web Application Security in the Real World OWASP App. Sec June 2004 NYC OWASP App. Sec Conference 2004 Dave Aitel www. immunitysec. com Copyright © 2004 - The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. The OWASP Foundation http: //www. owasp. org

Immunity, Inc. <A NYC based application security professional services firm <Two years of work as Immunity in and around the financial district <Previous experiences in government and private sector firms OWASP App. Sec 2004

Immunity Tools and Resources < GPL Software 4 SPIKE Proxy 4 SPIKE < Commercial Software 4 CANVAS < Books 4 The Hacker's Handbook/The Shellcoder's Handbook < Conferences 4 NYC Security Shindigs 4 Black. Hat, Can. Sec. West/Pac. Sec, etc OWASP App. Sec 2004

Agenda <What are current web application security best practices (from a CISO perspective) <What are the gaps in these practices, as commonly used <How can these gaps be filled in the future OWASP App. Sec 2004

Note <There currently exists no one document describing best practices for web application security at the CISO level <This makes critiquing them hard <We'll use our experience to describe what companies are doing instead OWASP App. Sec 2004

Drivers For Web App Security <News Reports 4 damage to company image <Monetary loss 4 Esp. with on-line stores <Rules and Regulations 4 Sarbanes this and that OWASP App. Sec 2004
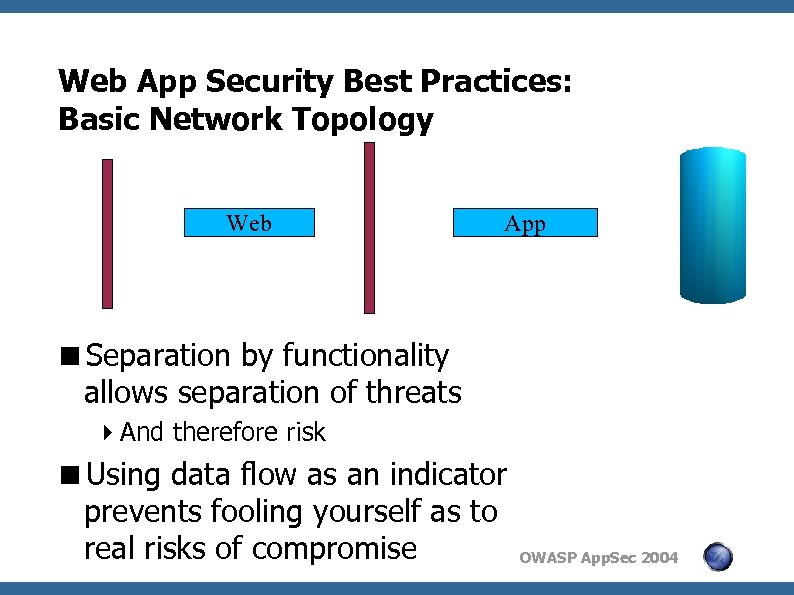
Web App Security Best Practices: Basic Network Topology Web App <Separation by functionality allows separation of threats 4 And therefore risk <Using data flow as an indicator prevents fooling yourself as to real risks of compromise OWASP App. Sec 2004
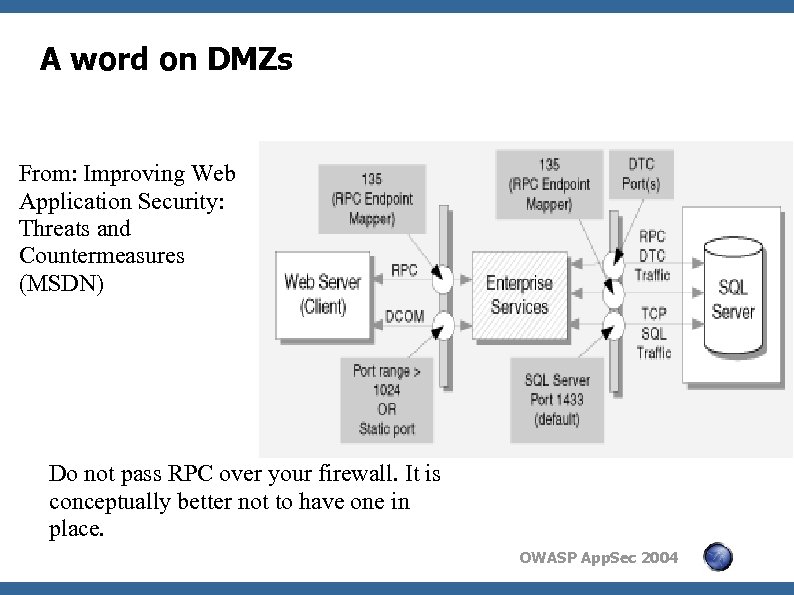
A word on DMZs From: Improving Web Application Security: Threats and Countermeasures (MSDN) Do not pass RPC over your firewall. It is conceptually better not to have one in place. OWASP App. Sec 2004
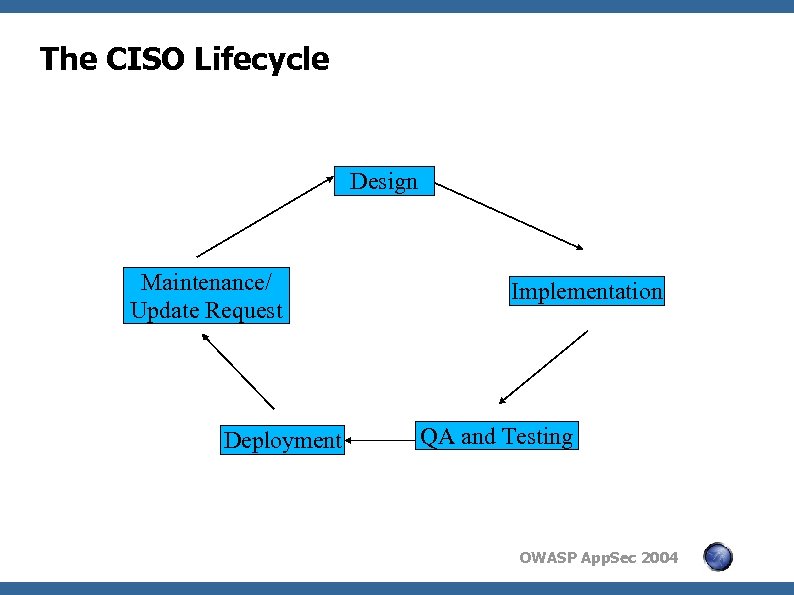
The CISO Lifecycle Design Maintenance/ Update Request Deployment Implementation QA and Testing OWASP App. Sec 2004
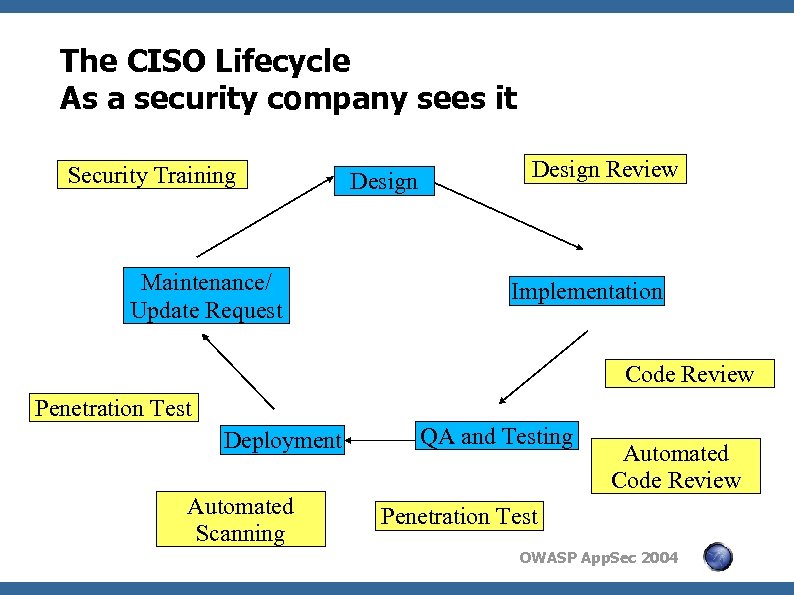
The CISO Lifecycle As a security company sees it Security Training Maintenance/ Update Request Design Review Implementation Code Review Penetration Test Deployment Automated Scanning QA and Testing Automated Code Review Penetration Test OWASP App. Sec 2004
Bottom Rung < Infrastructure-related vulnerabilities 4 Overflows, etc. 4 Do. S or other attack < SQL Injection < Accepting File Names from the client < Cross-Site Scripting (the “blue moon” threat) < Poor management of user-input 4 Being able to replace dollar values < Poor firewall rule-set maintenance OWASP App. Sec 2004
Best Practices: Infrastructure-related vulnerabilities < Do. S is just as bad as penetration in many cases 4 4 hours preventable downtime==lost job for CISO < Patch deployment 4 Patch alert services (i. Defense, ISS. net, etc) 4 Simply due-diligence < Lockdown scripts and configurations 4 Expensive, custom, and sometimes externally generated < Penetration Tests 4 Internally or externally resourced 4 Periodic OWASP App. Sec 2004

Problems with these Best Practices <Periodic is not periodic enough <Penetration tests done by consultants are expensive and over-thorough <Patch deployment is far too slow <Patch deployment doesn't account for actual risk of already having been owned OWASP App. Sec 2004

Automation <Everything in the bottom rung can be found by a product or novice except: 4 Trying to buy goods on your site for less than you want me to (bypassing business logic) <Major Products include 4 Web. Inspect (SPIdynamics) 4 App. Scan 4 Kava. Do OWASP App. Sec 2004
Purchasing Automation <10 -50 K <Licensing restrictions 4 Per person, rather than per-seat 4 Per-host <Difficult to update and customize <Unknown reliability and coverage OWASP App. Sec 2004
Enhancing Automation <Automation is great until you realize that you need to work around some quirk in your site and your automated tool can't support that <Use Open Source tools, such as SPIKE Proxy or OWASP Web. Scarab to fill these gaps 4 Modifying the code to fit your environment is a key philosophical change that can make you more secure for less money and resources OWASP App. Sec 2004

Some Examples <URL formats for sites don't always fit the http: //site/bob. cgi? value=thing&value 2=thing 2 format. <This makes them hard to scan via commercial automated tools http: //us. rd. yahoo. com/classsite/fd/hj/evt=7540/*http: //hotjobs. com http: //g. msn. co. kr/KRJ 9/5279. 10? http: //ad 1. targetgraph. com/click. kti/msnkore a/hockeystick@? ads_no=13487&&CE=i 01 OWASP App. Sec 2004

Server Security <All web and application servers have had buffer overflows <Don't look to W xor X (XP SP 2, Fedora CORE) or stack canaries (W 2 K 3) as some sort of savior <Install a HIDS 4 Won't protect you against data or injection issues 4 It's a backwards thing for me to hit your actual server <Optimally, use grsecurity on Linux OWASP App. Sec 2004

Cross-Site-Scripting <SQL Injection can be solved with a library or API policy 4 See MSDN documentation on the new ASP. NET way to do so <However, that very same MSDN documentation notes that you should use code review and trial and error penetration testing to find XSS OWASP App. Sec 2004

SQL Injection <Fairly simple to scan for 4 Turn off custom error handler pages 4 Spider website, insert quotes, parens as necessary 4 Record error messages and send to development team <Current practice of hiring consultants/expensive software to find this is wasteful 4 Especially if you leave error handler pages on OWASP App. Sec 2004
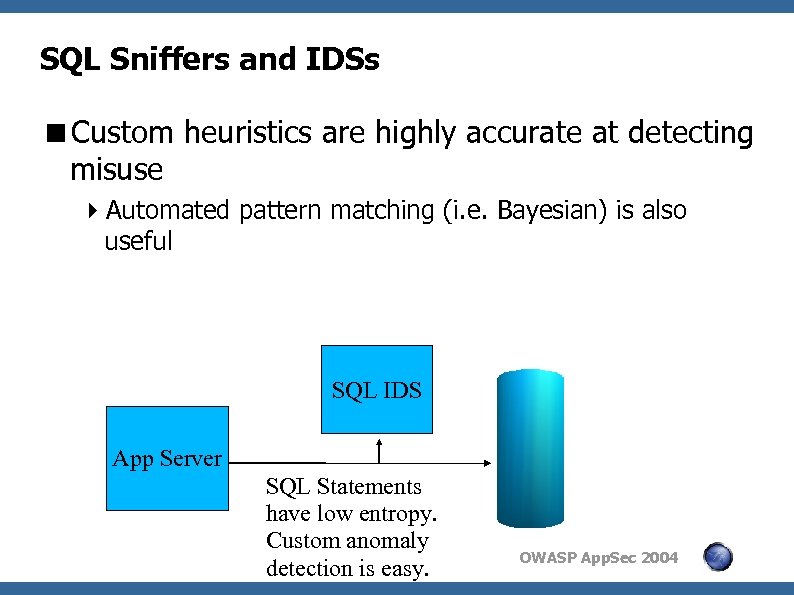
SQL Sniffers and IDSs <Custom heuristics are highly accurate at detecting misuse 4 Automated pattern matching (i. e. Bayesian) is also useful SQL IDS App Server SQL Statements have low entropy. Custom anomaly detection is easy. OWASP App. Sec 2004
Top Rung Vulnerabilities <Being able to access “data” that I should not be able to access <Attacking session-id or other randomization weaknesses <Manipulating session-state variables to bypass business logic and authentication OWASP App. Sec 2004

The 1% Rule <The top 1% of hackers are extremely differentiated 4 Each of them may get into your site, but via very different methods 4 This makes them impossible to model, predict, and defend against OWASP App. Sec 2004

Current Top Rung Best Practices <Hire penetration test experts to code review and analyze live systems <Hire outside experts to train your developers OWASP App. Sec 2004

Better Top Run Best Practices <Develop internal experts to train your developers in a manner specific to your application <Establish an internal team accountable for application security <Develop custom application security code review tools <Hire outside experts to find new CLASSES of vulnerabilities in your application, not new vulnerabilities OWASP App. Sec 2004
Your Idealistic Web App Lifecycle 1. Design 2. Implement 3. QA 4. Test for security 5. Deploy 6. Modify and Maintain 7. Periodically test for security OWASP App. Sec 2004
Security in the Design Phase <. . Is a Myth. <Your team often didn't do the design 4 And sometimes not the implementation as well 4 Many products are purchased 4 Or have large components that are purchased 4 You may not even have code or documentation to them <Requirements change during development 4 And after deployment OWASP App. Sec 2004

Auditing and Logging <Currently, few people look at their log files for security issues unless an incident occurs <The correct way to use your auditing and logging is to use it as a feedback loop into your custom security applications OWASP App. Sec 2004
APS versus HIDS <An application layer IDS can find vulnerabilities, rather than intrusions 4 Much harder problem to generalize 4 There is no “Application Level” IP § XML transactions generally top out at 300 TPS <A HIDS does not protect data 4 It protects files and other OS resources OWASP App. Sec 2004
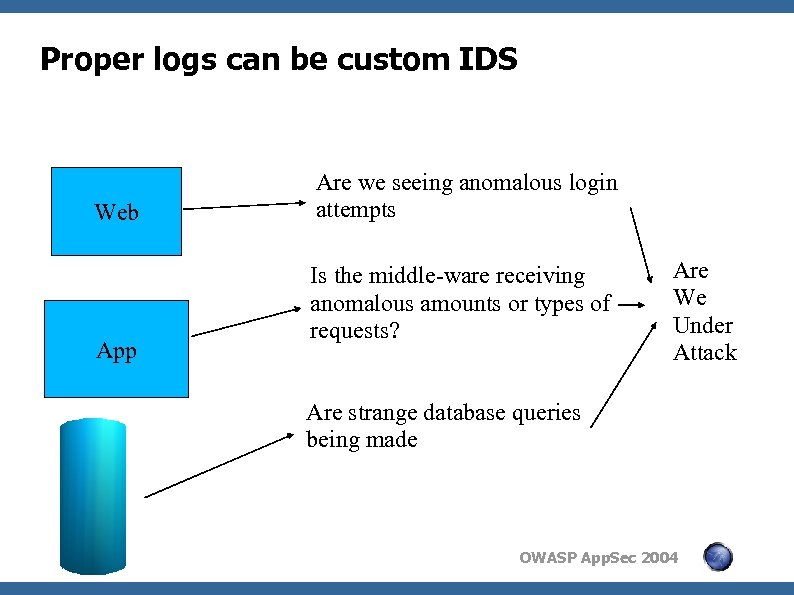
Proper logs can be custom IDS Web App Are we seeing anomalous login attempts Is the middle-ware receiving anomalous amounts or types of requests? Are We Under Attack Are strange database queries being made OWASP App. Sec 2004
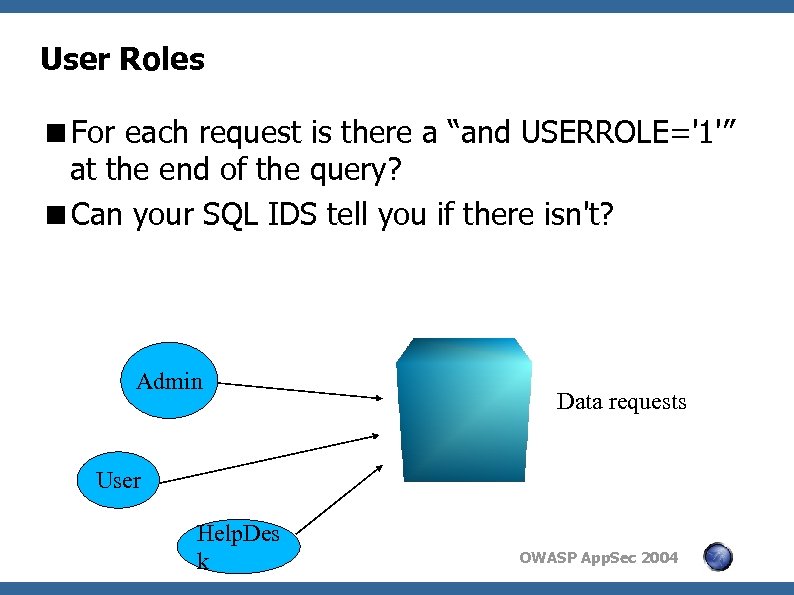
User Roles <For each request is there a “and USERROLE='1'” at the end of the query? <Can your SQL IDS tell you if there isn't? Admin Data requests User Help. Des k OWASP App. Sec 2004

Dealing with third party components <Stop buying third party software on an “AS IS” basis <Conduct or obtain assurances that this software is free from glaring defects, such as buffer overflows <Perform due diligence testing OWASP App. Sec 2004
Database Encryption <Storing the key on the same application as the vulnerabilities is still considered “Best practices” as long as encryption is being used. . . <If you have 30 K users a day, and an attacker manages to sit on your App server for 20 minutes, how many passwords do they now have? How many of them live in CA? Web App OWASP App. Sec 2004

SSL Object Lesson <The QA site needs to contain every aspect of the production site, including F 5 load balancers, customer support infrastructure, etc. <These things are part and parcel of your application OWASP App. Sec 2004

HMACS <Often used to prevent users from manipulating cookie or session variables 4 Cookie: Admin=0; HASH=MD 5(“Admin=0”+”secretkey”) <Don't hard-code your HMAC into your application <Don't use a small, English string as your HMAC seed OWASP App. Sec 2004
Automated Code/Binary Auditing Tools < New and old offerings 4 Fortify Software 4 @stake SRA 4 Microsoft Pre. Fix/Pre. Fast 4 Coverity 4 Ounce Labs 4 HBGary Bugscan 4 Secure Software OWASP App. Sec 2004
Automated code assessment downsides <Extremely first generation <May require special build configurations <Cannot scan across component boundaries <Expensive 4 People underestimate the time it takes for a good code reviewer to find bugs OWASP App. Sec 2004

Parsing for Success <Analyzing each component's interactions with the system in depth is impossible 4 Component use changes over time <But quick scripts can be written that work for your application and can be included in your QA process <Looking for strcpy() is a waste of time – verify that YOUR API is used properly instead OWASP App. Sec 2004

Cover Review Best Practices Improved <Train for specifics <Don't let security consultants work off-site <Do daily scans for application vulnerabilities across every site OWASP App. Sec 2004

Filling the Gaps <Customized code review applications <Customized Application Layer IDS <Customized Data Mining IDS's <Customized Developer Training <Actually Writing Security Documentation <Getting the most out of your security money <QA Testing of 3 rd party components OWASP App. Sec 2004

What's Missing? <Policy 4 Useless unless monitored § via technical measures 4 Make your policy documentation of existing efforts <Audits (ISO 31337, etc) 4 Providing no security value and little marketing value 4 Eschew OWASP App. Sec 2004

Questions and War Stories <Thank you. OWASP App. Sec 2004
88026ed663cbb7501d42c17d6f65c14c.ppt