69a9a7c3d69a4ee70f7b0ba5592db138.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66

Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System U. S. Customer Training Program D 01564 D 04/04

Agenda • Introduction • Product System Review • Procedural Use and Application Pointers • Hands-on Applications Workshop • Site Training Guidelines D 01564 D 04/04
Introduction The 3. 5 F System is a modification of the existing Beta -Cath™ System platform, designed to work with a smaller Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) and 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter. Key Benefits • Smaller 6 F Guide Catheter Compatibility • Integral Catheter Tool Eliminates Conventional “Dummy” Run • Single Catheter Accommodates Multiple Source Train Lengths (30 mm, 40 mm, and 60 mm) D 01564 D 04/04

Introduction The objective of this training program is to familiarize the user with the unique features of the Novoste™ Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System via Novoste didactic, work-shop and proctored training. D 01564 D 04/04

Agenda • Introduction • Product System Review – Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) – β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter (standard and XL lengths) – 3. 5 F Transfer Device • Procedural Use and Application Pointers • Hands-on Applications Workshop • Site Training Guidelines D 01564 D 04/04

Product System Review • Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) ™ • β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter • 3. 5 F Transfer Device D 01564 D 04/04
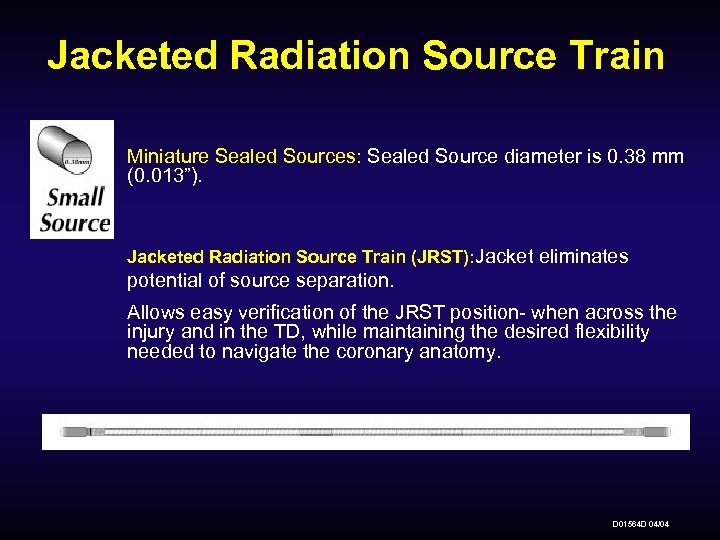
Jacketed Radiation Source Train Miniature Sealed Sources: Sealed Source diameter is 0. 38 mm (0. 013”). Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST): Jacket eliminates potential of source separation. Allows easy verification of the JRST position- when across the injury and in the TD, while maintaining the desired flexibility needed to navigate the coronary anatomy. D 01564 D 04/04

Jacketed Radiation Source Train End Marker Coil Jacket D 01564 D 04/04
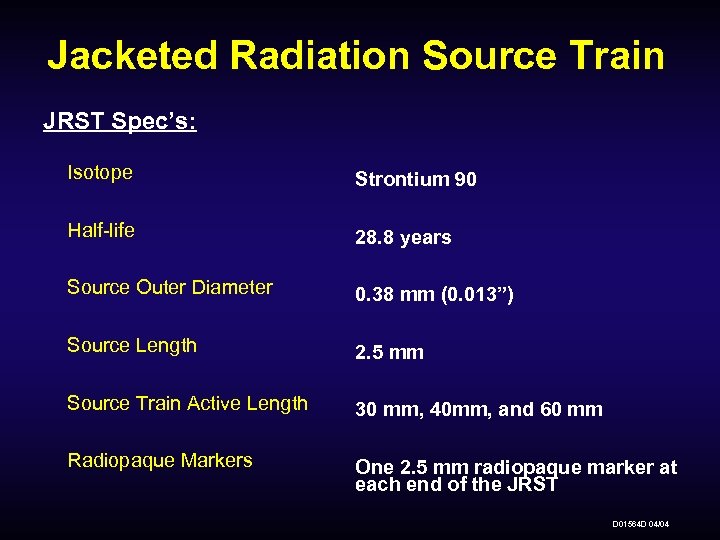
Jacketed Radiation Source Train JRST Spec’s: Isotope Strontium 90 Half-life 28. 8 years Source Outer Diameter 0. 38 mm (0. 013”) Source Length 2. 5 mm Source Train Active Length 30 mm, 40 mm, and 60 mm Radiopaque Markers One 2. 5 mm radiopaque marker at each end of the JRST D 01564 D 04/04
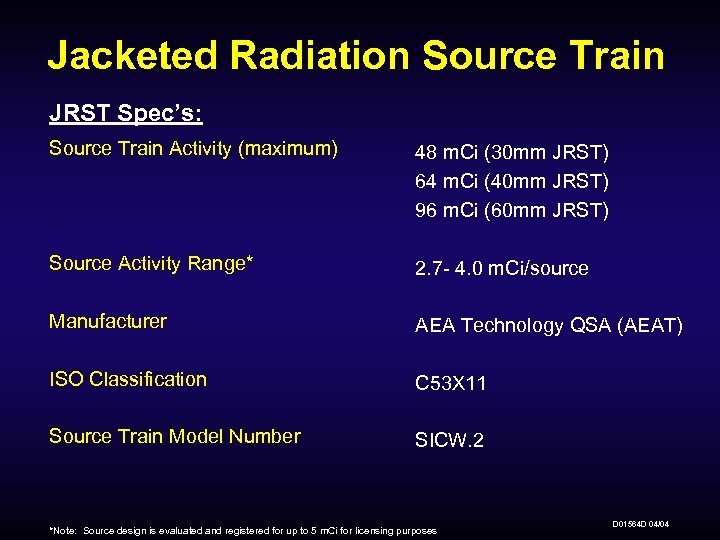
Jacketed Radiation Source Train JRST Spec’s: Source Train Activity (maximum) 48 m. Ci (30 mm JRST) 64 m. Ci (40 mm JRST) 96 m. Ci (60 mm JRST) Source Activity Range* 2. 7 - 4. 0 m. Ci/source Manufacturer AEA Technology QSA (AEAT) ISO Classification C 53 X 11 Source Train Model Number SICW. 2 *Note: Source design is evaluated and registered for up to 5 m. Ci for licensing purposes D 01564 D 04/04
Jacketed Radiation Source Train JRST Manufacturing Process: • Sr-90 wire matrix inserted into stainless steel capsule and welded closed. • Radioactive Sources are inserted into the stainless steel coil along with two radiopaque markers (one on each end). • Coil is permanently attached to radiopaque markers at each end. D 01564 D 04/04

Product System Review • Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) • β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter • 3. 5 F Transfer Device D 01564 D 04/04
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter: The Delivery Catheter was reduced from 5 F (1. 67 mm) to 3. 5 F (1. 17 mm). This permits use of a 6 F (ID 0. 067”/1. 7 mm) Guide Catheter. Standard and XL lengths. Delivery Catheter Placement: Single Catheter: Catheter placed across lesion prior to TD attachment. Single catheter accommodates multiple source train lengths (30 mm, 40 mm and 60 mm). D 01564 D 04/04
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter 1 cm Distal rail: The 1 cm radiopaque distal rail tip allows visualization of the tip on Fluoro during the procedure. Coaxial Design: The coaxial design (versus the 3 lumen 5 F design) allows down-sizing of the system and is more crush resistant than the 5 F design. No need for an Arrow® Sheath. NOTE: VBT is conducted post-PTCA, so access with a distal rail is not an issue as it might be for a distal rail used for primary PTCA. D 01564 D 04/04
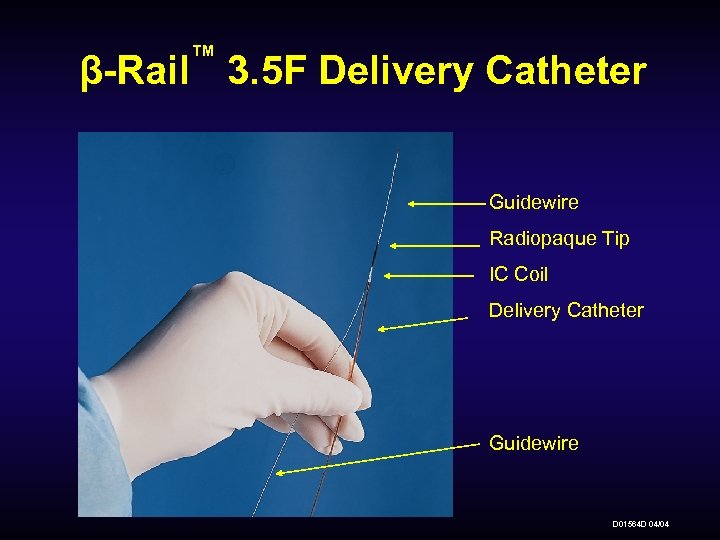
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Guidewire Radiopaque Tip IC Coil Delivery Catheter Guidewire D 01564 D 04/04
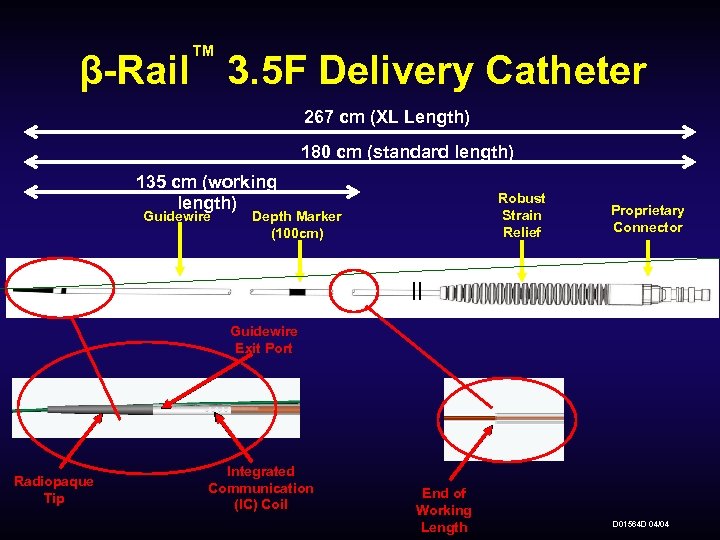
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter 267 cm (XL Length) 180 cm (standard length) 135 cm (working length) Guidewire Robust Strain Relief Depth Marker (100 cm) Proprietary Connector Guidewire Exit Port Radiopaque Tip Integrated Communication (IC) Coil End of Working Length D 01564 D 04/04
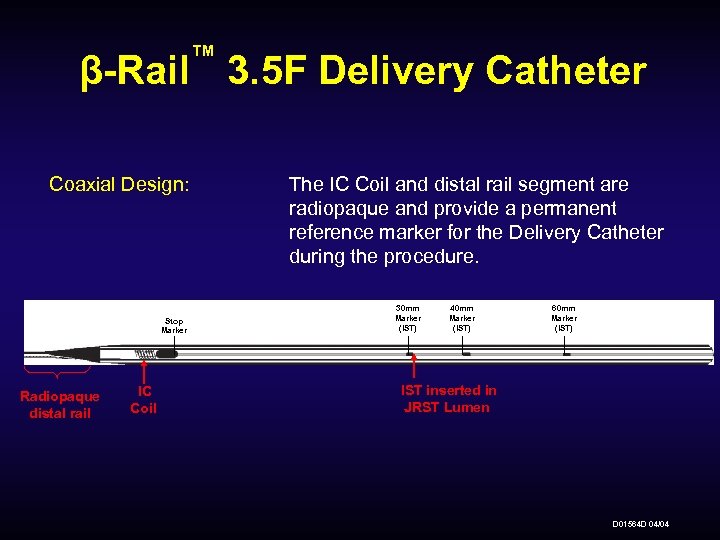
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Coaxial Design: Stop Marker Radiopaque distal rail IC Coil The IC Coil and distal rail segment are radiopaque and provide a permanent reference marker for the Delivery Catheter during the procedure. 30 mm Marker (IST) 40 mm Marker (IST) 60 mm Marker (IST) IST inserted in JRST Lumen D 01564 D 04/04
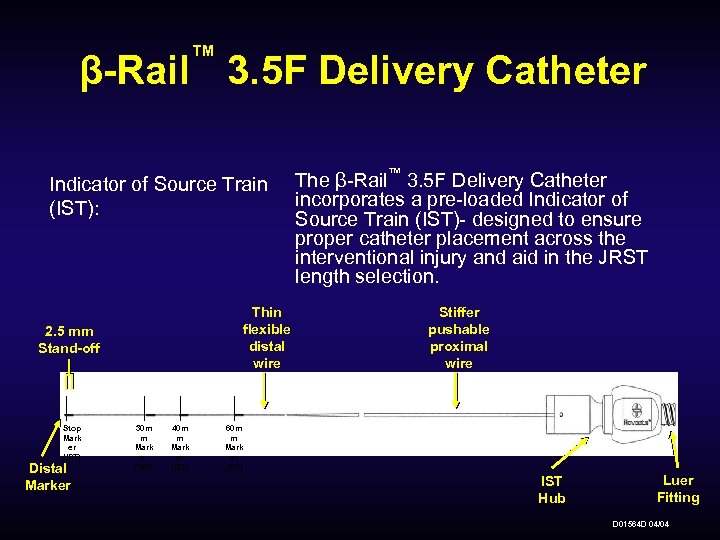
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Indicator of Source Train (IST): Thin flexible distal wire 2. 5 mm Stand-off Stop Mark er (IST) Distal Marker 30 m m Mark er (IST) 40 m m Mark er (IST) The β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter incorporates a pre-loaded Indicator of Source Train (IST)- designed to ensure proper catheter placement across the interventional injury and aid in the JRST length selection. Stiffer pushable proximal wire 60 m m Mark er (IST) IST Hub Luer Fitting D 01564 D 04/04
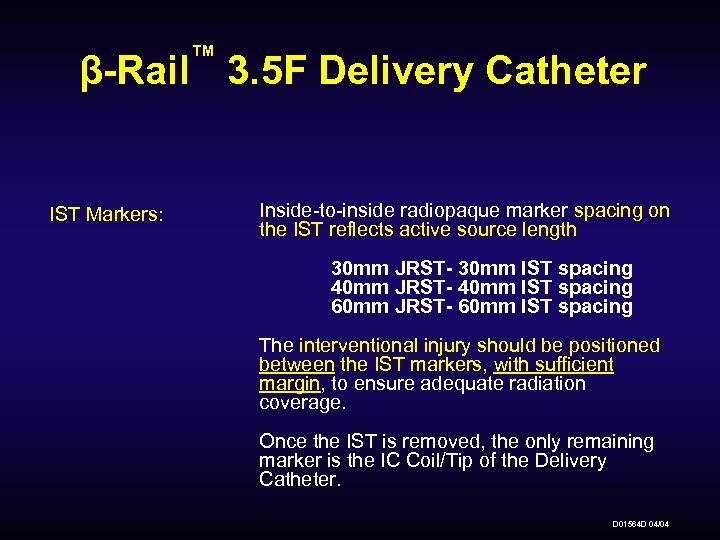
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter IST Markers: Inside-to-inside radiopaque marker spacing on the IST reflects active source length 30 mm JRST- 30 mm IST spacing 40 mm JRST- 40 mm IST spacing 60 mm JRST- 60 mm IST spacing The interventional injury should be positioned between the IST markers, with sufficient margin, to ensure adequate radiation coverage. Once the IST is removed, the only remaining marker is the IC Coil/Tip of the Delivery Catheter. D 01564 D 04/04
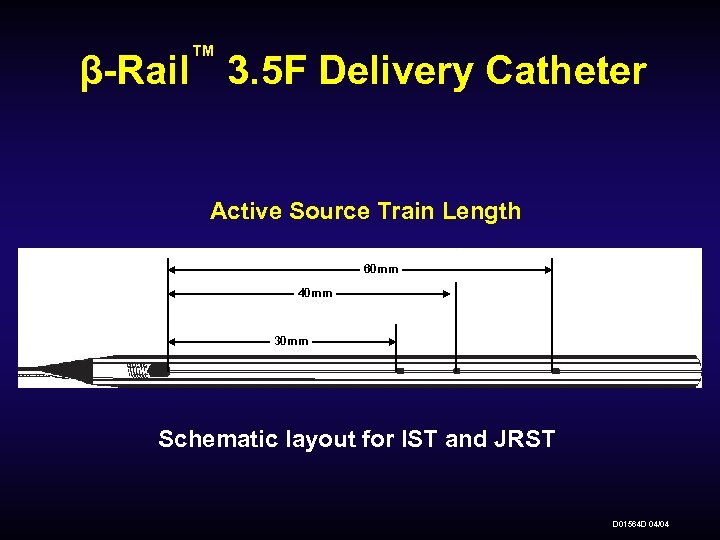
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Active Source Train Length 60 mm 40 mm 30 mm Schematic layout for IST and JRST D 01564 D 04/04
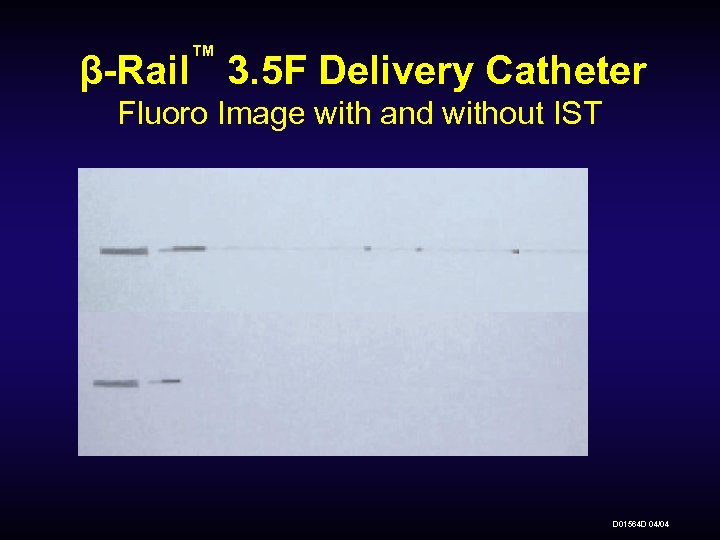
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Fluoro Image with and without IST D 01564 D 04/04
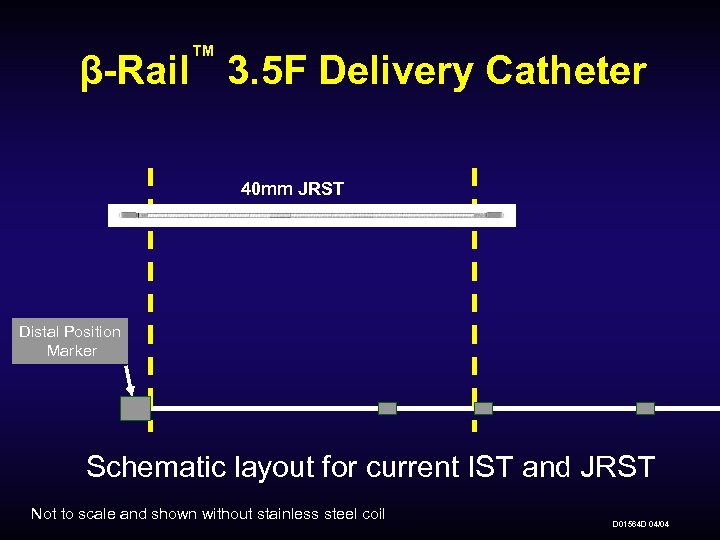
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter 40 mm JRST Distal Position Marker Schematic layout for current IST and JRST Not to scale and shown without stainless steel coil D 01564 D 04/04
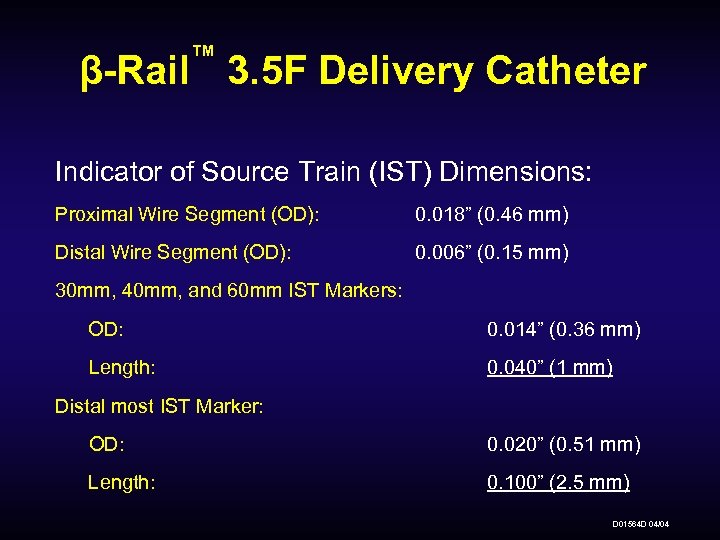
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Indicator of Source Train (IST) Dimensions: Proximal Wire Segment (OD): 0. 018” (0. 46 mm) Distal Wire Segment (OD): 0. 006” (0. 15 mm) 30 mm, 40 mm, and 60 mm IST Markers: OD: 0. 014” (0. 36 mm) Length: 0. 040” (1 mm) Distal most IST Marker: OD: 0. 020” (0. 51 mm) Length: 0. 100” (2. 5 mm) D 01564 D 04/04
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Simulated “Dummy Run” with the IST: The IST is also designed to simulate a Dummy Run during IST removal from a positioned Delivery Catheter: • The distal marker on the IST is designed to be slightly larger than the JRST. • Removal of the IST provides “tactile feel” of catheter lumen patency. D 01564 D 04/04
™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter-Transfer Device Attachment: The 3. 5 F Transfer Device is brought to the patient and attached to the Delivery Catheter pre-positioned at the injury site. Standard Length (180 cm Total Length): The 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter has a total length of 180 cm (versus the 5 F Delivery Catheter’s 155 cm). XL Length (267 cm Total Length): The 3. 5 F XL Delivery Catheter has a total length of 267 cm (versus the 5 F Delivery Catheter’s 155 cm). 100 cm Depth Marker: A white 100 cm Depth Marker (versus a 90 cm Depth Marker) is used as a reference point during the Delivery Catheter insertion. D 01564 D 04/04

™ β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter • 0. 014” Guidewire compatibility • Hydraulic sending and returning of the sources • Use of Sterile Water for Irrigation • Packaged sterile, single use only D 01564 D 04/04

Product System Review • Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) • β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter • 3. 5 F Transfer Device D 01564 D 04/04
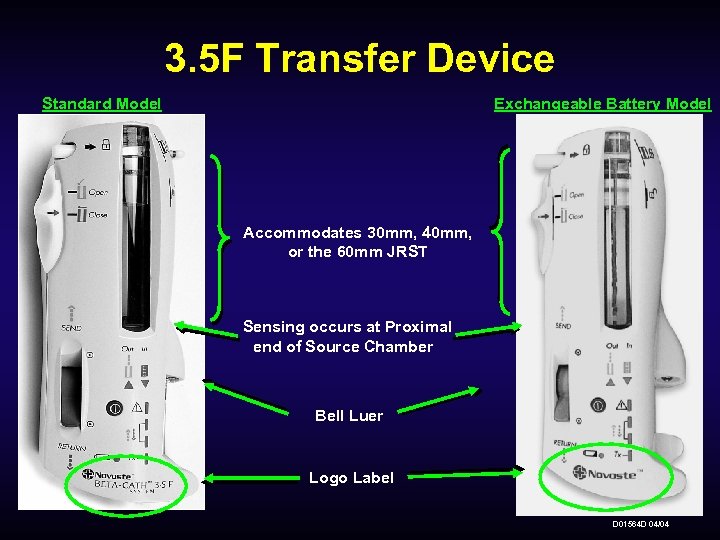
3. 5 F Transfer Device Standard Model Exchangeable Battery Model Accommodates 30 mm, 40 mm, or the 60 mm JRST Sensing occurs at Proximal end of Source Chamber Bell Luer Logo Label D 01564 D 04/04
3. 5 F Transfer Device Standard Model: 6 -Month Service Cycle Simplified Source Sensing: The 3. 5 F Transfer Device (TD) utilizes a simple photo-reflectance sensing system (at the proximal end of the Source Chamber) that senses whether the JRST is IN or OUT. 3. 5 F Proprietary Connector (PC): The 3. 5 F PC is only compatible with the 3. 5 F Transfer Device. 125 Uses: The 3. 5 F battery provides for 125 uses with treatment counter. Bell Luer: The Bell Luer is inserted around the Syringe Luer to prevent fluid entry into the TD. Complete Visualization of The 3. 5 F TD shell is light grey and is labeled: “Beta-Cath. TM 3. 5 F System”. the JRST: D 01564 D 04/04
3. 5 F Transfer Device Exchangeable Battery Model: 12 -Month Service Cycle Simplified Source Sensing: The 3. 5 F Transfer Device (TD) utilizes a simple photo-reflectance sensing system (at the proximal end of the Source Chamber) that senses whether the JRST is IN or OUT. 3. 5 F Proprietary Connector (PC): The 3. 5 F PC is only compatible with the 3. 5 F Transfer Device. Exchangeable Battery: A 6 -volt Lithium Battery powers the TD to allow for easy exchange of the power source. Bell Luer: The Bell Luer is inserted around the Syringe Luer to prevent fluid entry into the TD. Complete Visualization of The 3. 5 F TD shell is light grey and is labeled: “Beta-Cath. TM 3. 5 F System”. the JRST: D 01564 D 04/04

Product System Review • Jacketed Radiation Source Train (JRST) ™ • β-Rail 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter • 3. 5 F Transfer Device D 01564 D 04/04

Procedural Use and Application Pointers • Pre-Procedure Surveillance • 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter (Standard and XL Lengths) – Catheter Unpacking – Catheter Inspection and Preparation – Catheter Placement and JRST Selection • IST Lumen Check and Removal • TD Preparation • PC to TD Attachment and Priming – DC Positioning • JRST Delivery and Return – Troubleshooting Tips • Delivery Catheter Withdrawal • Optional Instructions: IST Reinsertion D 01564 D 04/04

Pre-Procedure Surveillance Determine which Transfer Device you are using and refer to the appropriate Instructions for Use. • Standard (6 -month Service Cycle) Model • Exchangeable Battery (12 -month Service Cycle) Model – Battery must be installed in the Transfer Device before the TD can be operational. * Operation and treatment with both Transfer Devices is identical; the major differences between the two models is the power source • Do not use without leak test after six months • Remove Calibration Certificate from Shipping Container and identify Effective Use period(s) • Inventory the Source Train within the TD • Conduct a Radiation Survey of the Transfer Device and note results for future reference as TD baseline reading. D 01564 D 04/04

Catheter Unpacking • Soft pack contains sterile catheter which comes in a hoop. • Carefully remove catheter from package, especially if hub is not fixed to the hoop. • Assure that the hub does not hang up at the package. D 01564 D 04/04
Catheter Inspection and Preparation • Examine the Delivery Catheter upon removal for bends or kinks or other signs of damage. • Flush guidewire lumen with 1 ml heparinized saline. • May use blunt Flushing Cannula or syringe • Visually confirm that the IST is seated against the internal distal catheter marker/stop. D 01564 D 04/04

Catheter Inspection and Preparation Attach syringe filled with Sterile Water for Irrigation to the IST hub and flush the inner (RST) lumen of the Delivery Catheter (DC) with 2 -3 ml while observing the tip of the Delivery Catheter for leakage. • Hold PC and IST hub together when flushing. • Do not use excessive pressure or force when flushing. • Lumen is small • Risk of bending or kinking of DC • You will see fluid exit at the IST hub vent. D 01564 D 04/04

Catheter Inspection and Preparation • Visually confirm that the IST is seated against the internal distal marker/stop in the Delivery Catheter. If the IST is not properly seated: • Check that the IST hub has been fully inserted onto the Delivery Catheter PC. • If a gap still exists between the distal marker of the IST and the internal stop of the Delivery Catheter, select another Delivery Catheter and return the original to Novoste. D 01564 D 04/04

Delivery Catheter Advancement • Advance the β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter over the. 014” guidewire to the interventional injury site. – – Insert with IST in position Do not advance over floppy portion of wire Depth marker is at 100 cm Catheter working length is 135 cm D 01564 D 04/04
Delivery Catheter Advancement • The handling requirements of a “Distal Rail” catheter, such as the Novoste™ β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter , differ from those of traditional “rapid exchange” or “monorail” designed catheters. • Always handle the β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter with the IST in place to avoid kinking. • Be aware that 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter Standard length is 180 cm vs. 155 cm. The XL catheter length is 267 cm and permits TD attachment inside or outside the sterile field. • Once the Delivery Catheter is positioned and the IST has been removed, slight advancement and retraction of the Delivery Catheter can be done without kinking. D 01564 D 04/04
Delivery Catheter Advancement • In case of crossing problems, the IST can be retracted a few centimeters to improve trackability. • Excessive pushing to advance the catheter may increase the risk of Delivery Catheter kinking. • Tips to avoid kinking at the guidewire exit area during advancement: – Use extra support wire – Improve alignment of the guiding catheter – Deep intubations of the guiding catheter D 01564 D 04/04
Delivery Catheter Advancement • Observe tracking or kinking of the guide catheter under fluoroscopy during positioning. - Guide catheter curve and tortuous Ao-iliac bifurcation • When using the Novoste™ β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter, care must be exercised during insertion and removal of the system. • Always insert and remove the DC slowly and observe under fluoroscopy. If any resistance is felt, stop immediately and determine cause of resistance. • The distal rail segment of the β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter is radiopaque, to allow visualization of catheter tip position on the guidewire. D 01564 D 04/04
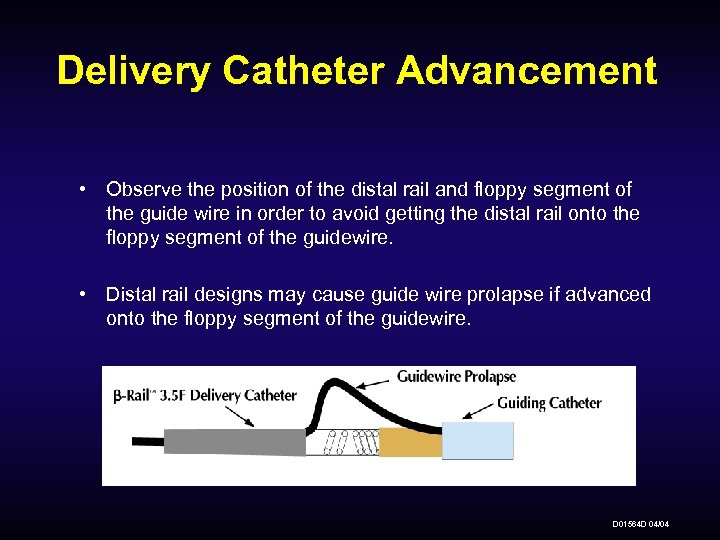
Delivery Catheter Advancement • Observe the position of the distal rail and floppy segment of the guide wire in order to avoid getting the distal rail onto the floppy segment of the guidewire. • Distal rail designs may cause guide wire prolapse if advanced onto the floppy segment of the guidewire. D 01564 D 04/04
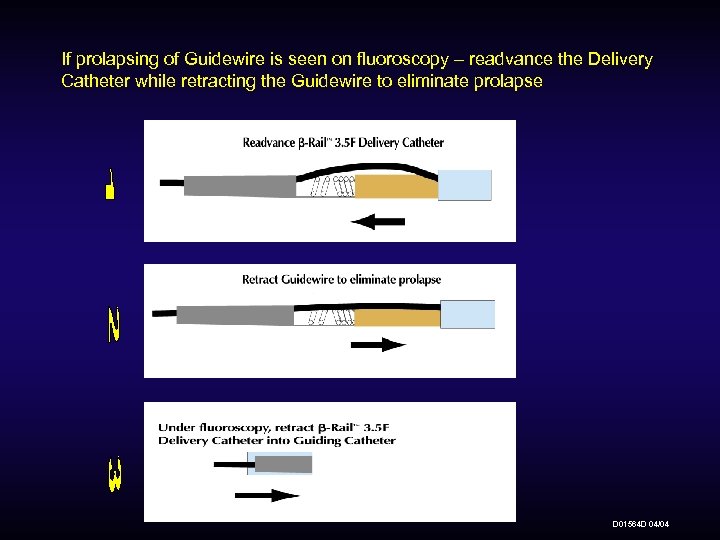
If prolapsing of Guidewire is seen on fluoroscopy – readvance the Delivery Catheter while retracting the Guidewire to eliminate prolapse D 01564 D 04/04
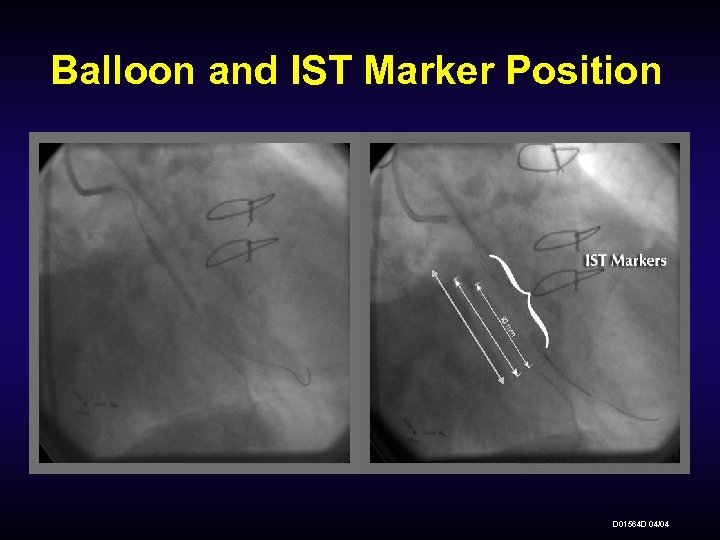
Balloon and IST Marker Position D 01564 D 04/04
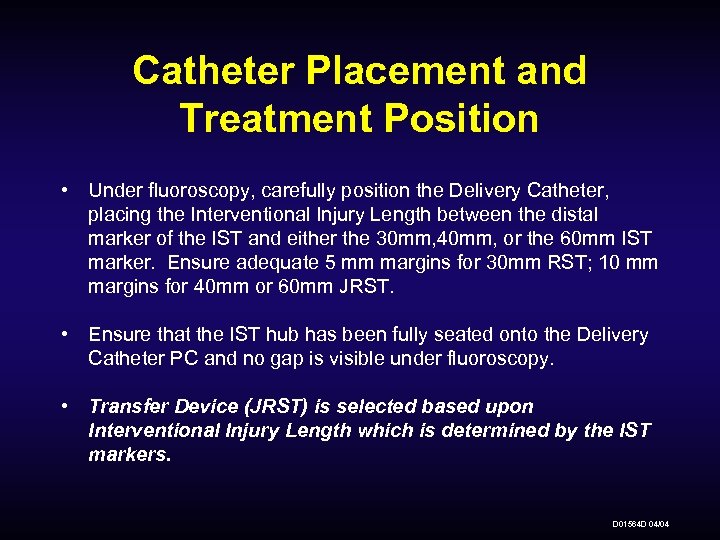
Catheter Placement and Treatment Position • Under fluoroscopy, carefully position the Delivery Catheter, placing the Interventional Injury Length between the distal marker of the IST and either the 30 mm, 40 mm, or the 60 mm IST marker. Ensure adequate 5 mm margins for 30 mm RST; 10 mm margins for 40 mm or 60 mm JRST. • Ensure that the IST hub has been fully seated onto the Delivery Catheter PC and no gap is visible under fluoroscopy. • Transfer Device (JRST) is selected based upon Interventional Injury Length which is determined by the IST markers. D 01564 D 04/04
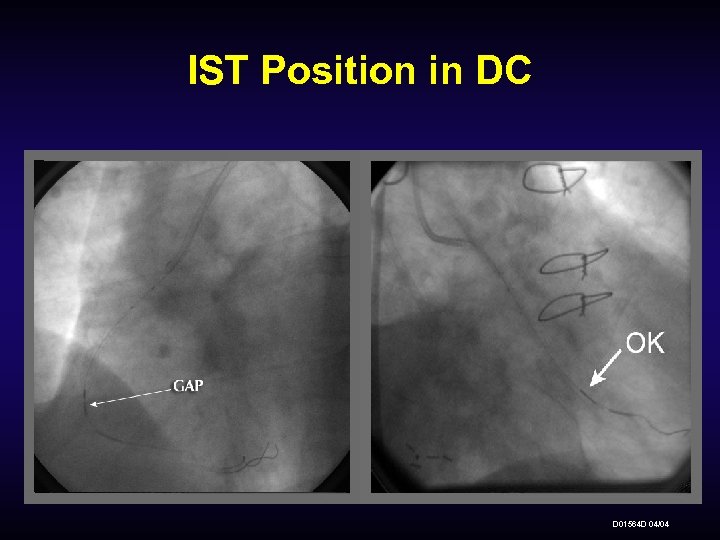
IST Position in DC D 01564 D 04/04

IST Lumen Check and Removal • Once the Delivery Catheter is properly positioned with adequate margins, gently close the hemostatic valve. • Gently withdraw the IST into the guiding catheter to approximately the aortic arch and readvance x 2. • If resistance is felt, stop immediately and determine cause of resistance. • If resistance is felt due to patient anatomy, remove the DC and optimize intervention and/or guiding catheter. D 01564 D 04/04
IST Lumen Check and Removal • If resistance is believed to be due to the DC, remove the DC and replace with new catheter • Gently withdraw IST to the end of the Delivery Catheter. • Reinsert a few centimeters to ensure patency of proximal end of catheter, then remove entirely. • Visually inspect the IST to ensure the delivery catheter did not kink. • Secure Delivery Catheter to ensure that catheter position remains stable. • Coil IST and loop ends to stabilize. Store on sterile table. • Verify correct catheter position under fluoroscopy. D 01564 D 04/04

PC to TD Connection Orientation • The Delivery Catheter must be handled carefully once IST support has been removed. • Wet O-rings with Sterile Water for Irrigation before inserting the PC into TD. • Keep the PC end of the catheter straight while connecting to the TD and throughout the procedure!! D 01564 D 04/04
PC to TD Connection Orientation • The Delivery Catheter PC should be held only by the skirt when attaching it (the PC) to the Transfer Device. • Holding the PC and the adjoining catheter just distal of the PC (at the strain relief), can result in an internal kink to the Delivery Catheter and an inability to transport the JRST. • The β-Rail™ 3. 5 F Delivery Catheter and 3. 5 F Transfer Device should be connected and maintained throughout the procedure in an “inline” orientation- to avoid any possibility of catheter kinking just distal of the PC. • The proximal end of the DC must not be placed at an angle approaching 85 -90º. (Data on file at Novoste) D 01564 D 04/04

Delivery of the JRST • Ensure sufficient sterile water-filled syringe volume (14 ml). • Open the hemostatic valve. • Move the Fluid Control Lever to SEND. • While observing under fluoroscopy, depress the syringe to transport the source train to the interventional injury site. All three pressure indicator lights should be illuminated during transport. • Once sent, confirm JRST placement under fluoroscopy approximately every 15 -30 seconds and obtain cine films to confirm placement. • The first fluid pressure indicator light should be illuminated throughout radiation treatment. D 01564 D 04/04
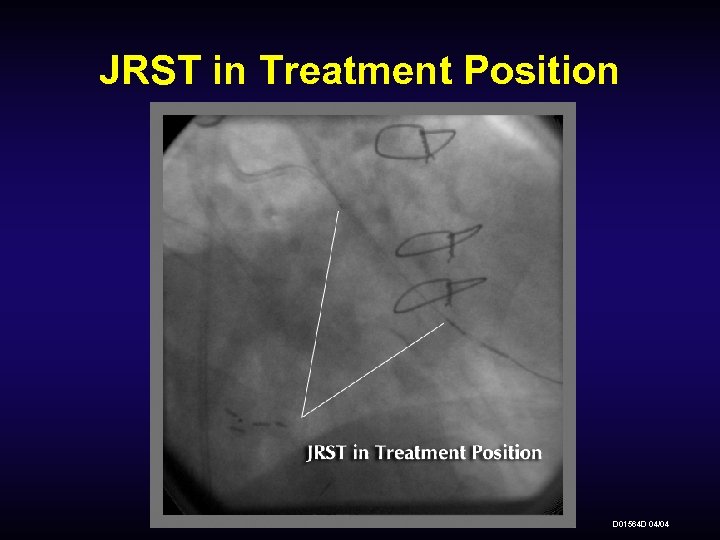
JRST in Treatment Position D 01564 D 04/04
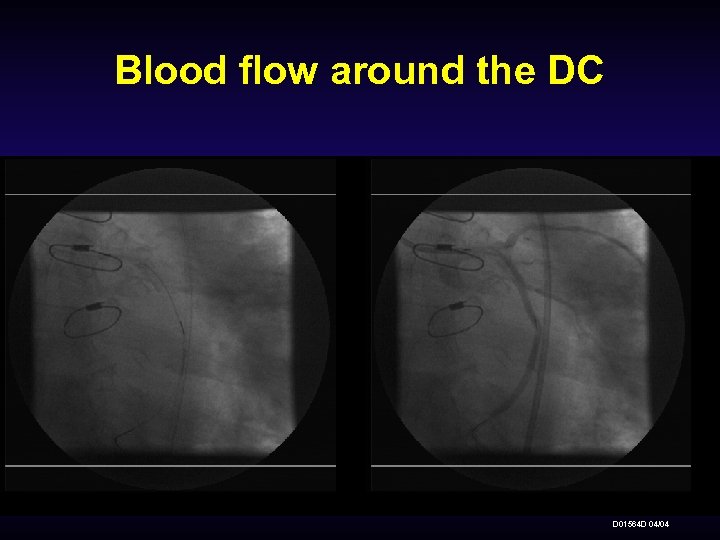
Blood flow around the DC D 01564 D 04/04
Returning the JRST • Open the hemostatic valve. • Move the Fluid Control Lever to RETURN. • Provide sufficient pressure to illuminate three pressure indicator lights when returning the JRST. • The source sensing system is located at the proximal end of the quartz chamber. - Always visually confirm return of the JRST • Difficulty returning sources: – Ensure hemostatic valve is open. – Send JRST a few cms in the opposite direction. – Use high pressure (3 lights) again to return JRST. • NOTE: Withdraw the entire 3. 5 F System, if 15 seconds have elapsed and the JRST has not reached the treatment site or been returned to the TD. D 01564 D 04/04

Delivery Catheter Withdrawal • Exercise care when withdrawing the Delivery Catheter through any area of increased restriction, such as a stent, guide catheter tip or hemostatic valve. Always withdraw the Delivery Catheter slowly and observe under fluoroscopy. • Never withdraw the Delivery Catheter against resistance. If resistance is felt, stop immediately and determine the cause of resistance before proceeding. • Distal rail designs may cause guide wire prolapse upon withdrawal. If prolapse persists and cannot be resolved, withdraw the Delivery Catheter and guidewire together as one unit. D 01564 D 04/04
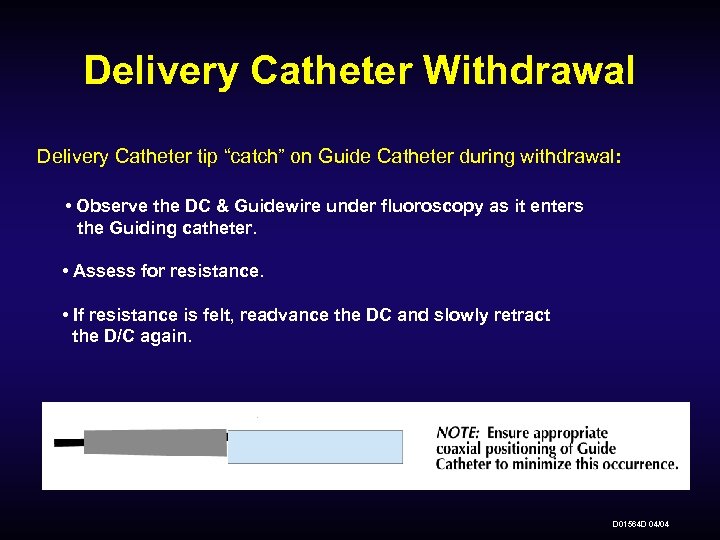
Delivery Catheter Withdrawal Delivery Catheter tip “catch” on Guide Catheter during withdrawal: • Observe the DC & Guidewire under fluoroscopy as it enters the Guiding catheter. • Assess for resistance. • If resistance is felt, readvance the DC and slowly retract the D/C again. D 01564 D 04/04
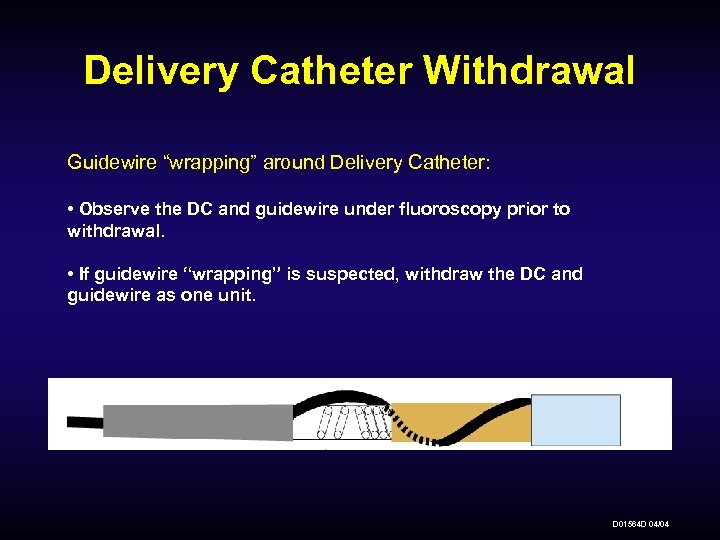
Delivery Catheter Withdrawal Guidewire “wrapping” around Delivery Catheter: • Observe the DC and guidewire under fluoroscopy prior to withdrawal. • If guidewire “wrapping” is suspected, withdraw the DC and guidewire as one unit. D 01564 D 04/04
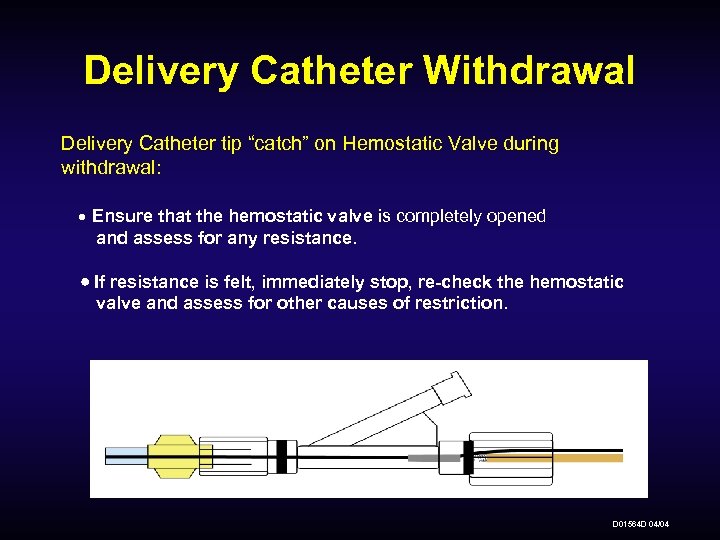
Delivery Catheter Withdrawal Delivery Catheter tip “catch” on Hemostatic Valve during withdrawal: Ensure that the hemostatic valve is completely opened and assess for any resistance. If resistance is felt, immediately stop, re-check the hemostatic valve and assess for other causes of restriction. D 01564 D 04/04

System Removal and Disassembly • Conduct standard Post-Procedural Radiation Checks. • Dry and store the Transfer Device in the appropriate storage container. D 01564 D 04/04

Optional Instructions: IST Reinsertion This procedure is only used to reposition the DC - Not for additional radiation treatments • Remove DC from patient • Place PC Cover PC and take to sterile table • Put on second pair of sterile gloves • Uncoil IST • Hold PC with sterile gauze pad and discard PC Cover D 01564 D 04/04

Optional Instructions: IST Reinsertion • Reinsert IST into DC over non-absorbent backed sterile gauze pads. § Approximately 4 drops of displaced non-sterile water will drip from PC. § Verify that IST is firmly against the distal marker/stop of the DC (IST may not reach distal marker stop). • Remove non-sterile gloves. • Reinsert DC over guidewire. • Conduct IST lumen check and removal (with a sterile gauze pad) as previously described. Discard the non-sterile IST D 01564 D 04/04

Agenda • • • Introduction Product System Review Procedural Use and Application Pointers Hands-on Application Workshop Site Proctoring Guidelines D 01564 D 04/04

Hands-on Applications Workshop Hands-on experience with: • Standard Procedure Flow • Key Product Sensitivities – Catheter handling & mishandling • Review of Trouble-shooting and Emergency Source Recovery Procedures • Questions & Answers D 01564 D 04/04

Agenda • • • Introduction Product System Review Procedural Use and Application Pointers Hands-on Application Workshop Site Training Guidelines D 01564 D 04/04

Site Training Guidelines Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System specific training is required of VBT clinicians at each site, with requisite training signoffs. – Each member of the VBT Team must complete a didactic review of the Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System. – A Mock Training Procedure is required at each site which has not received basic Beta-Cath™ (5 F) System training. – Each clinician is to be proctored for their initial 3 -5 Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System procedures by a qualified Novoste Representative. – The Novoste Representative will determine clinician 3. 5 F proficiency and will authorize the award of a Beta-Cath™ 3. 5 F System Training Certificate. D 01564 D 04/04
Beta-Cath. TM 3. 5 F System Summary Smaller diameter source train and 3. 5 F catheter design provides additional clinical benefits, while building on the key advantages of the original Beta-Cath. TM 5 F System: • Ideal low, user-friendly maintenance Sr-90 Isotope • Small, portable, hand-held device uniquely designed for the Cath Lab • Minimally restrictive, passive-centered catheter design D 01564 D 04/04
69a9a7c3d69a4ee70f7b0ba5592db138.ppt