fcf424a004aae41382be4c7050f92353.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Benefits of the MAGIC Grid Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E Status report of an EGEE generic application Harald Kornmayer, Ariel Garcia (Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe) Toni Coarasa (Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München) Ciro Bigongiari (INFN, Padua) Esther Accion, Gonzalo Merino, Andreu Pacheco, Manuel Delfino (PIC, Barcelona) Mirco Mazzucato (CNAF/INFN Bologna) in cooperation with MAGIC collaboration H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 1

Outline Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • Introduction • What kind of MAGIC? • The idea of a MAGIC Grid • Grid added value • Expectations vs. reality? • Data challenges • Experience • Conclusion and Outlook H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 2

Introduction: The MAGIC Telescope • Ground based Air Cerenkov Telescope • Gamma ray: 30 Ge. V - Te. V • La. Palma, Canary Islands (28° North, 18° West) • 17 m diameter • operation since autumn 2003 (still in commissioning) • Collaborators: IFAE Barcelona, UAB Barcelona, Humboldt U. Berlin, UC Davis, U. Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E Lodz, UC Madrid, MPI München, INFN / U. Padova, U. Potchefstrom, INFN / U. Siena, Tuorla Observatory, INFN / U. Udine, U. Würzburg, Yerevan Physics Inst. , ETH Zürich Physics Goals: Origin of VHE Gamma rays Active Galactic Nuclei Supernova Remnants Unidentified EGRET sources Gamma Ray Burst H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 3
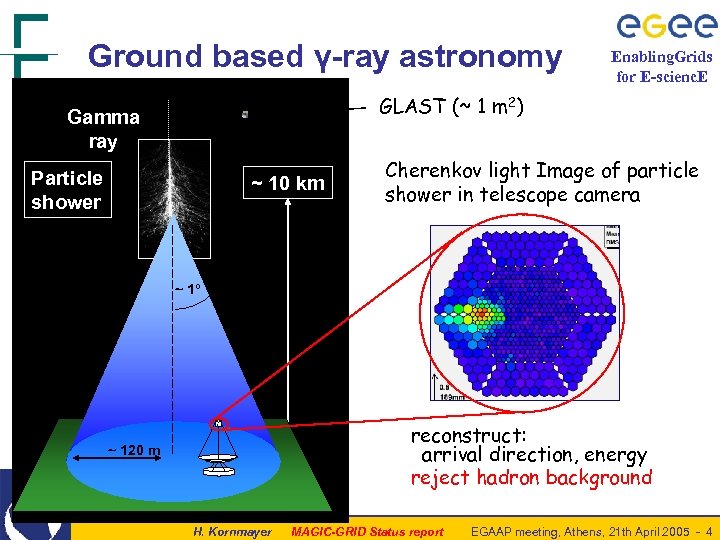
Ground based γ-ray astronomy Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E GLAST (~ 1 m 2) Gamma ray Particle shower Cherenkov light Image of particle shower in telescope camera ~ 1 o Che ren k ov l igh t ~ 10 km reconstruct: arrival direction, energy reject hadron background ~ 120 m H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 4
MAGIC – Why the Grid? MAGIC is an international collaboration • Partners distributed all over Europe Analysis is based on Monte Carlo simulations • CORSIKA • CPU • Amount of data can NOT be handled by one partner only (up to 200 GB per night) • Access to data and computing needs to be more efficient • MAGIC will build a second telescope code consuming • 1 night of hadronic background needs 20000 days on 70 computer • Lowering the threshold of MAGIC telescope requires new methods based on MC simulations • More H. Kornmayer Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E MAGIC-GRID Status report CPU power needed! EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 5
Developments - Requirements Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • MAGIC needs a lot of CPU to simulate the hadronic background to explore the energy range 10 Ge. V – 100 Ge. V • MAGIC needs a coordinated effort for the Monte. Carlo production • MAGIC needs an easy accessible system (Where are the data from run_1002 and run_1003? ) • MAGIC needs an scalable system (as MAGIC II will come 2007) • MAGIC needs the possibility to access data from other experiments (HESS, Vertias, GLAST, PLANCK(? )) for multi wavelength campaigns H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 6
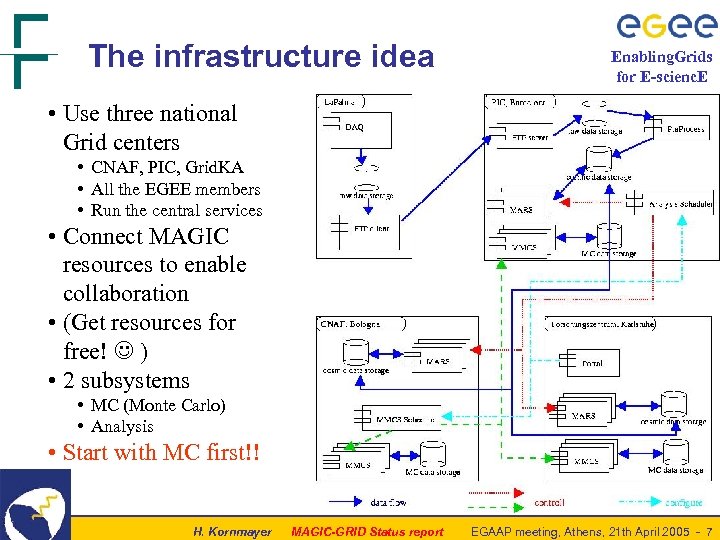
The infrastructure idea Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • Use three national Grid centers • CNAF, PIC, Grid. KA • All the EGEE members • Run the central services • Connect MAGIC resources to enable collaboration • (Get resources for free! ) • 2 subsystems • MC (Monte Carlo) • Analysis • Start with MC first!! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 7
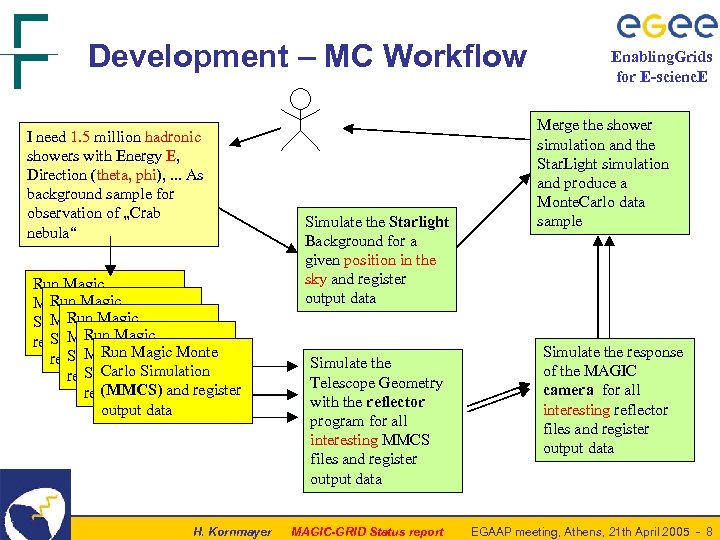
Development – MC Workflow I need 1. 5 million hadronic showers with Energy E, Direction (theta, phi), . . . As background sample for observation of „Crab nebula“ Run Magic Monte. Carlo Simulation and register Run Magic output data Monte. Carlo Monte Simulation and register Run Magic output data Carlo Simulation data register outputand (MMCS) and register output data H. Kornmayer Simulate the Starlight Background for a given position in the sky and register output data Simulate the Telescope Geometry with the reflector program for all interesting MMCS files and register output data MAGIC-GRID Status report Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E Merge the shower simulation and the Star. Light simulation and produce a Monte. Carlo data sample Simulate the response of the MAGIC camera for all interesting reflector files and register output data EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 8
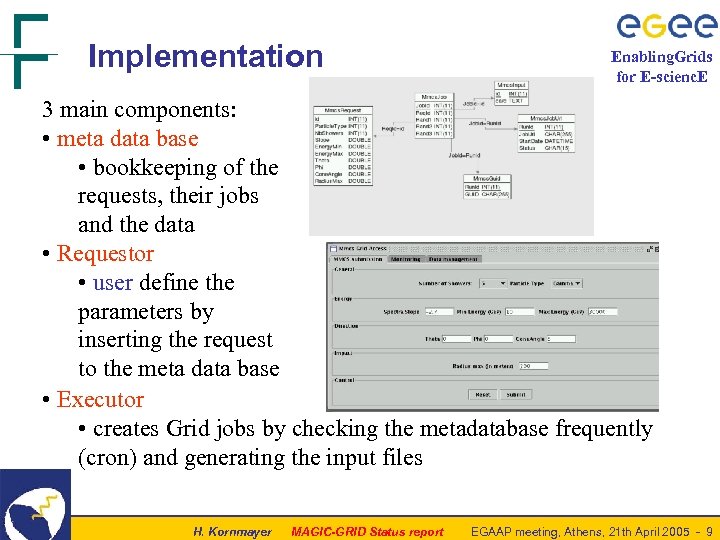
Implementation Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E 3 main components: • meta data base • bookkeeping of the requests, their jobs and the data • Requestor • user define the parameters by inserting the request to the meta data base • Executor • creates Grid jobs by checking the metadatabase frequently (cron) and generating the input files H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 9
Grid added value Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E expectations vs. reality : • Collaboration (-) Complex software, limited # of OS, limited # of batch systems make the integration of new sites of MAGIC collaborators difficult • The final integration of a cluster (SUSE, SGE batch system, AFS, firewall) took too long (9 months) • • Speed up of MC production (+) The reliable infrastructure and the good support from many sites made that possible! Many thanks to sk, bg, pl, uk, gr, it, es, de, … • Service offered was overall good • • with problems when new releases appeared (every time! : –( ) • with problems to have a sustainable configuration (for VO, replica service, …) • Central services run by EGEE were stable! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 10
Grid added value II Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E expectations vs. reality II: • Persistent storage (+) • of Monte Carlo data • Some problems during the first runs – (Too many small files on a tape system is equal to /dev/null). We learnt that lesson! • of observation data • Started the automated production data transfer of real observation data from La. Palma to PIC, Barcelona in november 2001 • 3. 2 TB of real data are available on the Grid now • Improvements of data availability (? ) Replica mechanisms needs to be tested! • Measurements needed in the future! • Ongoing work! • H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 11
Grid added value III Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E expectations vs. reality III: • Cost reduction (-) • additional implementations were necessary (-) • MAGIC implemented its own prototype meta data base system – to monitor the status of many jobs of a mass production – to check the “status” of a job! ( later) • MAGIC implemented its own rudimentary workflow system – Nothing was available at the beginning • GGUS reduced the costs definitely (+) • MAGIC Grid participants appreciated the support structure of the GGUS portal • Every new middleware release forced (-) • a downtime of the system • customization of the system H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 12
Data challenges Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E Last data challenge - December - today - Successful: 13500 Past experience - Three MMCS data challenges: - Mar/Apr 2005: 10% failure - July 2005: 3. 9%failure - Sept 2005: 3. 4% failure - Improvements: - - FAILED: 4567 () - Underlying Middleware - Operation of Services - Many lessons learnt - Data management - Additional checks H. Kornmayer Success (Data available) Mmcs output registered in the Grid - MAGIC-GRID Status report ? Done (Failed): 249 Done (Success): 2830 Scheduled: 86 Submitted: 9 Aborted: 930 Waiting: 473 EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 13
Useless status of jobs Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • Data storage site is selected by the JDL • …. Output. Data = { [Output. File="data/cer 012345" ; Logical. File. Name="lfn: mmcs_cer 012345“; Storage. Element=" castorgrid. pic. es“; ], …. . • The WMS should register the file automatically on the Grid! • BUT: If the job fails • (RLS service down, SE not available, . . . ) • the WMS mention the STATUS as “Done (Successful)” „DONE (Successful)“ has NO meaning for the output of data specified in the JDL! • A more sophisticated system is necessary for a production system! • We developed it for out own! (As every VO? ) • Can we get a WMS that takes data output into account? H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 14

Missing VO support in WMS Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • Mass production is managed by one member of the VO • VO production manager • No need to be a Grid expert! • Every job is assigned to him exclusively! • edg-job-submit -- vo magic mmcs_012345. jdl • NO other member of the VO can get information • about the status of the job • edg-job-status https: //the. Unique. Identifier. Of. The. Job • about the stdout/stderr of the job • edg-job-get-output https: //the. Unique. Identifier. Of. The. Job • The basic commands MUST have more VO support! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 15
Meta data base Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • The output data files should stored and registered on the Grid! • But the files are only useful if “content describing” information can be attached to the files! • “From Storage to knowledge!” • “from Grid to e-Science” • We implemented a “separate” meta data base that links this information and the file URI One extensible framework for replica and meta data services would be nice! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 16

Workflows Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • The MAGIC Monte Carlo system is a good example for a scientific workflow • 1000 jobs can be started in parallel (embarrassingly!) • MAGIC looked for a middleware tool which support workflows • Using standard workflow description • Support for self recovery of failed jobs • 3% of jobs “fail” 30 out of 1000 • Without this feature NO workflow will succeed! • There are tools around • but we need something like a “best practise guide” for one tool! • We don’t want to program it by our own on top of the meta data base! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 17
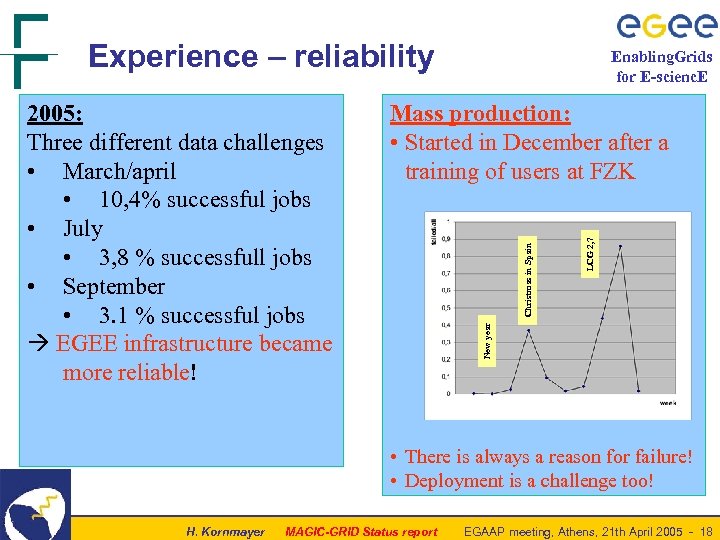
Experience – reliability LCG 2, 7 Christmas in Spain Mass production: • Started in December after a training of users at FZK New year 2005: Three different data challenges • March/april • 10, 4% successful jobs • July • 3, 8 % successfull jobs • September • 3. 1 % successful jobs EGEE infrastructure became more reliable! Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • There is always a reason for failure! • Deployment is a challenge too! H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 18

EGEE – MAGIC Grid Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • MAGIC Grid is reality • Production of MC using MAGIC Grid resources started in december! – We plan to ask (temporarily) for more CPUs for stress testing! • MAGIC collaboration will put their real data on the Grid • The challenges for computing will increase with the second telescope H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 19

MAGIC Grid – future prospects Enabling. Grids for E-scienc. E • MAGIC is a good example • to do e-Science • to use the e-Infrastructure • to exploit Grid-Technology • What is about a „GRID“ of different VHE gamma ray observatories? „Towards a virtual observatory for VHE g-rays“ MAGIC/EU Kangaroo - AUS/JP Veritas/US HESS/EU/Africa H. Kornmayer MAGIC-GRID Status report EGAAP meeting, Athens, 21 th April 2005 - 20
fcf424a004aae41382be4c7050f92353.ppt